Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Polystyrene-Based 2-Oxoacetates for the Light-Induced Release of Fragrances Under Realistic Application Conditions
- First Published: 22 September 2020

Front Cover: In article number 2000196, Andreas Herrmann and co-workers report on the light-induced release of fragrances from monomeric and polymeric 2-oxoacetates. The compounds can be used in laundry products to provide a long-lasting, pleasant, and fresh fragrance impression on fabric under everyday sunlight conditions. Cover design: Diane Marra (Firmenich).
Masthead
Trend
Polymers in the Blender
- First Published: 18 August 2020

Since the birth of controlled polymerizations, scientists always strived toward polymers with low dispersity. Yet, such polymers are not always advantageous, and only recently methods have started to develop that allow to create polymers with controllable molecular weight distribution shape. These novel methods have tremendous potential for developing materials with superior and more precise physical properties.
Full Papers
Polystyrene-Based 2-Oxoacetates for the Light-Induced Release of Fragrances Under Realistic Application Conditions
- First Published: 13 August 2020
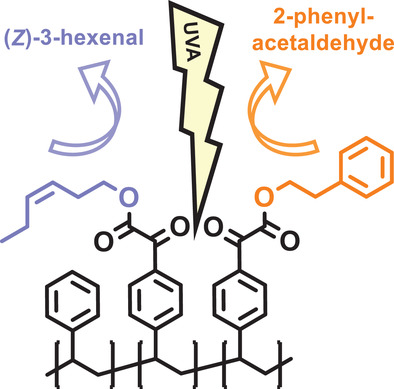
Simultaneous Friedel–Crafts acylation and cationic polymerization of styrene give access to 2-oxoacetate-derived polystyrenes for light-induced release of fragrances. The performance of a series of copolymer conjugates is evaluated by dynamic headspace analysis in different applications of functional perfumery and compared with their non-polymeric analogues.
Determination of Head-Addition Incidence of Methyl Acrylate and Temperature Dependence in Radical Polymerization by Coupling Reversible Addition-Fragmentation Chain Transfer Block Polymerization Derivatization and Gradient Polymer Elution Chromatography
- First Published: 17 August 2020
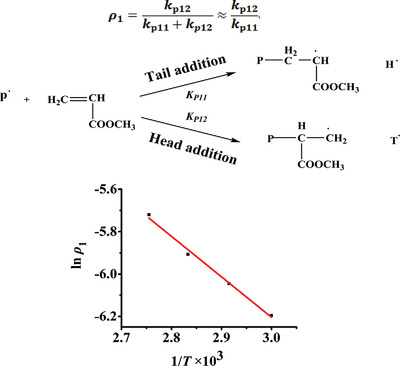
Based on the previously-developed equation and the determination method of dead dormant species content, the ρ1 values of methyl acrylate (MA) at different temperatures are determined. The results show that the ρ1 values of MA at 60, 70, 80, and 90 °C are 2.04 × 10−3, 2.37 × 10−3, 2.72 × 10−3, and 3.28 × 10−3, respectively, and the activation energy for ρ1 is 15.8 kJ mol−1.
Synthesis and Characterization of Polyrotaxanes Comprising γ-CDs and Distal Azide-Terminated PHEMA Using Propargylamine Monosubstituted β-CDs as End Stoppers
- First Published: 24 August 2020
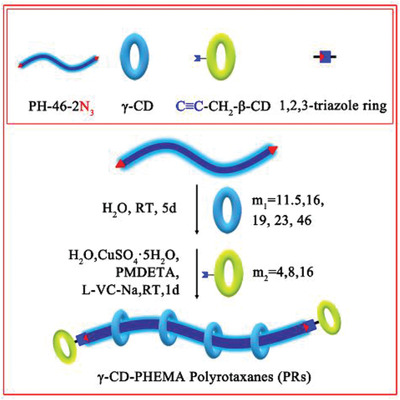
When a distal azide terminated poly(2-hydroxyethylmethacrylate) (PHEMA) is self-assembled with a varying amount of γ-cyclodextrins (CDs) in water followed by the in situ copper-catalyzed azide/alkyne cycloaddition with PA-β-CDs, γ-CDs cannot promote PA-β-CDs to be entrapped on the PHEMA chain and linear γ-CD-PHEMA PRs are invariably formed thereof.
Effect of Polymer Network Topology on the Electro-Optical Performance of Polymer Stabilized Liquid Crystal (PSLC) Devices
- First Published: 25 August 2020
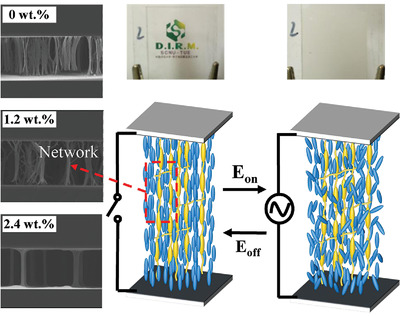
In this study, the effect of polymer network topology on the electro-optical performance of polymer-stabilized liquid crystal (PSLC) devices are investigated. With the decrease of density and strength of the polymer network, the threshold voltage and response time of PSLC devices reduced 50% and 87% respectively, this can further accelerate the marketization of smart windows.
