Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Cover Story: Eur. J. Immunol. 4'25
- First Published: 01 April 2025

Our cover features images related to flow cytometry techniques widely used for analysis of function and phenotypes of major human and murine immune cell subsets, superimposed on a multidimensional immune cell population scatter plot. These images are taken from the third edition of EJI's Flow Cytometry Guidelines by Cossarizza et al., a comprehensive resource prepared by flow cytometry and immunology research experts from around the world.
Issue Information
Editorial
Guidelines and Advances in Basic and Applied Dendritic Cell Biology
- First Published: 01 April 2025
Highlights - Reviews
Mini Review
Basic
Modulation of Host Immunity by Microbiome-Derived Indole-3-Propionic Acid and Other Bacterial Metabolites
- First Published: 01 April 2025
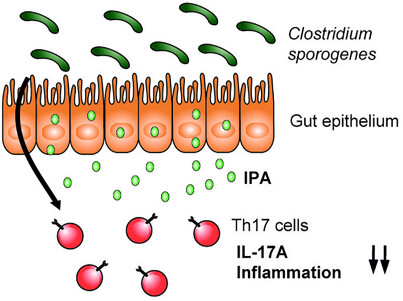
The gut commensal Clostridium sporogenes metabolizes dietary tryptophan into indole-3-propionic acid (IPA). In this review, we highlight recent findings suggesting that IPA acts as an effective signaling molecule, modulating the function of Th17 lymphocytes and resulting in protection against intestinal inflammation.
Notes and Insights
Interleukin-18 Binding Protein (IL-18BP) Deficiency Affects Lymphocyte Activation and IL-18 Expression in a Mouse Model of Liver Inflammation
- First Published: 01 April 2025
Innate Immunity
Research Article
Basic
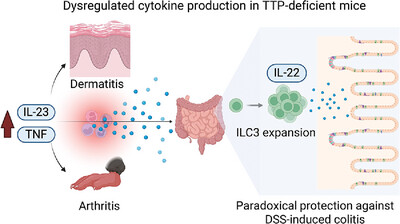
Expansion of Interleukin-22-Producing Type 3 Innate Lymphoid Cells in the Gut of Tristetraprolin-Deficient Mice
- First Published: 01 April 2025
Immunity to Infection
Research Article
Basic
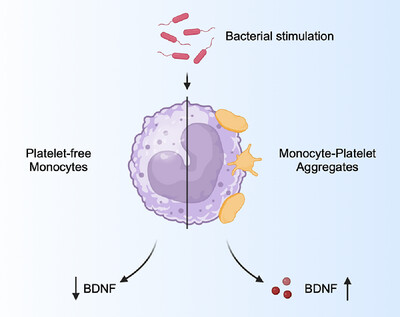
Monocyte-Platelet Aggregates Are Major Source of BDNF after Bacterial Stimulation of Human Peripheral Blood Immune Cells
- First Published: 01 April 2025
Highlights–Reviews
Review
Clinical
Metabolic Reprogramming in Stromal and Immune Cells in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Osteoarthritis: Therapeutic Possibilities
- First Published: 01 April 2025
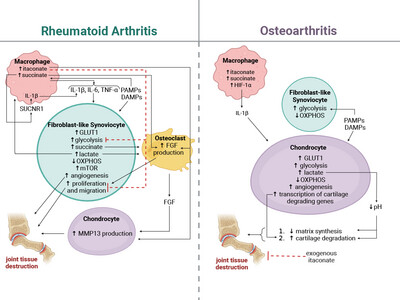
Immune cells and stromal cells undergo metabolic reprogramming in both rheumatoid and osteoarthritis. This review summarises current evidence on the metabolic changes within and the crosstalk between immune and stromal cells in these diseases. In addition, we explore the therapeutic potential of targeting metabolic processes for the treatment of arthritis.
