Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Issue Information
Articles
Visualizing and Interacting with Geospatial Networks: A Survey and Design Space
- Pages: 5-33
- First Published: 09 April 2021
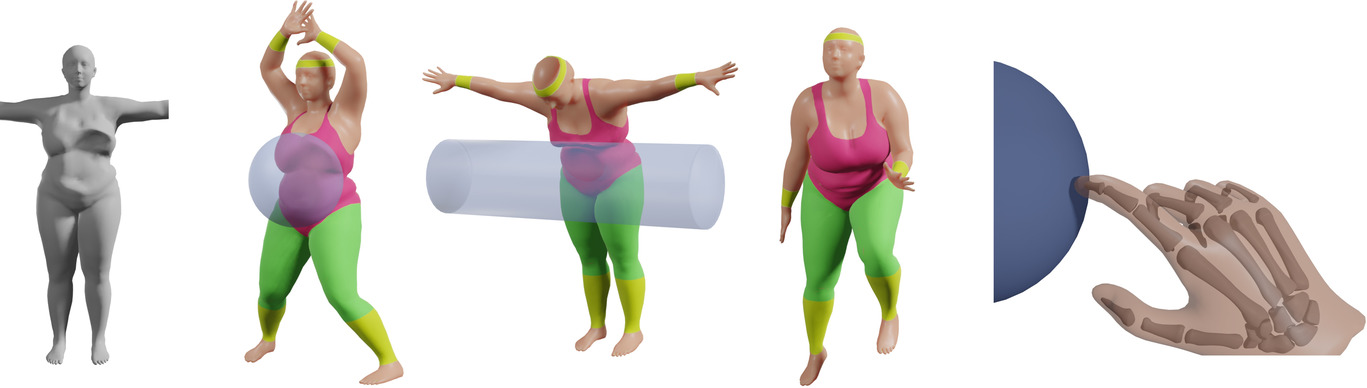
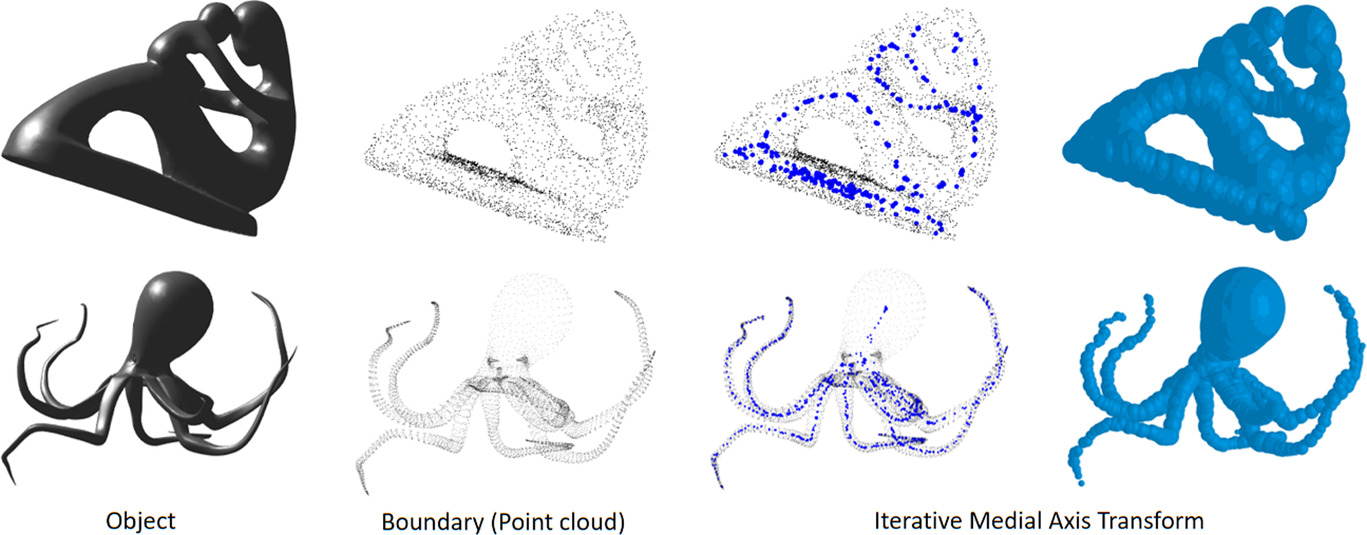
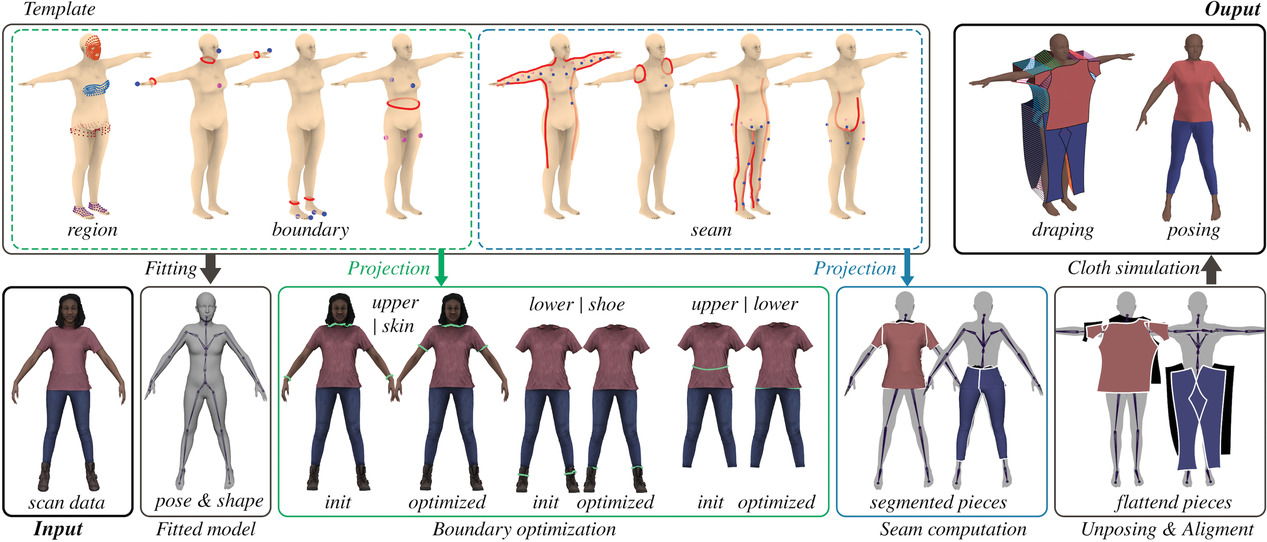
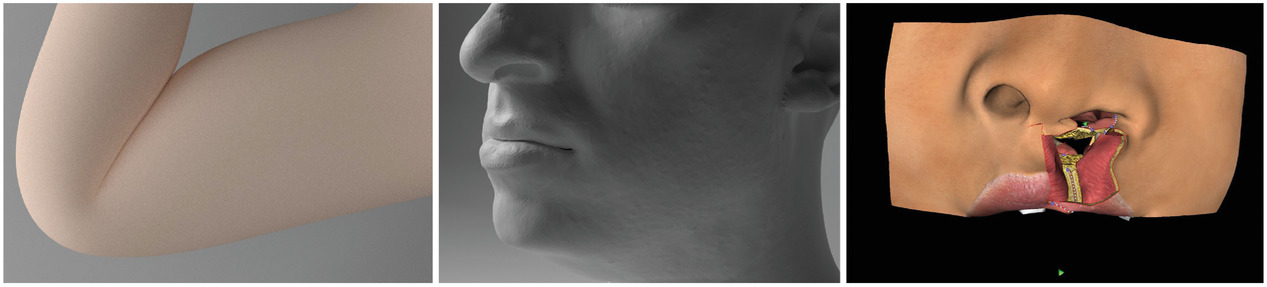
Parametric Skeletons with Reduced Soft-Tissue Deformations
- Pages: 34-46
- First Published: 02 February 2021
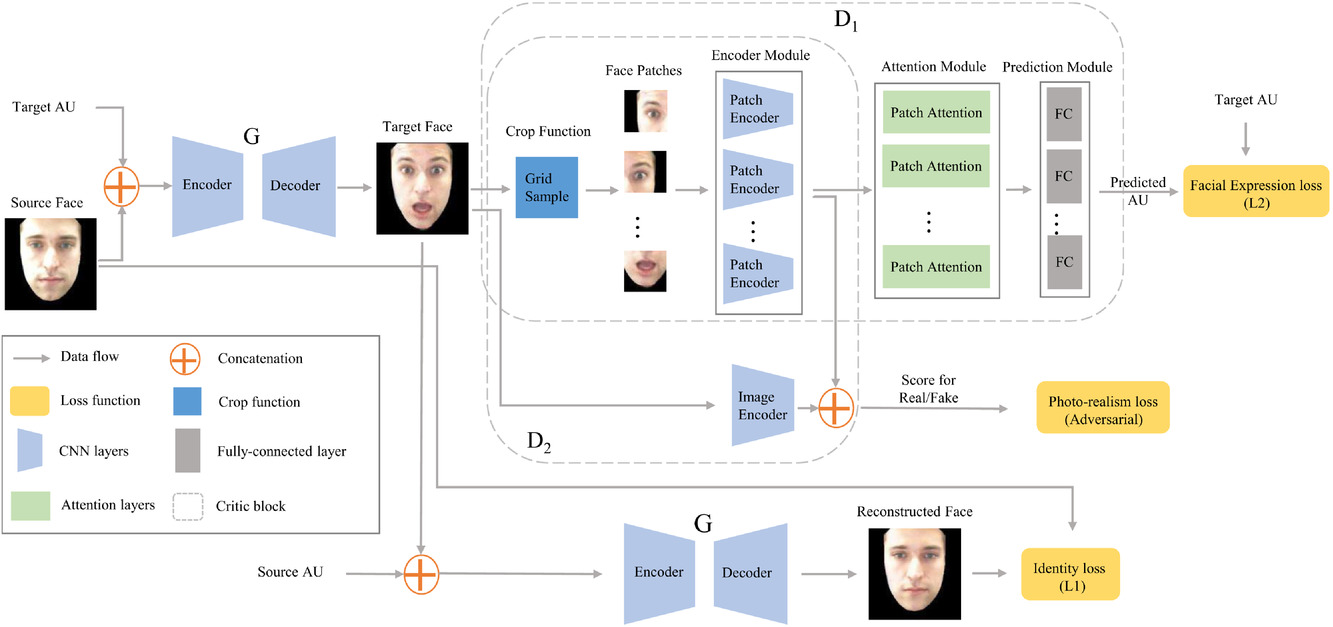
Action Unit Driven Facial Expression Synthesis from a Single Image with Patch Attentive GAN
- Pages: 47-61
- First Published: 17 March 2021
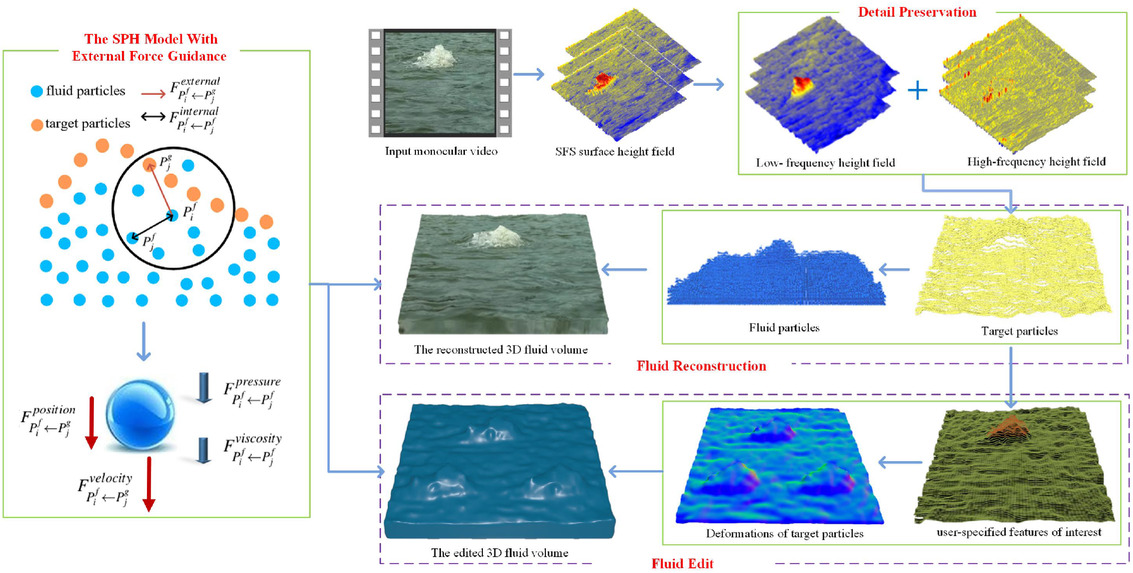
Fluid Reconstruction and Editing from a Monocular Video based on the SPH Model with External Force Guidance
- Pages: 62-76
- First Published: 05 March 2021
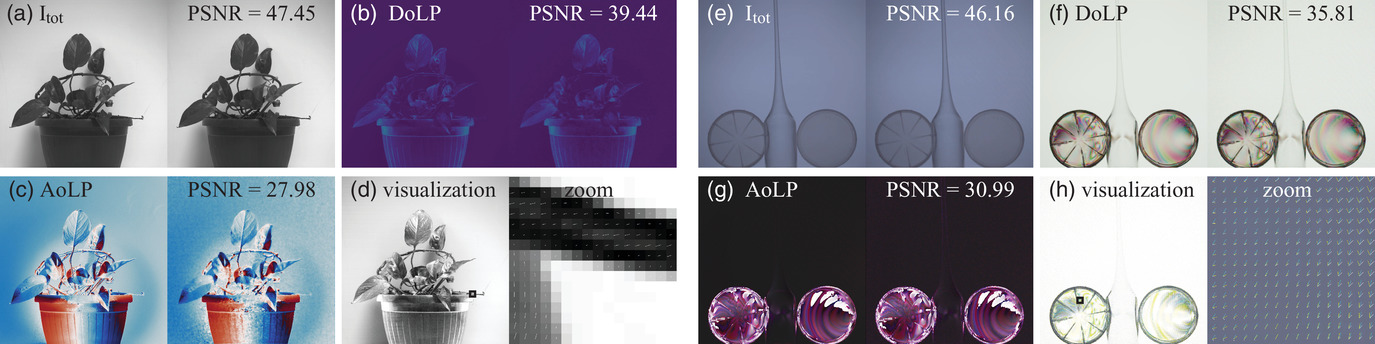
Linear Polarization Demosaicking for Monochrome and Colour Polarization Focal Plane Arrays
- Pages: 77-89
- First Published: 02 March 2021
