Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER IMAGE
ISSUE INFORMATION
HEPATOLOGY HIGHLIGHTS
EDITORIALS
Stromal yin-yang of myofibroblasts and endothelial cells in the progression of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
- Pages: 1233-1236
- First Published: 03 May 2022
New kid on the block: Netrin-1 as a novel player in the delicate molecular network of hepatic inflammation
- Pages: 1237-1239
- First Published: 06 April 2022
Portal fibroblasts: A renewable source of liver myofibroblasts
- Pages: 1240-1242
- First Published: 16 April 2022
The transition from NAFLD to MAFLD: One size still does not fit all—Time for a tailored approach?
- Pages: 1243-1245
- First Published: 03 May 2022
Should PNPLA3 polymorphism be performed in clinical practice in patients with NAFLD to predict the risk of disease progression?
- Pages: 1246-1247
- First Published: 05 April 2022
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
IMMUNE-MEDIATED DISEASES, DILI, AND BILIARY TRACT DISEASE
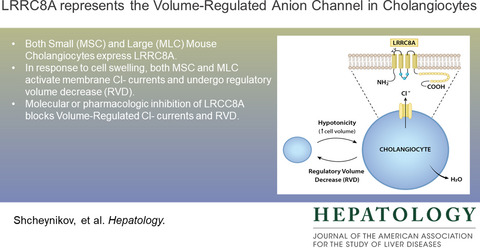
Identification of the chloride channel, leucine-rich repeat-containing protein 8, subfamily a (LRRC8A), in mouse cholangiocytes
- Pages: 1248-1258
- First Published: 21 April 2022
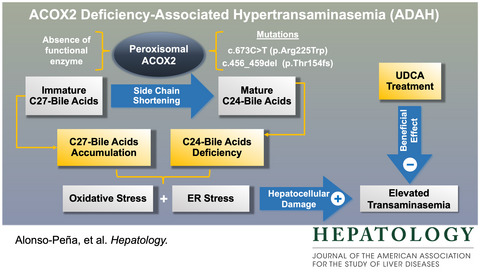
Beneficial effect of ursodeoxycholic acid in patients with acyl-CoA oxidase 2 (ACOX2) deficiency–associated hypertransaminasemia
- Pages: 1259-1274
- First Published: 08 April 2022
LIVER CANCER
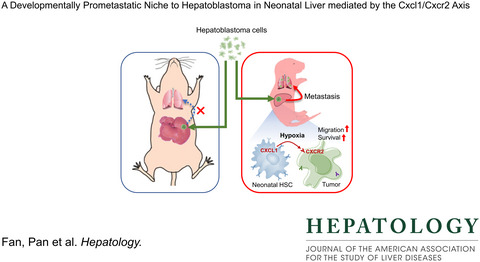
A developmentally prometastatic niche to hepatoblastoma in neonatal liver mediated by the Cxcl1/Cxcr2 axis
- Pages: 1275-1290
- First Published: 18 February 2022
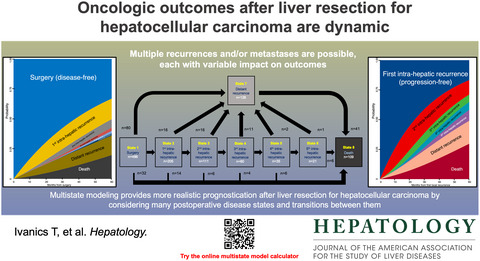
Dynamic risk profiling of HCC recurrence after curative intent liver resection
- Pages: 1291-1301
- First Published: 18 February 2022
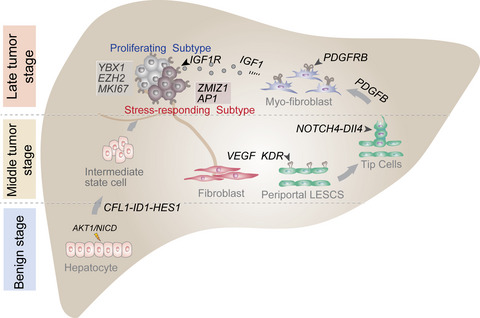
Cellular heterogeneity and transcriptomic profiles during intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma initiation and progression
- Pages: 1302-1317
- First Published: 27 March 2022
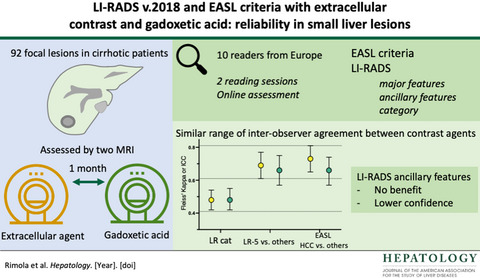
