Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
FEATURED COVER
Featured Cover
- First Published: 19 February 2025
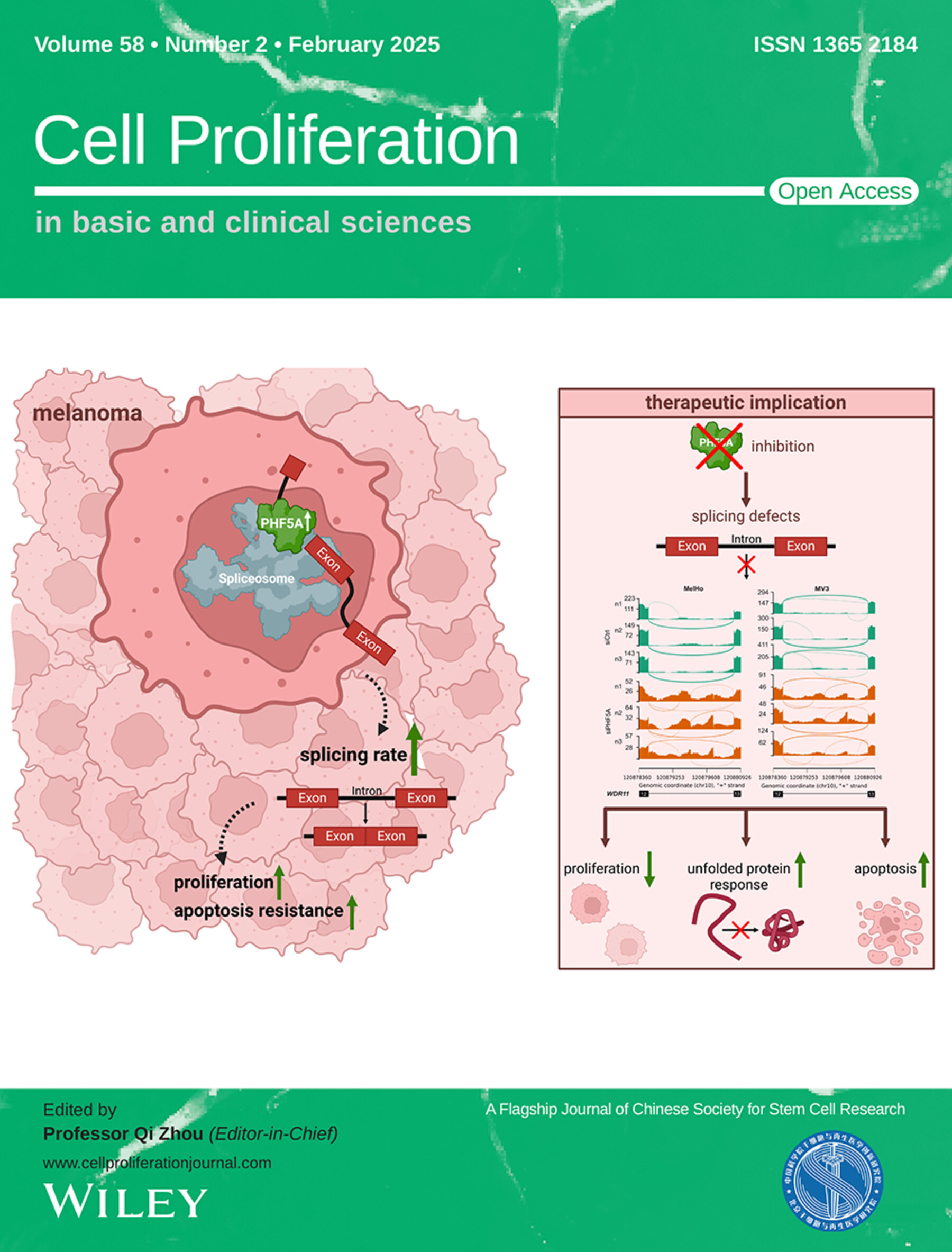
The cover image is based on the article Splicing control by PHF5A is crucial for melanoma cell survival by Anja Katrin Bosserhoff et al., https://doi.org/10.1111/cpr.13741.
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEW
Synergy between pluripotent stem cell-derived macrophages and self-renewing macrophages: Envisioning a promising avenue for the modelling and cell therapy of infectious diseases
- First Published: 13 November 2024
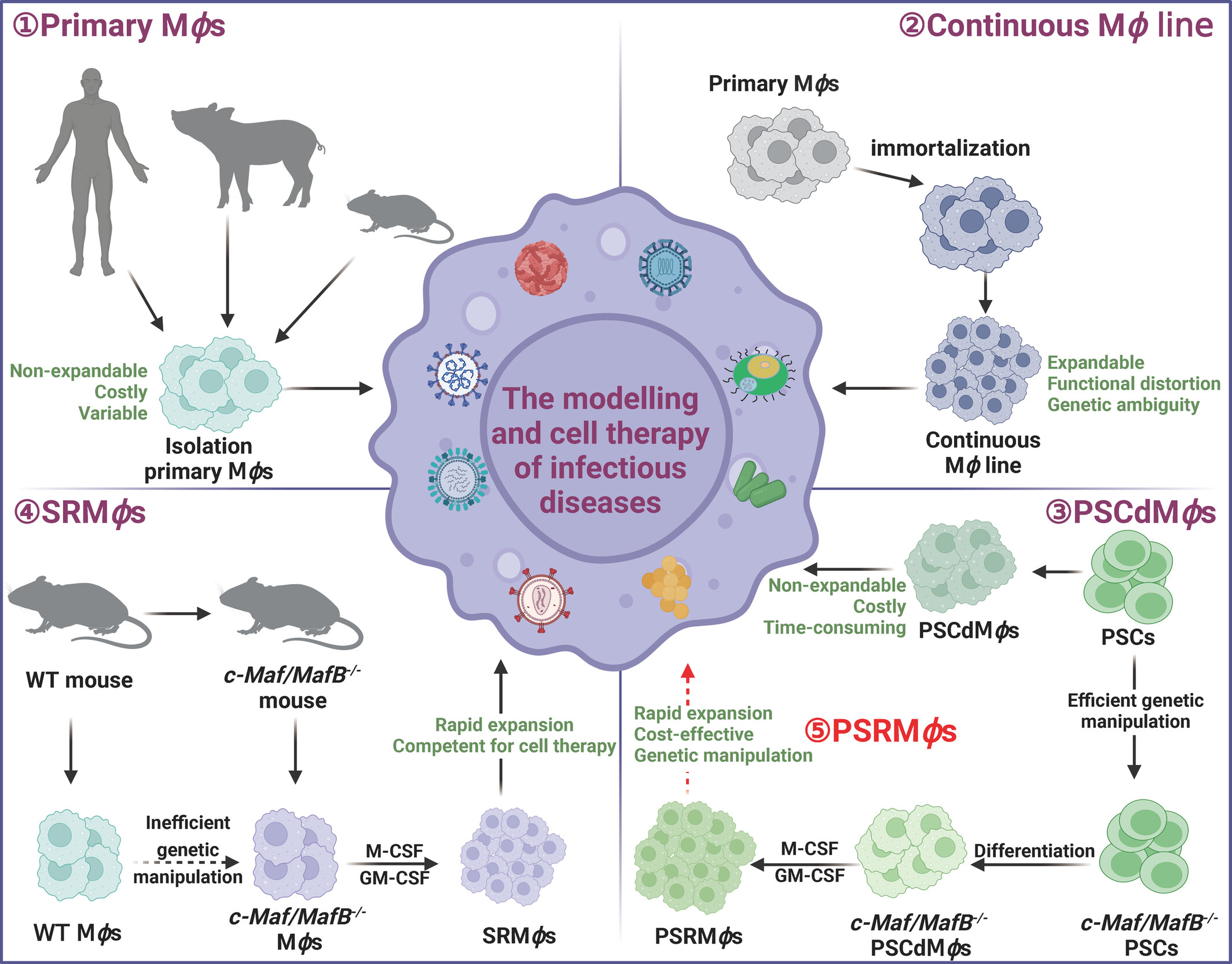
This review highlights the use of pluripotent stem cell-derived macrophages (PSCdMϕs) in modelling and treating infectious diseases and explores methods to create self-renewing macrophages (SRMϕs). We further propose that pluripotent stem cells can be utilized as a gene editing platform to develop self-renewing macrophages (PSRMϕs).