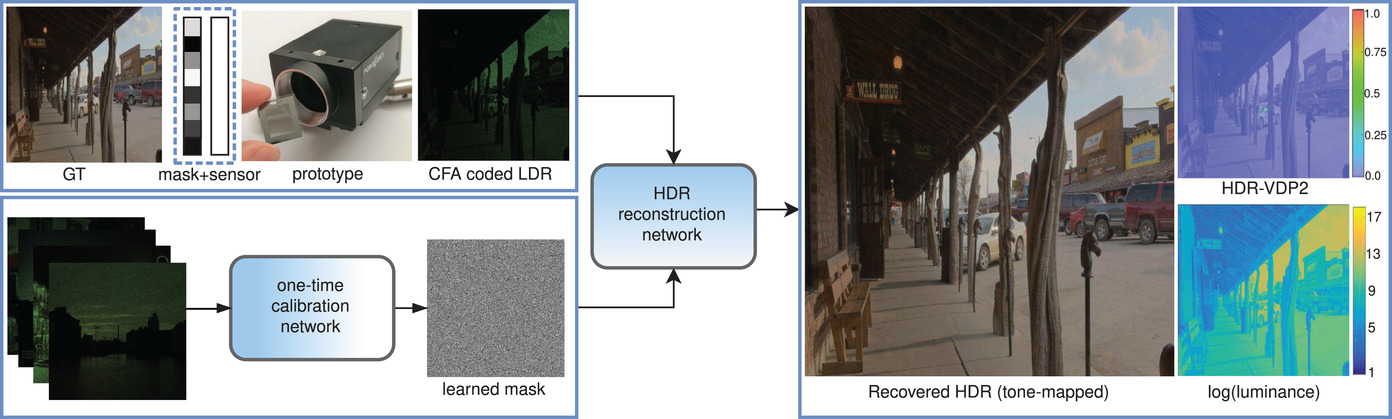
Transfer Deep Learning for Reconfigurable Snapshot HDR Imaging Using Coded Masks
- Pages: 90-103
- First Published: 11 March 2021
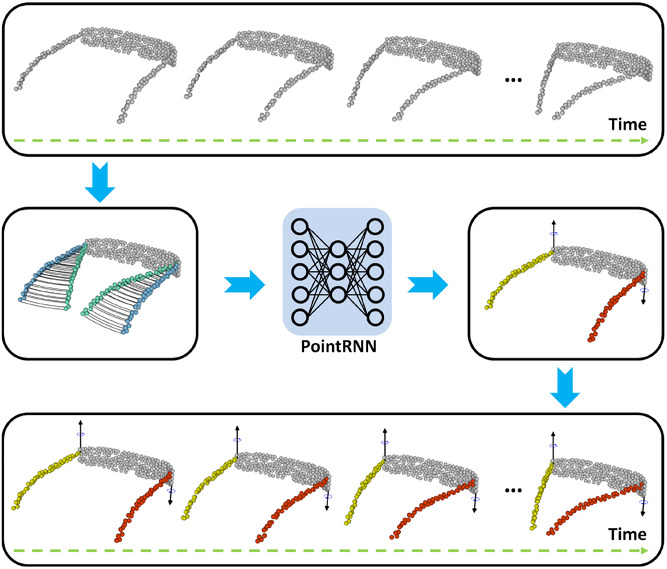
Self-Supervised Learning of Part Mobility from Point Cloud Sequence
- Pages: 104-116
- First Published: 11 March 2021
Fast Ray Tracing of Scale-Invariant Integral Surfaces
- Pages: 117-134
- First Published: 22 March 2021
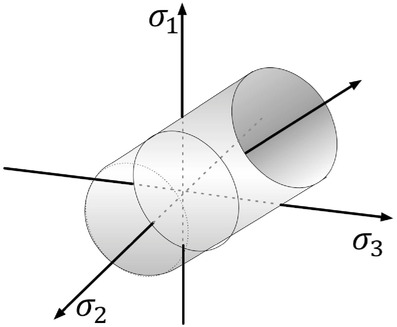
Visualization of Tensor Fields in Mechanics
- Pages: 135-161
- First Published: 30 March 2021
Efficient Rendering of Ocular Wavefront Aberrations using Tiled Point-Spread Function Splatting
- Pages: 182-199
- First Published: 07 May 2021
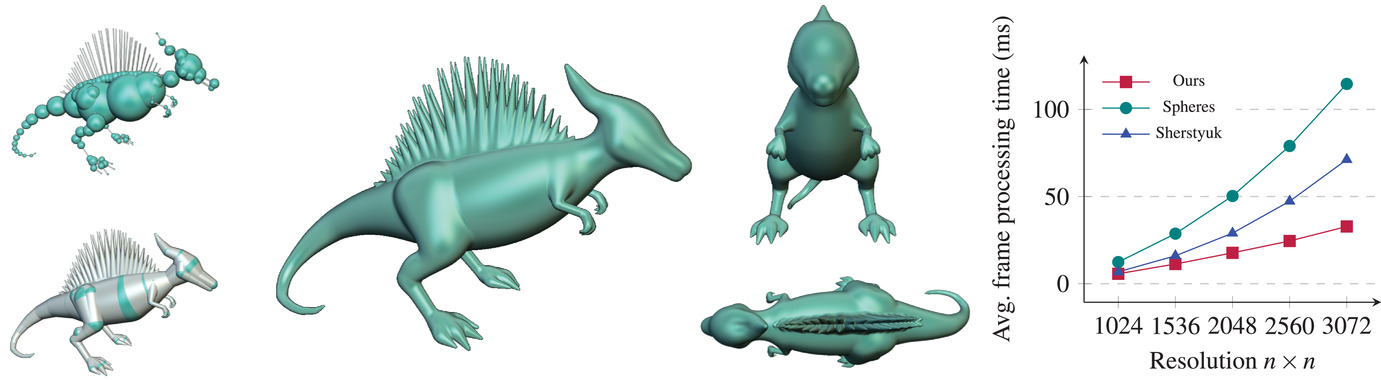
SREC-RT: A Structure for Ray Tracing Rounded Edges and Corners
- Pages: 200-214
- First Published: 18 April 2021
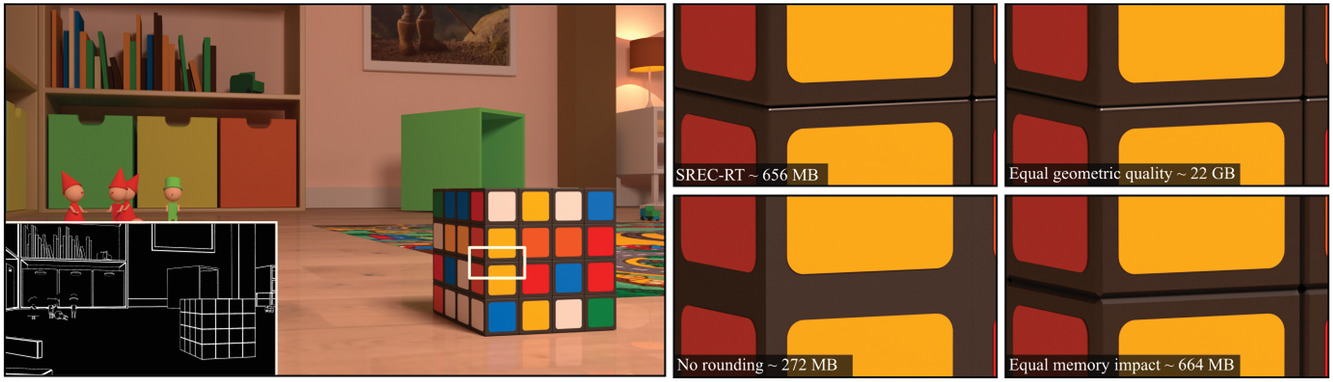
Man-made objects commonly exhibit rounded edges and corners. The variation of surface normals at these locations produces shading details essential to the realism of