Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION - TOC
POSITION PAPER
Endotypes in Immune Mediated Drug Reactions: Present and Future of Relevant Biomarkers. An EAACI Task Force Report
- Pages: 1831-1847
- First Published: 07 May 2025

REVIEW
The Evolution, Immunopathogenesis and Biomarkers of Type 2 Inflammation in Common Allergic Disorders
- Pages: 1848-1877
- First Published: 30 June 2025
The Impact of Rhinovirus, Syncytial Respiratory Virus and Helminth Infection on the Risk of New-Onset Asthma and Other Allergic Conditions—A Systematic Review for the EAACI Guidelines on Environmental Science for Allergic Diseases and Asthma
- Pages: 1878-1898
- First Published: 10 June 2025

ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Asthma and Lower Airway Disease
Multiomic Integration Analysis for Monitoring Severe Asthma Treated With Mepolizumab or Omalizumab
- Pages: 1899-1911
- First Published: 18 December 2024
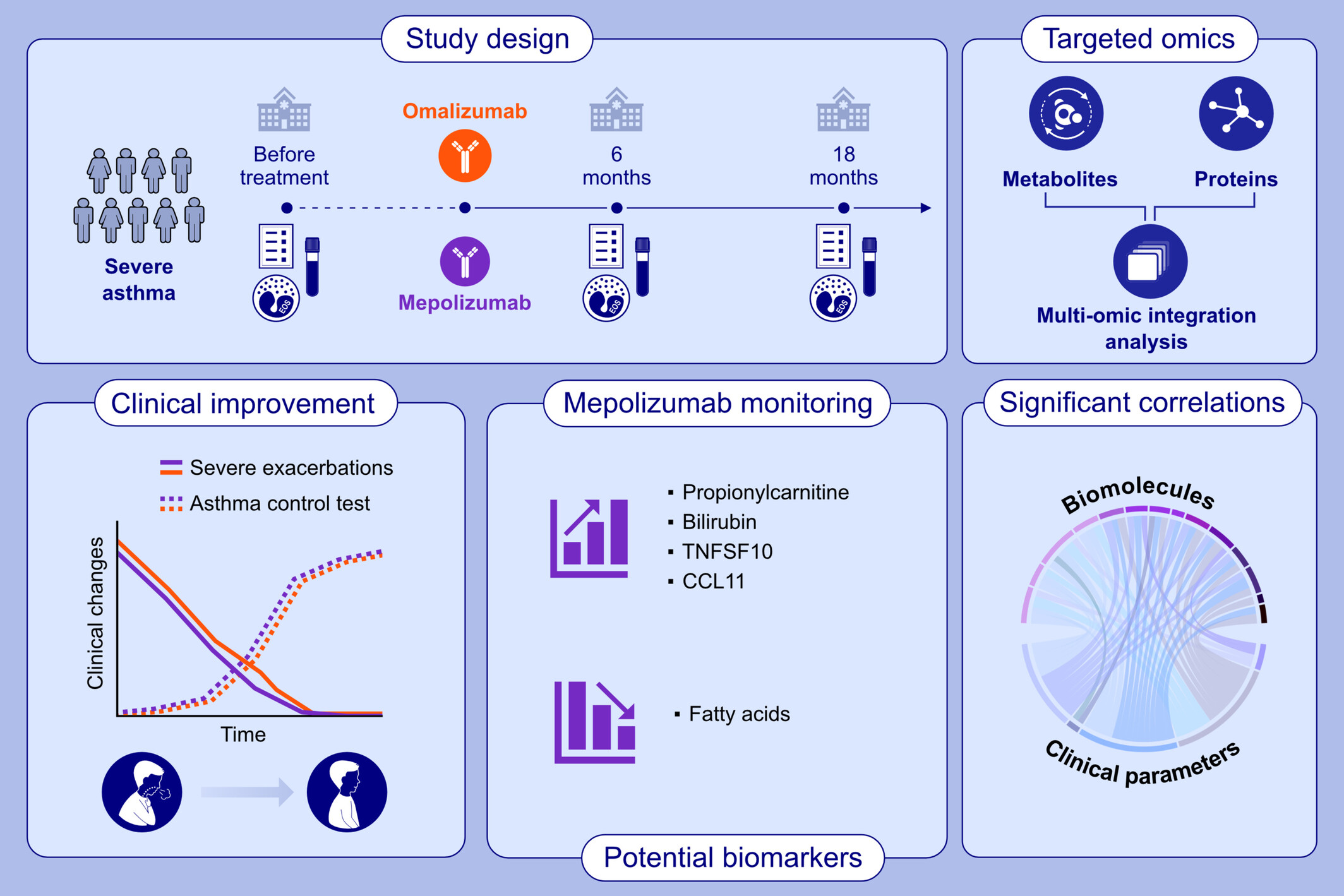
Mepolizumab and omalizumab induce a distinct clinical effect. Mepolizumab and omalizumab induce both common and treatment-specific metabolic and protein profiles over time in patients with severe asthma. Multiomic integration and receiver operating characteristic curve analyses reveal a specific set of biomolecules suggesting their value as potential biomarkers for mepolizumab treatment. CCL11, C-C motif chemokine 11; TNFSF10, superfamily member 10.Abbreviations: CCL11, C-C motif chemokine 11; ROC, receiver operating characteristic; TNFSF10, superfamily member 10.