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Splicing control by PHF5A is crucial for melanoma cell survival
- First Published: 30 August 2024
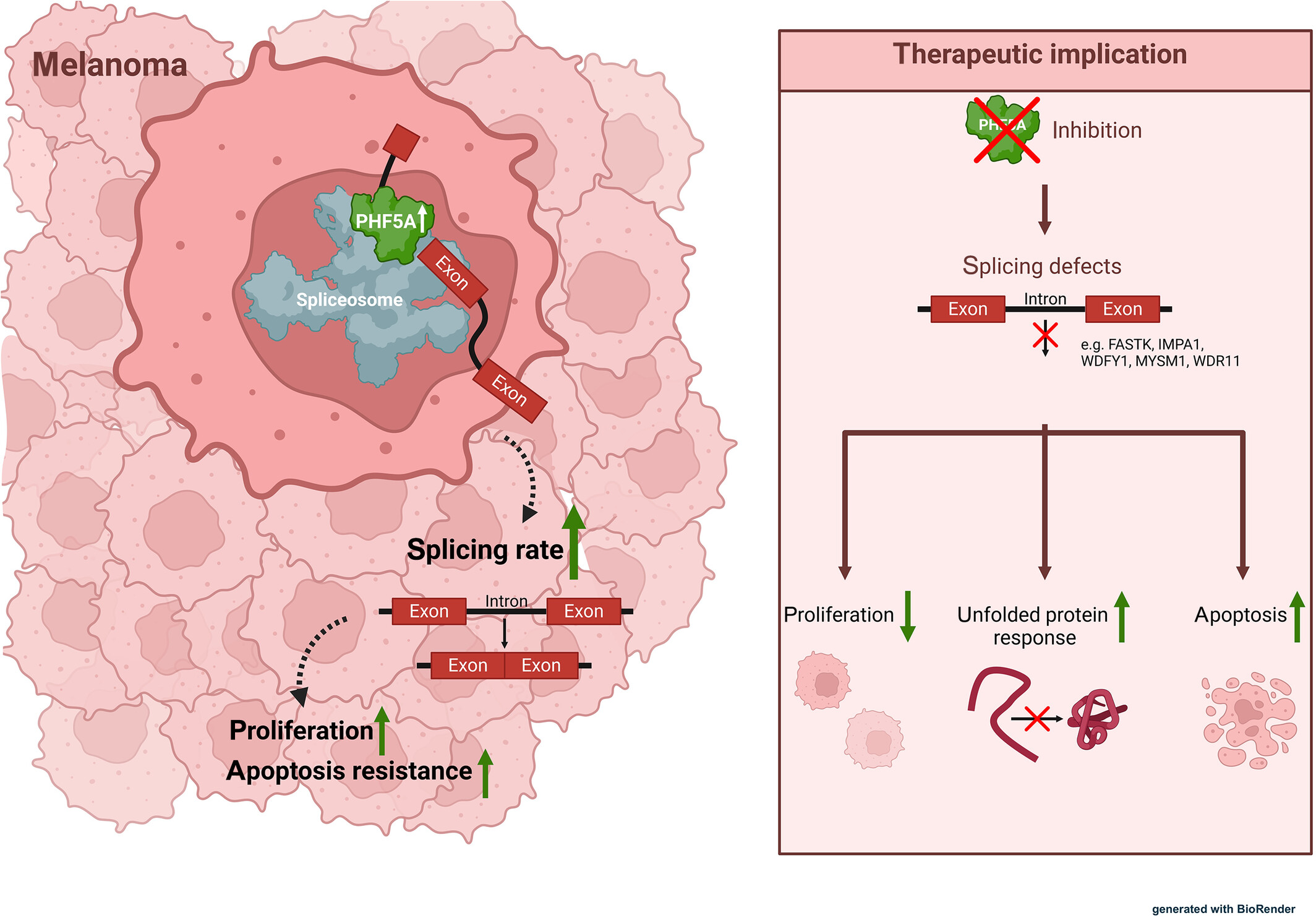
This work investigates the role of the splicing factor PHD Finger Protein 5A (PHF5A) in melanoma progression. PHF5A is upregulated in melanoma cells, leading to an increased splicing rate, which ensures the tumour typical high proliferation rate and apoptosis resistance. An inhibition of PHF5A results in splicing defects, inhibited proliferation and increased apoptosis by UPR activation.
Matrix stiffness regulates mitochondria-lysosome contacts to modulate the mitochondrial network, alleviate the senescence of MSCs
- First Published: 01 October 2024
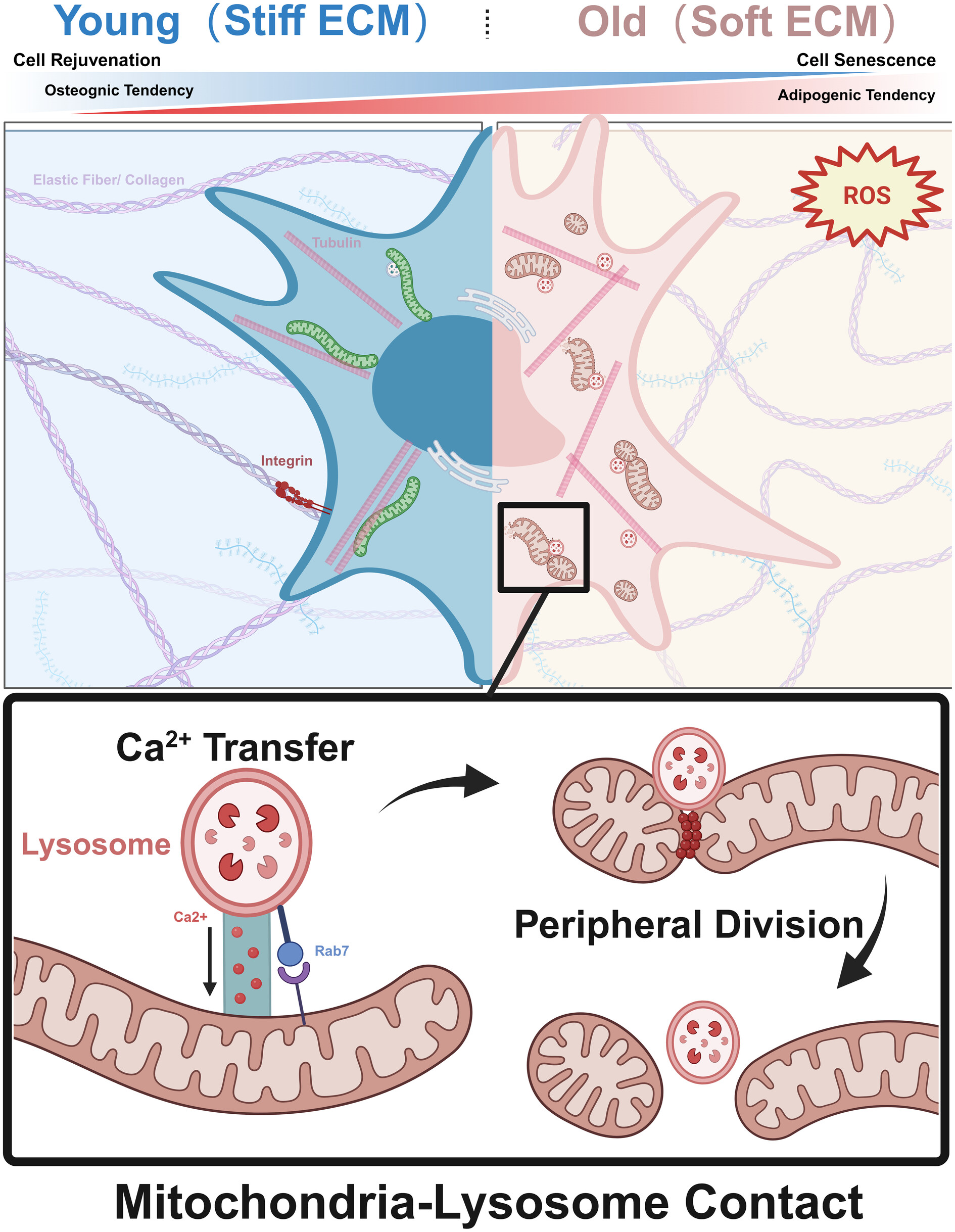
Under soft matrix stiffness, lysosomes make more contacts with mitochondria through disorganized cytoskeleton, leading to calcium ion transfer and subsequently causing mitochondrial redox imbalance. Additionally, M-L contact results in imbalanced mitochondrial fission dynamics, ultimately leading to the aging of MSCs.
