Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Issue Information
Contents
REVIEW
Enzymatic Debranching of Starch: Techniques for Improving Drug Delivery and Industrial Applications
- First Published: 12 March 2025
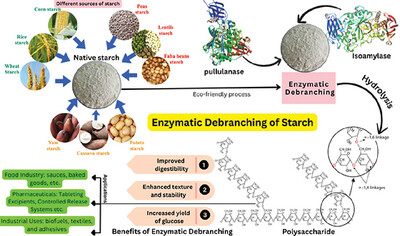
This study demonstrates the eco-friendly enzymatic debranching of starch from various sources, utilizing pullulanase and isoamylase enzymes. The process improves starch digestibility, enhances texture and stability, and increases glucose yield, with broad applications in the food industry, pharmaceuticals, and industrial sectors.
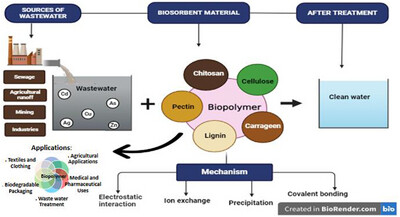
Chitosan: A Novel Approach and Sustainable Way to Remove Contaminants and Treat Wastewater
- First Published: 09 February 2025
Research Article
Isolation and Characterization of Non-Conventional and Underutilized Starch from Water Lily (Nymphaea lotus): Functional, Rheological, and Thermal Properties
- First Published: 10 July 2024
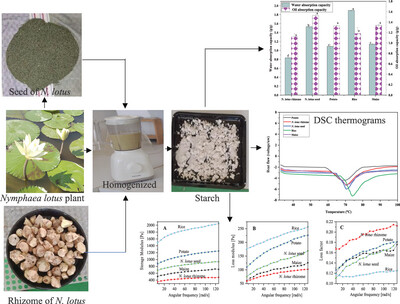
Starch isolated from N. lotus seed demonstrates the lowest paste clarity. N. lotus rhizome starch demonstrates a lower storage and loss modulus than seed. N. lotus rhizome starch has shown a higher shear stress and apparent viscosity. The onset and peak temperature of N. lotus rhizome are lower than seed.
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Exploring the Potential and Properties of Lotus (Nelumbo nucifera G.) Starches in Comparison With Conventional Starches for Food and Non-Food Applications
- First Published: 29 January 2025
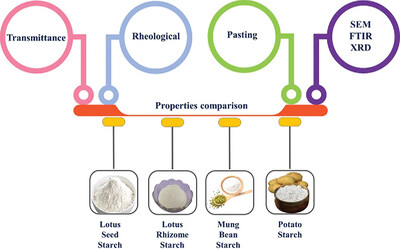
Lotus starches, that is, lotus seed starch (LS) and lotus rhizome starch (LRS) were comparatively characterized with mung bean starch (MBS) and potato starch (PS) based on physicochemical, pasting, morphological, structural, thermal, and rheological properties. The LS had the highest amylose content, but LRS showed the lowest value. The LS, LRS, and MBS exhibited typical A-type, while PS showed B-type pattern. MBS and PS showed higher transition temperatures than LS and LRS.
Design of Starch Coatings to Control the In Vitro Release of Insulin From Chitosan Hydrogels
- First Published: 19 January 2025
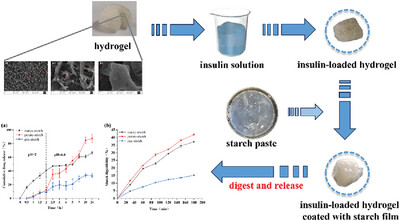
Chitosan-based hydrogel was used to carry insulin, then it was coated by starch films (prepared by A-, B-, and C-type starches at different glycerol contents) to regulate the release process of insulin in the simulated stomach and intestine, respectively. The results showed that pea starch film exhibited the best water-blocking properties when the glycerol content was 4% (w/v). And the potato film showed the best advantage in protecting the insulin-loaded hydrogel in the stomach and controlling the release of insulin in the intestine.
