Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Macromol. Chem. Phys. 8/2015
- Page: 813
- First Published: 16 April 2015

Front Cover: Polymers cured by free-radical/cationic ring-opening hybrid polymerization under visible-light irradiation are studied to determine the effects of photo-polymerization kinetics and chemical miscibility on their crosslinking structure and mechanical properties. The chain transfer reaction between the epoxy group of the epoxide and the hydroxyl group of the methacrylate plays an important role in the formation of the crosslinking network, not only enhancing the crosslinking density, but also preventing the micro-sized phase separation. Further details can be found in the article by X. Ge, Q. Ye,* L. Song, A. Misra, and P. Spencer* on page 856.
Masthead
Contents
Contents: Macromol. Chem. Phys. 8/2015
- Pages: 815-817
- First Published: 16 April 2015
Talents & Trends
Regioselective Metal-Free Click Polymerization of Azides and Alkynes
- Pages: 818-828
- First Published: 16 February 2015
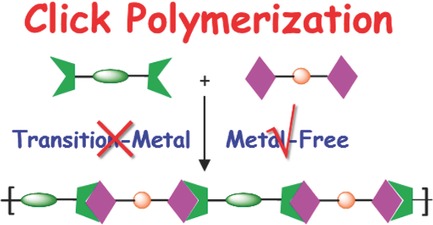
Metal-free click polymerization (MFCP) has been developed to circumvent the problems inherent in the broadly-applied Cu(I)-catalyzed azide-alkyne click polymerization reactions. The regioselective MFCP of azides and alkynes to produce regioregular polytriazoles is summarized, and the properties and applications of the resultant polymers are also discussed.
Full Papers
A Novel Near-IR Effective Pyrene-Based Donor–Acceptor Electrochrome
- Pages: 829-836
- First Published: 23 February 2015
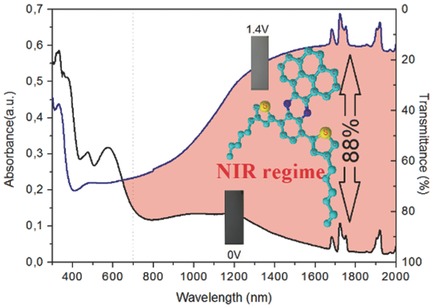
A novel donor–acceptor electrochromic material (poly-3HTP) containing a pyrene subunit is directly deposited onto an indium tin oxide (ITO)/glass surface via an electrochemical process. The polymer film exhibits a multielectrochromic feature, a strong near-infrared absorption at the oxidized state with an optical contrast of 88% (at 1800 nm), a very fast response time of 0.5 s and fast switching times, and long-term stability.
Tuning of Sol–Gel Transition in the Mixed Polymer Micelle Solutions of Copolymer Mixtures Consisting of Enantiomeric Diblock and Triblock Copolymers of Polylactide and Poly(ethylene glycol)
- Pages: 837-846
- First Published: 19 February 2015
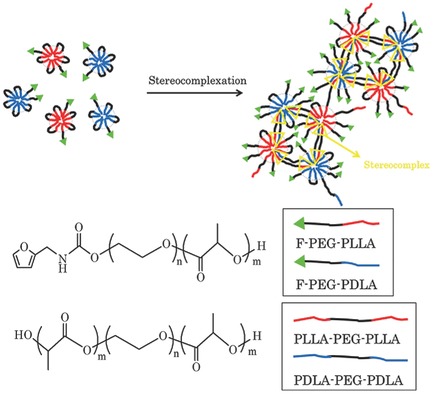
Diblock/triblock copolymer mixtures consisting of polylactide and poly(ethylene glycol) blocks form “sunflower-type” micelle particles in aqueous media with furanyl groups on the corona terminals. A mixed micelle solution of the enantiomeric copolymer mixtures undergoes a sol–gel transition, which is affected by the diblock/triblock copolymer ratio.
Polyethylene-Assisted Exfoliation of Hexagonal Boron Nitride in Composite Fibers: A Combined Experimental and Computational Study
- Pages: 847-855
- First Published: 14 February 2015
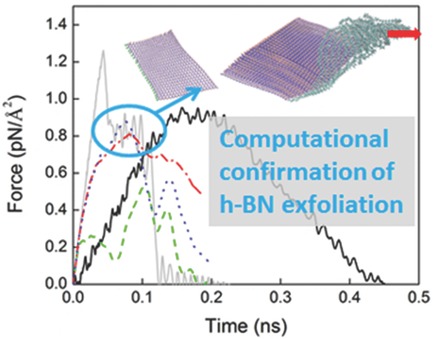
Joint experimental and computational methods are used to study the hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) exfoliation behavior in h-BN/PE composite fibers during hot-drawing. Experimental evidence suggests a polymer-assisted exfoliation process of h-BN under the drawing conditions, which is then morphologically confirmed and statistically analyzed using molecular dynamics simulation.