Role of Wnt5a in modulation of osteoporotic adipose-derived stem cells and osteogenesis
- First Published: 17 September 2024
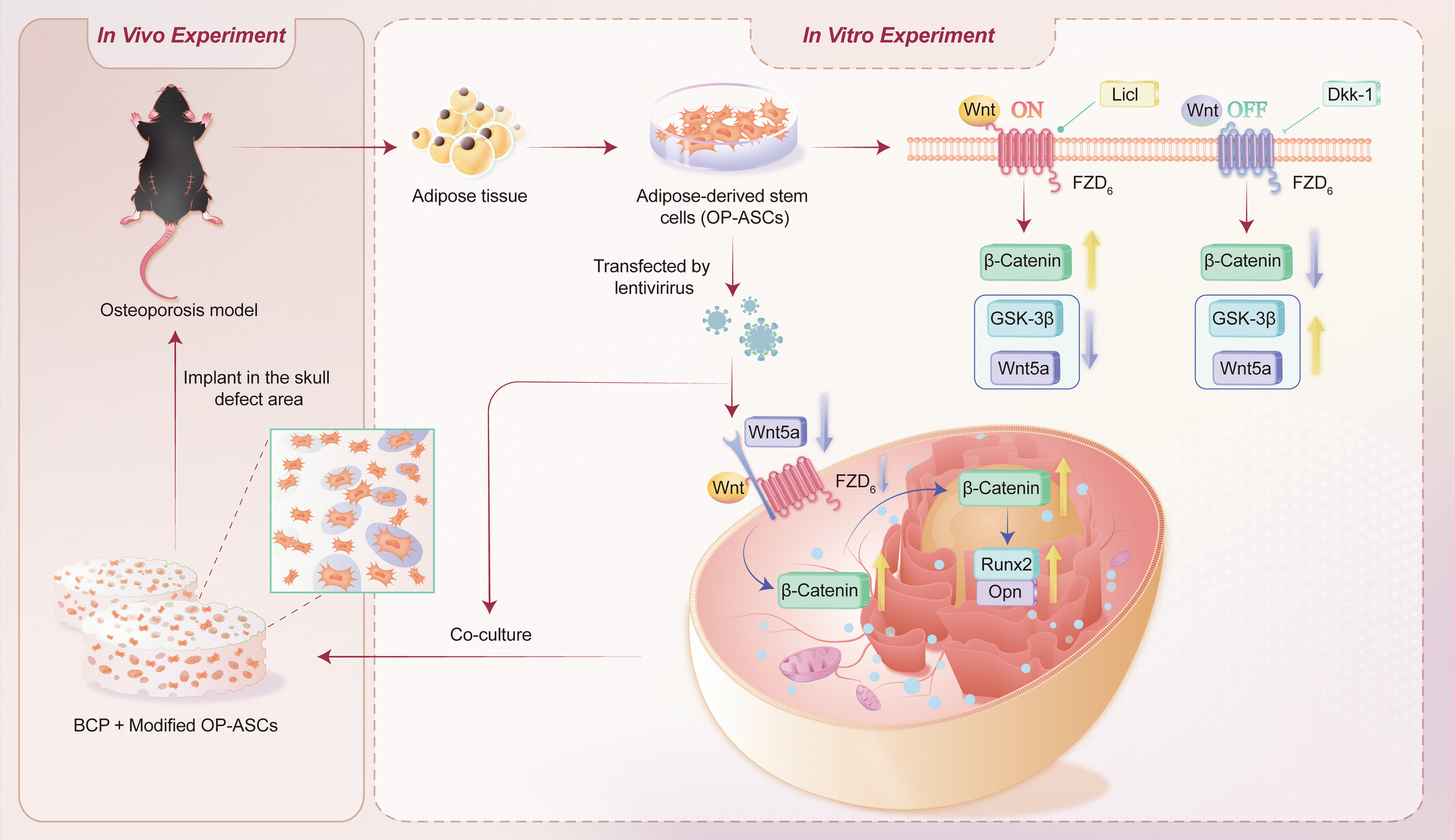
In this study, OP-ASCs were successfully isolated and cultured from the inguinal fat of the OP mouse with bilateral ovariotomy (OVX). Activation of the canonical Wnt signalling pathway markedly enhanced osteogenesis in OP-ASCs, concurrently suppressing Wnt5a and GSK-3β expression. Lentiviral-mediated silenced of Wnt5a could enhance the osteogenic ability of OP-ASCs by activating the canonical Wnt signalling pathway to promote the repair of critical-sized calvarial defects in osteoporotic mice.
