Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Cover image from M. M. Shawrav, H. D. Wanzenboeck, and co-workers (Chem. Vap. Deposition 2014, 20, 251)
- First Published: 10 September 2014
Masthead
Contents
Chem. Vap. Deposition (7–8–9/2014)
- Pages: 181-185
- First Published: 10 September 2014
Editorial
Preface to the CVD Special Issue: Atomic-Scale-Engineered Materials (ASEM)
- Pages: 186-188
- First Published: 10 September 2014
Reviews
Atomic Layer Deposition of Groups 4 and 5 Transition Metal Oxide Thin Films: Focus on Heteroleptic Precursors†
- Pages: 189-208
- First Published: 20 July 2014
Review: This review provides a brief description of ALD and presents studies on the deposition of thin films of groups 4 and 5 metal oxides using ALD. A description of the general ALD properties of homoleptic precursors, in addition to a review of the thermal ALD of groups 4 and 5 metal oxides from heteroleptic precursors, is presented. Trends in the properties of heteroleptic ALD precursors based on the literature review and recent experimental data are discussed.
Full Papers
Atomic Layer Deposition of TiO2 and ZrO2 Thin Films Using Heteroleptic Guanidinate Precursors†
- Pages: 209-216
- First Published: 24 July 2014
Full Paper: Atomic layer deposition of TiO2 and ZrO2 is performed using heteroleptic amido/guanidinate metal precursors, and ozone and water as oxygen sources. The results are compared to previous studies and the effect of the ligands on the precursor properties are discussed.
Cyclopentadienyl Precursors for the Atomic Layer Deposition of Erbium Oxide Thin Films†
- Pages: 217-223
- First Published: 20 July 2014
Full Paper: The ALD processes for three novel precursors for the ALD of Er2O3, namely Er(nBuCp)3, Er(iPrCp)3, and Er(MeCp)2(iPr-amd), are developed and the films are characterized. The first report of the conformal ALD growth of Er2O3 thin film on a high-aspect-ratio structure is also included.
MOCVD of TiO2 Thin Films using a Heteroleptic Titanium Complex: Precursor Evaluation and Investigation of Optical, Photoelectrochemical and Electrical Properties†
- Pages: 224-233
- First Published: 25 July 2014
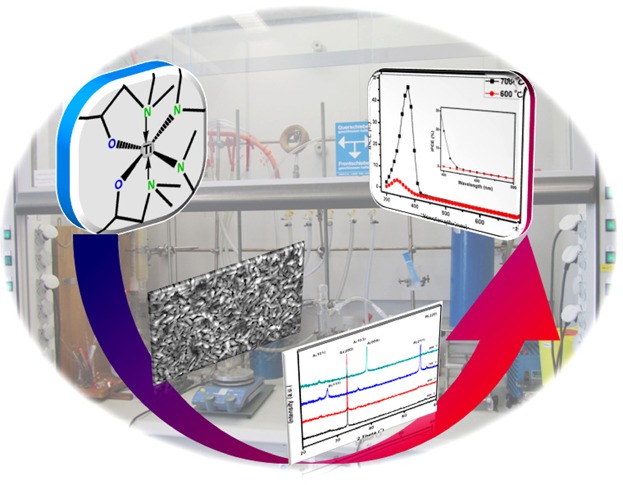
Full Paper: A Ti amide complex stabilized by a substituted aminoalcohol is synthesized for the first time. The compound exhibits promising thermal properties and is successfully applied as a MOCVD precursor for the growth of TiO2 thin films. The new precursor is very efficient in terms of high growth rates, with the possibility of tuning the morphology by controlling the CVD process parameters, which is particularly important in regard to photoelectrochemical applications.
