Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIAL
2023 focused update of the 2021 ESC heart failure guidelines: Key messages for clinical practice
- First Published: 18 January 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Atrial fibrosis heterogeneity is a risk for atrial fibrillation in pigs with ischaemic heart failure
- First Published: 27 November 2023
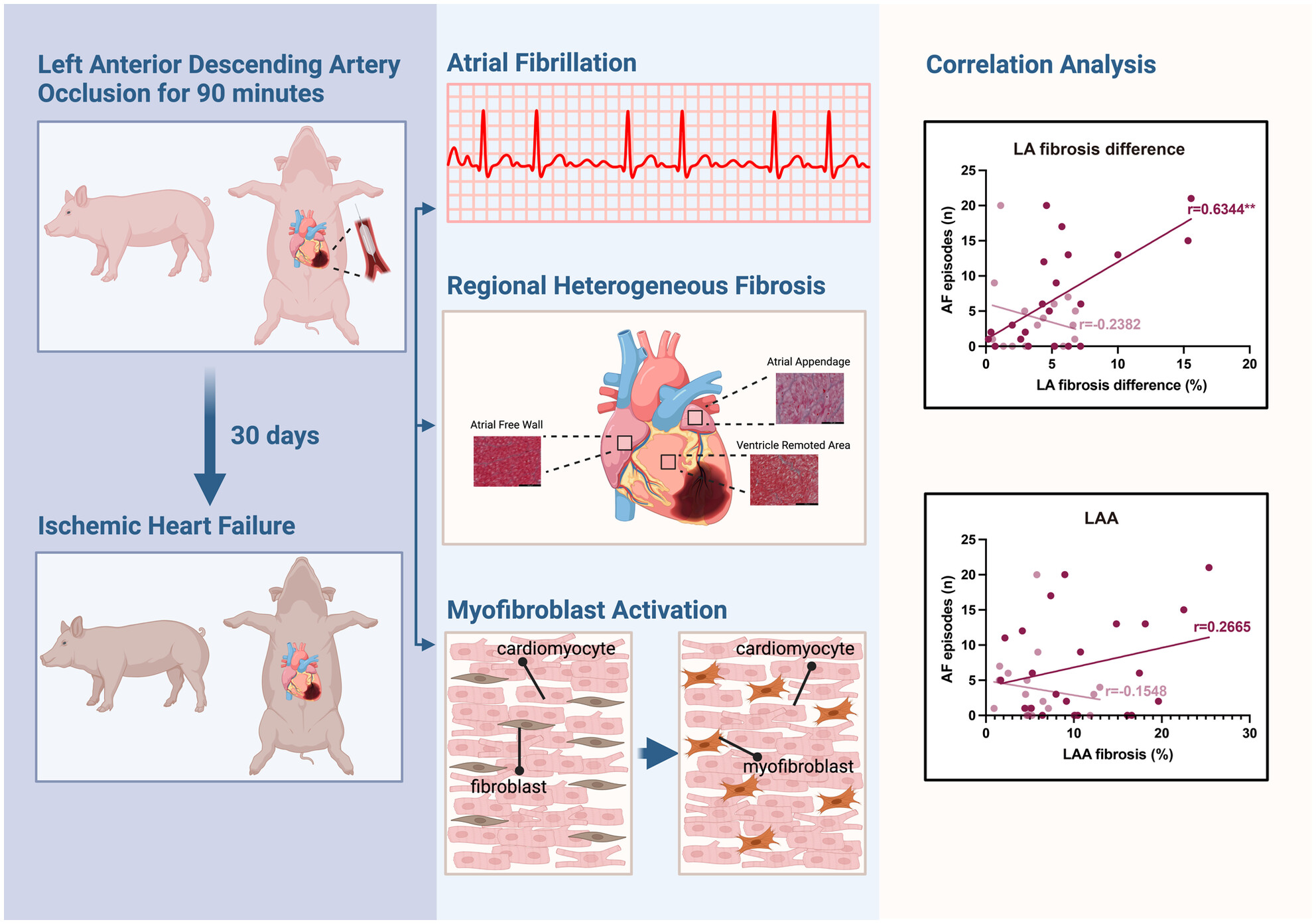
In pigs with ischaemic heart failure (IHF), we found a higher susceptibility to atrial fibrillation (AF) compared with control pigs. Electrical conduction properties did not differ between the two groups. However, histological assessment revealed aggravated fibrosis in atrial appendages but not in atrial free walls in pigs with IHF, which was paralleled by enhanced myofibroblast activation. Correlation analysis indicated that not fibrosis per se but its cross-regional heterogeneous distribution across the left atrium was associated with AF susceptibility.
