Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
(Ann. Phys. 12/2024)
- First Published: 09 December 2024
Kirigami/Origami Metasurfaces for Controlling Electromagnetic Waves
Kirigami and origami provide versatile spatial deformations in the design of reconfigurable metasurfaces, leading to various applications in deployable devices. In article number 2400213, Yilin Zheng, Ke Chen, and Yijun Feng provide an overview highlighting the implementations of kirigami/origami metasurfaces and their applications in controlling electromagnetic waves.
Masthead
Correction
Correction to “Unconventional Light-Matter Interactions Between Giant Atoms and Structured Baths with Next-Nearest-Neighbor Coplings”
- First Published: 10 November 2024
Perspective
Then & Now
The Young Einstein in Italy and the Annalen der Physik
- First Published: 24 October 2024

Thanks to the Annalen der Physik, we can trace the budding Einstein's footsteps in Italy: his interest in capillarity and his links with Carlo Marangoni, his bibliographical work in the library of the Lombard Institute, Milan's Academy of Sciences and Letters, and his connection with Giuseppe Jung, Michele Besso's uncle.
Review
A Review of Kirigami/Origami Metasurfaces for Controlling Electromagnetic Waves
- First Published: 10 September 2024
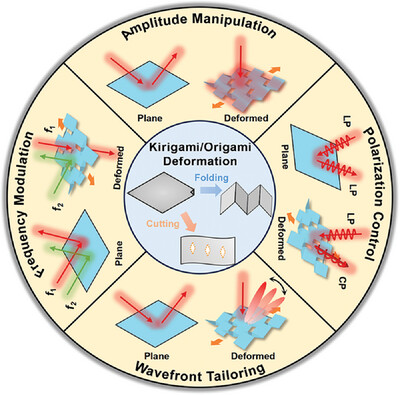
Kirigami/origami techniques have enabled the adaptable transformation of planar patterns into intricate three-dimensional (3D) forms, providing a novel approach to dynamically manipulating electromagnetic waves. An overview of the most recent developments in kirigami/origami metasurfaces for the manipulation of electromagnetic waves in the microwave band is proposed, as well as the potential avenues and forthcoming obstacles from this own perspective.
Research Article
Revisiting Relativistic Electrically Charged Polytropic Spheres
- First Published: 20 August 2024
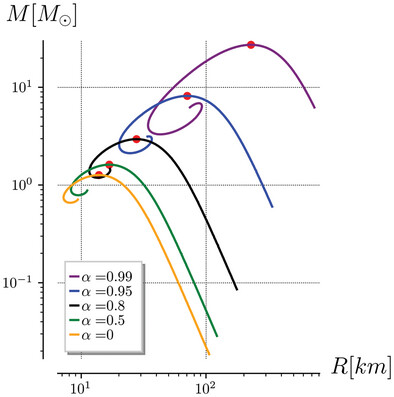
This work studies properties of electrically charged static spherically symmetric solutions of the Einstein-Maxwell system of equations, where the matter model is a polytropic gas and the electric charge density is proportional to the rest mass density. As a main conclusion, the only way to construct a black hole mimicker is if it's made of electrically counterpoised dust.
The Conformal Image of the Electron
- First Published: 23 August 2024
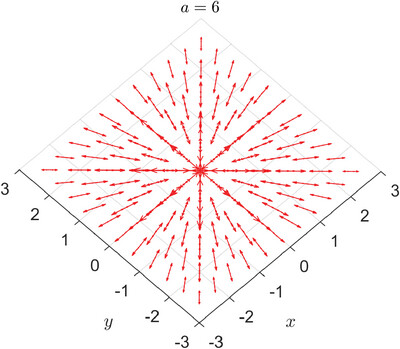
The spin structure of the electron on a surface with conformal deformation is constructed by the interaction of a vector potential with the electron on the surface without deformation. Together with introducing a scalar potential to facilitate the generation of a conformal metric structure and differential operator, the conformal image of the electron is shown to be realizable in an electromagnetic field.
Low-Energy Spin Manipulation Using Ferromagnetism
- First Published: 04 September 2024
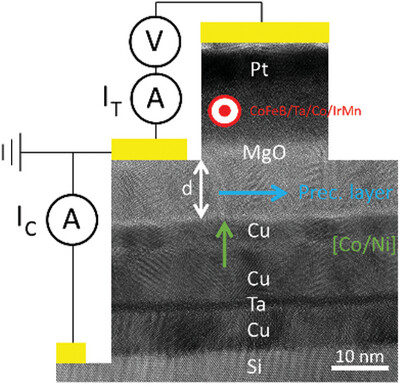
The manipulation of the electron spin direction at very low energies is a key issue to control in future integrated devices. The design of a lab-on-chip integrated magnetic tunnel transistor allows to measure the precession angle in various magnetic materials. The variation of film thickness or exchange field strength through it temperature dependence led to the control of precession angle from 700°/nm down to 0°/nm.