Reliability of extracellular contrast versus gadoxetic acid in assessing small liver lesions using liver imaging reporting and data system v.2018 and European association for the study of the liver criteria
- Pages: 1318-1328
- First Published: 29 March 2022
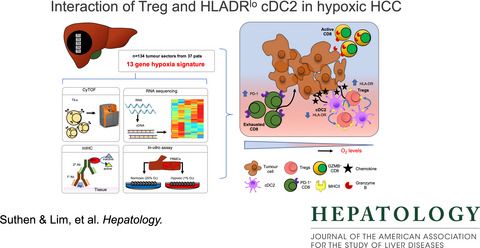
Hypoxia-driven immunosuppression by Treg and type-2 conventional dendritic cells in HCC
- Pages: 1329-1344
- First Published: 20 February 2022
LIVER PATHOBIOLOGY
Hepatic inflammation elicits production of proinflammatory netrin-1 through exclusive activation of translation
- Pages: 1345-1359
- First Published: 07 March 2022
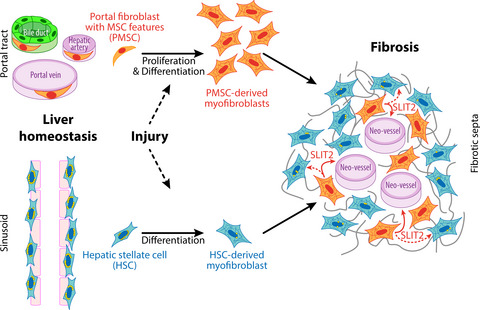
Portal fibroblasts with mesenchymal stem cell features form a reservoir of proliferative myofibroblasts in liver fibrosis
- Pages: 1360-1375
- First Published: 12 March 2022
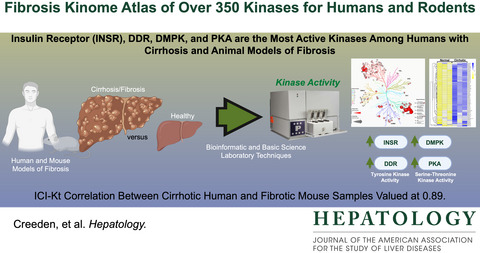
Hepatic kinome atlas: An in-depth identification of kinase pathways in liver fibrosis of humans and rodents
- Pages: 1376-1388
- First Published: 21 March 2022
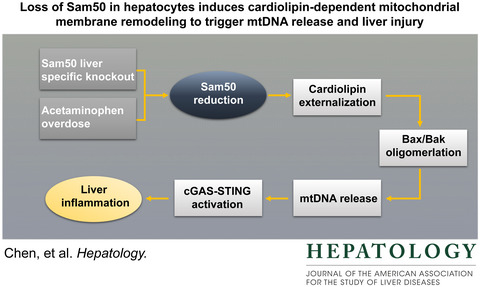
Loss of Sam50 in hepatocytes induces cardiolipin-dependent mitochondrial membrane remodeling to trigger mtDNA release and liver injury
- Pages: 1389-1408
- First Published: 21 March 2022
LIVER FAILURE/CIRRHOSIS/PORTAL HYPERTENSION
Risk of liver-related events by age and diabetes duration in patients with diabetes and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- Pages: 1409-1422
- First Published: 25 March 2022
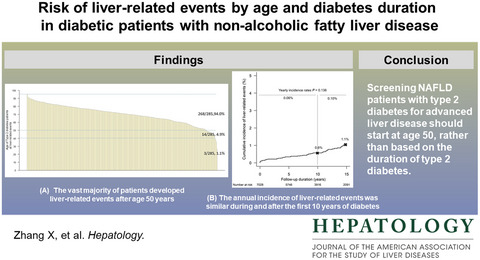
Diabetes is an important risk factor for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and its severity. However, it is difficult to screen every diabetic patient for NAFLD because of the large number of patients. In a study of 7028 patients with NAFLD and type 2 diabetes from Hong Kong, we showed that the vast majority of patients developed liver-related complications after the age of 50 years. In contrast, liver-related events increased linearly with the duration of diabetes with no threshold effect. Our study suggests that screening for liver disease should be based on age instead of the duration of diabetes.