Imaging-based risk stratification of patients with pulmonary embolism based on dual-energy CT-derived radiomics
- First Published: 08 December 2023
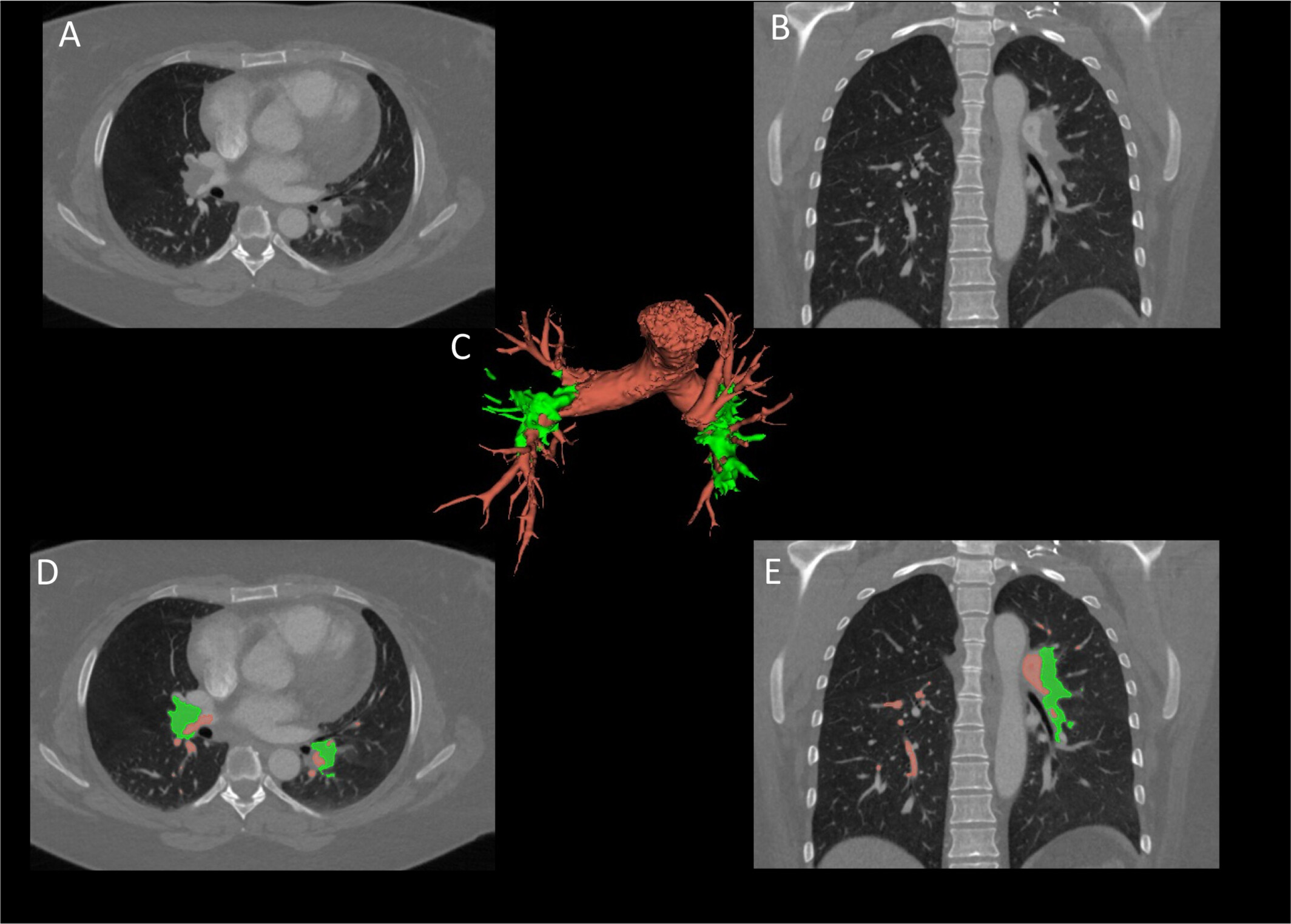
This study explores the potential of a machine learning classifier based on dual-energy computed tomography (DECT) radiomics to classify pulmonary embolism (PE) severity and assessing the risk for early death. The trained machine learning classifier achieved a classification accuracy of .90 for identifying high-risk PE patients with an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of .59. This CT-based radiomics signature showed good diagnostic accuracy for risk stratification in individuals presenting with central PE, particularly within higher risk groups.
Effect of traditional or heat-not-burn cigarette smoking on circulating miRNAs in healthy subjects
- First Published: 05 December 2023
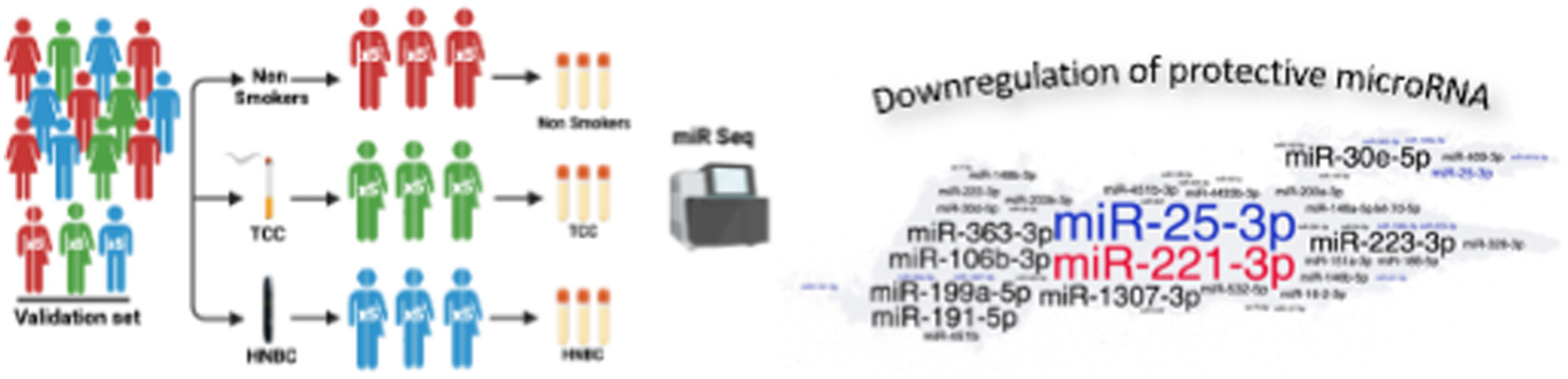
The use of heat-not-burn cigarettes (HNBCs) as alternative smoking devices is rising worldwide, and the circulating miRNA profile of chronic HNBC smokers is unknown. We aimed at defining the circulating miRNA profile of chronic exclusive HNBC smokers, and identifying the targeted pathways. Serum samples were obtained from 60 healthy young subjects, stratified in chronic exclusive HNBC smokers, TCC smokers and nonsmokers. Our results define the miRNA profile in the serum of chronic HNBC smokers and suggest an impact of HNBCs on circulating miRNAs comparable to that of traditional combustion cigarettes.