Design of a 10.8 to 34.6 GHz Ultra-Wideband Transparent Metamaterial Absorber Using an Equivalent Circuit Model
- First Published: 08 September 2024
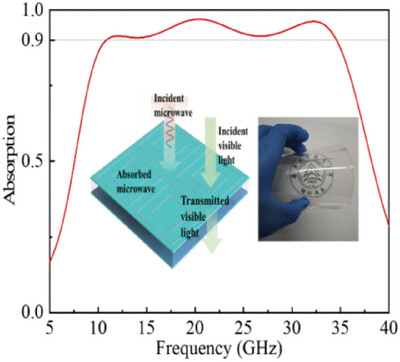
The article introduces an ultra-wideband metamaterial absorber (UWMA) achieving over 90% absorption from 10.82 to 34.59 GHz, along with its equivalent circuit model analysis. The UWMA has an ultra-thin thickness of 2.2 mm and boasts over 75% optical transparency in the visible spectrum. It holds significant potential for applications in aircraft stealth, transparent chambers, and flexible electronic screens.
Electromagnetically Induced Transparency-Like on All-Dielectric Metamaterials
- First Published: 26 September 2024
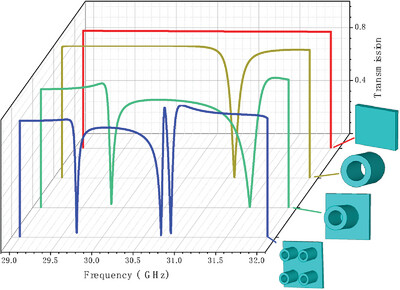
An all-dielectric metamaterial structure composed of a 2 × 2 array of hollow cylinders based on 3D printed is studied. The electromagnetically induced transparency-like (EIT-like) effect is obtained by analyzing its transmission, and the mechanism of EIT-like is analyzed by electromagnetic field distribution and CMT theory. The results demonstrate that the structure can obtain slow light effect, and the group index is >800.
Quantized Orbital Angular Momentums of Dipolar Magnons and Magnetoelectric Cavity Polaritons
- First Published: 26 September 2024
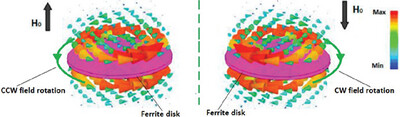
An analysis of spin and orbital angular momenta in magnetic insulators is important for the realization of magnetoelectric (ME) meta-atoms. In a quasi-2D ferrites disk, ME resonances are due to interaction the ferromagnetic and electric polarization orders. In near fields, simultaneous violation of time reversal and inversion symmetry are observed. The spectrum of ME oscillations is viewed as virtual photons.
Quantum Secure Communication Based on Interferometric Teleportation
- First Published: 17 October 2024
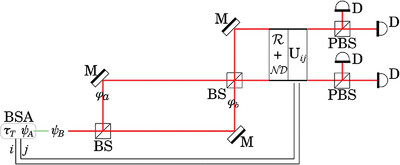
The concept of interferometric teleportation is reported. Also, based on this concept, a quantum secure communication protocol is proposed. Higher efficiency and rate are achieved by the proposed protocol in comparison with the original teleportation-based protocol. The security of the proposed scheme is based on the principles of both quantum mechanics and special relativity.
Microwave-to-Optical Conversion and Amplification in Cavity Optomagnonics System
- First Published: 26 September 2024
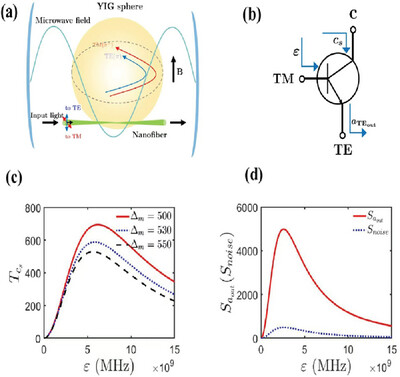
A scheme to construct a quantum transistor using a hybrid cavity optomagnonics system is presented. The TM classical mode can control the transmission of the quantum signals input from the microwave mode into the optical TE mode, meanwhile the microwave quantum signals can be amplified due to the nonlinearity of the magnon mode as well as the effective magnon-optical nondegenerate parametric amplification.





