Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
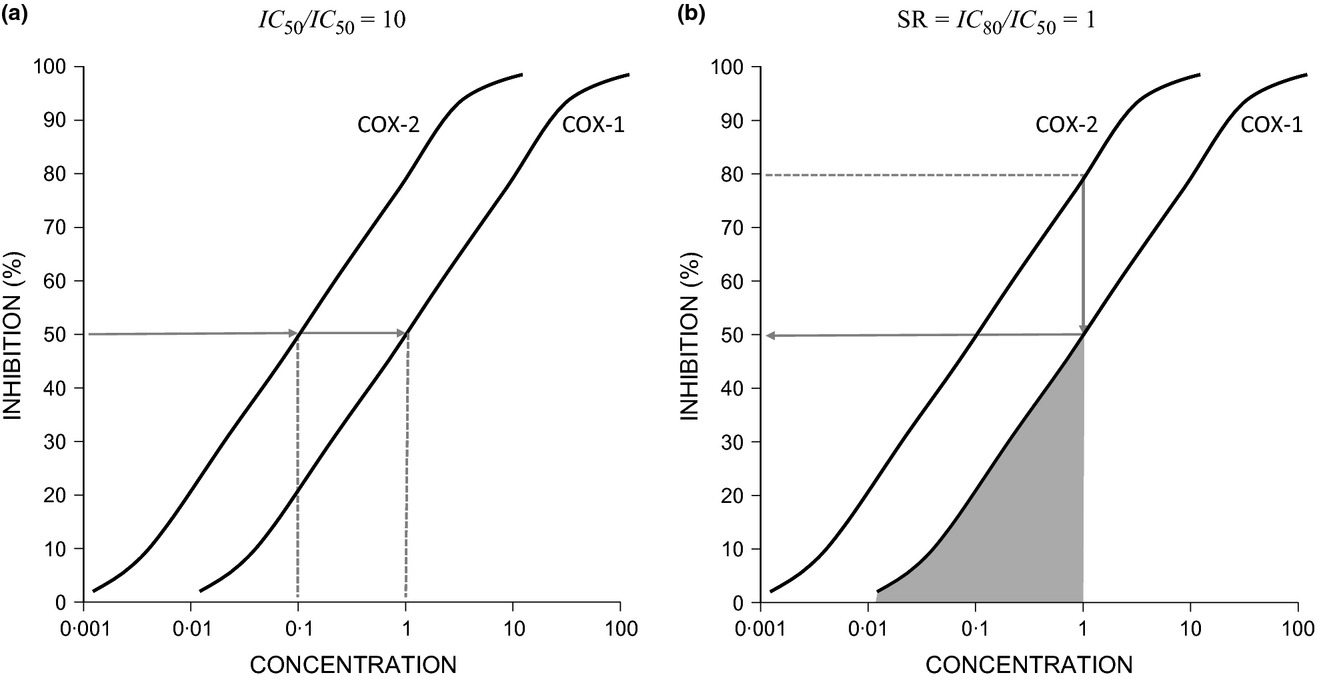
‘Selective’ COX-1 or COX-2 NSAIDs: time to change a misleading measure
- Pages: 455-456
- First Published: 29 July 2014
Involvement of neuronal β2 subunit-containing nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in nicotine reward and withdrawal: Implications for pharmacotherapies
- Pages: 457-467
- First Published: 14 May 2014
Reliability of self-reporting of antibiotic consumption in the community – Index of Reliability
- Pages: 468-470
- First Published: 09 June 2014
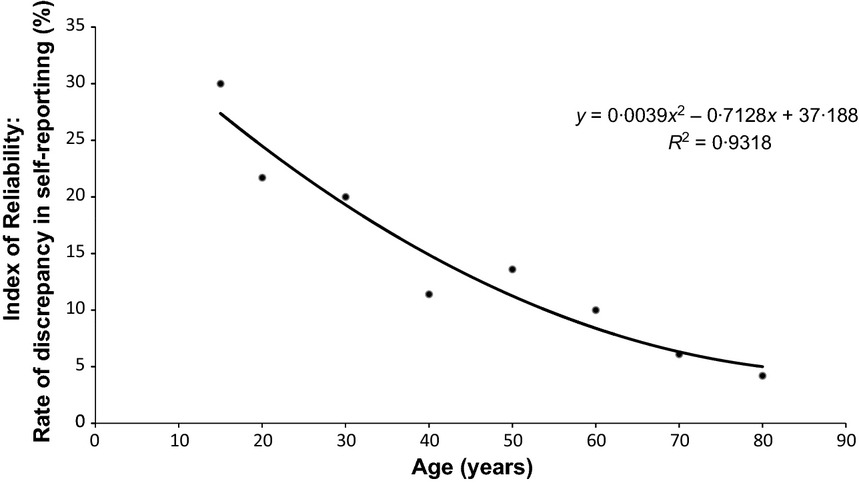
Self-reporting of antibiotic consumption is relatively reliable by the patient. This varies depending on the age and sex of the individual. Older people (up to 80 years old) tend to be more accurate in reporting their antibiotic consumption than younger persons (<20 years), and males tend to be more accurate in their reporting than females.