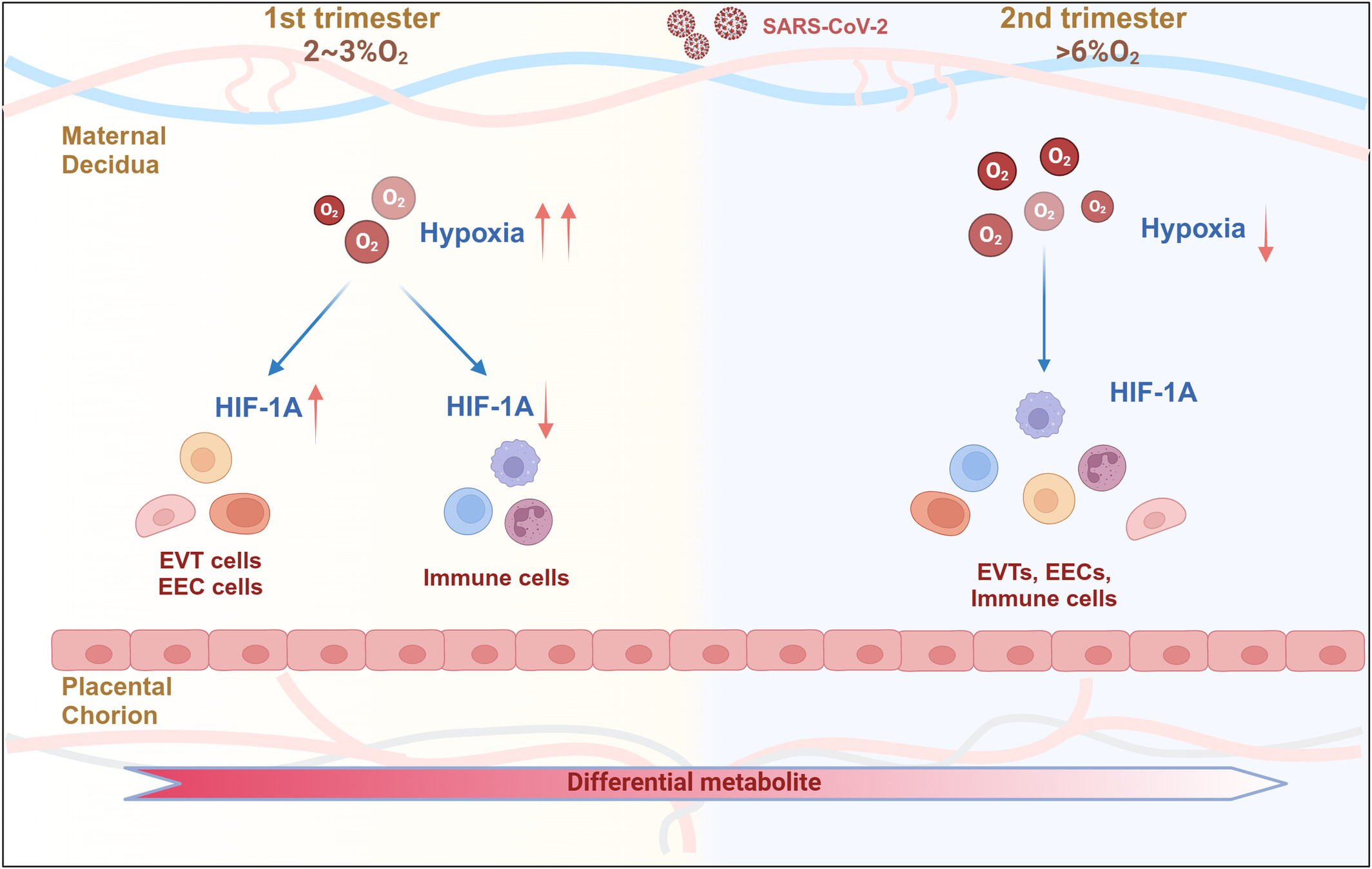
Maternal infection with SARS-CoV-2 during early pregnancy induces hypoxia at the maternal–fetal interface
- First Published: 07 October 2024
Deletion of Transmembrane protein 184b leads to retina degeneration in mice
- First Published: 07 October 2024
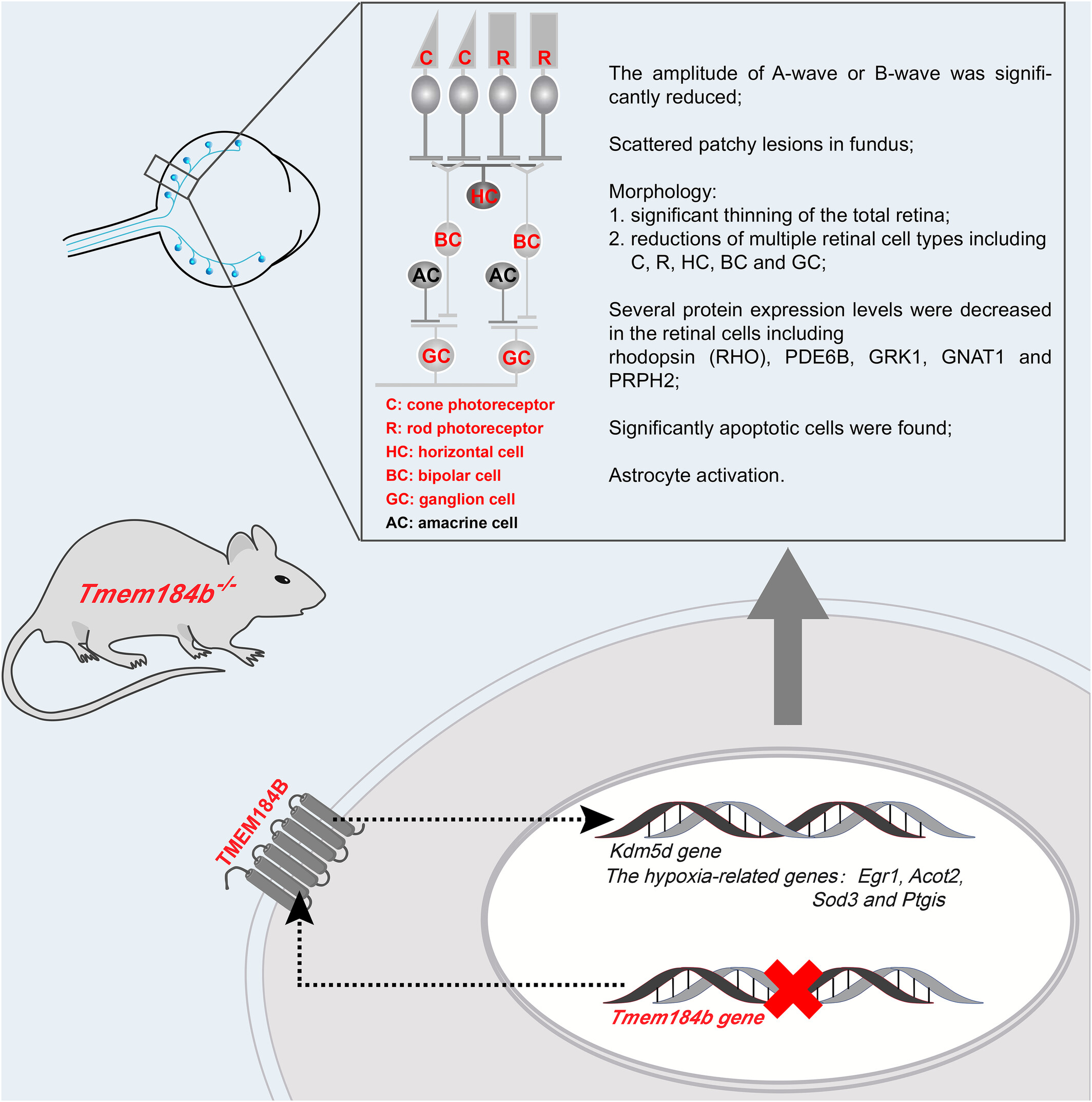
Our study characterized the retinal phenotypes of Tmem184b KO mice and confirmed the underlying mechanisms including cell death, inflammation and response to hypoxia pathway for retinal degeneration (RD) in the absence of TMEM184B, providing a rationale for therapeutic and diagnostic applications of RD.
Notch-1 regulates collective breast cancer cell migration by controlling intercellular junction and cytoskeletal organization
- First Published: 29 September 2024

Notch-1 activation (NICD) inhibits collective cell migration by promoting high intracellular force and strong cell–cell adhesion. Notch-1 activation leads to GSK-3β activity by inhibiting ILK phosphorylation, β- catenin is degraded and cannot enter the nucleus, resulting in higher expression of E-cadherin and tighter intercellular connections. Additionally, Notch-1 stimulates the Rho/ROCK pathway, which enhances adhesions between cells and the extracellular matrix and ultimately impedes collective cell migration.