Immunodeficiencies and Autoimmunity
Research Article
Clinical
Interleukin-8/Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 Axis Impairs Wound Healing in Type 2 Diabetes through Neutrophil Extracellular Traps-Fibroblast Crosstalk
- First Published: 01 April 2025
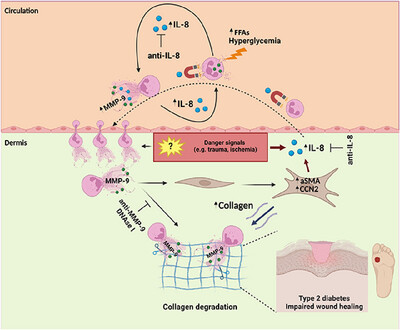
Neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) in type 2 diabetes induce a pro-fibrotic but functionally impaired phenotype in cutaneous fibroblasts, associated with collagen breakdown by NET-bound MMP-9. IL-8 released in NETs promotes its own expression in both neutrophils/fibroblasts and neutrophil MMP-9 production, creating positive feedback loops that hinder wound healing.
Molecular Immunology and Signaling
Research Article
Basic
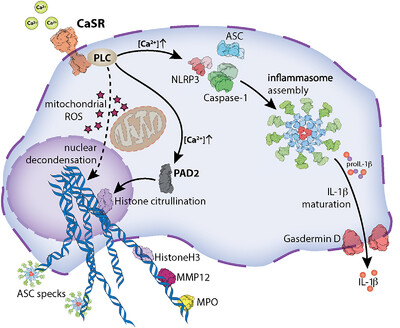
PLC and PAD2 Regulate Extracellular Calcium-Triggered Release of Macrophage Extracellular DNA Traps
- First Published: 01 April 2025
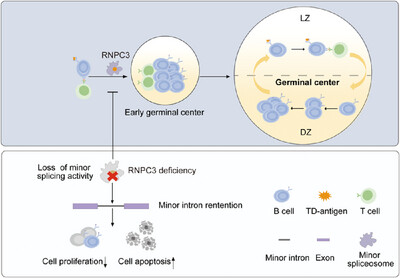
Minor Splicing Factor RNPC3 Is Essential for the Germinal Center B Cell Response
- First Published: 01 April 2025
News
Innate Immunity
Research Article
Basic
IgA2 ACPA Drives a Hyper-Inflammatory Phenotype in Macrophages via ATP Synthase and COX2
- First Published: 01 April 2025
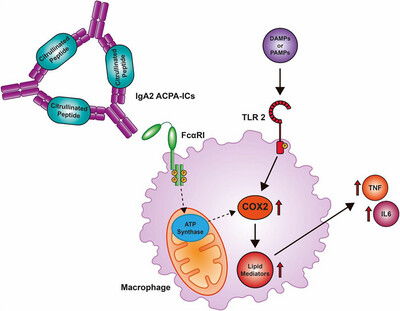
IgA autoantibodies have been implicated in promoting inflammation associated with rheumatoid arthritis by engaging Fc receptors on myeloid cells. However, underlying mechanisms are still poorly defined. Here, we identified immune complexed IgA2, but not IgA1, to induce hyper-inflammatory macrophages, and that it is dependent on ATP synthase and COX2 activity.
Tumor Immunology
Research Article
Basic
CD3xHER2 bsAb-Mediated Activation of Resting T-cells at HER2 Positive Tumor Clusters Is Sufficient to Trigger Bystander Eradication of Distant HER2 Negative Clusters Through IFNγ and TNFα
- First Published: 03 April 2025
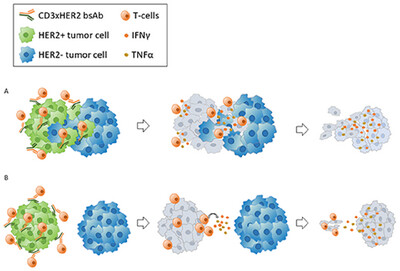
Spatiotemporal aspects of bystander killing triggered by bispecific antibodies: (1) Resting T-cells recognize HER2+ tumors via CD3xHER2 bsAbs. (2) Local T-cell activation induces direct HER2+ tumor killing and IFNγ/TNFα release. (3) IFNγ/TNFα mediate paracrine killing of HER2− cells. (4) HER2− cells are eliminated in mixed (A) and distant (B) areas.