Reviews
Recent Advances in Atmospheric Vapor-Phase Deposition of Transparent and Conductive Zinc Oxide†
- Pages: 234-242
- First Published: 25 July 2014
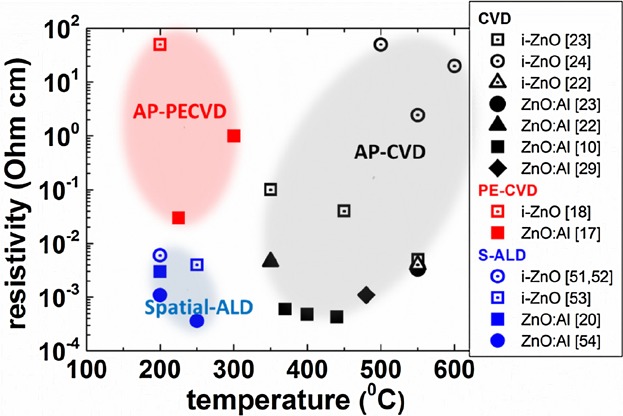
New atmospheric vapor-phase-deposition techniques are being developed to meet the industrial need for high-throughput and low-cost deposition processes. While atmospheric CVD is a mature technology, novel processes for the growth of transparent conductive oxides on thermally sensitive materials or flexible substrates are being developed, such as atmospheric PE-CVD and atmospheric spatial-ALD. The challenges and recent results on the growth of ZnO by atmospheric CVD, PE-CVD and spatial-ALD are presented.
Full Papers
Focused Electron Beam-Induced CVD of Iron: a Practical Guide for Direct Writing†
- Pages: 243-250
- First Published: 20 August 2014
Full Paper: Focused electron beam-induced deposition (FEBID) is used as a direct-write approach for the fabrication of Fe-based nanostructures on Si(100), starting from Fe(CO)5. FEBID uses an electron beam to locally induce a CVD process. A systematic variation of FEBID parameters is performed to study their influence on the geometry and composition of the deposit. Based on the results, specific deposition conditions are suggested for nanomagnetic applications and the fabrication of large structures.
Electron Beam-Induced CVD of Nanoalloys for Nanoelectronics†
- Pages: 251-257
- First Published: 19 August 2014
Full Paper: Focused electron beam-induced deposition is utilized to co-deposit gold and iron structures using dimethyl-gold(III)-trifluoroacetylacetonate and iron pentacarbonyl metal-organic precursors. The deposition rate and chemical composition of these direct-write Au-Fe nanoalloys can be controlled by varying the working pressures.
Plasma-Assisted Atomic Layer Deposition of PtOx from (MeCp)PtMe3 and O2 Plasma†
- Pages: 258-268
- First Published: 06 August 2014
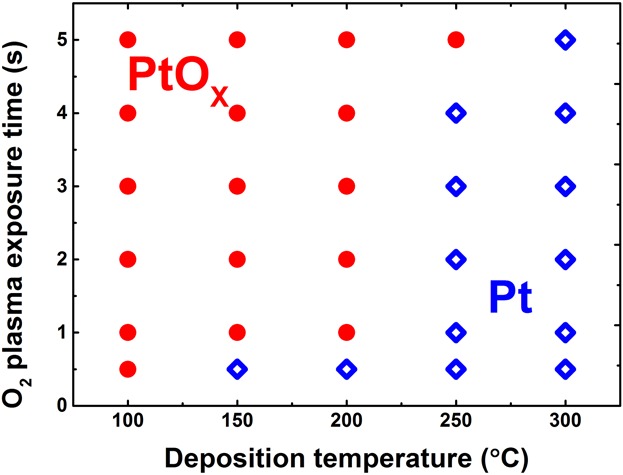
Thin films and nanoparticles of PtOx (2.5 < x < 2.7) are deposited by plasma-assisted ALD in a temperature window from room temperature to 300°C by controlling the O2 plasma and (MeCp)PtMe3 exposure. With increasing substrate temperature, the thermal stability of PtOx is found to decrease and the reducing activity of the precursor ligands is found to increase. The material properties of the PtOx films are studied and it is shown that a film conformality of 90% can be achieved in trenches with an aspect ratio of 9.
Atomic Layer Deposition of LaPO4 and Ca:LaPO4**
- Pages: 269-273
- First Published: 25 July 2014
Thin films of Ca-doped LaPO4 are produced using ALD with La(thd)3, (CH3)3PO4, H2O, and O3 as precursors. The films are studied using X-ray based techniques and TEM. The requirement of a mixed O3/H2O precursor for the growth of the phosphate is studied in detail using QCM.
