Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Macromol. Chem. Phys. 5/2015
- Page: 469
- First Published: 02 March 2015

Front Cover: Bulk self-assembly of polystyrene-block-poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PS-b-PNIPAM) is shown to form microphase-separated films. After dispersing the films in ethanol, nanocylinders stabilized by polystyrene cores were obtained. These kinetically trapped nanocylinders exhibited thermo-/ultrasound-responsive shape transition properties. The transition process could be modulated by the balance between energy input and kinetic barrier. Further details can be found in the article by Y. Li, B. Peng,* and Y. Chen* on page 495.
Back Cover
Macromol. Chem. Phys. 5/2015
- Page: 584
- First Published: 02 March 2015

Back Cover: A one-handed helical supramolecular polymer membrane of 1,3,5-trisubstituted benzenes was successfully prepared via the quantitative photocyclic aromatization reaction of a cis-cisoidal poly(chiral substituted acetylene) membrane. The resulting one-handed supramolecular helicity of the resulting polymer membrane could be retained even after in situ removal of the chiral substituents in the membrane. Further details can be found in the article by L. Liu,* Q. Long, T. Aoki,* T. Namikoshi, Y. Abe, M. Miyata, M. Teraguchi, T. Kaneko, Y. Wang, and C. Zhang on page 530.
Masthead
Contents
Contents: Macromol. Chem. Phys. 5/2015
- Pages: 471-474
- First Published: 02 March 2015
Full Papers
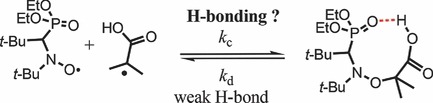
Hydrogen-Bonding Effects for the C–ON Bond Homolysis and Reformation Reactions of Alkoxyamines
- Pages: 475-488
- First Published: 22 December 2014
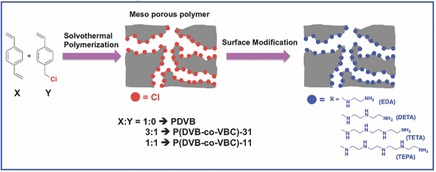
Amine-Functionalized Porous Polymer Network for Highly Selective Absorption of CO2 Over N2
- Pages: 489-494
- First Published: 22 December 2014
Kinetically Trapped Block Copolymer Nano-Objects with Cylinder to Sphere Shape Transition Properties
- Pages: 495-503
- First Published: 18 December 2014

A kinetically trapped system with a cylinder to sphere shape transition property is prepared by dispersing the microphase-separated polystyrene-block-poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PS-b-PNIPAM) block copolymer bulk materials in ethanol. The transition process is found to be modulated by the balance between energy input and kinetic barrier. Increasing the temperature, application of ultrasound or decreasing the length of the core-forming block also accelerates the morphology transition process.
Synthetic Control of Pore Properties in Conjugated Microporous Polymers Based on Carbazole Building Blocks
- Pages: 504-510
- First Published: 04 December 2014
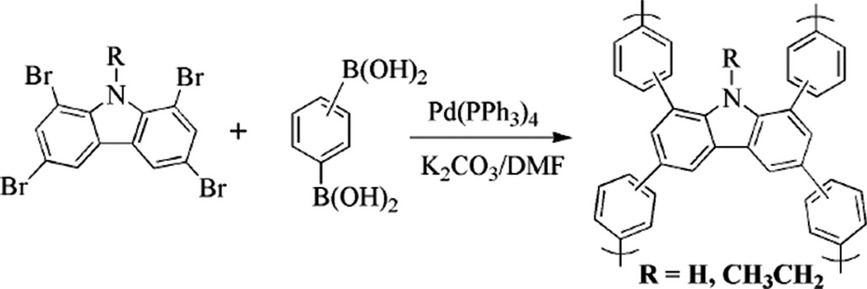
A series of conjugated microporous polymers from carbazole building blocks is designed and synthesized. The pore properties of the resulting polymers can be tuned by using either a linker with different geometries or carbazole substituted with alkyl groups. The polymer PPTBC shows a high Brunauer–Emmett–Teller specific surface area of 917 m2 g−1 with a high CO2 uptake ability of 2.93 mmol g−1 at 1.13 bar/273 K.