Molecular Immunology and Signaling
Short Communication
Basic
CST Is Epistatic With Shieldin to Limit DNA Double-Strand Break End Resection and Promote Repair During Igh Class Switch Recombination
- First Published: 03 April 2025
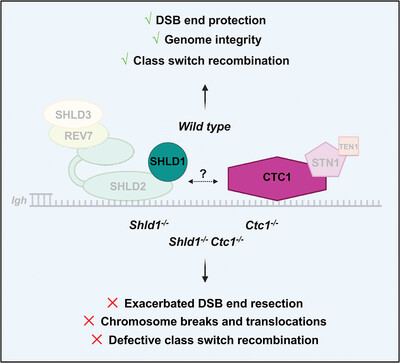
Here we show that CST and SHLD are required for CSR, while SHLD1-CTC1 interaction via the SHLD1 LDLP motif is dispensable. Mechanistically, we show that CTC1 and SHLD1 are epistatic during CSR, preventing genetic instability, exacerbated DSB end-resection, and microhomology-mediated end-joining at Igh switching sites. Created in Biorender.com.
Highlights - reviews
Mini-Review
Basic
Metabolic Dialogue Shapes Immune Response in the Tumor Microenvironment
- First Published: 14 April 2025
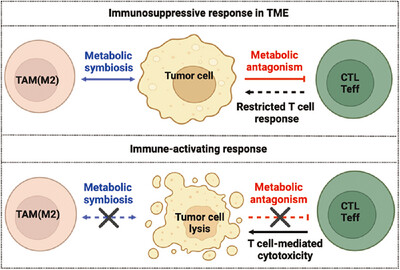
Metabolic antagonism in the TME suppresses CD8+ T cell function by depleting essential nutrients and generating toxic byproducts. Metabolic symbiosis between tumor cells and TAMs fosters an immunosuppressive microenvironment. Disrupting metabolic interactions can overcome immune suppression, boost antitumor immunity, and enhance immunotherapy efficacy.
Adaptive Immunity
Research Article
Basic
Investigating Polyreactivity of CD4+ T Cells to the Intestinal Microbiota
- First Published: 14 April 2025
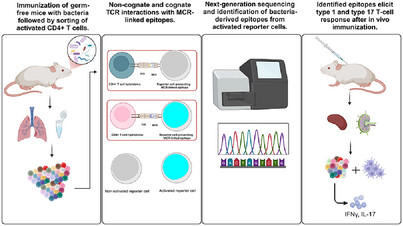
T-cell recognition of microbiota-derived epitopes is key to immune homeostasis. Here, we used an unbiased screening platform to identify novel immunogenic epitopes from Akkermansia muciniphila and Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron. We demonstrated that these epitopes are conserved across multiple other bacterial strains, suggesting their potential relevance in broader immune interactions.
Technical Report
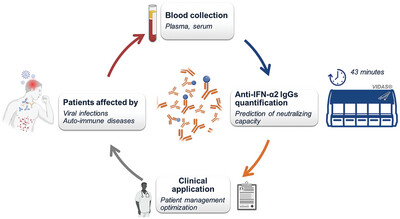
Rapid Detection of Anti-IFN-α2 Autoantibodies Using a New Automated VIDAS Assay Prototype
- First Published: 14 April 2025
Tumor Immunology
Basic
Combined Deletion of ZFP36L1 and ZFP36L2 Drives Superior Cytokine Production in T Cells at the Cost of Cell Fitness
- First Published: 18 April 2025
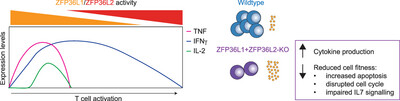
The RNA-binding proteins ZFP36L1 and ZFP36L2 regulate in T cells the production of the key effector molecules TNF, IL-2, and IFNγ. Genetic deletion of ZFP36L1 and ZFP36L2 induces superior cytokine production in continuously activated tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes. However, ZFP36L1+ZFP36L2-deficient T cells exhibit reduced cell fitness: they more frequently undergo apoptosis, potentially due to disrupted cell cycle progression and impaired signaling through the IL7 receptor.