Childhood Asthma and Allergy Are Related to Accelerated Epigenetic Aging
- Pages: 1912-1922
- First Published: 10 May 2025
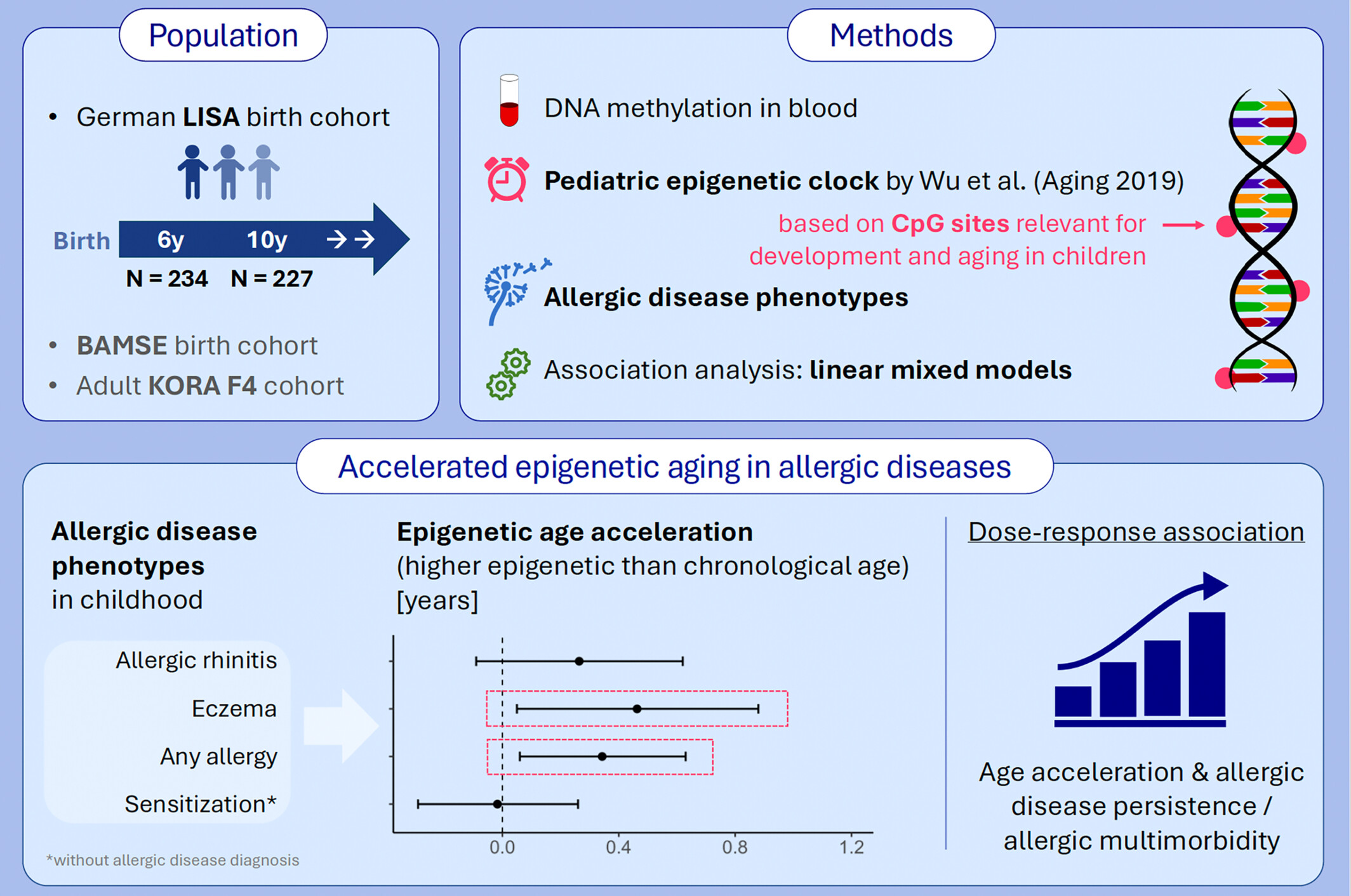
We used a pediatric epigenetic clock to assess epigenetic age in children from a German birth cohort. Accelerated epigenetic aging was found to be related to the presence of allergic diseases like asthma, rhinitis, or eczema, but not to non-symptomatic aeroallergen sensitization. This was supported by an epigenetic age acceleration gradient in response to allergic disease persistence and allergic multimorbidity. BAMSE, Swedish abbreviation for Children, Allergy, Milieu, Stockholm, Epidemiology; KORA F4, German population-based Cooperative Health Research in the Region of Augsburg; LISA, Life-style factors on the Development of the Immune System and Allergies in East and West Germany.
Patterns of Respiratory Symptoms and Asthma Diagnosis in School-Age Children: Three Birth Cohorts
- Pages: 1923-1934
- First Published: 12 June 2025
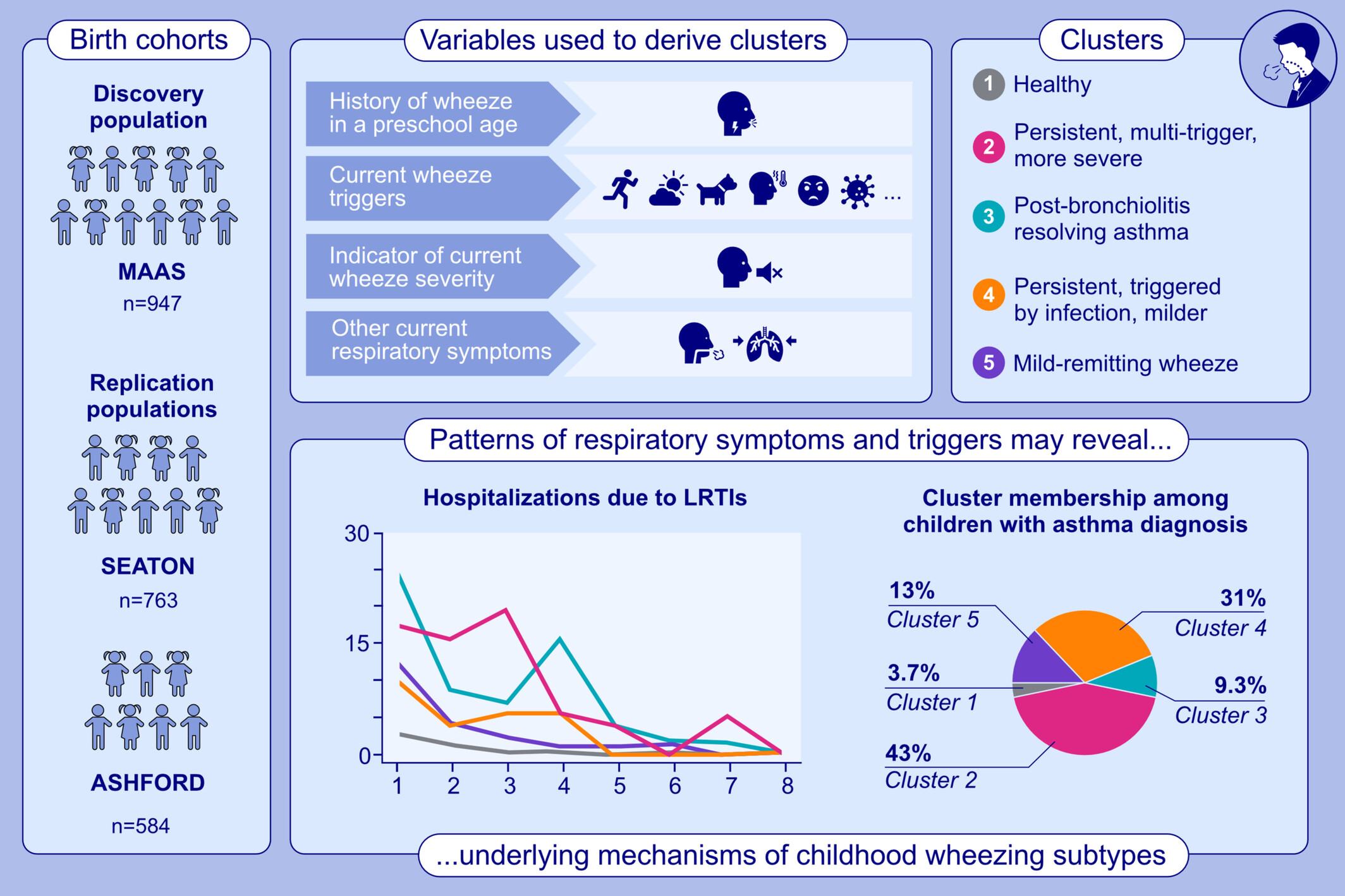
We performed guided multi-domain clustering of symptoms and triggers in school-age children across three birth cohorts. Using 15 variables, five clusters were identified. Two clusters showed a high prevalence of asthma with persistent symptoms. Questions on shortness of breath and chest tightness upon awakening were key to identifying ‘post-bronchiolitis resolving asthma’. ASHFORD, birth cohort study established in 1991 in Ashford, UK; LRTIs, lower respiratory tract infections; MAAS, Manchester Asthma and Allergy Study; SEATON, The Study of Eczema and Asthma to Observe the influence of Nutrition.