synthetic scenes. The more specular the surface, the finer and more prominent its highlights. Most geometric modelers represent rounded edges and corners with dense polygonal meshes that are limited in terms of smoothness increasing scene complexity. This paper proposes a method for the efficient modeling and rendering of smooth edges and corners from any input polygonal geometry. Our contribution is a geometric structure that automatically and accurately defines the geometry of edge and corner rounded areas, as well as the topological relationships at edges and vertices. This structure (SREC-RT) is integrated in a ray-tracing-based acceleration structure in order to determine the region of interest of each rounded edge and corner. It allows systematic rounding of all edges and vertices without increasing the 3D scene geometric complexity. While the underlying rounded geometry can be of any type, we propose a ray-edge and ray-corner intersection based on parametric surfaces. Our results present the advantages of our method, including extreme close-up views of surfaces with a much higher quality for very little additional memory, and reasonable computation time overhead.
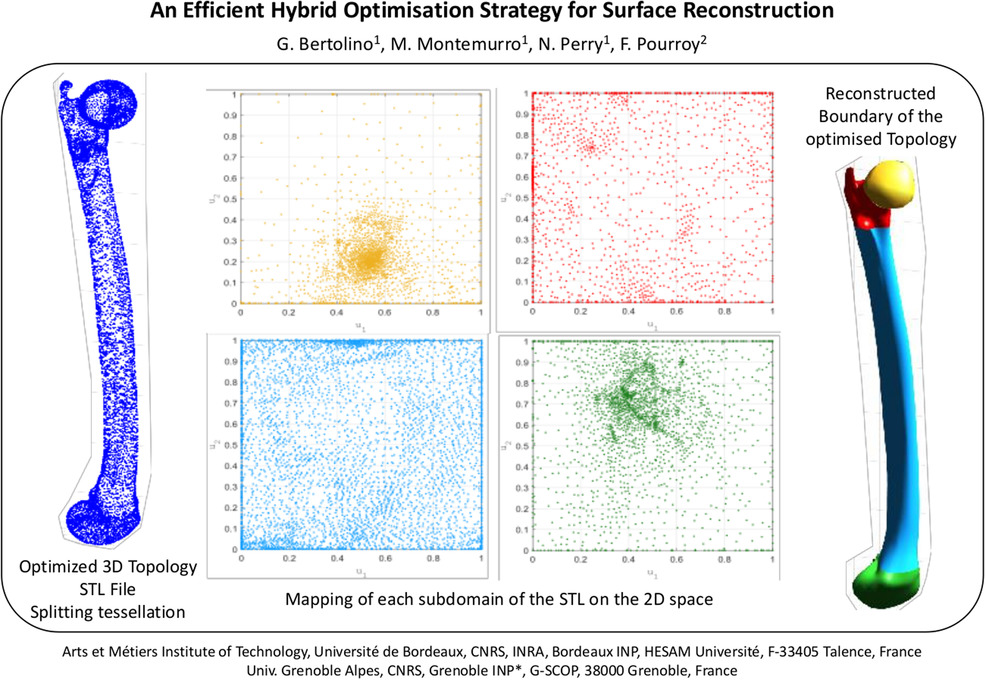
An Efficient Hybrid Optimization Strategy for Surface Reconstruction
- Pages: 215-241
- First Published: 22 April 2021
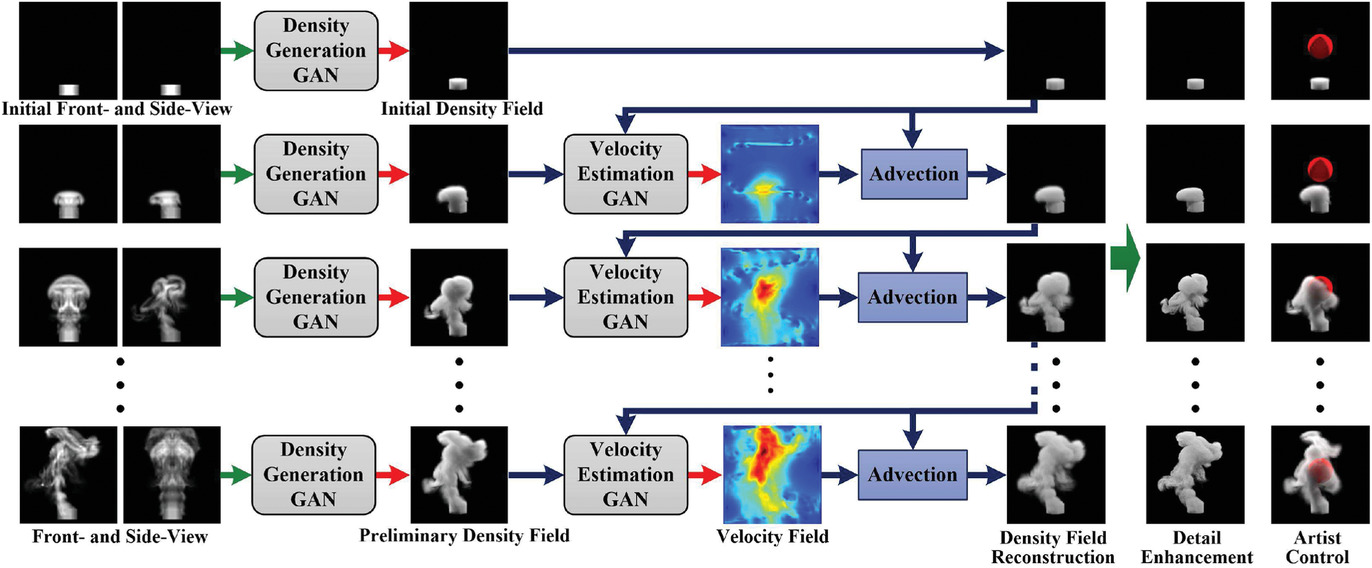
A Rapid, End-to-end, Generative Model for Gaseous Phenomena from Limited Views
- Pages: 242-257
- First Published: 27 April 2021
NOVA: Rendering Virtual Worlds with Humans for Computer Vision Tasks
- Pages: 258-272
- First Published: 08 May 2021
Neural Modelling of Flower Bas-relief from 2D Line Drawing
- Pages: 288-303
- First Published: 24 May 2021
Inverse Dynamics Filtering for Sampling-based Motion Control
- Pages: 304-314
- First Published: 10 June 2021
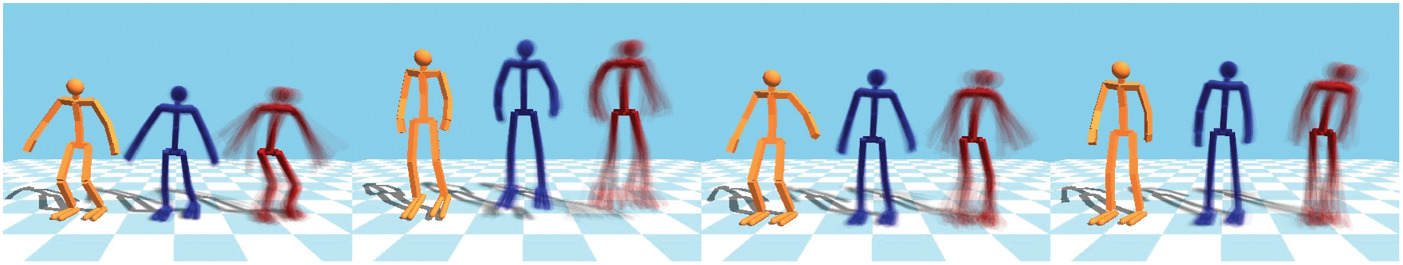
We improve the sampling-based motion control method proposed by Liu et al. using inverse dynamics. The figure shows samples drawn for different frames of a jumping motion. The orange is the reference motion. The blue