Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
FEATURED COVER
Featured Cover
- First Published: 03 November 2023

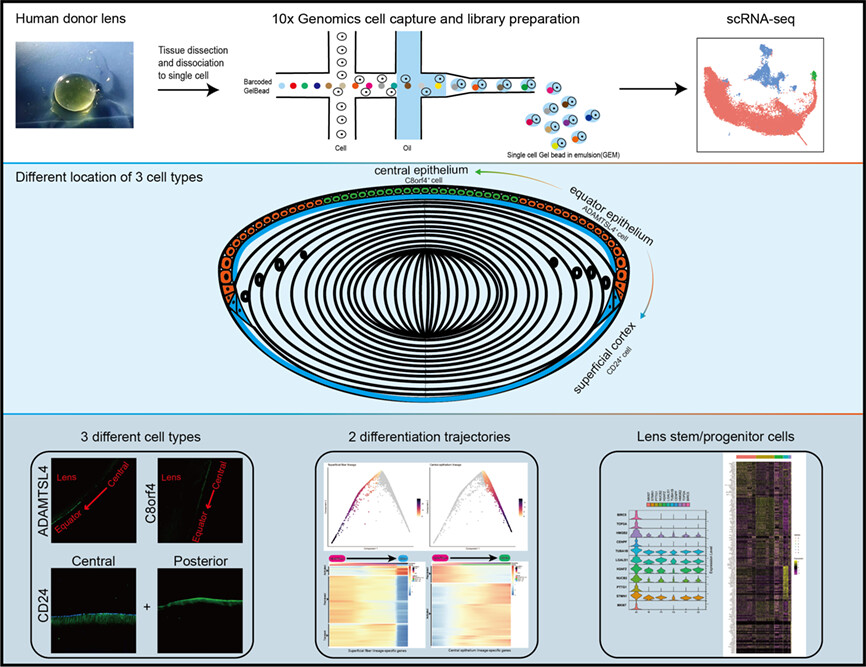
The cover image is based on the Original Article Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals new subtypes of lens superficial tissue in humans by Meng-Chao Zhu et al., https://doi.org/10.1111/cpr.13477.
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEW
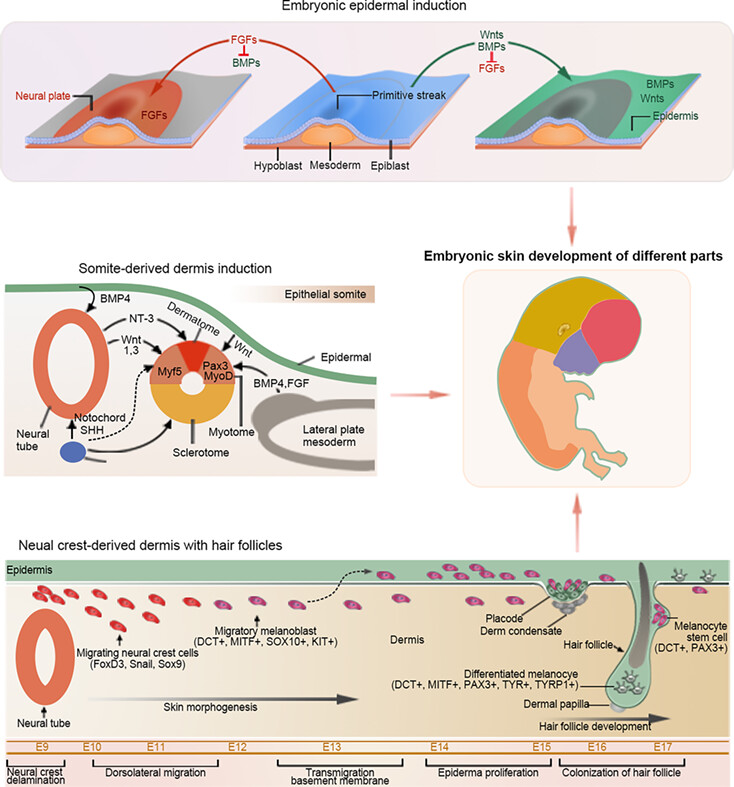
Cooperation of TGF-β and FGF signalling pathways in skin development
- First Published: 07 May 2023
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals new subtypes of lens superficial tissue in humans
- First Published: 14 April 2023
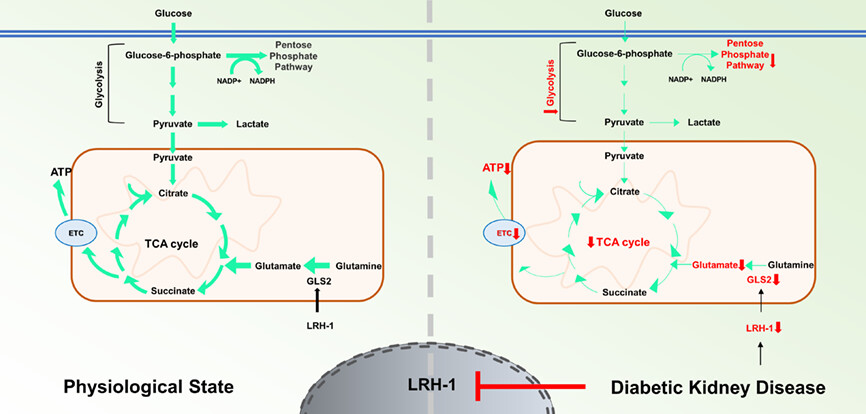
LRH-1 activation alleviates diabetes-induced podocyte injury by promoting GLS2-mediated glutaminolysis
- First Published: 13 April 2023
Derivation of new pluripotent stem cells from human extended pluripotent stem cells with formative features and trophectoderm potential
- First Published: 13 April 2023
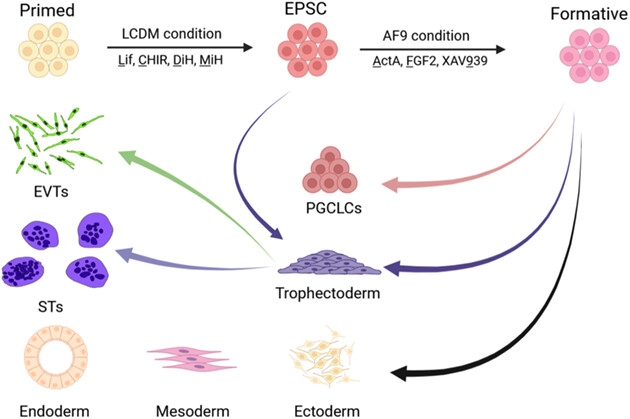