Tailor-Made Antimicrobial/Antiviral Star Polymer via ATRP of Cyclodextrin and Guanidine-Based Macromonomer
- Pages: 511-518
- First Published: 09 December 2014
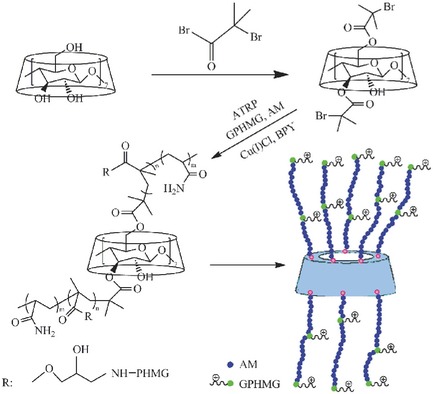
A range of novel star-like polymers are prepared via atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP) of modified guanidine-based macromonomer (GPHMG) and acrylamide (AM) using bromoisobutyryl-terminated β-cyclodextrin (Br-β-CD) with 5 or 8 active sites, as a macroinitiator to render the star-like polymers as antimicrobial and antiviral.
Solution-Processable Donor-Acceptor-Donor Oligomers with Cross-Linkable Functionality
- Pages: 519-529
- First Published: 18 December 2014
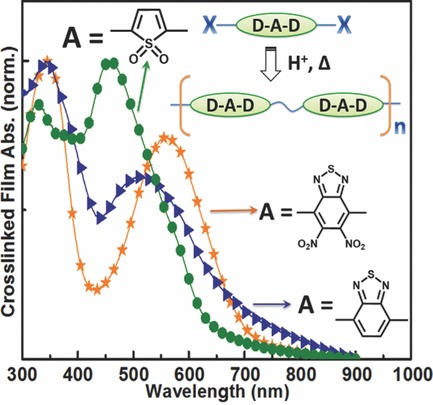
Cross-linkable oligomer-type molecules with a conjugated donor-acceptor-donor core are synthesized, and insoluble polymer films are prepared using different acid sources, including poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene):polystyrene sulfonate (PEDOT:PSS). The new compounds show broad absorption in the UV–vis spectrum and narrow optical bandgaps, the lowest being 1.46 eV. This work open prospects for organic optoelectronic devices, in particular photovoltaic cells, of enhanced performance stability.
A Chiral Supramolecular Polymer Membrane with no Chiral Substituents by Highly Selective Photocyclic Aromatization of a One-Handed Helical Cis-cisoidal Polyphenylacetylene
- Pages: 530-537
- First Published: 03 December 2014
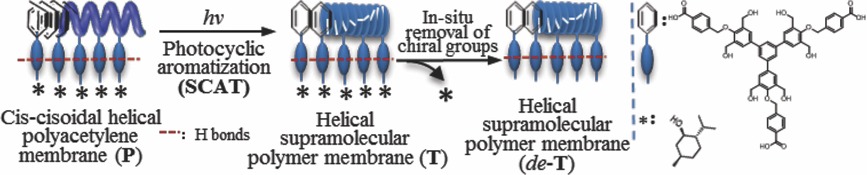
The quantitative photocyclic aromatization reaction in a cis-cisoidal polyacetylene (P) membrane affords a one-handed helical supramolecular polymer membrane of the corresponding cyclic trimers (T). Even after in situ removal of the chiral substituents in the T membrane, the resulting one-handed supramolecular helicity of T is retained.