Rhinitis, Sinusitis and Upper Airway Disease
Correlation Between N-Glycan GnGnXF3 and the Allergic Immune Response Against Juniperus ashei Pollen
- Pages: 1935-1944
- First Published: 06 February 2025
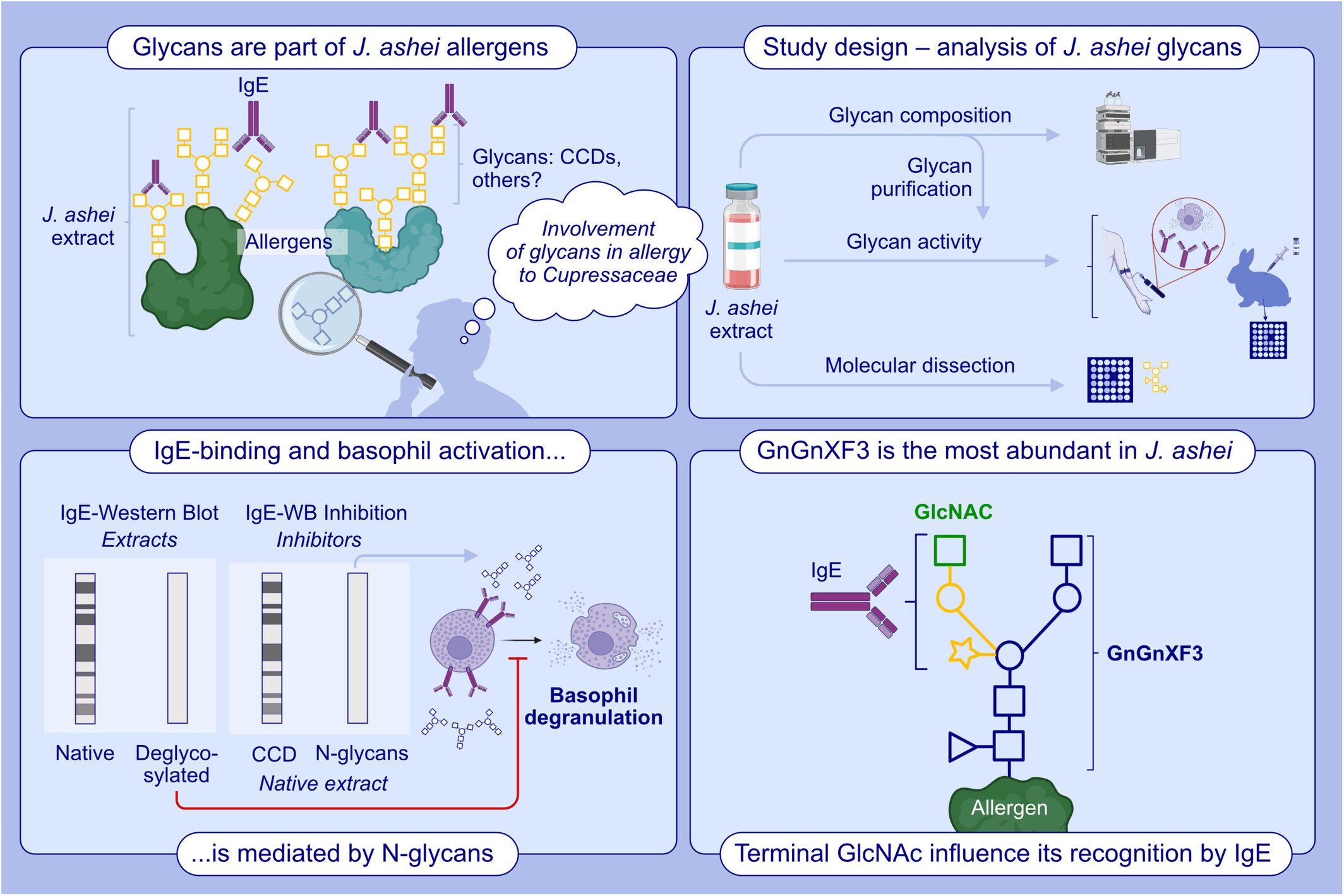
IgE binding to Juniperus ashei allergens is mediated by N-glycans different from classic CCDs. N-glycan from J. ashei pollen triggers basophil activation. GnGnXF3 is the most abundant glycan in J. ashei extract and contains a novel IgE glycotope. Abbreviations: CCD, cross-reactive carbohydrate determinant; GlcNAc, N-acetylglucosamine; GnGnXF3, biantennary N-glycan with terminal; GlcNAc, β-1,2 xylose and core α-1,3 fucose; IgE, immunoglobulin E; WB, Western blot.