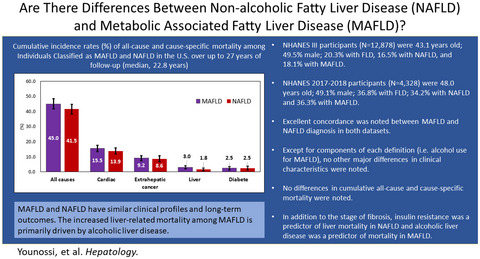
Are there outcome differences between NAFLD and metabolic-associated fatty liver disease?
- Pages: 1423-1437
- First Published: 01 April 2022
PEDIATRICS
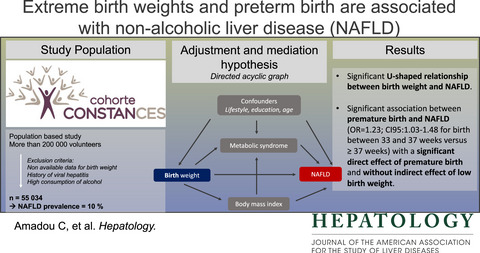
Association between birth weight, preterm birth, and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in a community-based cohort
- Pages: 1438-1451
- First Published: 26 April 2022
STEATOHEPATITIS
Compromised hepatic mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation and reduced markers of mitochondrial turnover in human NAFLD
- Pages: 1452-1465
- First Published: 09 January 2022
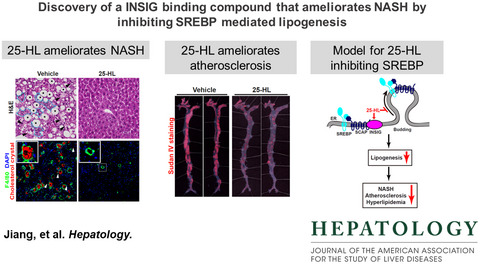
Discovery of an insulin-induced gene binding compound that ameliorates nonalcoholic steatohepatitis by inhibiting sterol regulatory element-binding protein–mediated lipogenesis
- Pages: 1466-1481
- First Published: 31 January 2022
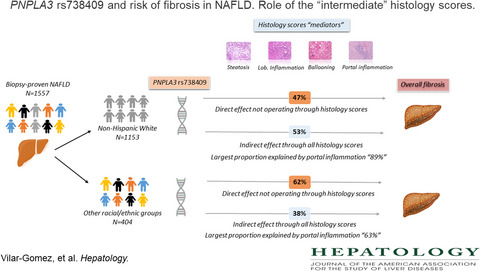
PNPLA3 rs738409 and risk of fibrosis in NAFLD: Exploring mediation pathways through intermediate histological features
- Pages: 1482-1494
- First Published: 29 March 2022
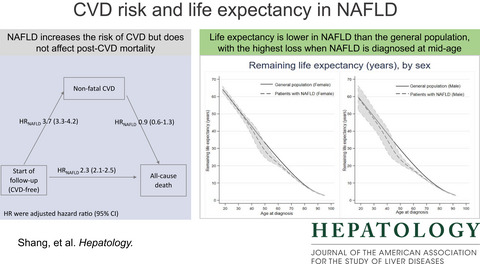
Risk of cardiovascular disease and loss in life expectancy in NAFLD
- Pages: 1495-1505
- First Published: 10 April 2022
VIRAL HEPATITIS
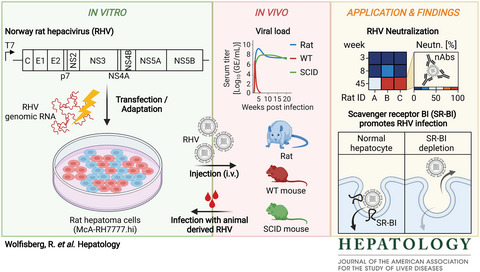
Neutralization and receptor use of infectious culture–derived rat hepacivirus as a model for HCV
- Pages: 1506-1519
- First Published: 21 April 2022
REVIEWS
Circulating HBV RNA: From biology to clinical applications
- Pages: 1520-1530
- First Published: 28 March 2022
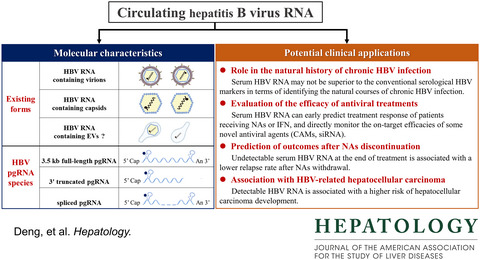
- Circulating HBV RNA, which is primarily composed of full-length, spliced, and 3’ truncated pregenomic RNA, circulates in the blood of patients with chronic HBV infection predominantly in the form of virus-like particles, including enveloped virions and naked capsids (capsid-antibody complexes in patients’ sera).
- HBV RNA–containing virions are secreted through the multivesicular body pathway, as are HBV DNA-virions, while the secretion pathway of HBV capsids remains elusive. HBV RNA–containing virions collected under HBV polymerase inhibitor treatment fail to establish de novo infection, but the infectivity of naive RNA virions remains to be investigated.