Study of the Curing Process of DGEBA Epoxy Resin Through Structural Investigation
- Pages: 538-546
- First Published: 19 January 2015
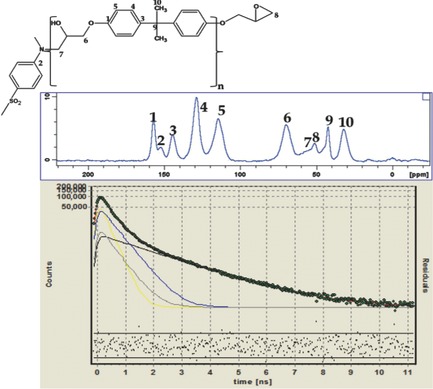
The curing process and structural properties of a diglycidyl ether of bisphenol A are studied using a multi-scale approach. The epoxy resin is analyzed at different cross-linking densities by differential scanning calorimetry, dynamic mechanical thermal analysis, solid-state NMR, and positron annihilation lifetime spectroscopy. The importance of this multi-method methodology is the possibility of obtaining a more complete knowledge of the system, overcoming the limits inherent to the use of a single technique.
Self-Assembly of Amphiphilic Block Copolypeptoids with C2-C5 Side Chains in Aqueous Solution
- Pages: 547-560
- First Published: 22 December 2014
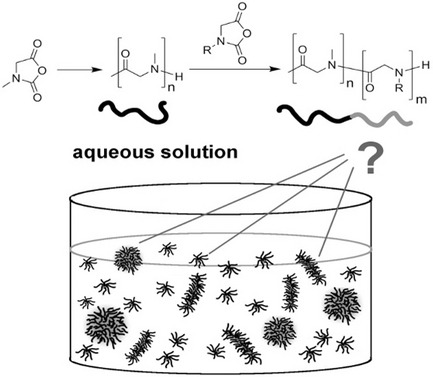
The aggregation behavior in aqueous solutions is reported for a series of different amphiphilic block copolypeptoids comprising polysarcosine as a hydrophilic part. The formation of aggregates is investigated with 1H NMR spectroscopy and dynamic light scattering, and the critical micelle concentration is determined using pyrene fluorescence spectroscopy. Final investigations regarding cytotoxicity reveal that the block copolypeptoids are well tolerated by mammalian cells up to high concentrations.
CO2-Redispersible Polymer Latexes with Low Glass Transition Temperatures
- Pages: 561-568
- First Published: 19 January 2015
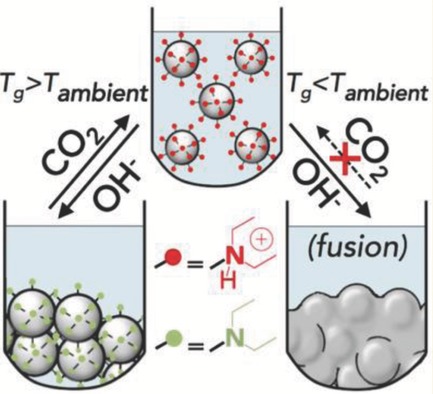
P(MMA-co-BA) latexes having different T g values are prepared with small amounts of 2-(diethyl)aminoethyl methacrylate (DEAEMA) as a comonomer through surfactant-free emulsion polymerization. It is found that particles of latexes having a T g higher than room temperature can be successfully redispersed by CO2 purging.
Synthesis of Novel Chain-End-Functionalized Polyethylenes via Thiol-ene Click Chemistry
- Pages: 569-581
- First Published: 29 January 2015
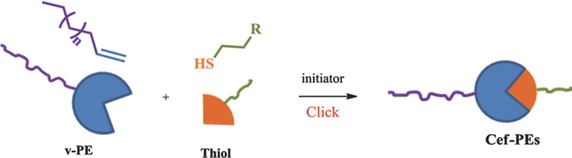
A library of low-molecular-weight, narrow-molecular-weight-distribution chain-end-functionalized polyethylenes (Cef-PEs) is prepared highly selectively and efficiently by thiol-ene addition of vinyl-terminated polyethylene (v-PE) with mercaptans under mild conditions. The conversions of all the reactions are up to 95%–100%. All the Cef-PEs are characterized by NMR, GPC, DSC, FT-IR, and TGA. It is found that alkaline mercaptans and solvents were adverse to the thiol-ene click reactions.