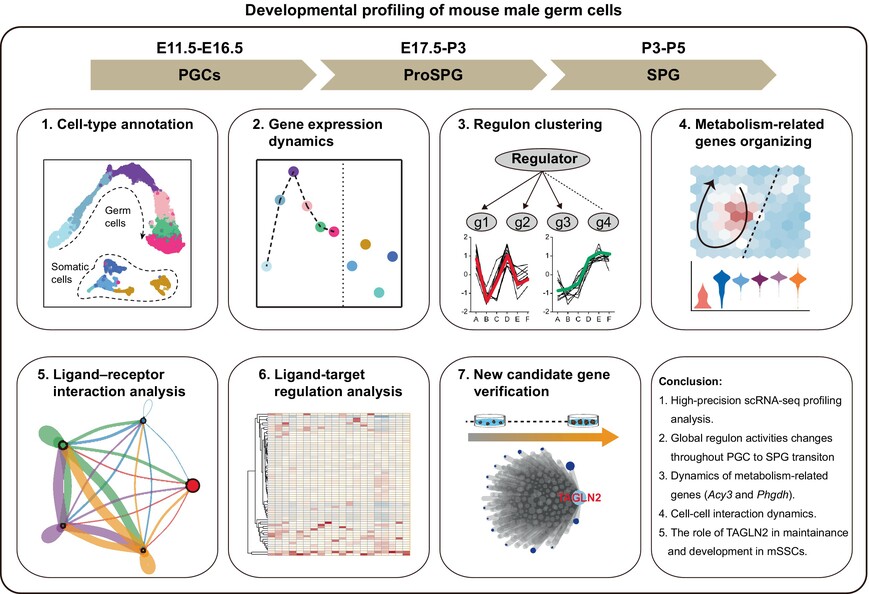
Dynamic transcriptomic and regulatory networks underpinning the transition from fetal primordial germ cells to spermatogonia in mice
- First Published: 27 September 2024
KDM2B and its peptides promote the stem cells from apical papilla mediated nerve injury repair in rats by intervening EZH2 function
- First Published: 02 October 2024
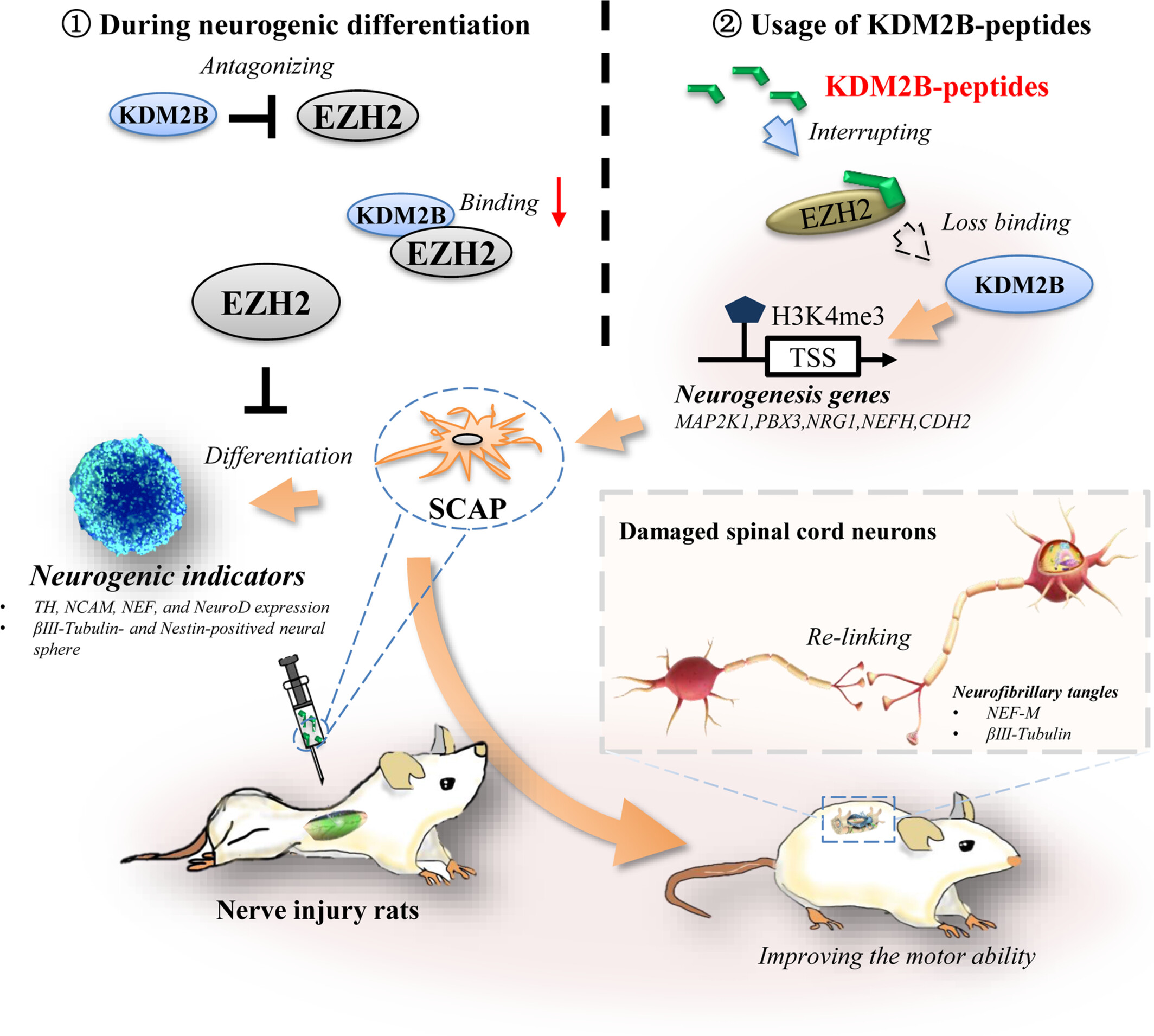
KDM2B promote the neurogenesis of stem cells from apical papilla (SCAP), through up-regulating mitogen-activated protein kinase-1 (MAP2K1), PBX3, Neuregulin-1 (NRG1), neurofilament heavy (NEFH) and Cadherin-2 (CDH2) via H3K4me3 methylation. Enhancer of zeste homologue 2 (EZH2) inhibited the neurogenic differentiation in SCAP, and was negatively regulated by KDM2B during neurogenic induction. KDM2B interacted with EZH2, and the binding between KDM2B and EZH2 was decreased during neurogenic induction. KDM2B-peptides were synthesized basing on KDM2B binding sequences with EZH2. By using KDM2B-peptides, the binding of EZH2 with KDM2B was effectively decreased. And KDM2B-peptides promoted the neurogenic differentiation ability of SCAP by intervening EZH2 function. The usage of KDM2B-peptides treated SCAP improved the motor ability of SCI rats.