Vitamin K insufficiency and the prophylaxis strategy in term healthy infants: A multicentre study
- First Published: 09 December 2023
HLA binding-groove motifs are associated with myocarditis induction after Pfizer-BioNTech BNT162b2 vaccination
- First Published: 09 December 2023
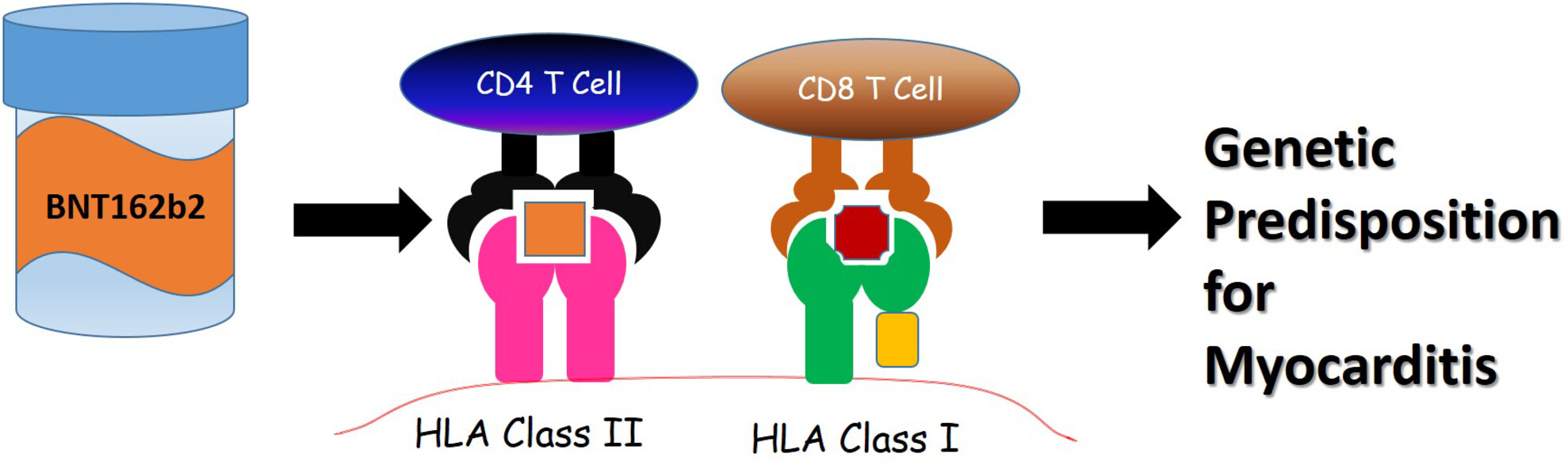
HLA loci were genotyped in 29 patients with post-vaccination myocarditis and compared with HLA data from 300 healthy controls. The HLA-DRB1*14:01, DRB1*15:03 alleles and the motifs in HLA-A − Leu62 and Gln63, which are part of binding pocket B and HLA-DR Tyr47, His60, Arg70 and Glu74, which are part of binding pockets P4, P7 and P9, were significantly associated with disease susceptibility. This suggests that immunogenetic fingerprints in HLA grooves may affect the presentation of peptides derived from the Pfizer-BioNTech BNT162b2 vaccination and induce myocarditis.