Clinical Benefits of a Randomized Allergy App Intervention in Grass Pollen Sufferers: A Controlled Trial
- Pages: 1945-1955
- First Published: 17 April 2025
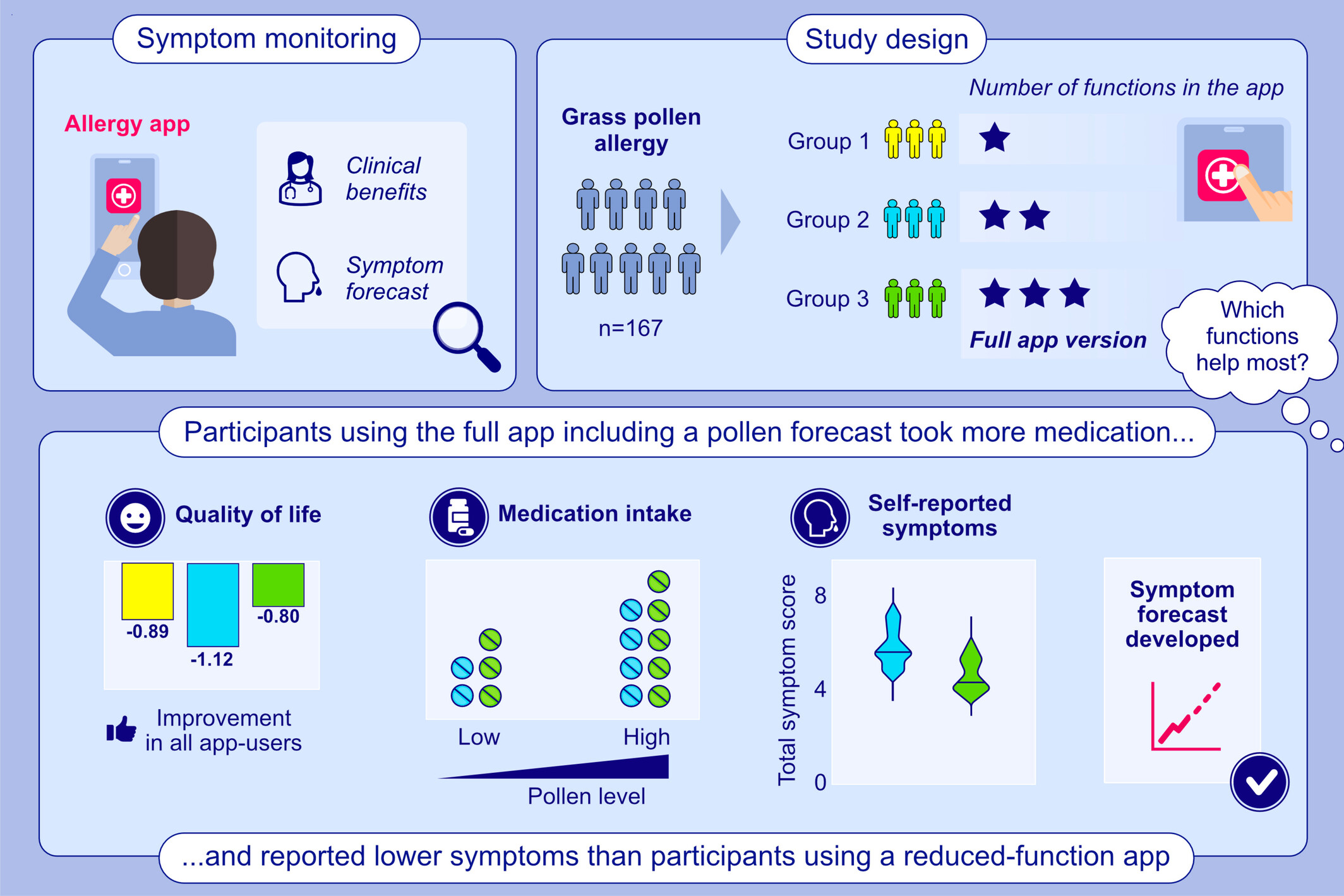
Different functions of an allergy app were tested for clinical benefit in a randomized, controlled trial in patients with grass pollen allergy. Participants with pollen forecast function took more medication and had fewer symptoms than participants without pollen forecast. A symptom forecast was developed based on the study data.
Atopic Dermatitis, Urticaria and Skin Disease
T Cells Induce Prolonged Downregulation of Barrier Molecules in a Mouse Model of Allergic Contact Dermatitis
- Pages: 1956-1966
- First Published: 14 December 2024
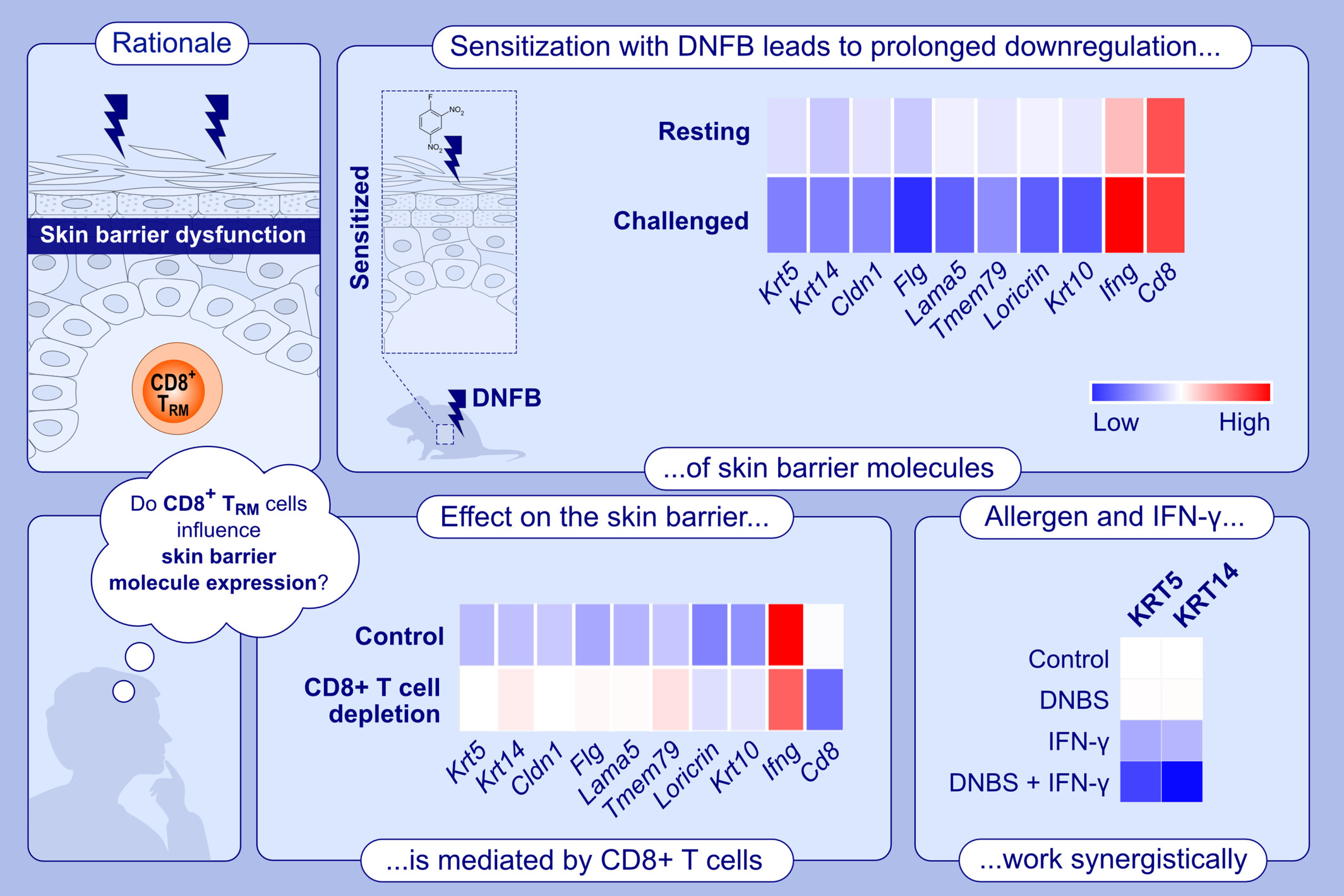
In a mouse model of allergic contact dermatitis, sensitization with DNFB increased numbers of CD8+ TRM cells and expression of IFN-γ with prolonged downregulation of KRT5 and KRT14 in the epidermis. Depletion of CD8+ T cells prevented this effect. In keratinocytes, IFN-γ and DNBS synergistically down-regulated the expression of KRT5 and KRT14. CD8+ TRM, epidermal-resident memory CD8+ T cell; Cldn1, claudin 1; DNBS, 2,4-dinitrobenzene sulfonic acid; DNFB, 1-fluoro 2,4-dinitrobenzene; Flg, filaggrin; Ifng/IFN-γ, interferon γ; Krt/KRT, keratin; Lama5, laminin subunit alpha-5; Tmem79, transmembrane protein 79