Is a flavonoid-rich diet with steamer cooking safe during calcineurin inhibitors therapy?
- Pages: 471-474
- First Published: 17 June 2014
Pharmacotherapy for weight loss: the cardiovascular effects of the old and new agents
- Pages: 475-484
- First Published: 13 June 2014
Psychopathy: clinical features, developmental basis and therapeutic challenges
- Pages: 485-495
- First Published: 23 May 2014
Psychopathy is a serious personality disorder with profound negative effects on individuals and society. There is little evidence that drug therapy has any significant effect on the deficits associated with this disorder. There is emerging evidence of phenotypic variants in psychopathy, including successful and unsuccessful types. It is important for clinicians to be cognizant of the psychopathic personality.
Transition from intravenous or subcutaneous prostacyclin therapy to inhaled treprostinil in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension: a retrospective case series
- Pages: 496-500
- First Published: 08 May 2014
Biomedical journals lack a consistent method to detect outcome reporting bias: a cross-sectional analysis
- Pages: 501-506
- First Published: 14 May 2014
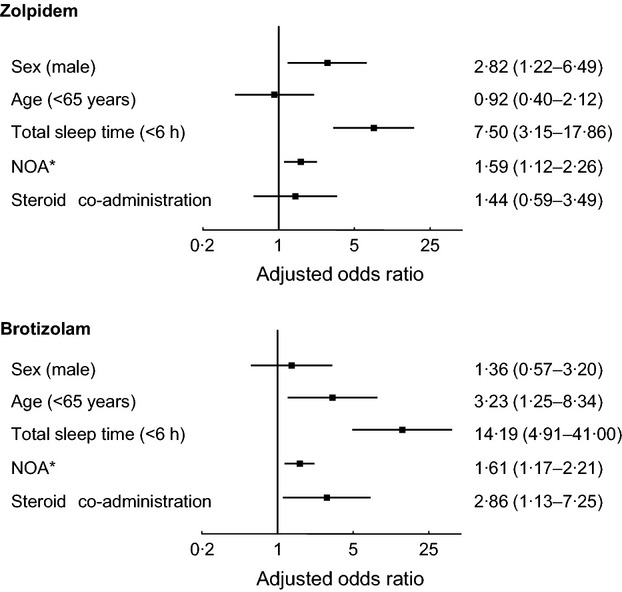
Variables influencing patient satisfaction for hypnotics: difference between zolpidem and brotizolam