Effects of CASZ1, WNT2B and PTPRG SNPs on stroke susceptibility in the Chinese Han population
- First Published: 07 December 2023
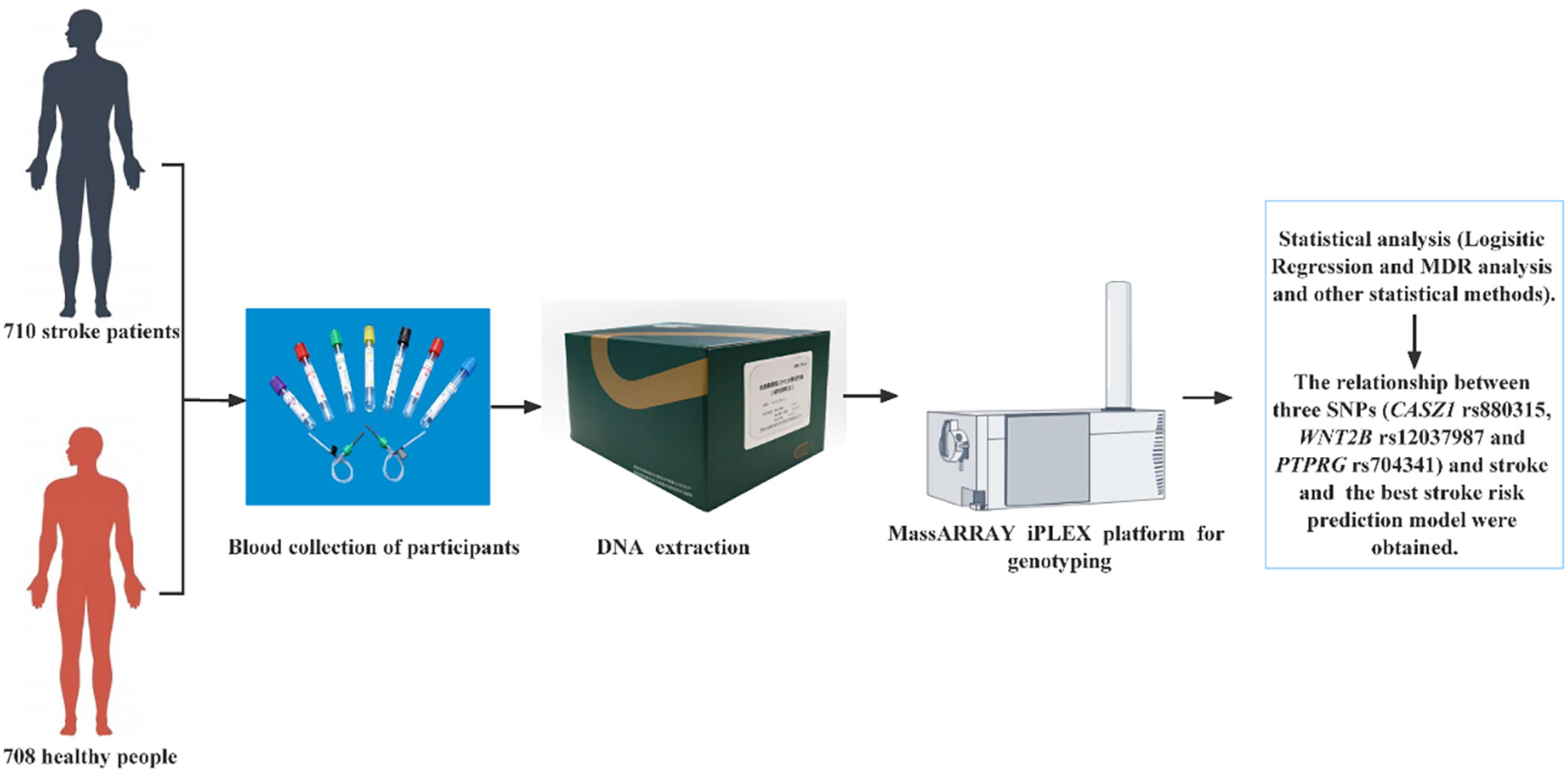
In this study, we collected blood samples from 710 stroke patients and 708 healthy people. We used the MassARRAY iPLEX GOLD method to genotype the 3 SNPs. Logistic regression was used to analyse the association between these SNPs and stroke. The interactions among SNPs were predicted by multi-factor dimensionality reduction (MDR) analysis. This research demonstrated that CASZ1 rs880315 and PTPRG rs704341 were associated with reduced stroke susceptibility. Our study concludes that the 3 SNPs are associated with stroke in the Han Chinese population.
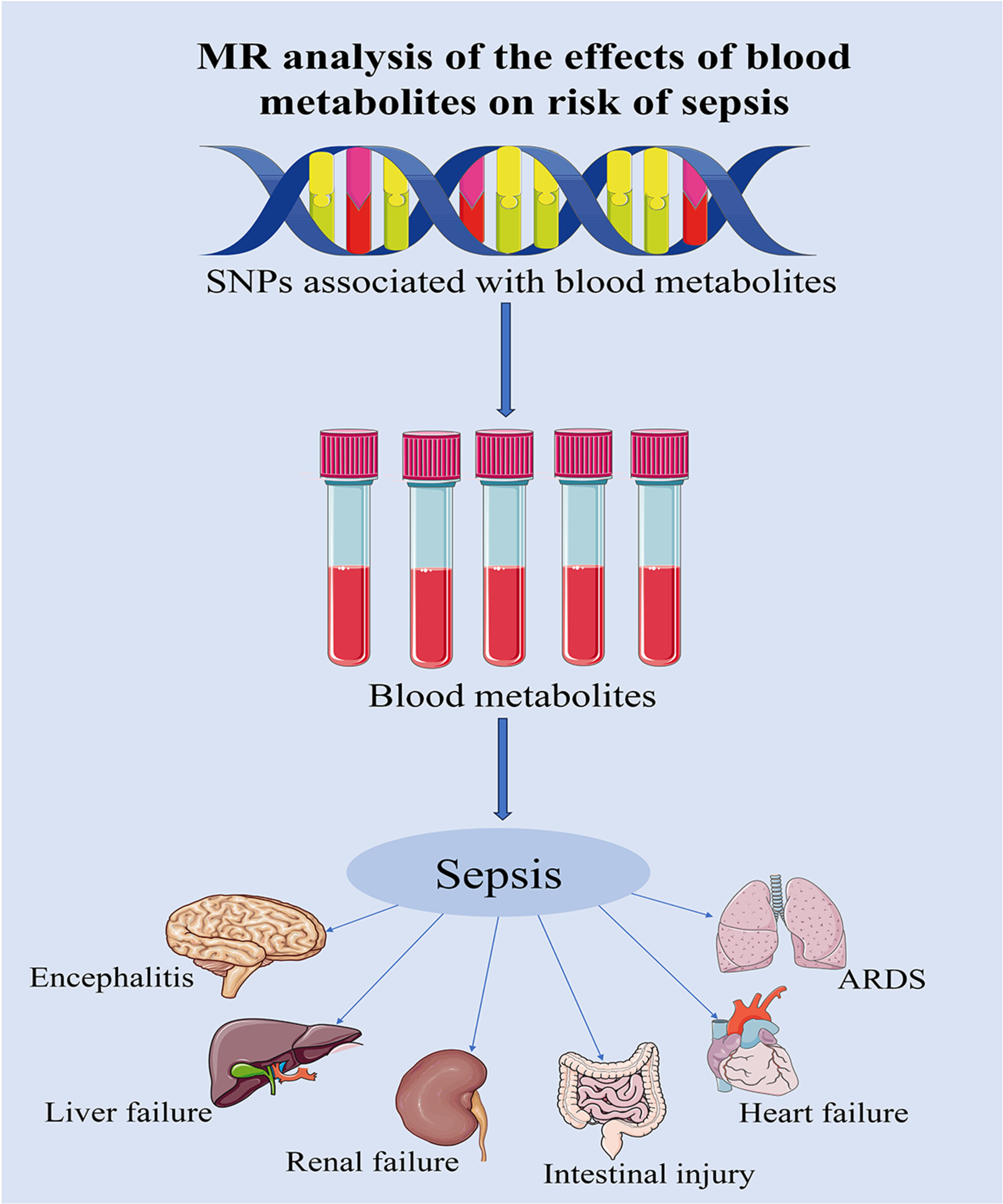