Food Allergy and Gastrointestinal Disease
Maternal Allergic Disease Phenotype and Infant Birth Season Influence the Human Milk Microbiome
- Pages: 1967-1981
- First Published: 26 December 2024
Allergen-Specific Immunotherapy and Biologics
Six Injections of Modified Adjuvanted PQ Grass Is Effective and Well-Tolerated in a Pivotal Phase III Trial
- Pages: 1982-1994
- First Published: 04 February 2025
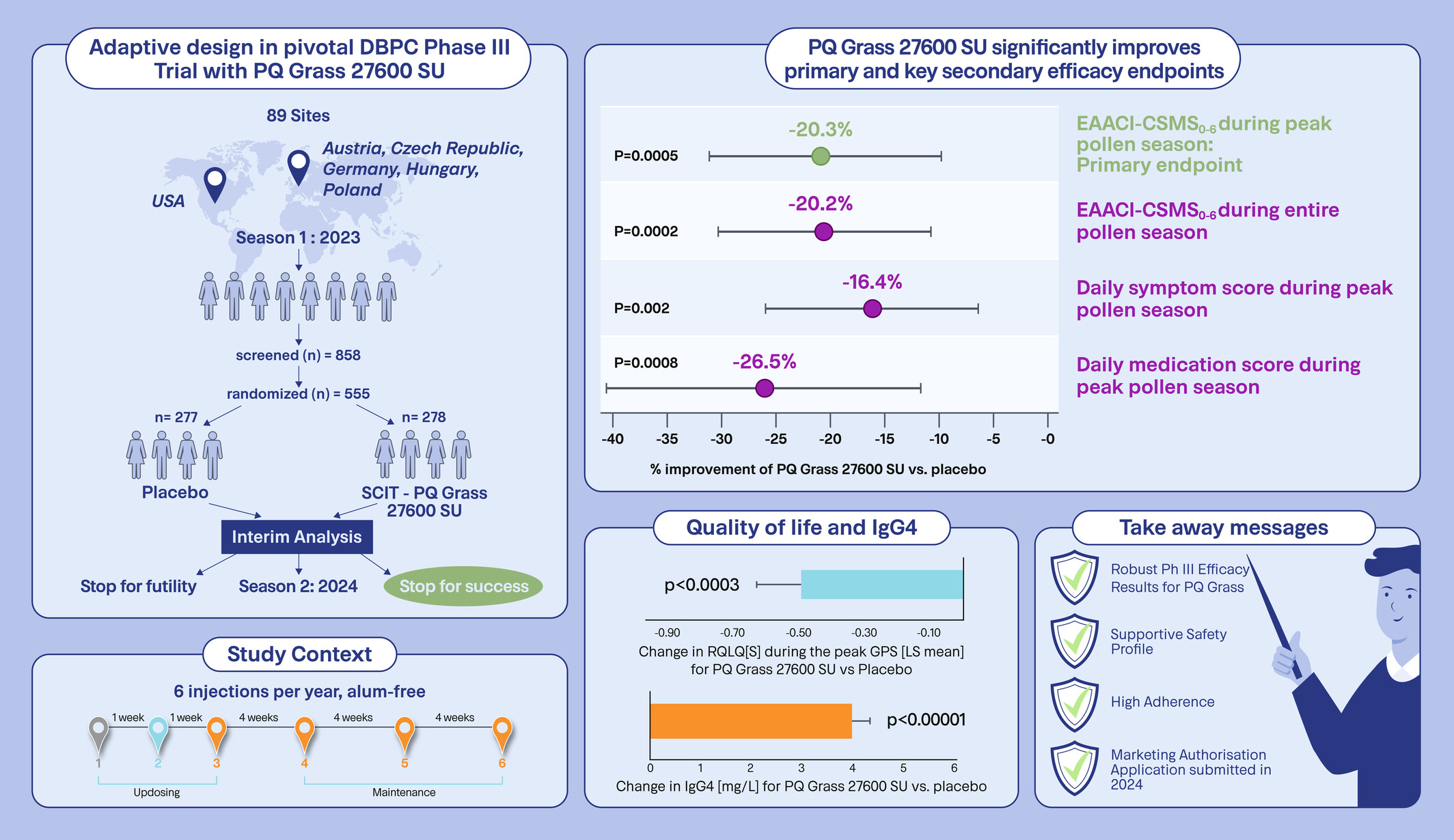
A pivotal Phase III DBPC adaptive trial was conducted with PQ Grass 27600 SU. The primary endpoint EAACI-CSMS0–6 demonstrated a highly significant, clinically meaningful improvement for PQ Grass of −0.27 points (95% CI: −0.42 to −0.12), corresponding to a relative difference of −20.3% (p = 0.0005) over placebo. Highly consistent secondary endpoints and a supportive safety profile were confirmed. CSMS, combined symptom and medication score; DBPC, double-blind, placebo-controlled; EAACI, European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology; GPS, grass pollen season; IgG4, immunoglobulin G4; PQ Grass, Grass MATA MPL or PQ Grass 27600 SU; RQLQ[S], rhinoconjunctivitis quality of life questionnaire standardised; SCIT, subcutaneous immunotherapy; SU, standardised unit.