- Pages: 507-510
- First Published: 14 May 2014
Prevalence of potentially inappropriate medications and risk of adverse clinical outcome in a cohort of hospitalized elderly patients: results from the REPOSI Study
- Pages: 511-515
- First Published: 21 May 2014
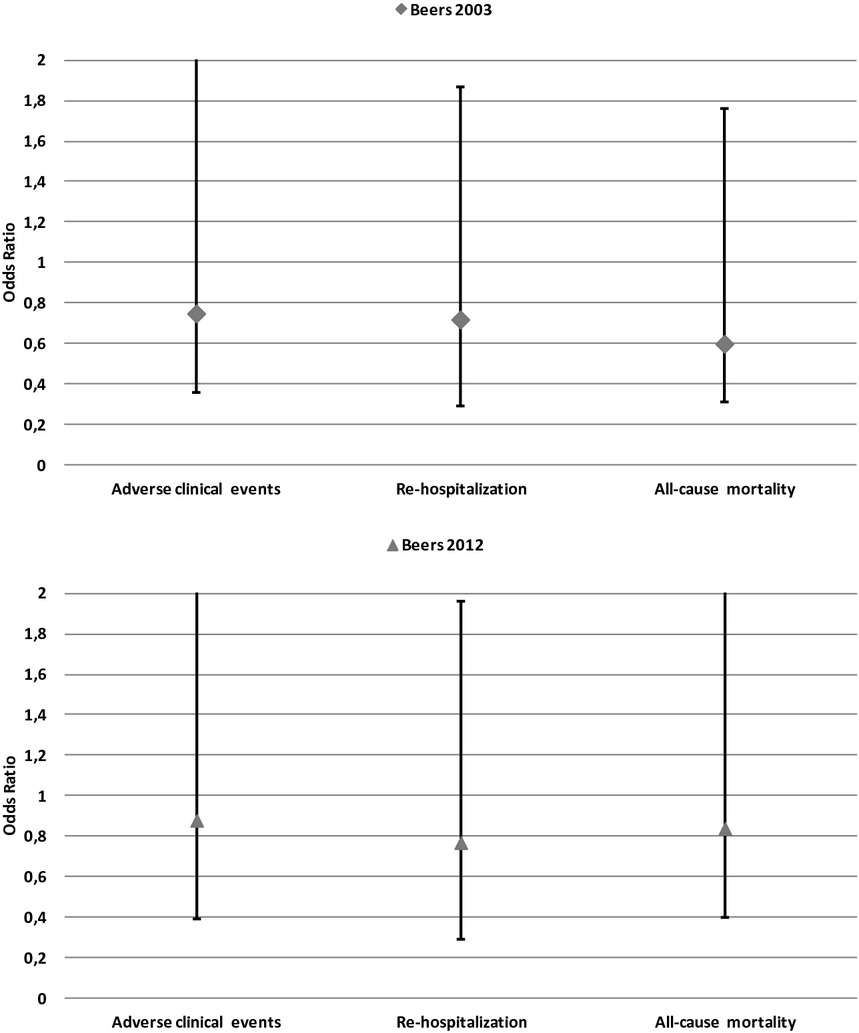
The prevalence of patients receiving at least one Potentially Inappropriate Medications (PIM) was 20·1% and 23·5% according to the 2003 and 2012 versions of the Beers criteria, respectively. Prescription of PIMs was not associated with a higher risk of adverse clinical events, re-hospitalization and all-cause mortality at three-month follow-up.
A cross-sectional survey of antimicrobial stewardship strategies in UK hospitals
- Pages: 516-520
- First Published: 29 May 2014
A clinical study of pingyangmycin sclerotherapy for venous malformation: an evaluation of 281 consecutive patients
- Pages: 521-526
- First Published: 13 June 2014
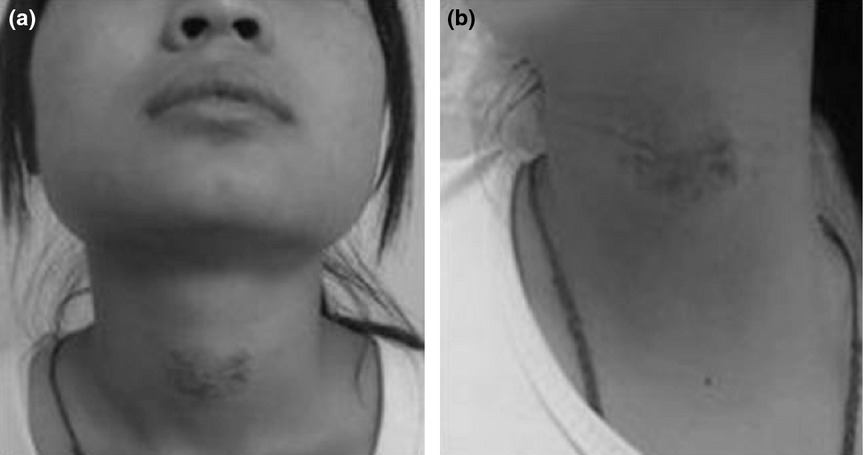
Lidocaine does not have a synergistic effect with PYM in improving the therapeutic outcomes of patients with VMs. Sclerotherapy with a low concentration of PYM (0·5 mg/mL) combined with lidocaine and DEX is a safe and effective therapy for small superficial VMs of critical organs, such as the lips and the glans penis.