shows the samples drawn by our method (with sample covariance initialization) and the red shows the samples drawn by our implementation of the sampling-based motion control method. With the use of inverse dynamics torques and sample covariance initialization, our sample simulations can have higher success rates, and we can choose to draw control samples from tighter distributions to produce smoother results.
Deep Neural Models for Illumination Estimation and Relighting: A Survey
- Pages: 315-331
- First Published: 09 June 2021
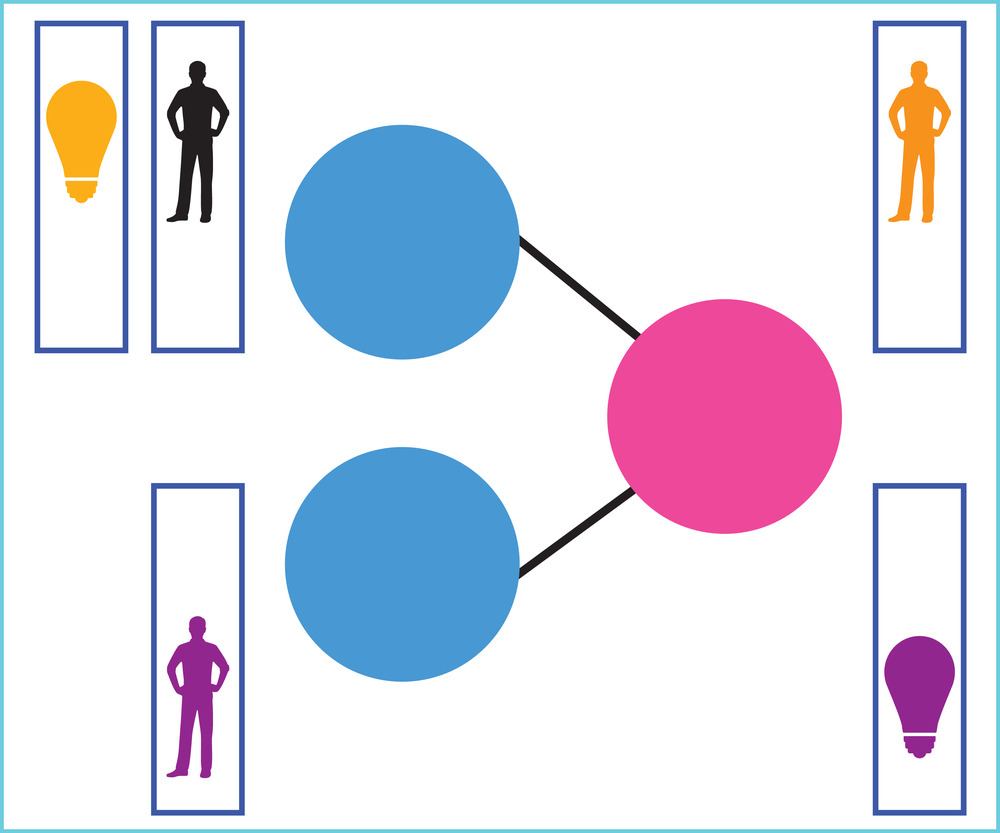
This contribution reviews the current advances in the application of deep neural computing to illumination estimation and relighting. We examine in detail the attributes of the proposed approaches, presented in three categories: scene illumination estimation, relighting with reflectance-aware scene-specific representations and finally relighting as image-to-image transformations. We also provide an overview of current publicly available datasets for neural lighting applications.