Vaccine-Induced Anti-IgE Antibodies Neutralize Free IgE but Fail to Bind and Activate Mast Cell-Displayed IgE
- Pages: 1995-2007
- First Published: 07 April 2025
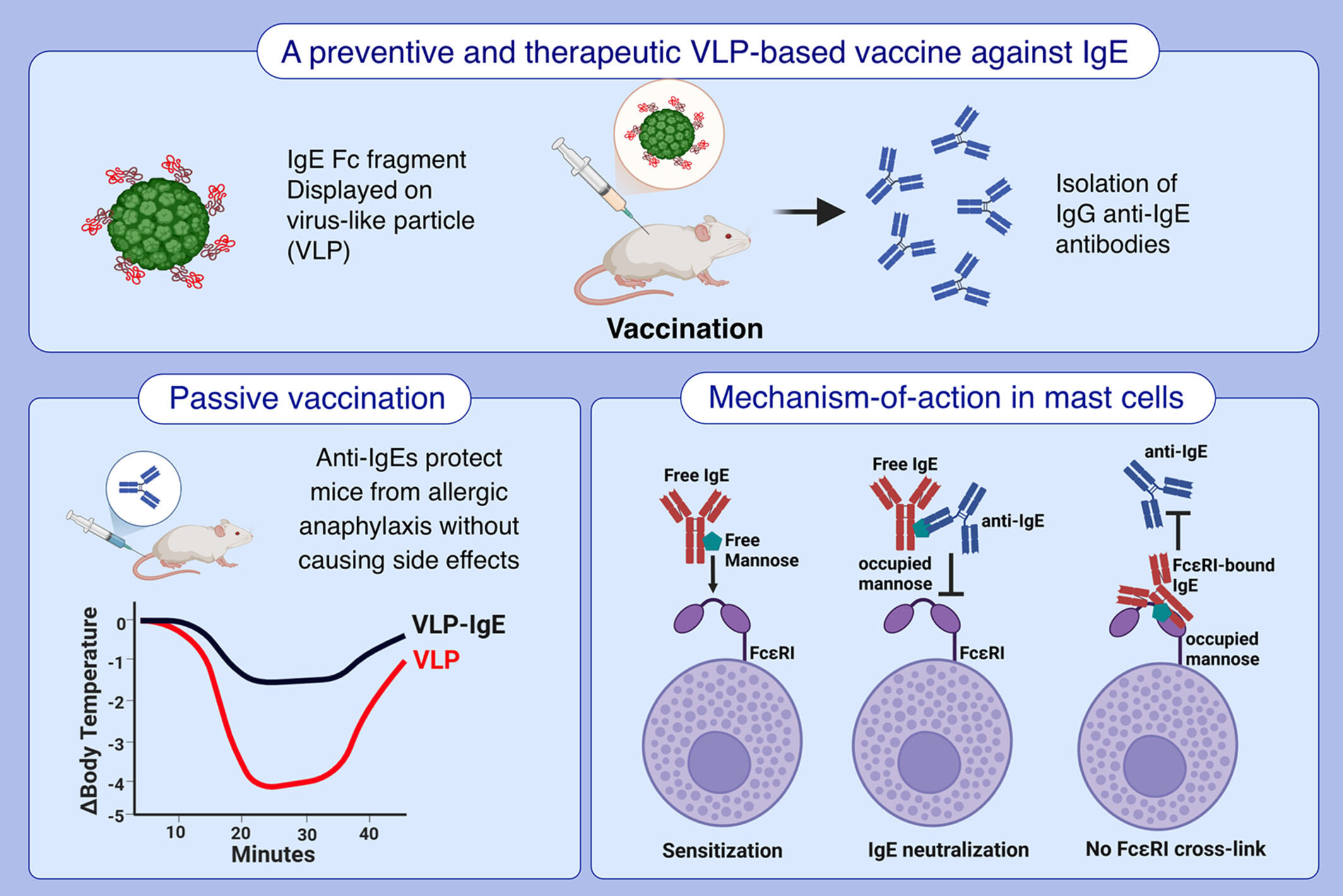
- We investigated the mechanisms by which a previously established VLP-based anti-IgE vaccine protects against allergic anaphylaxis.
- We show that passively administered vaccine-induced IgGs into allergic mice protects them from anaphylaxis without side effects.
- In mast cells, the IgGs prevent free IgE binding to FcεRI but fail to bind and activate FcεRI-displayed IgE.
Immunological In Vitro Assay for Quantification of Adjuvanted Allergoids
- Pages: 2008-2017
- First Published: 31 March 2025
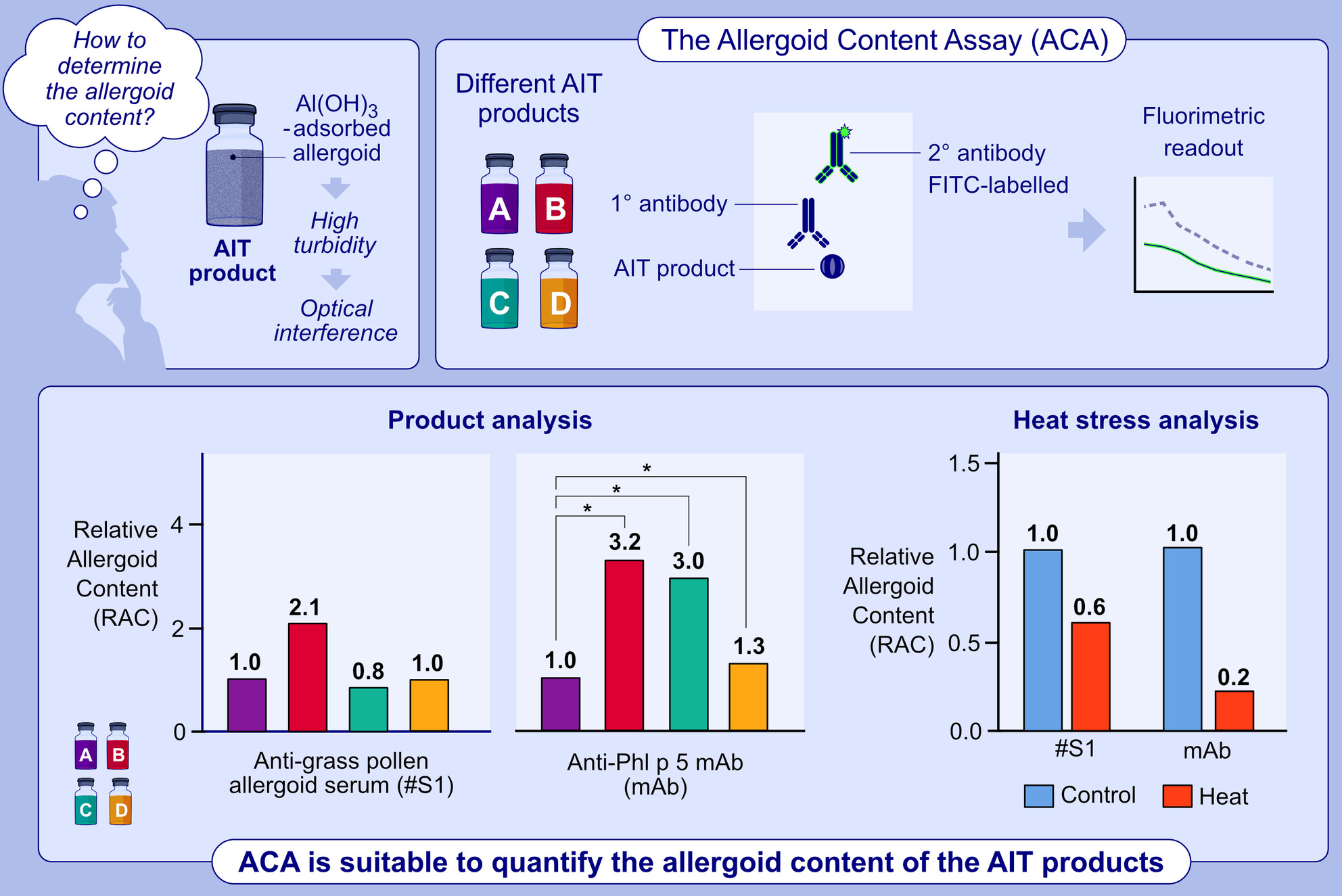
An assay was developed to measure the allergoid content in adjuvanted grass allergoid AIT drug product (AIT-DPs) at the finished product level. Both polyclonal rabbit sera or a mouse anti-Phl p 5 mAb can be used, allowing differential product analysis. All four tested grass pollen AIT-DPs of different manufacturers could be quantified using a defined reference, demonstrating broad applicability of the assay. ACA, allergoid content assay; AIT, allergen immunotherapy; AIT-DP, adjuvanted allergoid AIT drug product; Al(OH)3, aluminum hydroxide; FITC, fluorescein isothiocyanate; mAb, monoclonal antibody; Phl p 5, Group 5 allergen Phleum pratense; RAC, relative allergoid content.