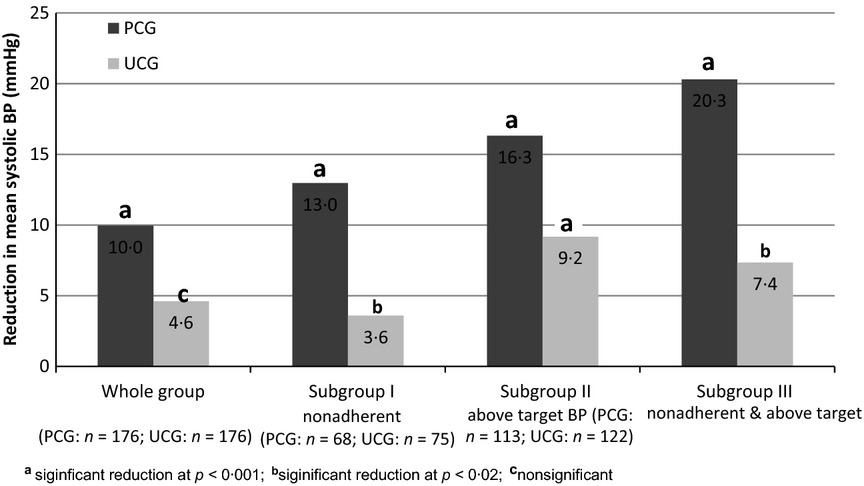
A multifaceted pharmacist intervention to improve antihypertensive adherence: a cluster-randomized, controlled trial (HAPPy trial)
- Pages: 527-534
- First Published: 19 June 2014
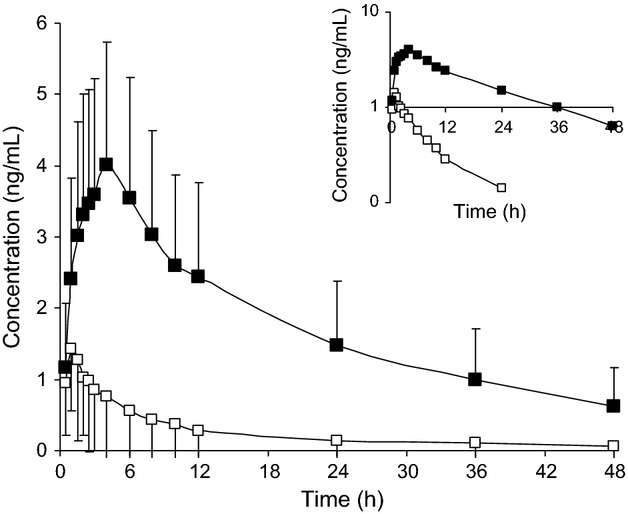
A pharmacokinetic drug interaction study between nebivolol and paroxetine in healthy volunteers
- Pages: 535-540
- First Published: 21 May 2014
Concentrations of venlafaxine and its main metabolite O-desmethylvenlafaxine during pregnancy
- Pages: 541-544
- First Published: 03 July 2014
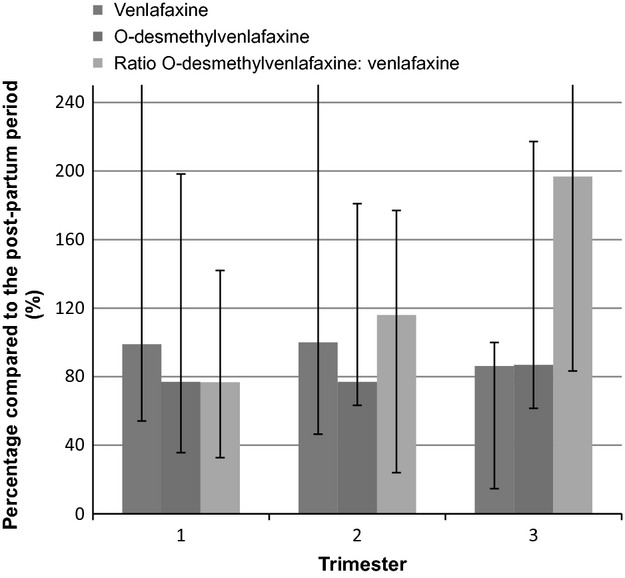
Venlafaxine concentrations decreases during pregnancy, and the ratio of the concentrations of O-desmethylvenlafaxine/venlafaxine increases during pregnancy. Pregnant women using venlafaxine are at risk for subtherapeutic concentrations; therefore, routine monitoring of concentrations venlafaxine and O-desmethylvenlafaxine is recommendable during pregnancy.