Highlights
Review
Basic
Updating the Discontinuity Theory to the Extended Immunity: The Symmunobiome Concept
- First Published: 19 April 2025
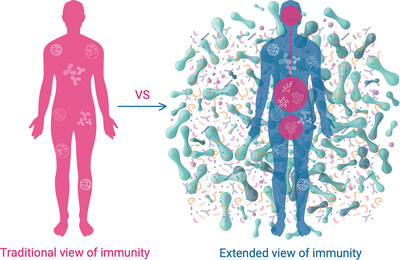
The evolution of the concept of the immune system from a set of composed cells and tissue that defend the host from exogenous agents into a system that has regulatory and homeostatic functions determined by the interaction with microorganisms as a functional part of an extended immune system, that we call symmunobiome.
Molecular Immunology and Signaling
Research Article
Basic
Dimethyl Fumarate Negatively Regulates MYC Signaling and Promotes Cell-Cycle Arrest in T-Cells through a GSH-Dependent Mechanism
- First Published: 19 April 2025
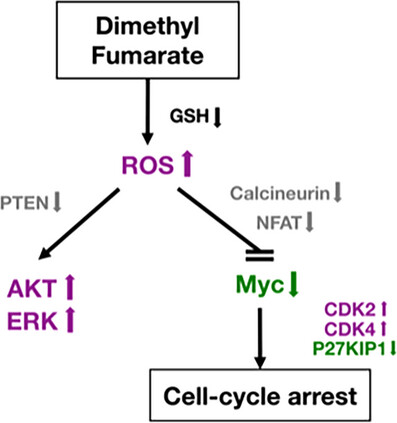
Dimethyl fumarate (DMF) inhibits T-cell proliferation and induces apoptosis by depleting glutathione (GSH) and accumulating reactive oxygen species (ROS). Here, we show that DMF-induced oxidative stress disrupts multiple cell-signaling pathways, including MYC, leading to cell cycle arrest and impaired proliferative responses in activated T-cells.
Immunity to Infection
Research Article
Clinical
Human IL-6-Producing B Cells Promote the Differentiation of Monocytes Toward an Anti-Inflammatory CD16⁺CD163⁺CD206⁺PD-L1⁺ Phenotype in Tuberculosis
- First Published: 19 April 2025
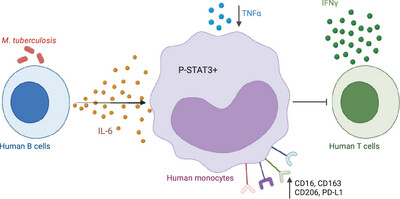
The supernatant of M. tuberculosis-stimulated B cells promotes monocyte polarization toward an anti-inflammatory CD16⁺CD163⁺CD206⁺PD-L1⁺ phenotype via an IL-6/STAT3 pathway. Confirmed with B cells from TB patients, this pathway impairs monocyte proinflammatory functions and may contribute to immune suppression in tuberculosis. Created in BioRender. Neyrolles, O. (2025) https://BioRender.com/930ras3
Notes and Insights
Clinical
Pamidronate-Induced Clinical Remission in Chronic Non-bacterial Osteomyelitis Is Associated with Reduced Vγ9Vδ2 T-Cell Receptor Expression
- First Published: 21 April 2025
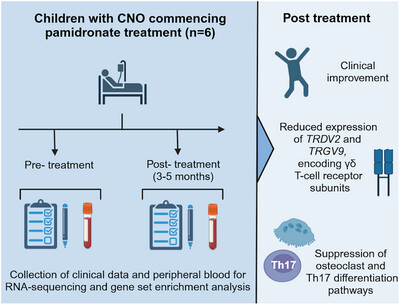
In children with chronic non-bacterial osteomyelitis, clinical and transcriptional changes in peripheral blood were examined after pamidronate treatment. Clinically effective treatment with pamidronate was associated with reduced expression of two genes (TRDV2 and TRGV9) that encode the subunits of the Vγ9Vδ2 T-cell receptor.