Luminescent Properties of Multilayered Eu2O3 and TiO2 Grown by Atomic Layer Deposition**
- Pages: 274-281
- First Published: 25 July 2014
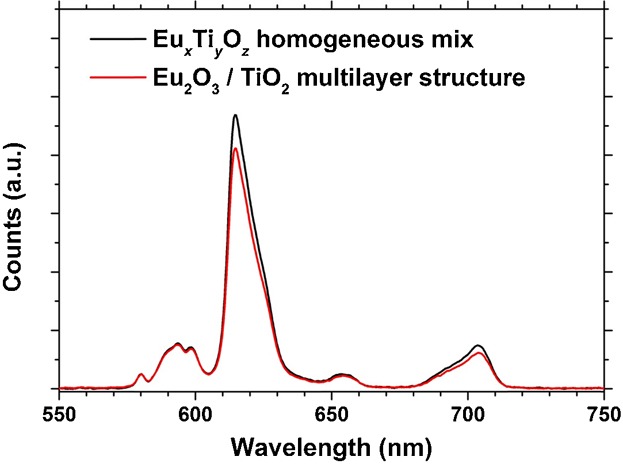
The luminescence properties of amorphous europium titanium oxide thin films grown by atomic layer deposition are investigated as a function of Eu2O3 and TiO2 layer thicknesses, varying from a homogeneous mixture to 2.9 nm repeating layer structures. Samples ranging from homogeneous to 0.8 nm repeating layers are optically similar while the luminescence intensity decreases for thicker layers.
Atomic Layer Deposition of TiOx/Al2O3 Bilayer Structures for Resistive Switching Memory Applications†
- Pages: 282-290
- First Published: 28 July 2014
The resistive switching of TiOx/Al2O3 bilayers integrated in µ-crossbar devices is investigated for future ReRAM. The bilayer stack is realized in consecutive atomic layer depositions (ALD) at 300 °C. Amorphous Al2O3 films exhibit a dielectric permittivity of 8.0 and disruptive field strength of 7 MV cm−1, whereas the oxygen-deficient TiOx is semiconducting. The bipolar-type resistive switching characteristics of TiN/TiOx/Al2O3/Pt cells show a strong dependence on both oxide layer thicknesses.
Atomic Layer Deposition of Transparent VOx Thin Films for Resistive Switching Applications†
- Pages: 291-297
- First Published: 04 August 2014
Frontispiece
Reviews
Vanadium Oxide Compounds: Structure, Properties, and Growth from the Gas Phase
- Pages: 299-311
- First Published: 22 July 2014
A thermodynamic analysis is performed to comment on the stability of vanadium oxide structures based on the calculated formation energies. The structure-related properties of the identified stable and metastable compounds are discussed, with an emphasis on the reported functional applications. Finally, the established gas-phase chemical deposition processes for the growth of vanadium oxide compounds are reviewed, referring to the type of precursors used.
Frontispiece
Full Papers
Surface Decoration of ϵ-Fe2O3 Nanorods by CuO Via a Two-Step CVD/Sputtering Approach**
- Pages: 313-319
- First Published: 22 July 2014
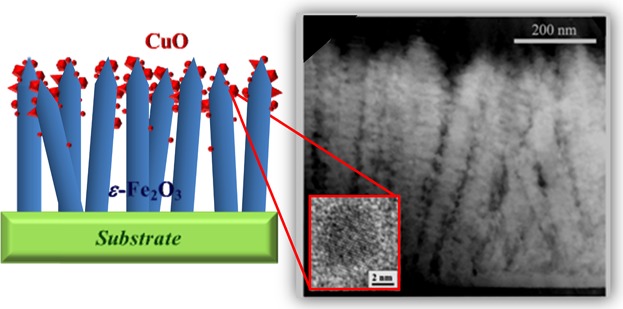
A two-step synthetic strategy for the synthesis of Fe2O3/CuO composites is presented. The approach consists of the growth of ϵ-Fe2O3 by CVD, followed by copper sputtering and annealing in air. A multi-technique characterization showed ϵ-Fe2O3 nanorod arrays possessing an intimate contact with nanometer-sized CuO particles, the loading and dispersion of which can be tuned as a function of the process duration.
Investigation of Optical, Electrical, and Mechanical Properties of MOCVD-grown ZrO2 Films†
- Pages: 320-327
- First Published: 01 September 2014
Full Paper: ZrO2 thin films are deposited by metal-organic (MO)CVD using the precursor (Zr(NMe2)2(guan)2) as the Zr source, together with oxygen. Functional properties, including the optical, electrical, and mechanical properties, of the resulting ZrO2 films are investigated.