Human blood metabolites and risk of sepsis: A Mendelian randomization investigation
- First Published: 02 December 2023
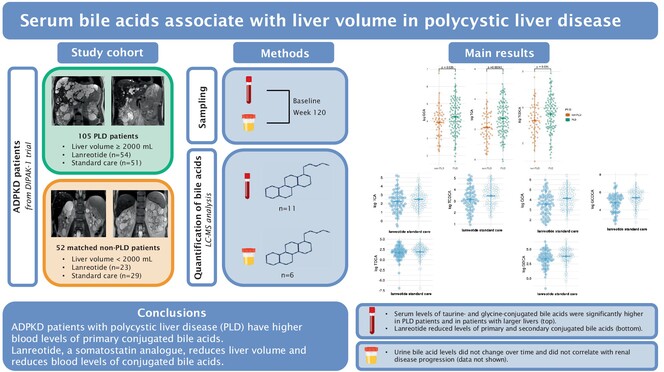
Serum bile acids associate with liver volume in polycystic liver disease and decrease upon treatment with lanreotide
- First Published: 09 December 2023
Circulating haematopoietic stem cells and long-term outcomes of COVID-19
- First Published: 13 December 2023
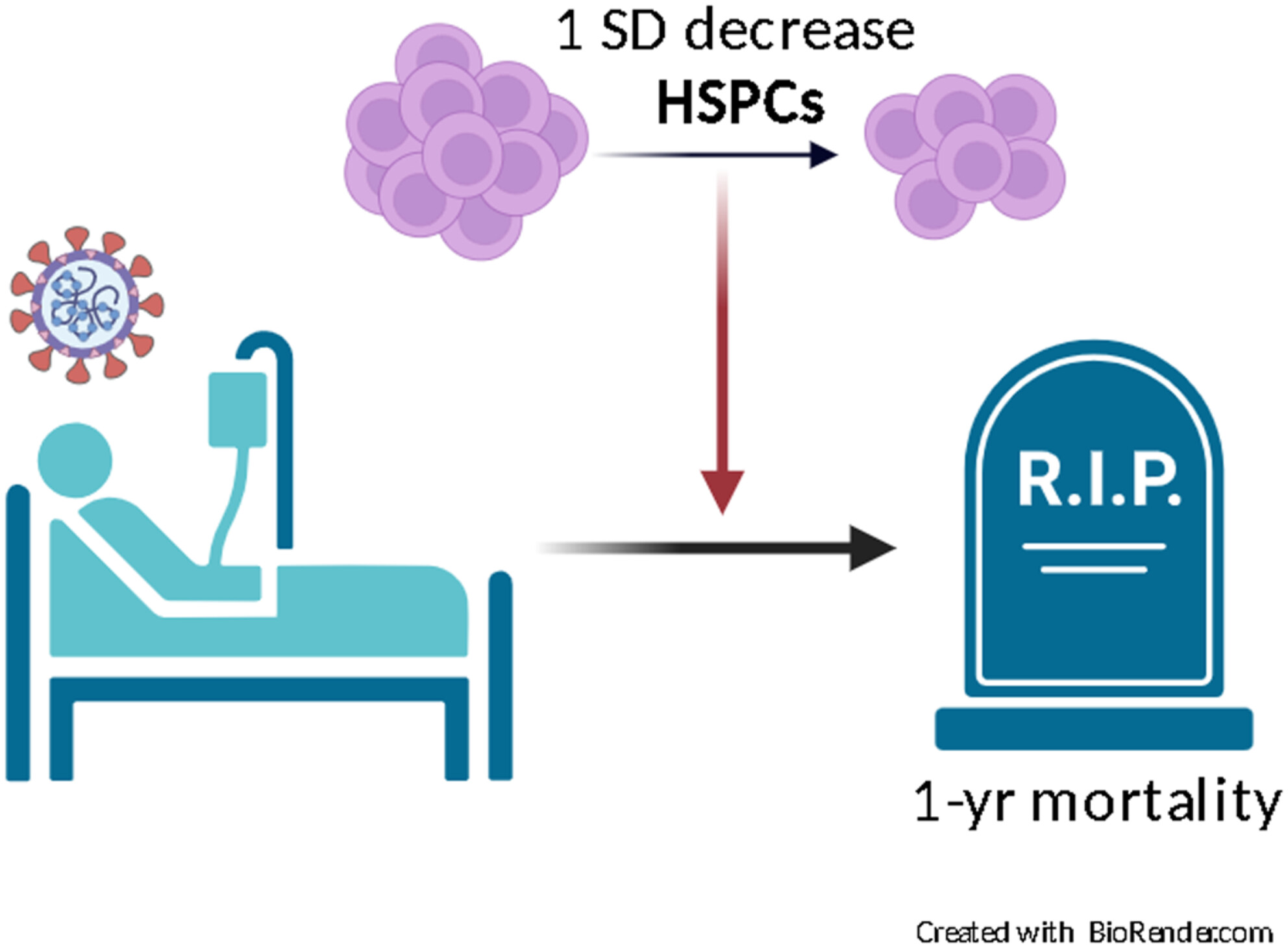
In a cohort of 100 patients hospitalized for COVID-19 consecutively enrolled, the reduction of 1 standard deviation of circulating haematopoietic stem/progenitor cells (HSPCs) was associated with a 3- to 5-fold increase in the risk of 1-year mortality. In multivariate