Subcutaneous Allergen Immunotherapy With Hypoallergenic Bet v 1 Compared to Conventional Extract: Poorer Blocking Antibody Capacity Dominated by IgG1 Instead of IgG4
- Pages: 2018-2030
- First Published: 02 June 2025
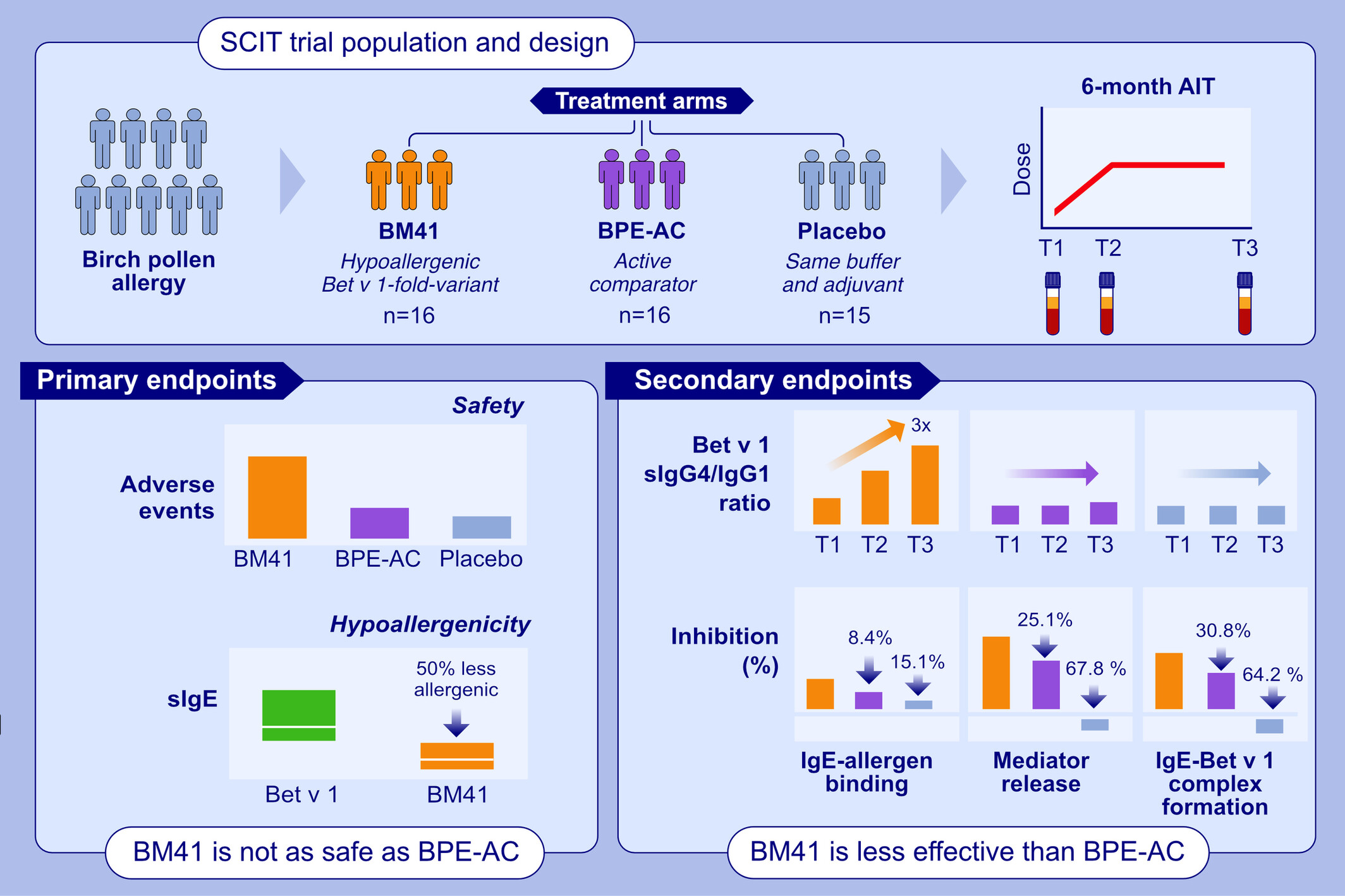
A 6-month randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled first-in-human clinical trial was conducted in birch pollen allergic patients comparing the Bet v 1-fold-variant BM41 with a licensed birch pollen extract-based treatment, as active comparator, and placebo. Despite SPT-confirmed hypo-allergenicity (~50% compared to natural Bet v 1), more adverse events occurred in response to BM41. In BPE-AC, the sIgG4/sIgG1 ratio tripled over time whereas for BM41 it stagnated. BM41 induced efficient serum inhibitory activity for sIgE compared to placebo but was 12-32% less efficient than BPE-AC.
Abbreviations: AIT, allergen immunotherapy; BM41, Bet v 1-fold-variant; BPE-AC, birch pollen extract-based active comparator; sIg, specific immunoglobulin; SPT, skin prick test.