Development of multiplex pyrosequencing for HLA-B*57:01 screening using single nucleotide polymorphism haplotype
- Pages: 545-550
- First Published: 26 May 2014
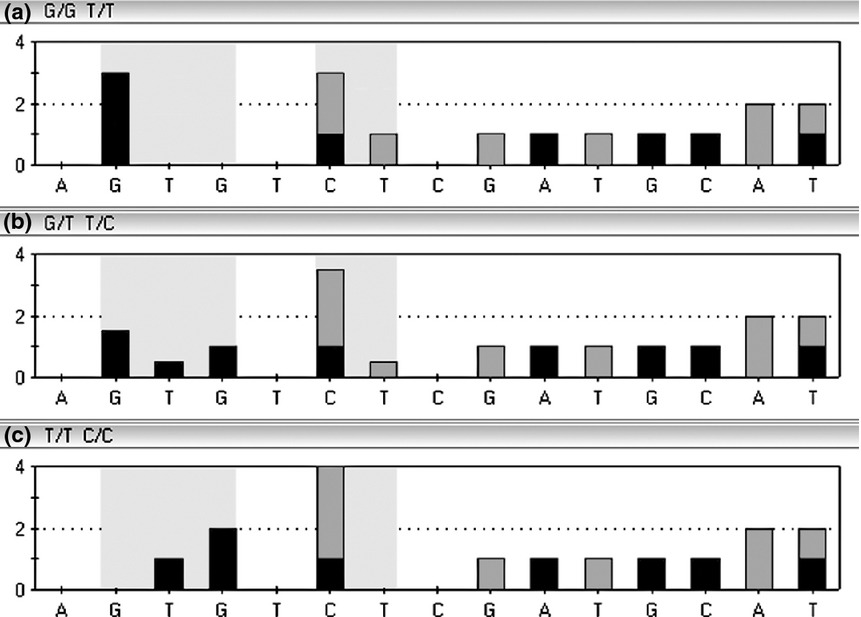
Multiplex pyrosequencing is a powerful tool for HLA-B*57:01 screening by using the rs2395029 and rs3093726 haplotype genotyping as surrogate marker for this HLA-B. The assay provides accurate, cost effective and rapid detection of this haplotype. It can be applied for ABC hypersensitivity screening of the Thai population before initiating treatment with ABC.
Gene polymorphism and frequencies of the NPC1L1 Gene (rs2072183, rs217434 and rs217428) in Japanese patients with dyslipidemia
- Pages: 551-554
- First Published: 26 May 2014
The purpose of this study is to elucidate genotype and allele frequencies of the NPC1L1 gene (rs2072183, rs217428 and rs217434) in Japanese patients with dyslipidemia. We found that there is a significant difference between healthy Japanese and dyslipidemic subjects in rs2072183. Our results are expected to facilitate research in the proper use of ezetimibe-based therapies.
The rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility polymorphism PTPN22 C1858T is not associated with leflunomide response or toxicity
- Pages: 555-560
- First Published: 08 July 2014
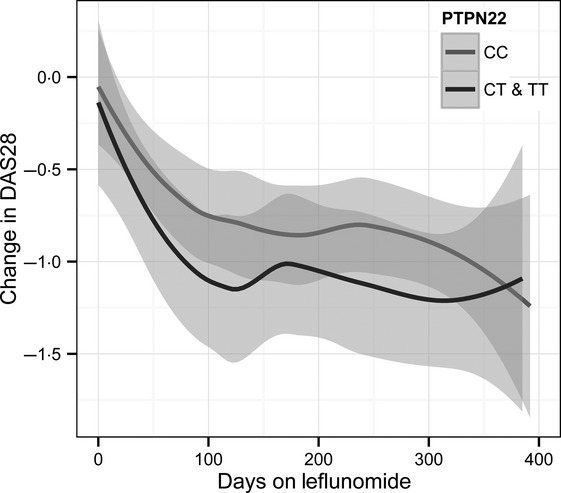
This is the first study to evaluate the biologically plausible hypothesis that PTPN22 C1858T genotype might be a predictor of response/toxicity to leflunomide therapy. Despite this, PTPN22 genotype was not associated with leflunomide response or toxicity in patients with RA. The LOESS smooth curve (Fig. 19) shows there is no difference in change in DAS28 across the 12 months according to PTPN22 genotype.