Neural BRDF Representation and Importance Sampling
- Pages: 332-346
- First Published: 29 June 2021
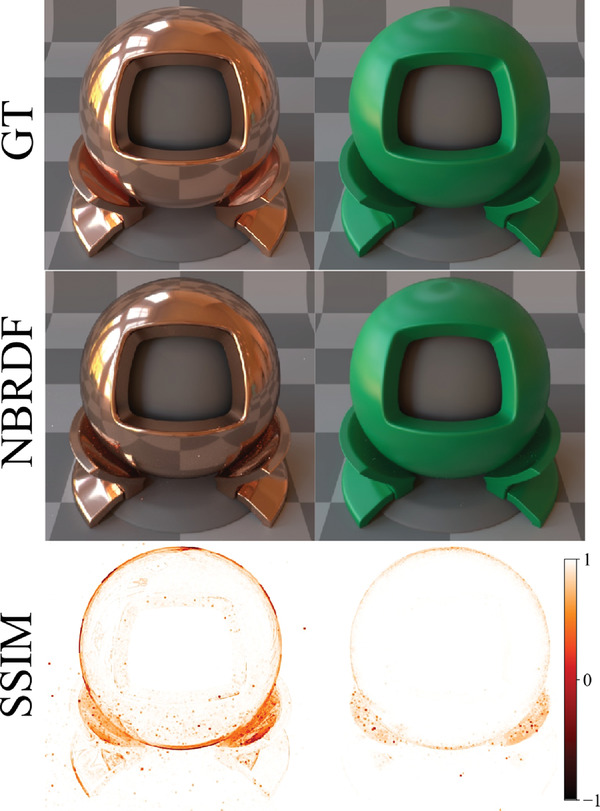
We present a compact neural network-based representation for measured BRDF data that combines high-accuracy reconstruction with efficient rendering via built-in interpolation of reflectance. Additionally, we implement a meta-learning autoencoder architecture that learns the space of real-world materials and generates compact embeddings, which we leverage for material generation through interpolation and efficient rendering via importance sampling.
Customized Summarizations of Visual Data Collections
- Pages: 347-370
- First Published: 12 July 2021
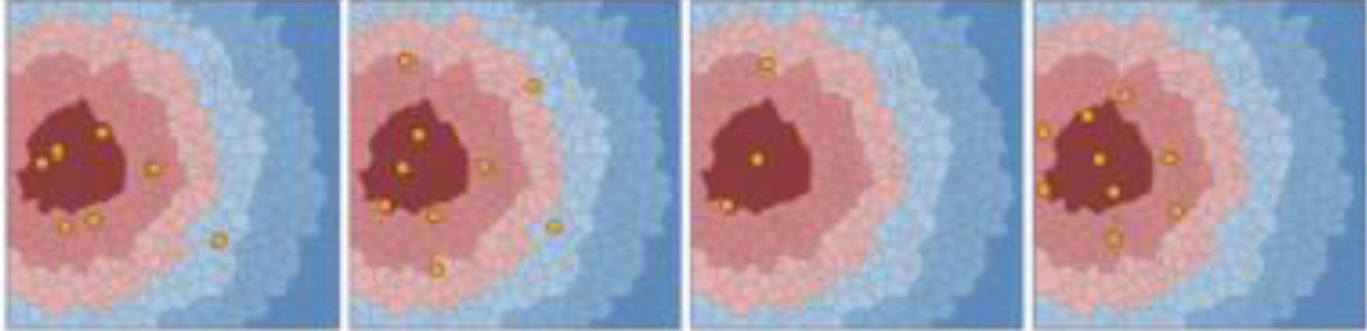
A visual comparison of various summarization methods. From left to right: classical sampling, clustering, contour trees, and CS-ADMM. CS-ADMM is able to distribute elements that are both fit and diverse. Our visualization scheme encodes high fitness values as dark red and low fitness values as dark blue. The individual elements are shown as black dots.
Half-body Portrait Relighting with Overcomplete Lighting Representation
- Pages: 371-381
- First Published: 01 July 2021
Optimized Processing of Localized Collisions in Projective Dynamics
- Pages: 382-393
- First Published: 21 July 2021
Visual Analysis of Large-Scale Protein-Ligand Interaction Data
- Pages: 394-408
- First Published: 02 August 2021
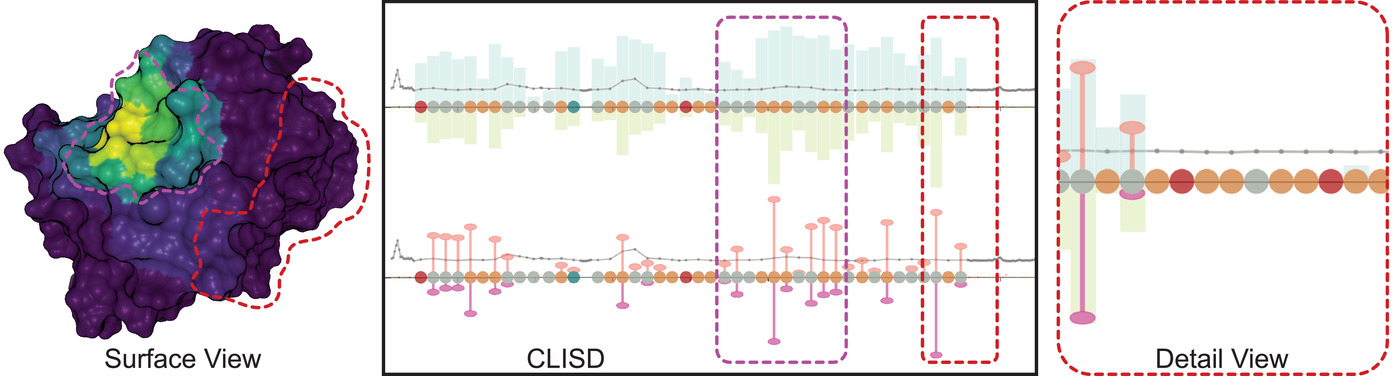
We present an approach that is able to calculate several important properties from arbitrarily large protein-ligand interaction data and display them interactively. Furthermore, our web-based visualisation framework shows the extracted properties in a surface view as well as in our newly introduced Compressed Ligand Interaction Sequence Diagram.