Isoindigo (IID)-Based Semiconductor with F⋯S Interaction Locked Conformation for High-Performance Ambipolar Bottom-Gate Top-Contact Field-Effect Transistors
- First Published: 13 August 2020
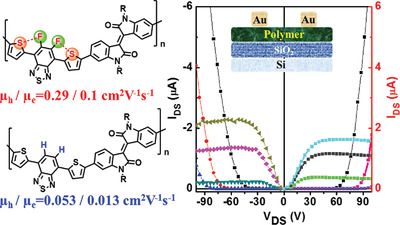
Isoindigo-based polymer semiconductor containing F⋯S intramolecular interactions is designed and synthesized. The bottom-gate/top-contact thin film transistors exhibit hole/electron mobilities of 0.29/0.1 cm2 V−1 s−1, much higher than the counterpart without F⋯S intramolecular interactions. These results demonstrate the introduction of F⋯S interactions is an effective strategy to design high-performance ambipolar polymer semiconductors.
Synthesis of Polyacrylate-Based Polyurethane by Organocatalyzed Group Transfer Polymerization and Polyaddition
- First Published: 25 August 2020
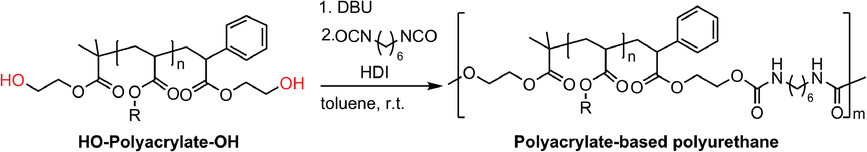
A series of novel polyacrylate-based linear polyurethanes are prepared by the combination of organocatalyzed group transfer polymerization (GTP) and polyaddition. The living nature of GTP method guarantees the accurate synthesis of polyacrylate diol by using hydroxyl functionalized initiator and terminator. The obtained polyurethanes with different side n-alkyl chains in the polyacrylate diols show various thermal behaviors.
Method of Preparation of Soluble PEDOT: Self-Polymerization of EDOT without Oxidant at Room Temperature
- First Published: 25 August 2020
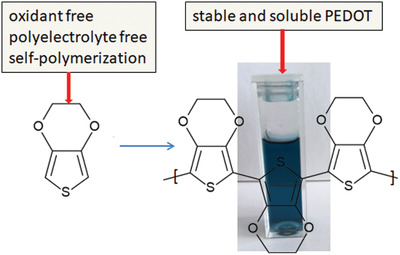
A simple method of ethylene-(3,4-dioxythiophne) self-polymerization without applying any oxidant and with the formation of polyethylene-(3,4-dioxythiophene) (PEDOT) solution at room temperature with a yield of 100% is reported. PEDOT solution could be deposited on many desirable surfaces (by simple evaporation of the solvent) for various applications from photovoltaic cell to pseudocapacitors.
Understanding the Performance of a Nanocomposite Based on a Conjugated Azo-Polymer and Reduced Graphene Oxide with Photoelectrically Switchable Properties by Analyzing the Potential Profile during Photocurrent Generation
- First Published: 26 August 2020
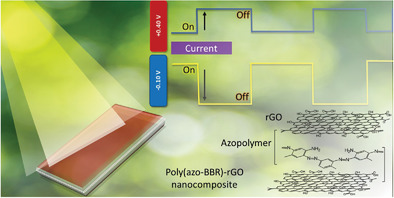
Properties of poly(azo-BBR) are useful evidence of the dynamics of the polymer as a photoelectrochemical switcher and molecular switching device for external stimuli. The nanocomposite film exhibit interesting photosynergetic properties based on the redox properties of the azo-polymer combined with the good electronic conductivity and stability of graphene.
Dot Nanopattern Self-Assembled from Rod-Coil Block Copolymer on Substrate
- First Published: 17 August 2020
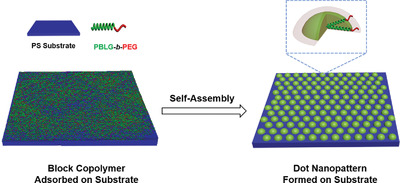
Dot nanopatterns are formed by polypeptide-based rod-coil block copolymers on the substrate through an adsorption-assembly process. The size of the dot-like surface micelles is readily regulated by the degree of the polymerization of the block copolymers. Most of the surface micelles are six-fold coordinated. Theoretical simulations qualitatively reproduce the experiments and provide the polymer packing information of the surface micelles.






