Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Carbon Nanotubes: Controllable and Predictable Viscoelastic Behavior of 3D Boron-Doped Multiwalled Carbon Nanotube Sponges (Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 1/2016)
- Page: 1
- First Published: 15 January 2016

3D boron-doped multiwalled carbon nanotube (CBxMWNT) sponges are synthesized with covalent junctions by X. L. Lu, J. Suhr, and co-workers as described on page 21. The boron atoms that are introduced in the hexagonal sp2 carbon lattice permanently change the morphology of the nanotubes by inducing elbow-like junctions that lead to the formation of a 3D solid. Measurements of the mechanical properties of the CBxMWNT sponges demonstrate that the elbow-like structures can endow these solids with improved resilience ability and density-dependent viscoelastic properties.
Inside Front Cover
Graphene Quantum Dots: Highly Pure and Luminescent Graphene Quantum Dots on Silicon Directly Grown by Chemical Vapor Deposition (Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 1/2016)
- Page: 2
- First Published: 15 January 2016
Highly pure graphene quantum dots (GQDs) are directly grown on a silicon wafer using the chemical vapor deposition method by X. Yu, D. Yang, and co-workers on page 8. Two fluorescence and two phosphorescence components are emitted from the GQDs. The image shows a luminescent silicon wafer with GQDs on top. The insets display an atomic force microscopy image and a schematic diagram of the GQDs' luminescence mechanism. The illustration of chips with a photonic interconnect suggests a possible application.
Masthead
Contents
Contents: (Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 1/2016)
- Pages: 3-6
- First Published: 15 January 2016
Editorial
Communications
Highly Pure and Luminescent Graphene Quantum Dots on Silicon Directly Grown by Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Pages: 8-14
- First Published: 07 December 2015
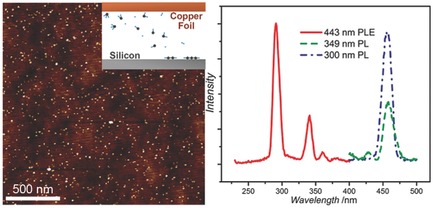
Highly pure graphene quantum dots (GQDs) are directly grown on a silicon wafer by the chemical vapor deposition method. Two fluorescence and two phosphorescence components are emitted from the GQDs. The size-independent luminescence of the GQDs suggests that the luminescence originates from edge defects of the GQDs.
CuO/WO3 Hybrid Nanocubes for High-Responsivity and Fast-Recovery H2S Sensors Operated at Low Temperature
- Pages: 15-20
- First Published: 10 December 2015
Full Papers
Controllable and Predictable Viscoelastic Behavior of 3D Boron-Doped Multiwalled Carbon Nanotube Sponges
- Pages: 21-26
- First Published: 17 November 2015

Boron-doped carbon nanotube (CNT) 3D sponges are compared with undoped CNT sponges in terms of their plastic, elastic, viscoelastic, and dynamic viscoelastic mechanical properties. The boron-doped CNT sponge shows more predictable and stable mechanical properties than the undoped sponge. The superior properties of these boron-doped CNT sponges are related to the “elbow-like” junctions on the doped carbon nanotubes.
Liquid-Crystal-Mediated Self-Assembly of Porous α-Fe2O3 Nanorods on PEDOT:PSS-Functionalized Graphene as a Flexible Ternary Architecture for Capacitive Energy Storage
- Pages: 27-37
- First Published: 30 November 2015
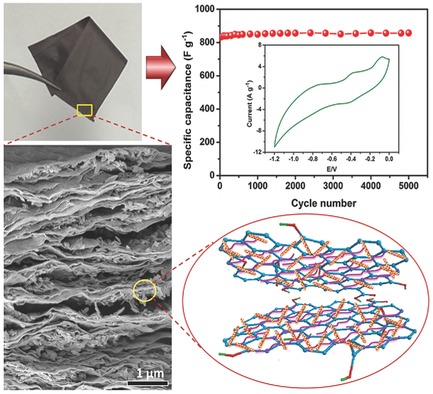
A liquid-crystalline novel self-assembly approach is used to develop a flexible material for charge capacitive applications. Highly porous hematite (α-Fe2O3) nanorods (HNRs) prepared by an advanced spray-precipitation method enable the fabrication with ultralarge graphene oxide (GO) functionalized by PEDOT:PSS in an aqueous medium to develop a novel self-assembled 3D architecture with excellent energy-storage performance.