Study on Dispersion Technology of Pigment Powder and Its Interaction Based on Octenyl Succinate Starch and Arabic Gum Complex
- First Published: 24 January 2025
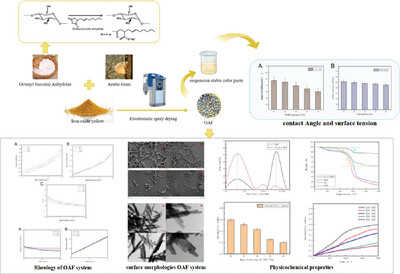
High concentrations of pigment powder dispersion stability are always a difficult problem in the cosmetics technology. It is necessary to improve iron oxide yellow dispersion and suspension stability of the paste to facilitate the application of iron oxide yellow powder in the cosmetics industry. In this study, octenyl succinate starch (OSA starch) and Arabic gum (AG) were used as composite wall materials to encapsulate iron oxide yellow and to find the best solution for the water-soluble pigment powder dispersion system.
Development of Biodegradable Films Based on Natural Extract From the Waste: Corn-Husk Derived Materials and Saffron Corm Starch
- First Published: 16 January 2025
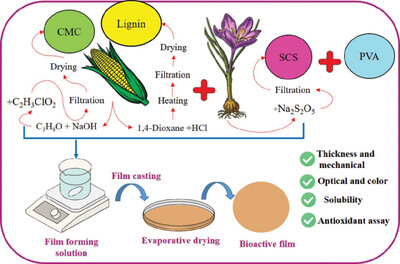
This flowchart presents a comprehensive experimental procedure for the production and evaluation of these novel bioactive films. It encompasses the entire process, including the extraction and processing of saffron corm starch (SCS), and the production of lignin (CL), and carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) from corn husk waste. The flowchart also highlights various analysis techniques that outline the characterization processes, enabling the evaluation of the films' properties and performance.
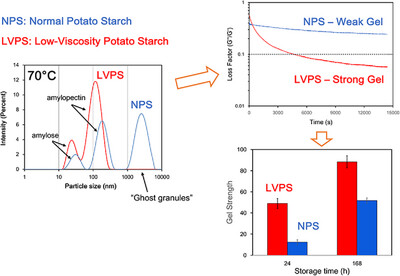
Molecular Ordering Determines the Formation of Strong Gels After Retrogradation of Low-Viscosity Potato Starch
- First Published: 11 February 2025
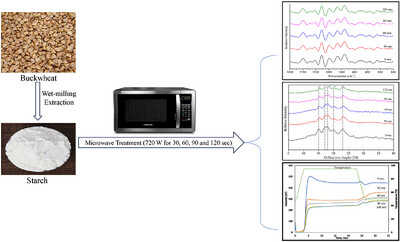
Impact of Microwave Treatment on the Physicochemical, Structural, and Rheological Properties of Buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum L.) Starch
- First Published: 09 February 2025
Research on Authenticity Identification and Physicochemical Properties of Various Commercially Available Lotus Rhizome Starch
- First Published: 31 January 2025
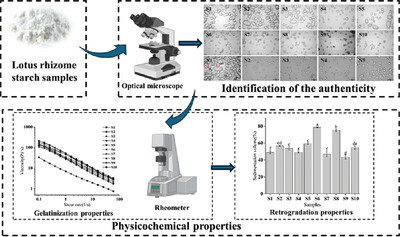
Unscrupulous merchants often add other inexpensive starches to lotus rhizome starch to reduce costs and seek profits, resulting in changes to the properties of starch. In this study, ten commerically available lotus rhizome starch samples were analyzed to obtain micrographs of their particles using an optical microscope, and their authenticity was verified. By measuring their physicochemical properties, including retrogradation and gelatinization characteristics, the differences in properties between genuine and adulterate lotus rhizome starch were compared.
Extraction, Purification, and Characterization of Galactomannan From Algerian Carob Seeds
- First Published: 31 January 2025
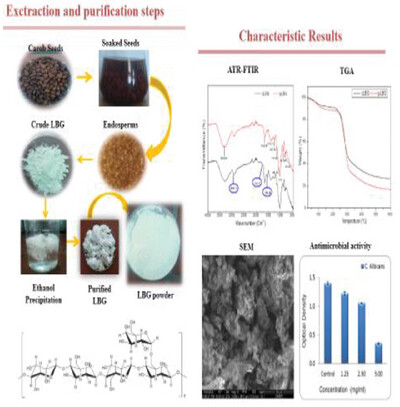
Extraction and purification of the natural polymer, nonstarch carob galactomannan (LBG), from Algerian carob seeds for industrial use. In order to obtain an efficient extraction of this biopolymer with high quality, the choice of the aqueous extraction method is important. Characterization results reveal crucial information for maximizing efficiency, making it suitable for diverse applications in food, biomedical, and other industries.