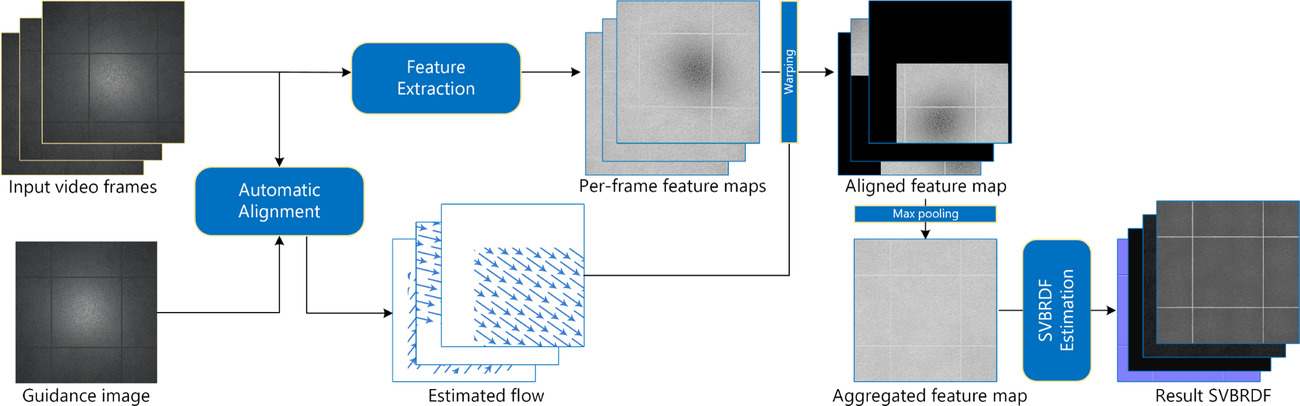
Deep Reflectance Scanning: Recovering Spatially-varying Material Appearance from a Flash-lit Video Sequence
- Pages: 409-427
- First Published: 18 August 2021
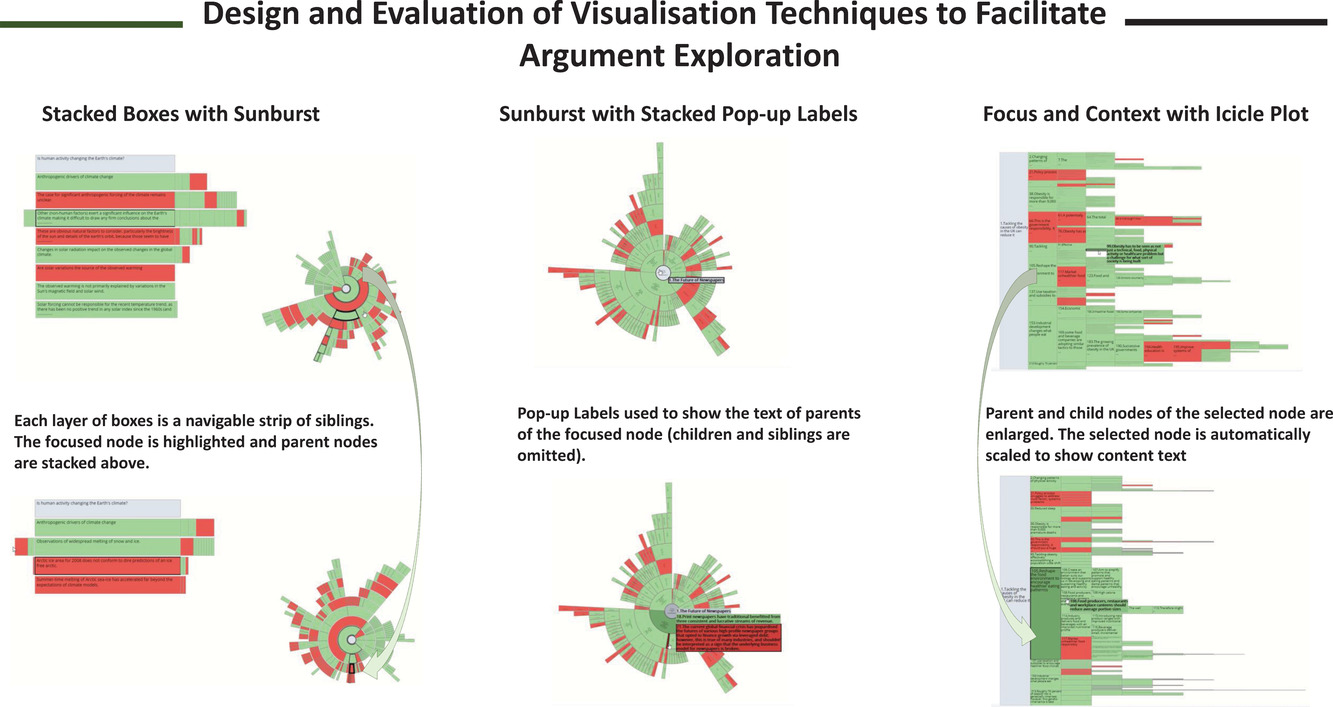
Design and Evaluation of Visualization Techniques to Facilitate Argument Exploration
- Pages: 447-465
- First Published: 09 August 2021
Fashion Transfer: Dressing 3D Characters from Stylized Fashion Sketches
- Pages: 466-483
- First Published: 29 July 2021
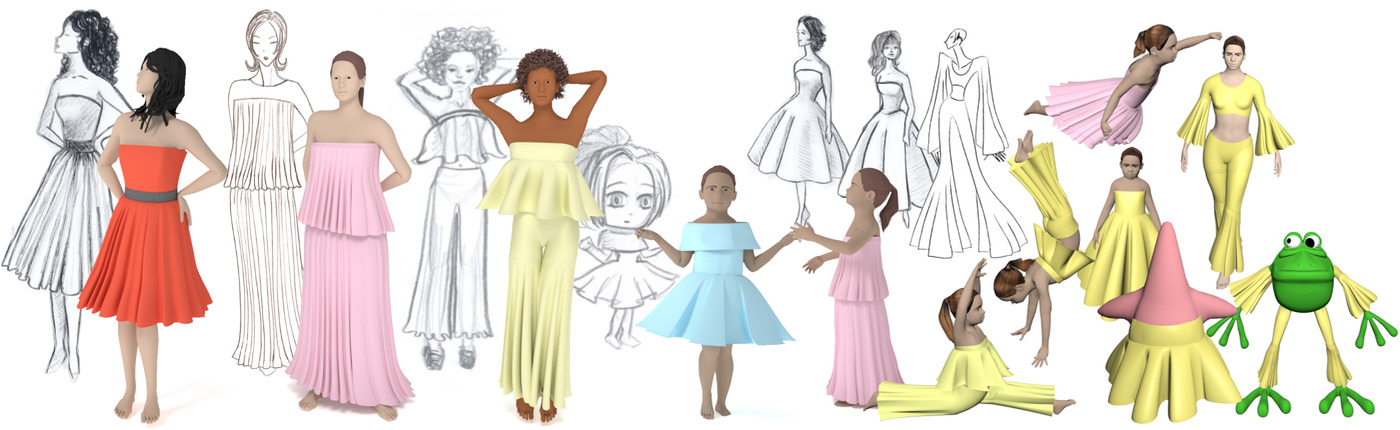

Our approach takes as input a single, annotated fashion drawing and synthesizes a 3D garment of similar style over any existing 3D character. The method handles deep folds and automatically adapts the garment to the morphology and pose of the target, allowing to easily dress human-looking to cartoon-style models.