- The quantitation levels of circulating HBV RNA and their performances on predicting treatment outcomes are largely methodology-dependent, calling for the standardization of serum HBV RNA detection assay.
- The area of clinical interest in circulating HBV RNA is predicting off-treatment responses and HCC development in patients treated with nucleos(t)ide analogues.
ERRATA
RETRACTION
Retracted: Antitumor effects of OSU-2S, a nonimmunosuppressive analogue of FTY720, in hepatocellular carcinoma
- Page: 1554
- First Published: 08 September 2022
CORRESPONDENCE
Letter to the editor: Loss of Sam50 in hepatocytes induces cardiolipin-dependent mitochondrial membrane remodeling to trigger mtDNA release and liver injury
- Pages: E94-E95
- First Published: 16 April 2022
Letter to the editor: Cautious use of multistate modeling in prognosis analysis of HCC
- Page: E97
- First Published: 17 April 2022
Letter to the editor: Pitfalls in the outcome differences between NAFLD and MAFLD
- Page: E100
- First Published: 09 May 2022
Letter to the editor: Apples should be compared with apples
- Page: E101
- First Published: 09 May 2022
Letter to the editor: Compromised hepatic mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation and reduced markers of mitochondrial turnover in human NAFLD
- Pages: E104-E105
- First Published: 01 May 2022
Letter to the editor: The perspective of GLP-1/GLP-2 receptors against NASH via diverse regulation
- Pages: E106-E107
- First Published: 26 June 2022
Letter to the editor: l-ornithine l-aspartate in acute treatment of severe hepatic encephalopathy: A double-blind randomized controlled trial
- Pages: E108-E109
- First Published: 05 July 2022
Letter to the editor: Combination treatment with IL-1 antagonist, pentoxifylline and zinc for severe alcoholic hepatitis: Are we there yet?
- Pages: E110-E111
- First Published: 01 July 2022
Letter to the editor: IL-1 receptor antagonist plus pentoxifylline and zinc for severe alcoholic hepatitis—More questions than answers!
- Pages: E112-E113
- First Published: 01 July 2022