miR-27a-3p regulates intestinal cell proliferation and differentiation through Wnt/β-catenin signalling
- First Published: 27 September 2024
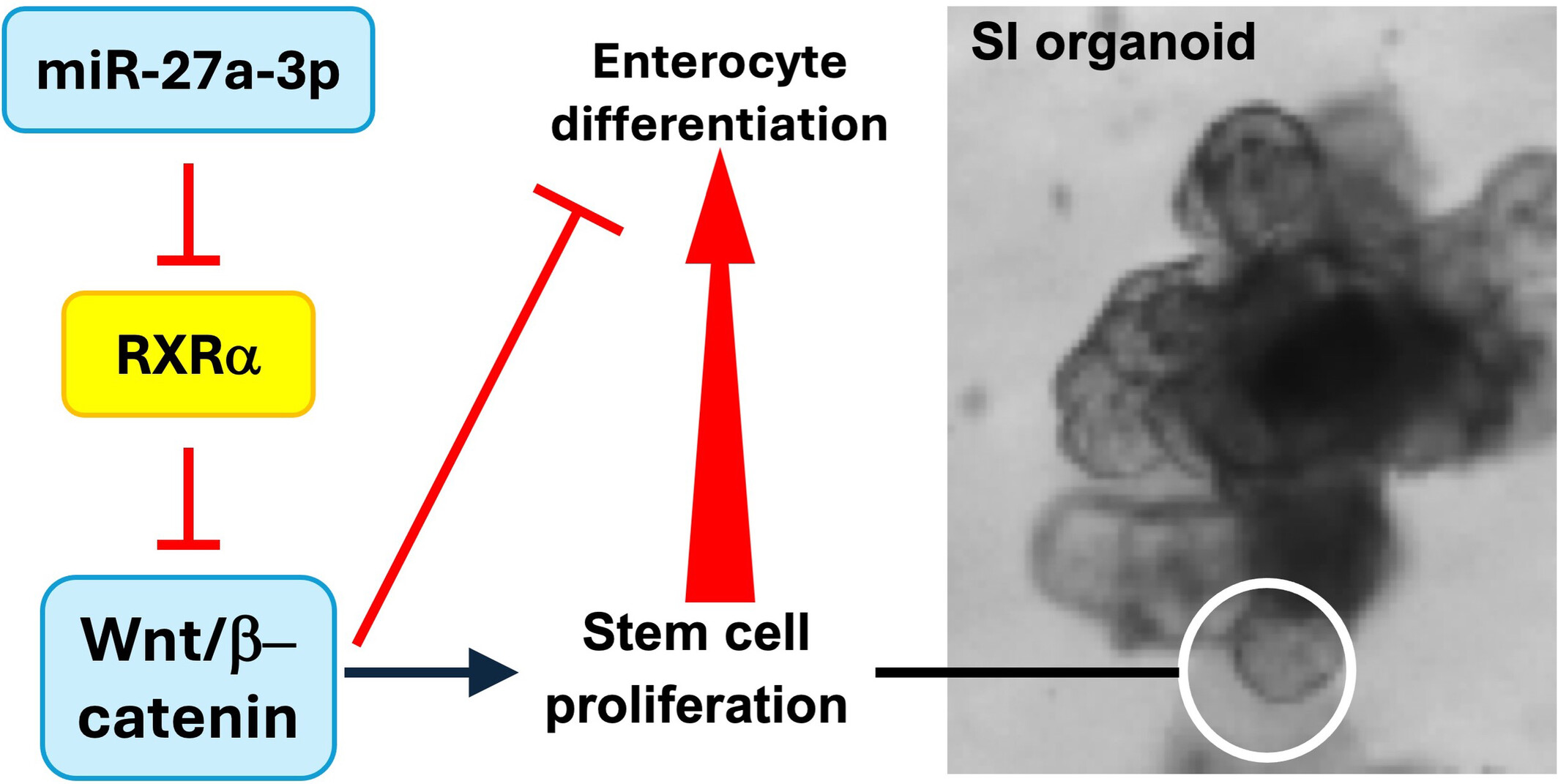
We show that the intestinal microRNA (miR)-27a-3p is an important regulator of intestinal epithelial cell proliferation and enterocyte differentiation. Repression of endogenous miR-27a-3p leads to increased enterocyte differentiation and decreased intestinal epithelial cell proliferation in mouse and human small intestinal organoids.
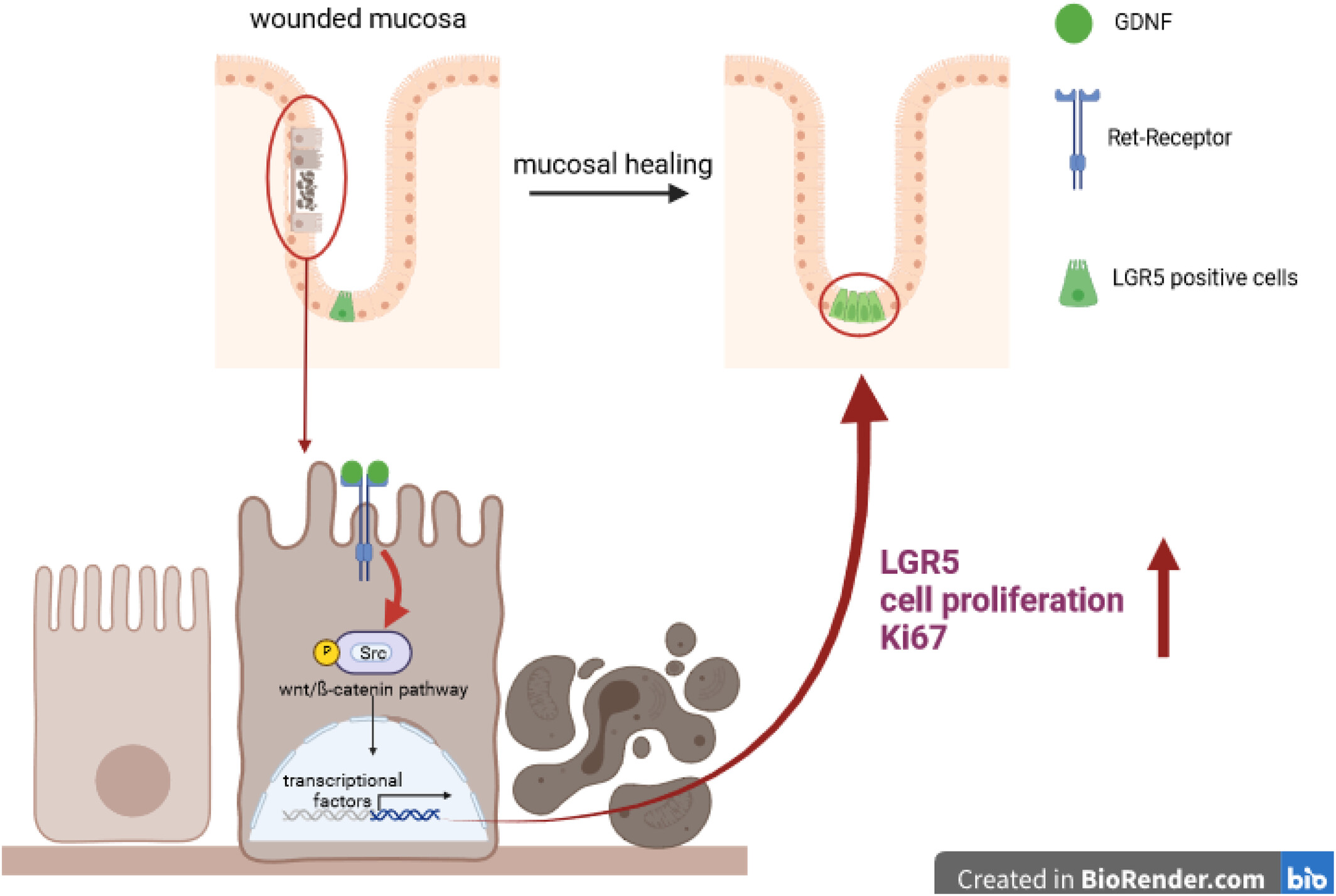
Glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) induces mucosal healing via intestinal stem cell niche activation
- First Published: 28 November 2024
Crotonylation of MCM6 enhances chemotherapeutics sensitivity of breast cancer via inducing DNA replication stress
- First Published: 30 October 2024
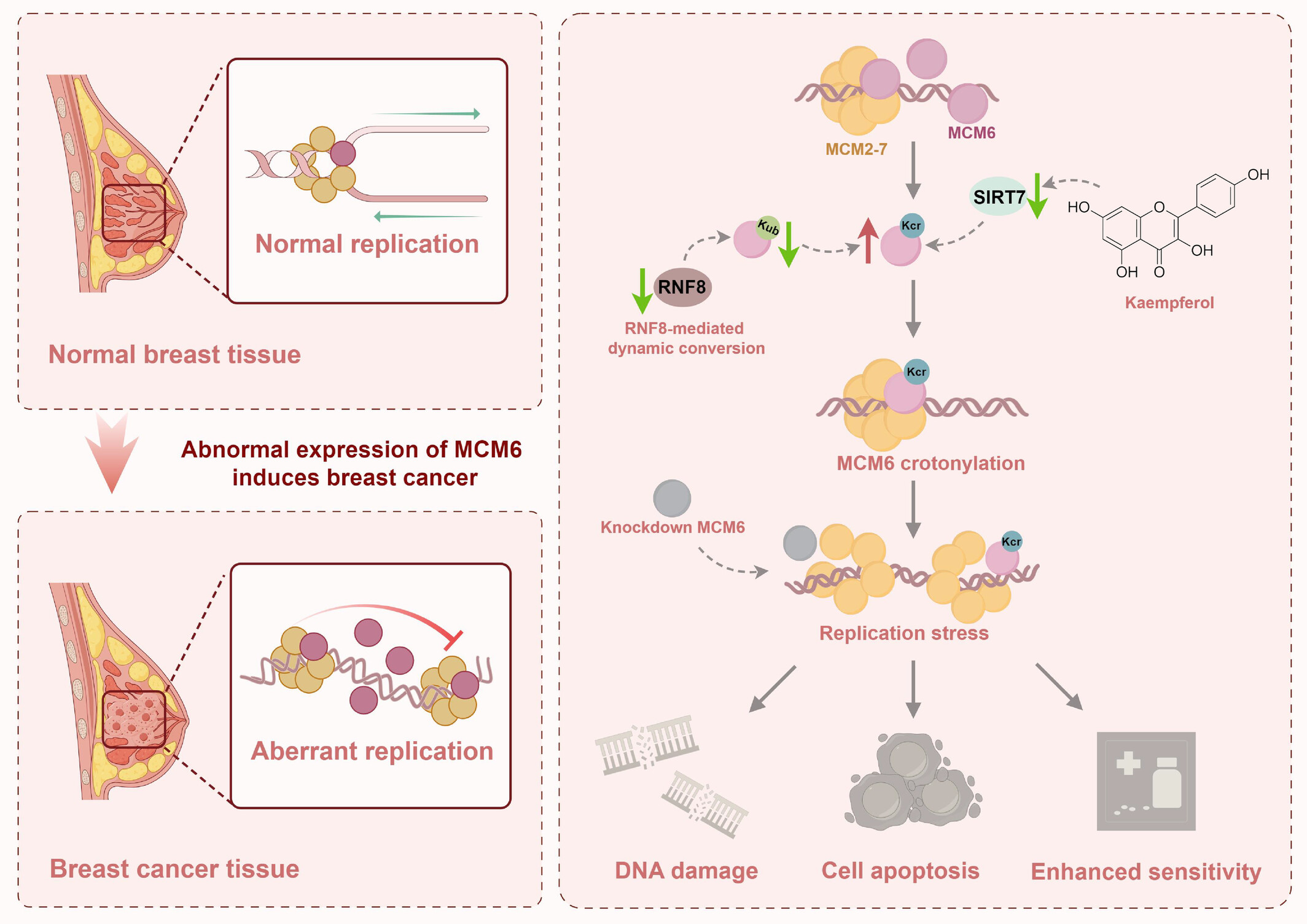
SIRT7-mediated crotonylation (Kr) of minichromosome maintenance 6 (MCM6) induced DNA replication stress and regulated by RNF8-mediated ubiquitination. Kaempferol, which acted as a regulator of SIRT7, could enhance MCM6 Kcr level, alleviating tumour weight, especially combined with paclitaxel, which presents a potential chemotherapeutic target for BRCA therapy.