Autoimmunity and Clinical Immunology
Phase 2-3 Trial: Prevention of the Progression to Moderate and Severe COVID-19 in SARS-CoV-2-Infected Non-Hospitalized Adults With Inhaled siRNA-Based MIR 19
- Pages: 2031-2042
- First Published: 03 March 2025
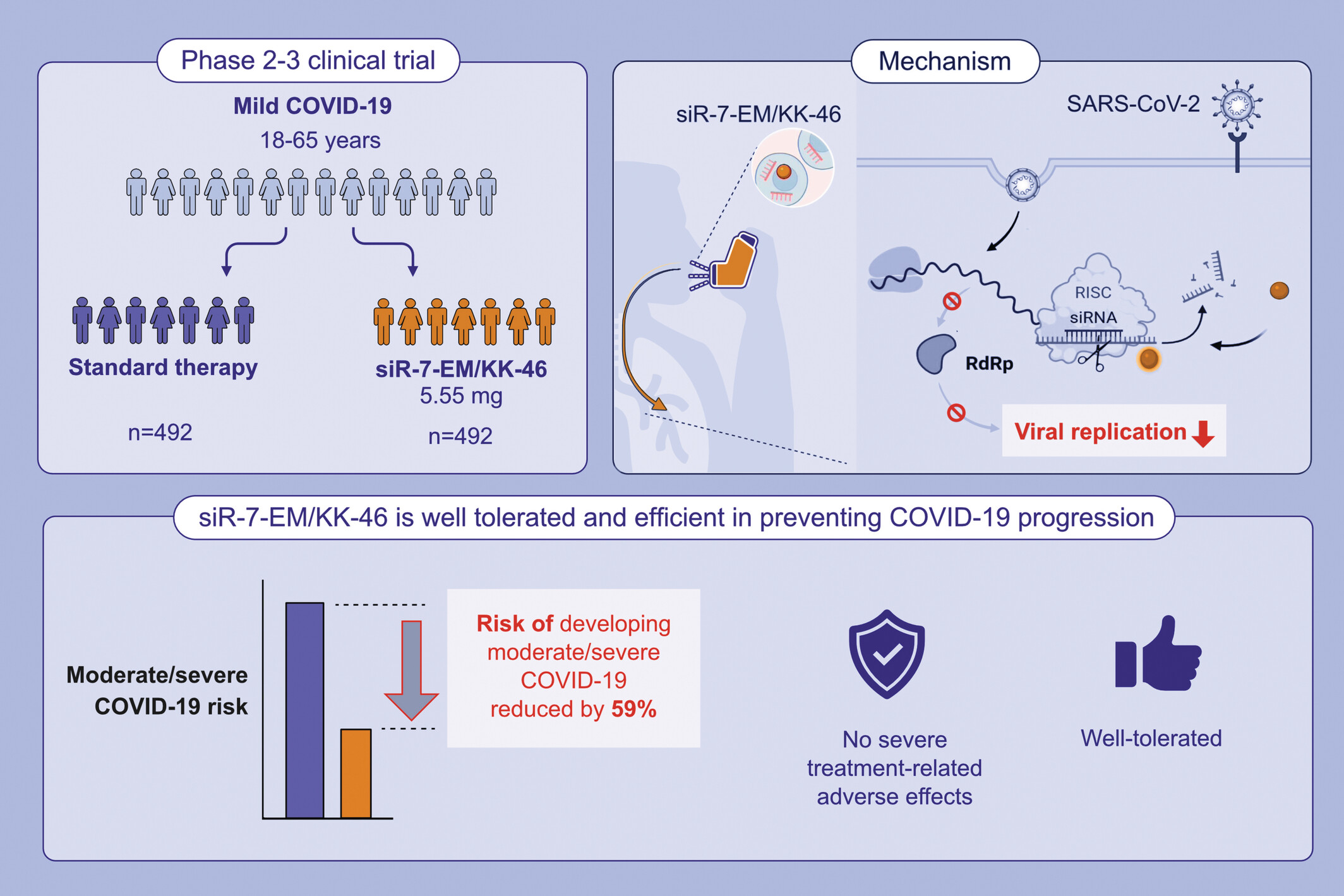
siR-7-EM/KK-46 (MIR 19) is a siRNA-based anti-SARS-CoV-2 antiviral targeting viral RdRp. In adult outpatients with mild COVID-19, inhaled 5.55 mg/day of MIR 19 reduces the risk of developing moderate/severe COVID-19 by more than 50% as compared to standard therapy. MIR 19 is effective and well tolerated in non-hospitalized adult patients (18–65 years old). COVID-19, coronavirus disease 2019; RdRp, RNA-dependent RNA polymerase; RISK, the RNA-induced silencing complex; SARS-CoV-2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; siRNA, short interfering RNA.
LETTER
A Distinct Genetic Signature Differentiates Inflamed and Noninflamed Fibrotic Tissues in Eosinophilic Esophagitis Patients
- Pages: 2043-2046
- First Published: 07 February 2025
Perinatal Photoperiod Associations With Allergic and Respiratory Disease in the UK Biobank Database
- Pages: 2047-2049
- First Published: 20 February 2025
Immunophenotyping in Vernal Keratoconjunctivitis: Schirmer Test for Therapy Response Prediction
- Pages: 2050-2054
- First Published: 12 March 2025
Meta-Analysis of PQ Grass 27600 SU Efficacy and Quality of Life From Phase III Trials
- Pages: 2055-2058
- First Published: 31 March 2025
Anatomical Distribution and Quantification of IgE Secretion in Mouse Models of House Dust Mite Allergy
- Pages: 2059-2062
- First Published: 31 March 2025
Association Between Occupational Exposure and Sinus Surgery Outcomes in Chronic Rhinosinusitis: A Prospective Study
- Pages: 2063-2067
- First Published: 10 April 2025
Possible In-Cabin Exposure to Cat Allergen: A 2025 Airline Survey on Live Animal Transport and a Review of Literature
- Pages: 2068-2069
- First Published: 30 April 2025
The Severity of Pollen-Induced Allergic Rhinitis at 16 Years of Age: Data From the Population-Based BAMSE Birth Cohort
- Pages: 2070-2072
- First Published: 29 April 2025
Linking Exosomal MicroRNA Signatures in Sputum and Peripheral Blood to Inflammatory Endotypes in Severe Asthma
- Pages: 2073-2076
- First Published: 20 May 2025
Preclinical Development of GR2002, a Novel Anti-TSLP Bispecific Antibody With Potent TSLP Inhibitory Effects
- Pages: 2077-2080
- First Published: 15 May 2025
Vulnerability to Pollen-Related Asthma Hospital Admissions in the UK Biobank: A Case-Crossover Study
- Pages: 2081-2083
- First Published: 03 June 2025
Uncontrolled Asthma, Intimate Partner Violence, and Inflammatory Pathways: Surprising Insights From Cytokine Profiles
- Pages: 2084-2087
- First Published: 12 June 2025