analyses, HSPCs remained significantly associated with 1-year mortality independently of confounders. HSPC level was not associated with the development of long-COVID symptoms.
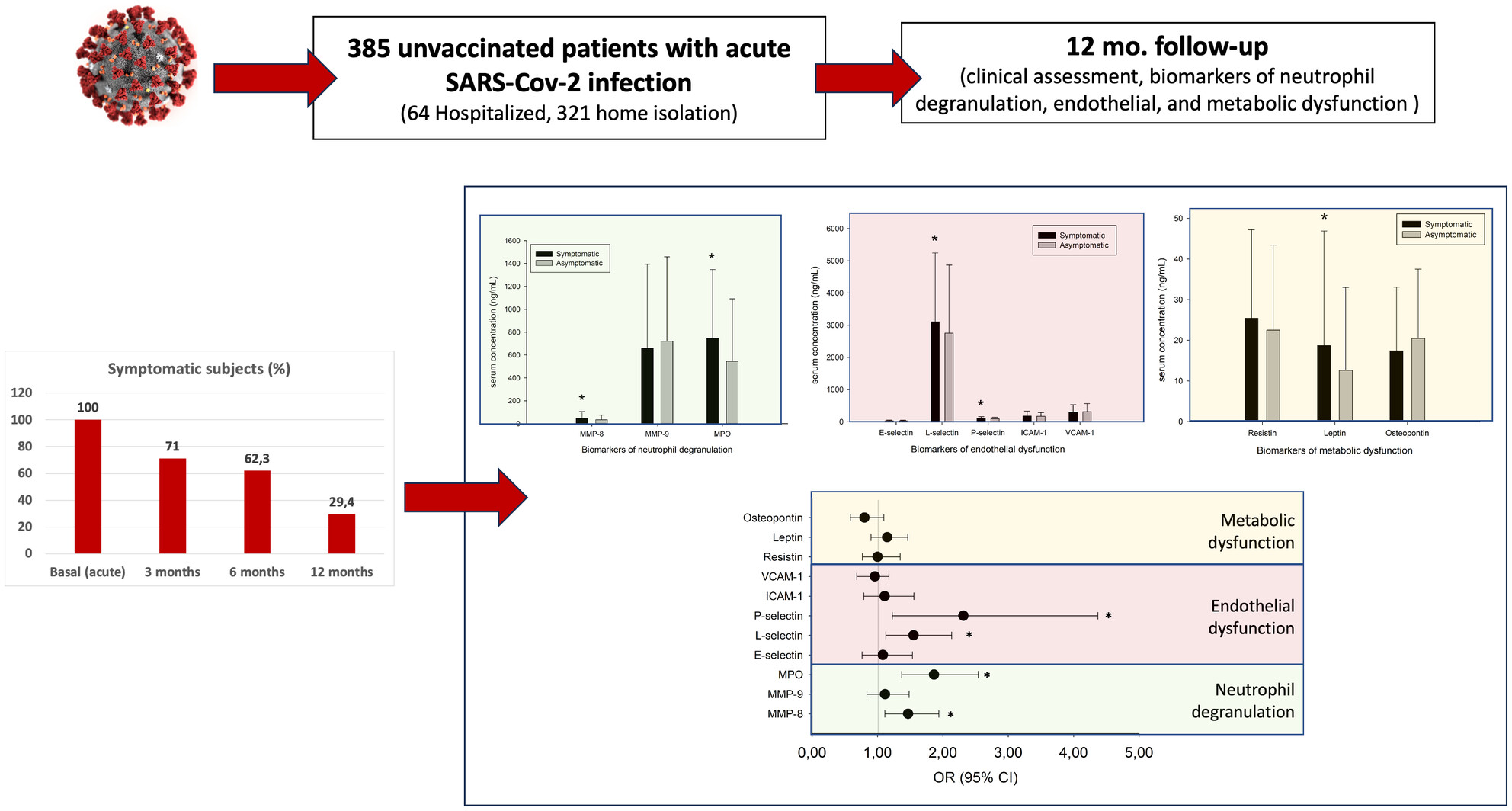
Neutrophil degranulation, endothelial and metabolic dysfunction in unvaccinated long COVID patients
- First Published: 16 January 2024
SYSTEMATIC REVIEWS
The effect of subcutaneous dulaglutide on weight loss in patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- First Published: 11 November 2023
Serological markers and long COVID—A rapid systematic review
- First Published: 11 December 2023
NARRATIVE REVIEWS
Sperm mitochondria dysfunction in response to testicular cancer
- First Published: 08 December 2023
META-ANALYSIS