Visible-Light Initiated Free-Radical/Cationic Ring-Opening Hybrid Photopolymerization of Methacrylate/Epoxy: Polymerization Kinetics, Crosslinking Structure, and Dynamic Mechanical Properties
- Pages: 856-872
- First Published: 11 February 2015
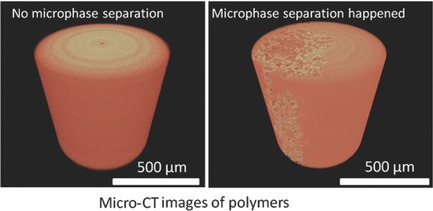
The effects of polymerization kinetics and chemical miscibility on the crosslinking structure and mechanical properties of polymers cured by visible-light initiated free-radical/cationic ring-opening hybrid photopolymerization are studied. The results support the important role that the chain transfer reaction between the epoxy and hydroxyl groups of methacrylate plays in the formation of the crosslinking network. The chain transfer reaction not only enhances the crosslinking density, but also prevents microphase separation.
Solution Behavior of Hydrolyzed Gradient Methyl/Phenyl Oxazoline Copolymers and Complexation with DNA
- Pages: 873-883
- First Published: 12 February 2015
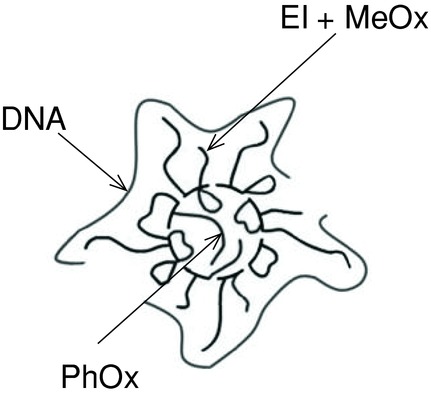
The self-assembly behavior of amphiphilic copolymers containing cationic ethylene imine, neutral hydrophilic 2-methyl-2-oxazoline, and hydrophobic 2-phenyl-2-oxazoline segments (HMPOx copolymers) in aqueous media and their complexation with DNA is investigated. The results are expected to have valuable implications for future utilization of these copolymers as nanocarriers of compounds of therapeutic interest.
Kinetic and Molecular Weight Modeling of Miniemulsion Polymerization Initiated by Oil-Soluble Initiators
- Pages: 884-893
- First Published: 14 February 2015
Kinetic Investigations of Cu-Mediated ATRP in Aqueous Solution
- Pages: 894-902
- First Published: 14 February 2015
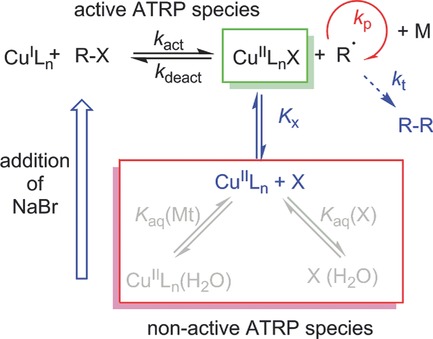
A monomer-free atom-transfer radical polymerization (ATRP) model system is studied in aqueous solution via on-line vis–NIR spectroscopy, with CuBr/2,2′-bipyridine as the catalyst. Addition of NaBr avoids water-assisted dissociation of the Br–Cu(II)/L bond. The ATRP activation–deactivation equilibrium constant and the activation rate coefficient increase significantly with water content.
Condensed Mode Cooling for Ethylene Polymerization: Part I. The Effect of Different Induced Condensing Agents on Polymerization Rate
- Pages: 903-913
- First Published: 14 February 2015
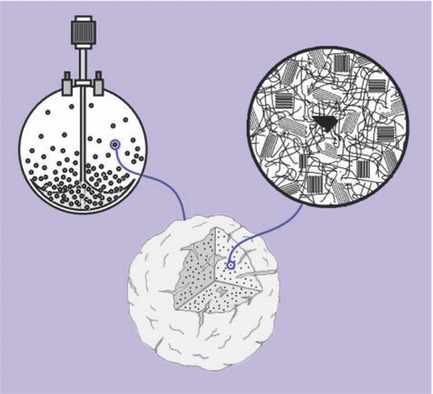
The instantaneous rate of gas-phase ethylene polymerization is promoted in presence of a variety of commonly used induced condensing agents (ICAs). This is attributed to the effect of the ICA compound in enhancing the local concentration of ethylene at the active polymerization sites dispersed through the growing polymer particles.
Controlled Remodeling of Hydrogel Networks and Subsequent Crosslinking: A Strategy for Preparation of Alginate Hydrogels with Ultrahigh Density and Enhanced Mechanical Properties
- Pages: 914-921
- First Published: 23 February 2015
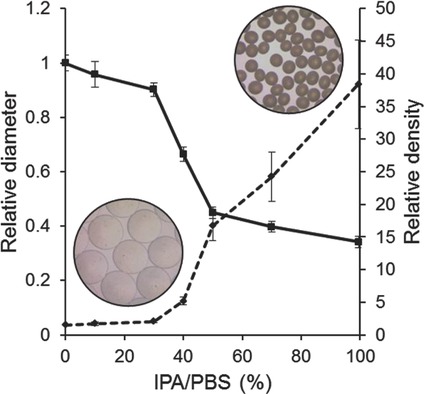
A simple strategy of remodeling of polymer networks and the subsequent crosslinking process (RsC process) is proposed, for preparation of uniform alginate microbeads with ultrahigh density, up to ≈38 wt%, via size reduction to 34% of the initial size. Such microbeads could be applied to prepare various alginate hydrogels of high density, with tailored mechanical properties.