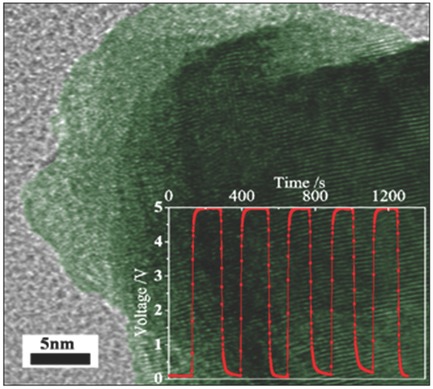
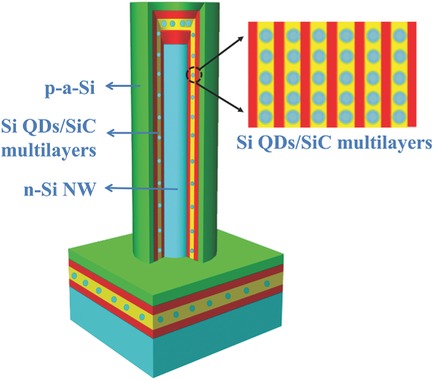
Light Harvesting and Enhanced Performance of Si Quantum Dot/Si Nanowire Heterojunction Solar Cells
- Pages: 38-43
- First Published: 10 December 2015
Optimum Quantum Yield of the Light Emission from 2 to 10 nm Hydrosilylated Silicon Quantum Dots
- Pages: 44-52
- First Published: 15 December 2015
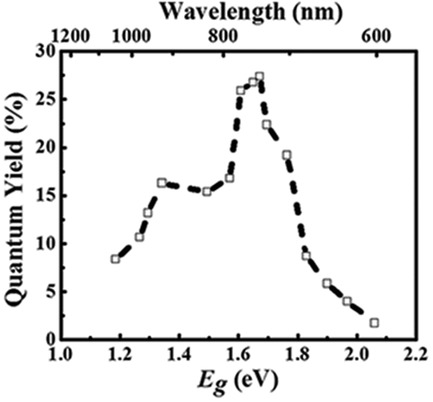
Silicon quantum dots (Si QDs) with sizes in the nearly whole quantum-confinement (QC) regime enable an equation for the dependence of the QD bandgap on the QD size to be formulated. An optimum photoluminescence (PL) quantum yield (QY) exists as the QD size varies, resulting from the interplay between the QC effect and the surface effect. The optimum PL QY may change with coating at the QD surface.
Human-Serum-Albumin-Coated Prussian Blue Nanoparticles as pH-/Thermotriggered Drug-Delivery Vehicles for Cancer Thermochemotherapy
- Pages: 53-62
- First Published: 07 December 2015
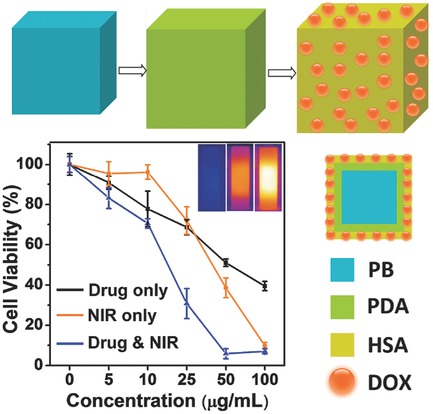
Human-serum-albumin-coated Prussian Blue nanoparticles with pH-/thermosensitive drug release are proposed for cancer thermochemotherapy, showing a remarkably superior synergistic effect. Such new drug-delivery systems made of approved materials may have promising biomedical applications for antitumor therapy.