Changes in lipid profile and glucose metabolism following administration of bupropion alone or in combination with naltrexone: A systematic review and meta-regression analysis
- First Published: 06 November 2023
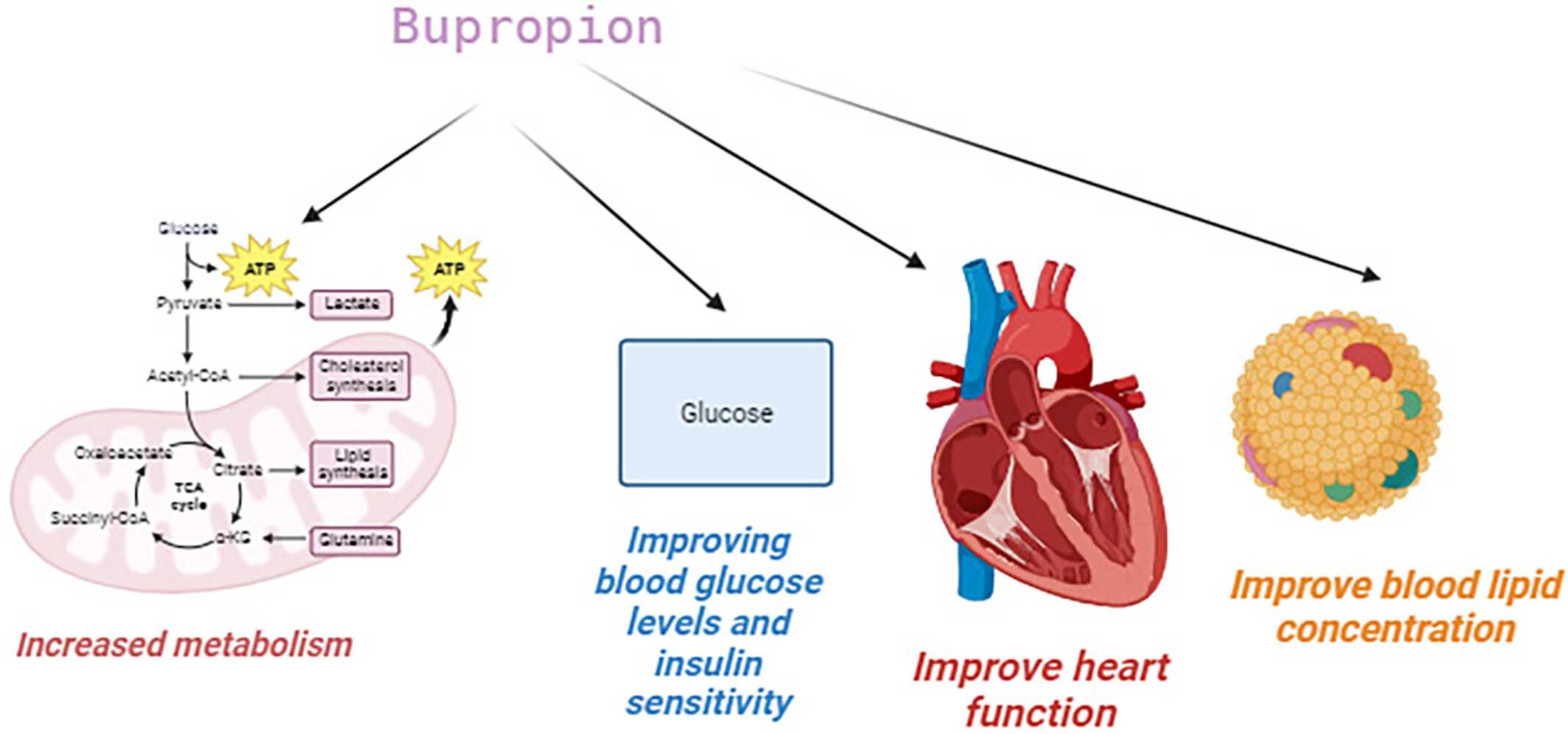
There are contradictory effects regarding the effect of bupropion alone or in combination with naltrexone on in lipid profile and glucose metabolism. The pooled findings showed that bupropion alone or in combination with naltrexone would significantly reduce glucose, (HOMA-IR), triglyceride and increase HDL. A Greater reduction in glucose levels was observed with duration >26 weeks. Dose of bupropion intake ≤360 mg and intervention for more than 26 weeks decreased insulin level significantly.