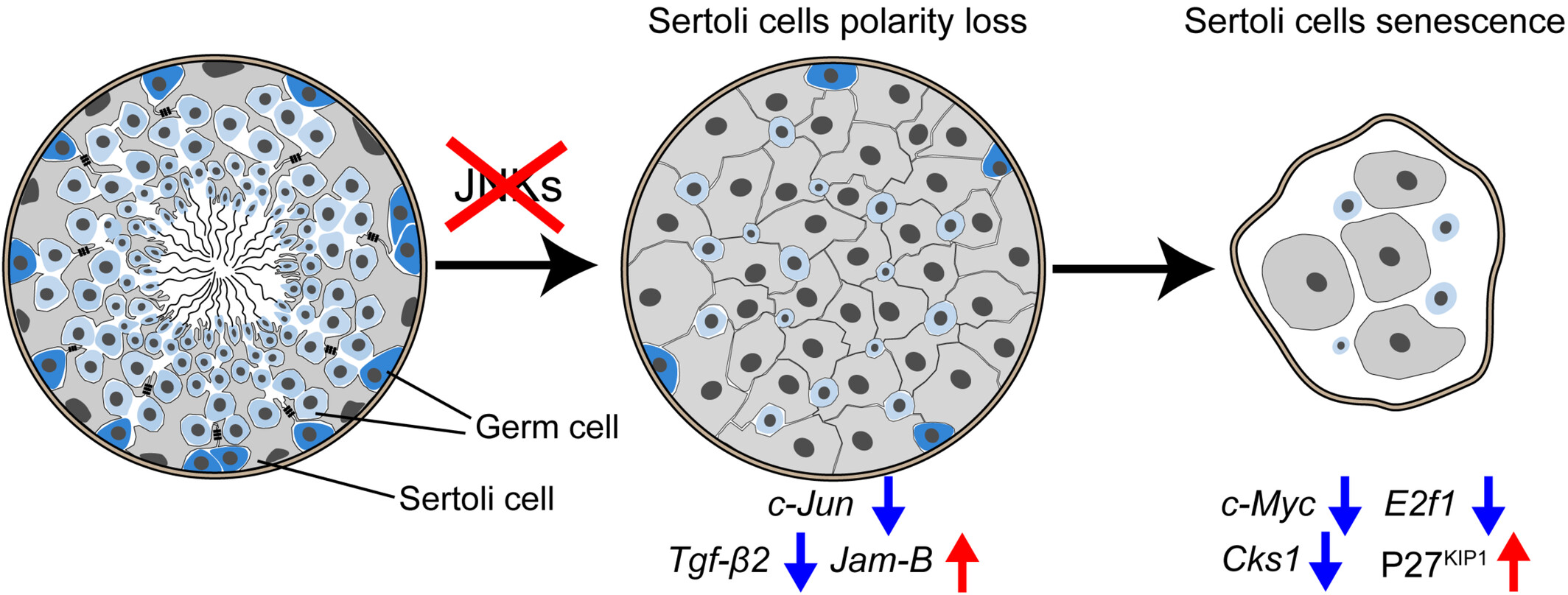
Inactivation of JNK signalling results in polarity loss and cell senescence of Sertoli cell
- First Published: 27 September 2024
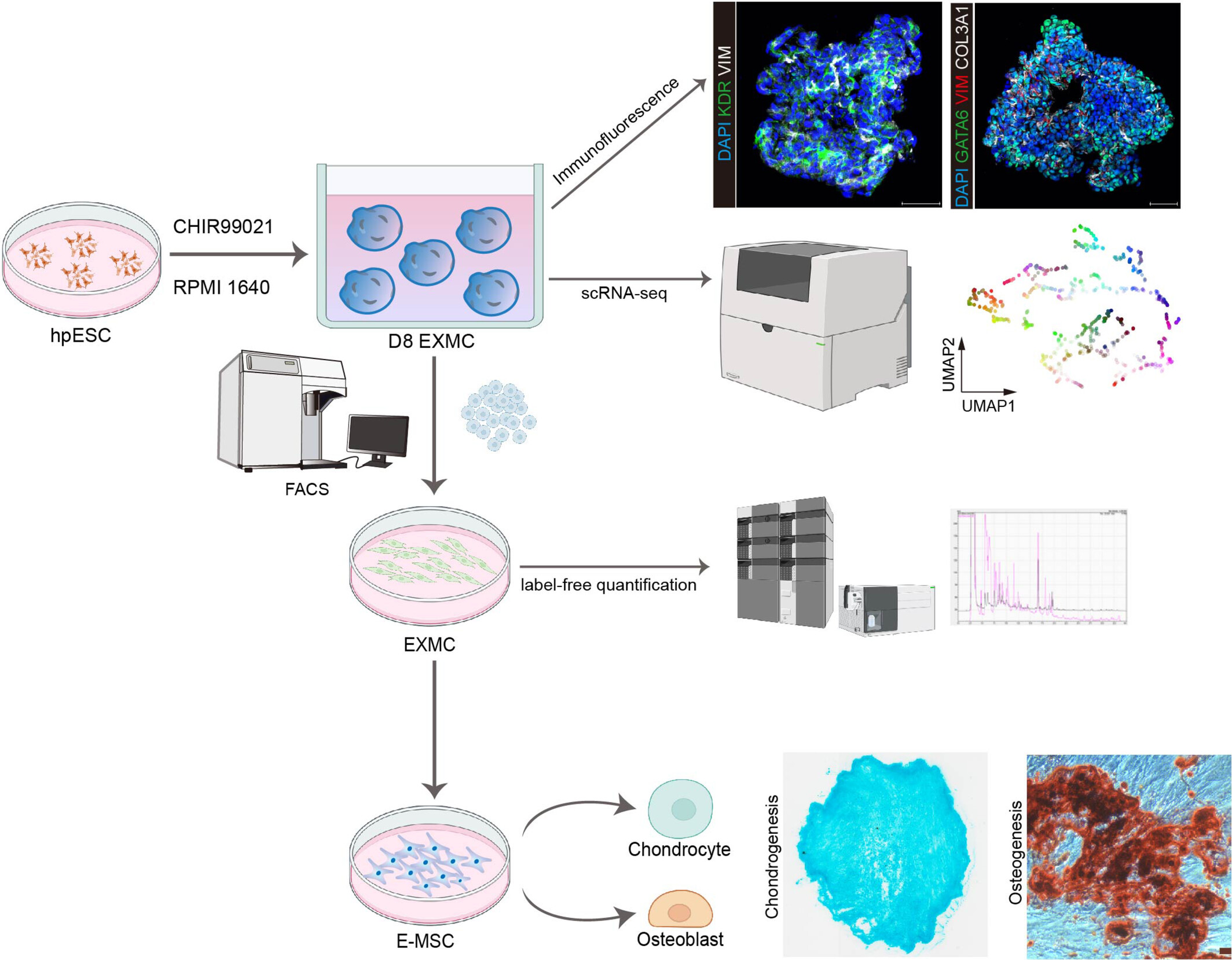
Extraembryonic mesoderm cells derived from human embryonic stem cells rely on Wnt pathway activation
- First Published: 09 October 2024
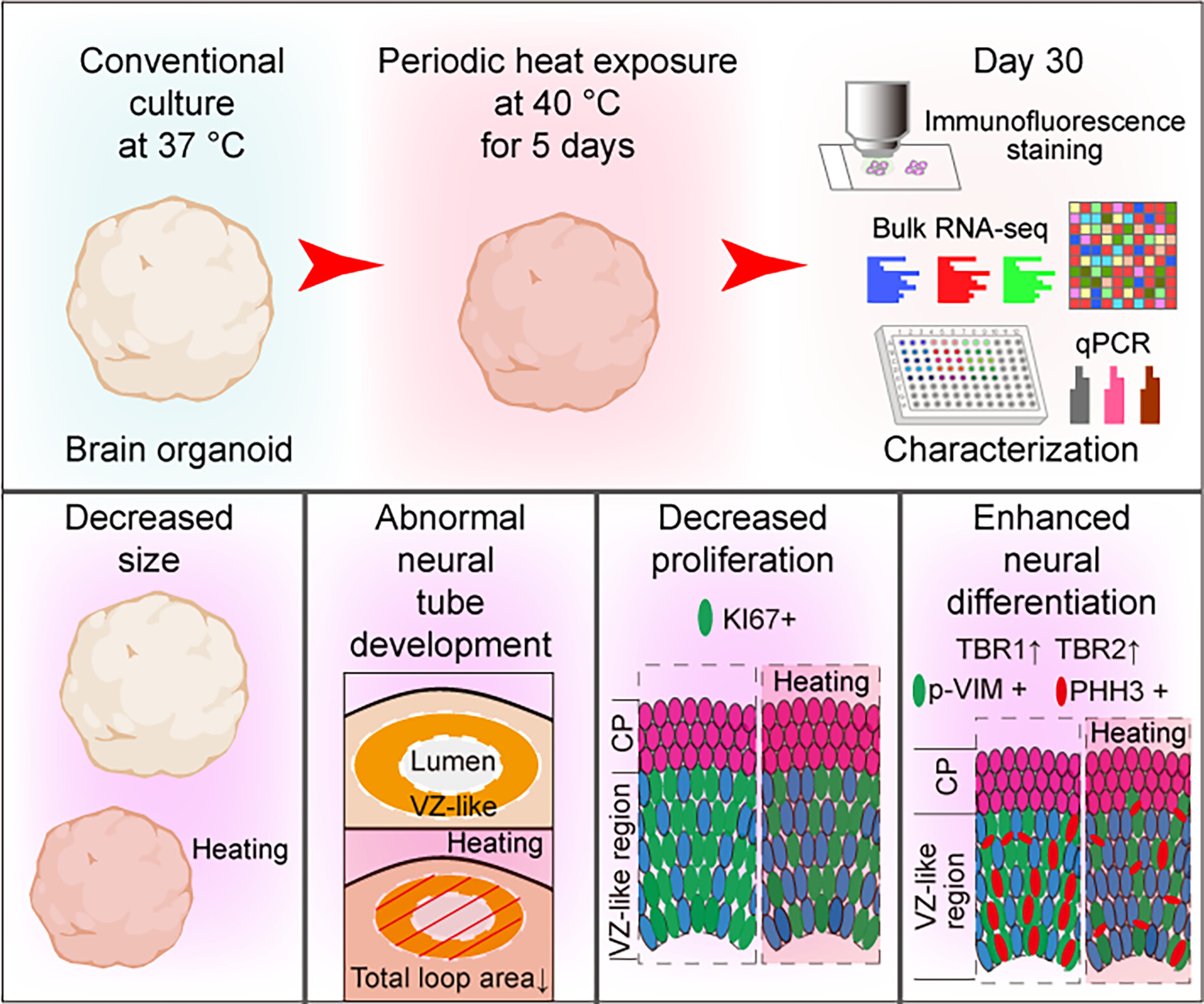
Human Brain Organoids Model Abnormal Prenatal Neural Development Induced by Thermal Stimulation
- First Published: 12 December 2024