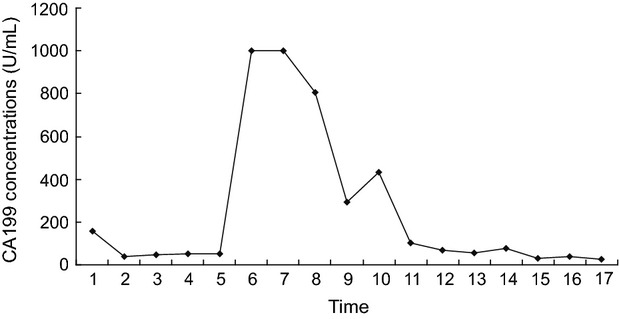
Astragalus membranaceus as a cause of increased CA19-9 and liver and kidney cysts: a case report
- Pages: 561-563
- First Published: 08 May 2014
Cannabidiol can improve complex sleep-related behaviours associated with rapid eye movement sleep behaviour disorder in Parkinson's disease patients: a case series
- Pages: 564-566
- First Published: 21 May 2014
Pharmacist review prevents evolving metformin-associated lactic acidosis
- Pages: 567-570
- First Published: 03 July 2014
Treatment of gout in a renal transplant patient leading to severe thrombocytopenia
- Pages: 571-572
- First Published: 11 July 2014
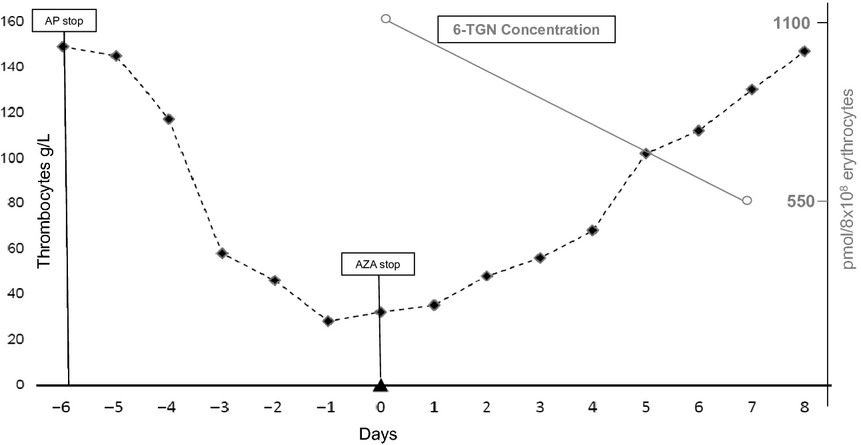
A 79-year old female developed symptomatic thrombocytopenia after combination therapy with azathioprine (75 mg/day) and allopurinol (100 mg/day) – after allopurinol had been stopped. Concentrations of the myelotoxic 6-TGN of azathioprine were increased. Thrombocyte counts normalized within 8 days of discontinuation of azathioprine.
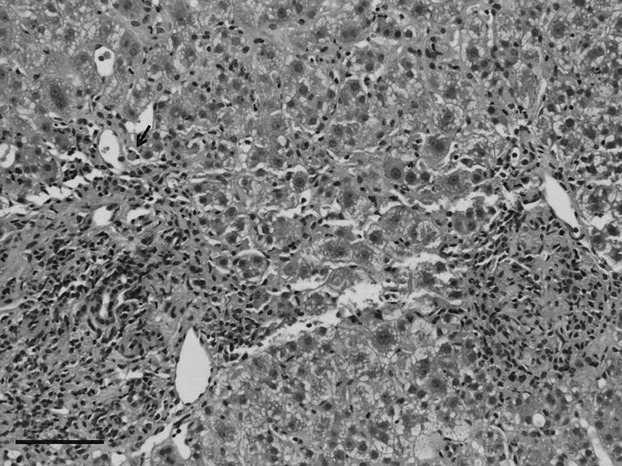
A case of synthetic oestrogen-induced autoimmune hepatitis with microvesicular steatosis
- Pages: 573-576
- First Published: 03 July 2014