Adaptive Immunity
Research Article
Gluten-Free Diet Induces Small-Scale Changes Across Multiple T-Cell Subsets in NOD Mice
- First Published: 21 April 2025
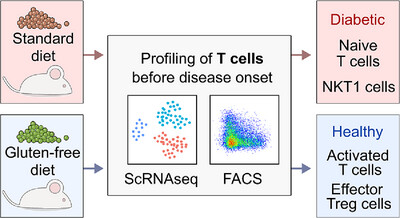
A gluten-free diet prevents Type I diabetes in NOD mice. We characterized T cells from prediabetic mice on gluten-free or standard diets using flow cytometry and single-cell transcriptomics. A gluten-free diet enhanced T-cell activation and effector differentiation, including regulatory T cells, suggesting immune modulation as a mechanism for diabetes prevention.
Immunity to infection
Research Article
Clinical
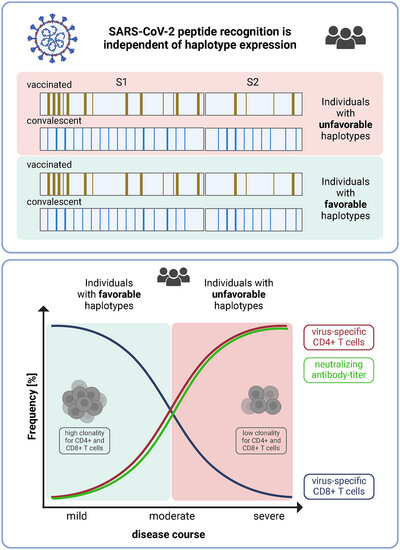
Distinct HLA Haplotypes Are Associated With an Altered Strength of SARS-CoV-2-Specific T-Cell Responses and Unfavorable Disease Courses
- First Published: 21 April 2025
Innate Immunity
Research Article
Basic
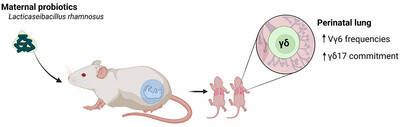
Maternal Administration of Probiotics Augments IL17-Committed γδ T Cells in the Newborn Lung
- First Published: 21 April 2025
Notes and Insights
Basic
Differential Induction of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Signaling by Antibody Isotypes: Implications for Plasma Cell Differentiation
- First Published: 25 April 2025
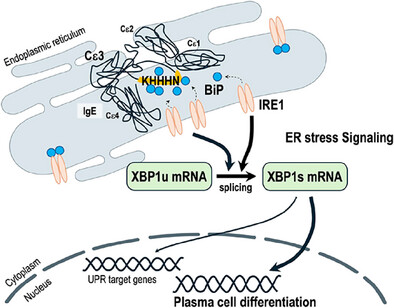
IgE induces stronger ER stress than IgG1 due to its constant region, particularly the Cε3 domain, which binds BiP more efficiently. Genetic and structural analyses confirmed IgE's higher BiP-binding capacity. ER stress, driven by IRE1-XBP1 signaling, regulates plasma cell differentiation, suggesting IgE-specific mechanisms in immune responses.
Immunity to Infection
Research Article
Basic
Plasmodium berghei Radiation-Attenuated Sporozoite-Immunized Mice Require Infectious Sporozoite Challenge to Maintain Protective Immunity
- First Published: 25 April 2025
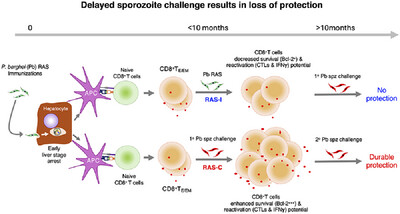
Multiple immunizations of mice with Plasmodium berghei radiation-attenuated sporozoites (Pb RAS) induce durable protective immunity, provided that 1° sporozoite (spz) challenge occurs early or within 10 months following the most recent RAS boost immunization. Delaying 1° challenge results in parasitemia. Pb RAS develops partially into early liver stages, is unable to progress to blood-stage parasites, and is taken up and presented by APCs to naïve CD8+T cells, which differentiate into CD8+TE/EM cells to eliminate infectious parasites. An early 1° challenge enhances CD8+TE/EM survival and functional properties necessary for durable protective immunity. By contrast, in the absence of an early infectious spz challenge, activated CD8+T cells exhibit decreased survival and functional attributes, resulting in a gradual loss of protection.