Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Enzyme Immobilization: Structural Insight into Stabilization of Pickering Emulsions with Fe3O4@SiO2 Nanoparticles for Enzyme Catalysis in Organic Media (Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 7/2017)
- First Published: 17 July 2017

In article number 1700117, Renliang Huang, Wei Qi, and co-workers describe the fabrication of Pickering emulsions with Fe3O4@SiO2 nanoparticles for enzyme encapsulation. The catalytic performance is shown to be highly dependent on the hydrophobicity of nanoparticles, which has great influence on the size of emulsion droplets and the mass transfer. The findings reveal a clear relation between nanoparticles' structure and enzyme activity.
Masthead
Contents
Communications
Atomically Precise Transformations and Millimeter-Scale Patterning of Nanoscale Assemblies by Ambient Electrospray Deposition
- First Published: 06 June 2017
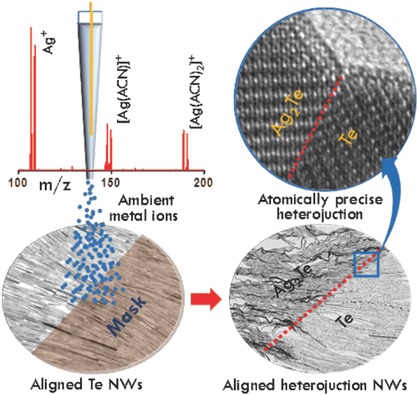
Ambient electrospray deposition of metal ions is used to bring about chemical transformation of nanowire assemblies, directly in the solid state. By suitably controlling the exposure to these ambient metal-ion-beams, such a transformation can be restricted to the precision of one atomic layer, forming aligned arrays of axial as well as radial heterojunction nanowires.
Full Papers
Structural Insight into Stabilization of Pickering Emulsions with Fe3O4@SiO2 Nanoparticles for Enzyme Catalysis in Organic Media
- First Published: 05 June 2017
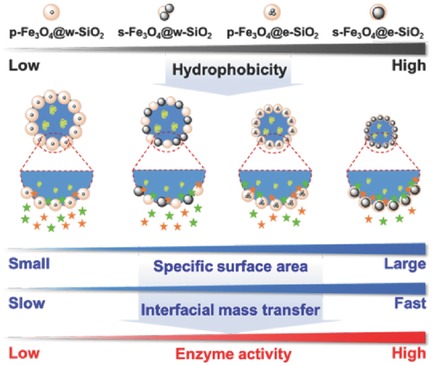
Various Pickering emulsions stabilized by Fe3O4@SiO2 nanoparticles (NPs) are produced for enzyme encapsulation. The catalytic performance is highly dependent on the hydrophobicity of NPs, which has great influence on the specific surface area of emulsion droplets and the interfacial mass transfer. The findings reveal a clear relation between NPs' structures and enzyme activity, facilitating the development of new emulsions for enzyme catalysis.
The 3D Nanoscale Evolution of Platinum–Niobium Oxide Fuel Cell Catalysts via Identical Location Electron Tomography
- First Published: 06 June 2017
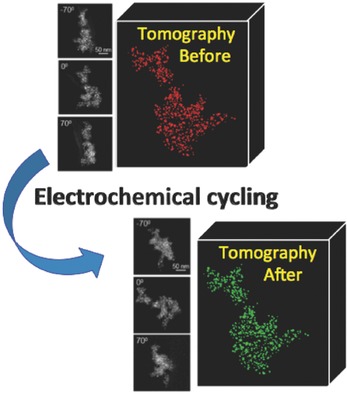
Identical location tomography of a hybrid Pt catalyst on NbOx/Carbon support material: The 3D distribution of the Pt nanoparticles on the support, generated from a series of tilted images, is shown before (red) and after electrochemical cycling (green). Subsequently, data quantification shows the evolution of the material following electrochemical cycling, such as particle size evolution, coalescence, and detachment.
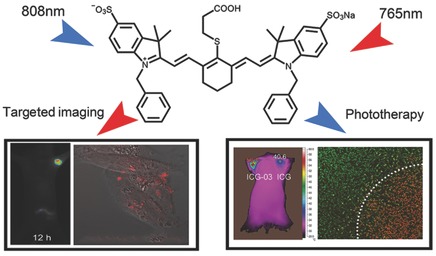
Multifunctional Small Molecule Fluorophore for Long-Duration Tumor-Targeted Monitoring and Dual Modal Phototherapy
- First Published: 06 June 2017
Colloidal Flower-Shaped Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Synthesis Strategies and Coatings
- First Published: 05 June 2017
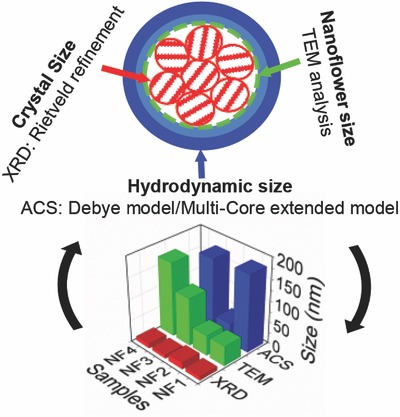
Different strategies to obtain multi-core nanoparticles with flower-shaped structures in the size range of 25–100 nm are examined. The core size within the nanoflower is measured, calculated, and modeled through structural and magnetic characterization, revealing multi-core nanoparticles that have very different intra- and interparticle interactions. The relevant synthesis parameters determining the core assembly are identified.
TiO2 Nanobelts Decorated with In2S3 Nanoparticles as Photocatalysts with Enhanced Full-Solar-Spectrum (UV–vis–NIR) Photocatalytic Activity toward the Degradation of Tetracycline
- First Published: 30 May 2017
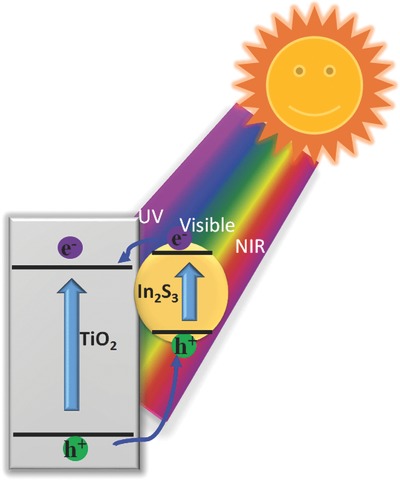
A solar full-spectrum (UV, visible, and near-infrared) photocatalytic property of In2S3 nanoparticle/TiO2 nanobelt heterostructures is found. The exceptional photocatalytic enhancement is due to the synergistic interactions of heterojunction with strong interfacial coupling effect, the In2S3 extended light absorption, efficient photogenerated e−/h+ pair separation, and fully exposed reactive sites induced by uniform packing of the ultrasmall In2S3.