Transsulfuration and folate pathways in rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- First Published: 12 January 2024
Our systematic review and meta-analysis reported specific alterations in homocysteine, methionine, and vitamin B6, metabolites within the transsulfuration and folic acid pathways, in patients with RA in remission when compared to healthy controls. By contrast, there were no significant between-group differences in folic acid or vitamin B12. Meta-regression and subgroup analyses showed significant associations between the effect size of the between-group differences in homocysteine (year of publication, CRP, triglycerides, and analytical method) and folic acid (biological matrix).
RESEARCH LETTER
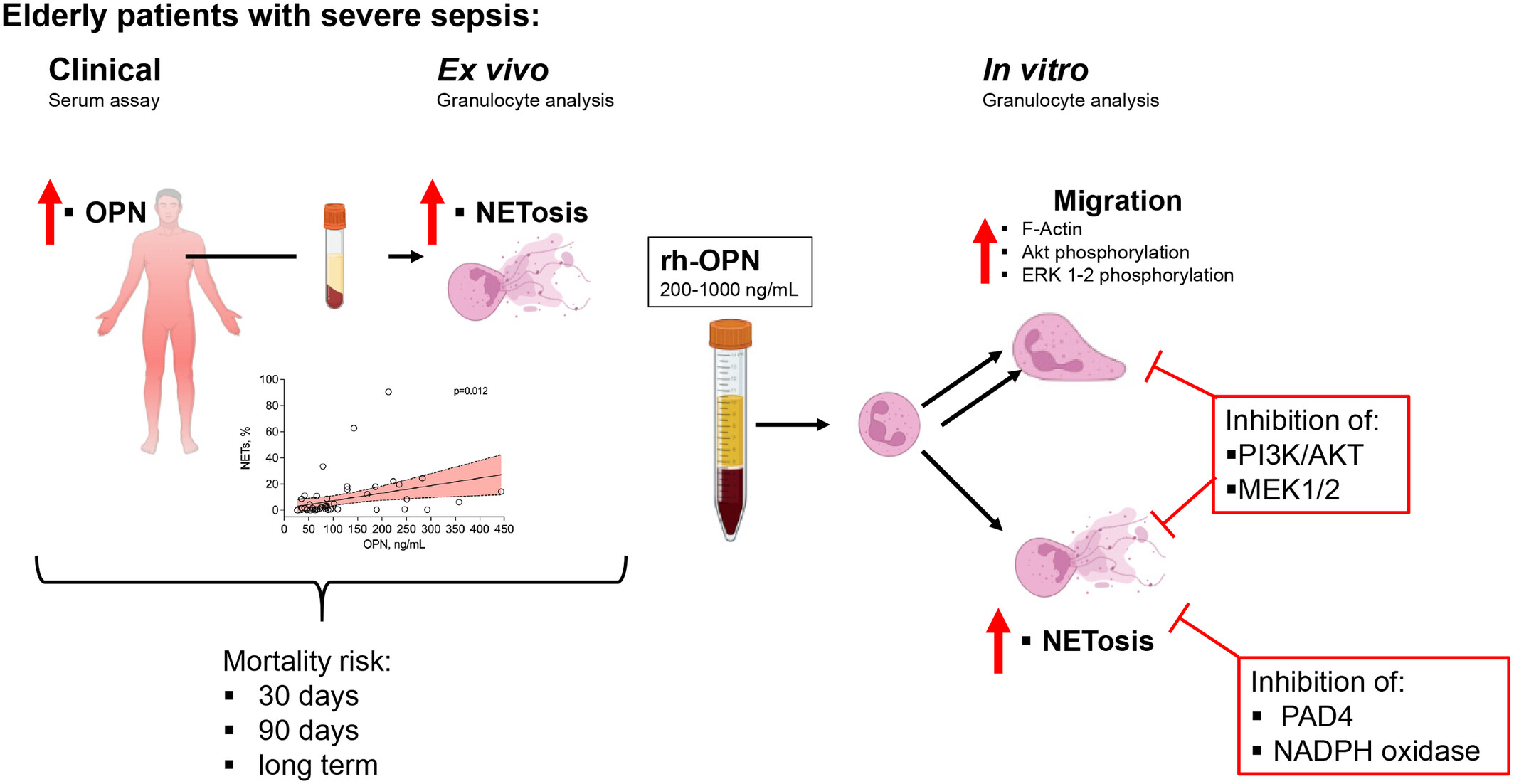
Osteopontin is associated with neutrophil extracellular trap formation in elderly patients with severe sepsis
- First Published: 24 January 2024