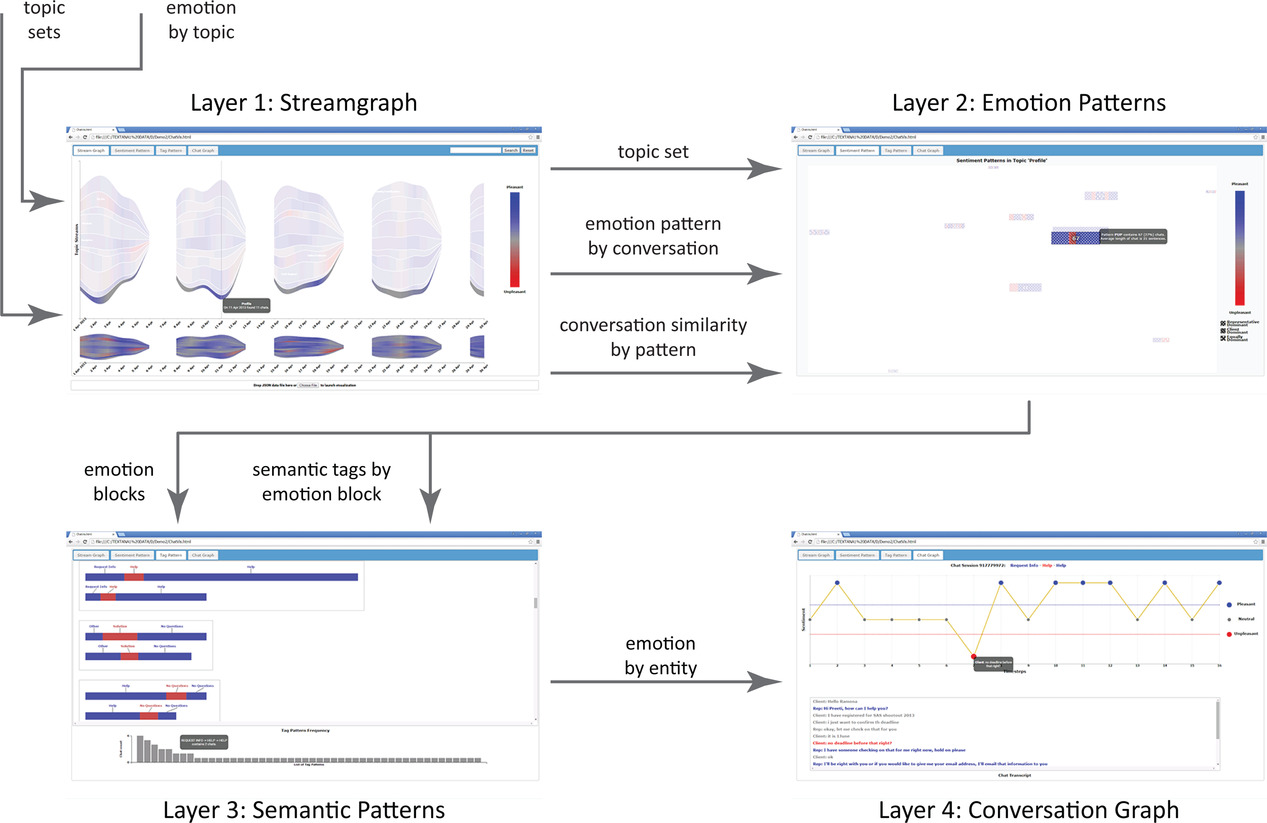
Visual Analytics of Text Conversation Sentiment and Semantics
- Pages: 484-499
- First Published: 13 August 2021
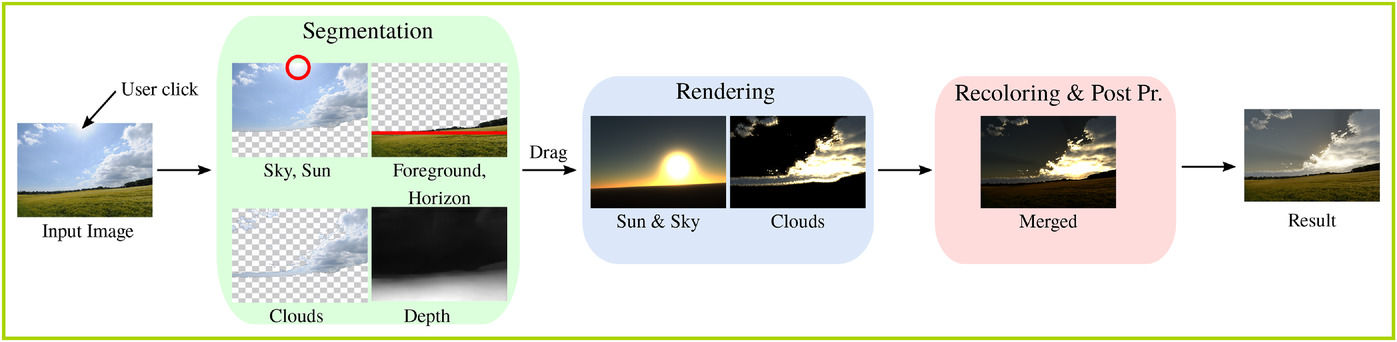
From Noon to Sunset: Interactive Rendering, Relighting, and Recolouring of Landscape Photographs by Modifying Solar Position
- Pages: 500-515
- First Published: 19 August 2021