We transformed primed-derived hEPSCs into a new type of pluripotent stem cell AF9-hPSC with similar transcriptomic properties to human E8-E9 epiblasts by the addition of Activin A, bFGF and XAV939, which related to early human embryogenesis. AF9-hPSCs possessed differentiation capacity towards three germ layer lineages and primordial germ cells-like cells in vitro. In addition, AF9-hPSCs allowed trophectoderm lineage induction.
The role of Espin in the stereocilia regeneration and protection in Atoh1-overexpressed cochlear epithelium
- First Published: 21 April 2023
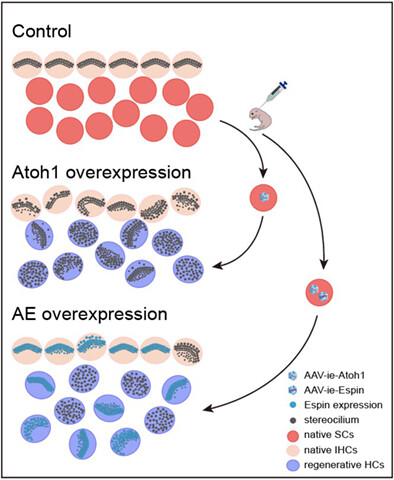
Persistent Atoh1 overexpression results in impaired stereocilia in both endogenous and regenerative hair cells (HCs). The enhanced expression of Espin optimizes the developmental process of stereocilia in Atoh1-induced HCs. The upregulation of Espin attenuates the damage to stereocilia caused by Atoh1 overexpression.
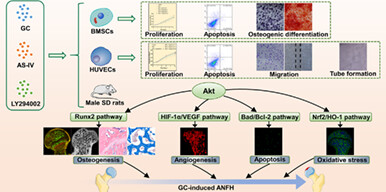
Effects of astragaloside IV on glucocorticoid-induced avascular necrosis of the femoral head via regulating Akt-related pathways
- First Published: 26 April 2023
Generation of Rh D-negative blood using CRISPR/Cas9
- First Published: 25 April 2023
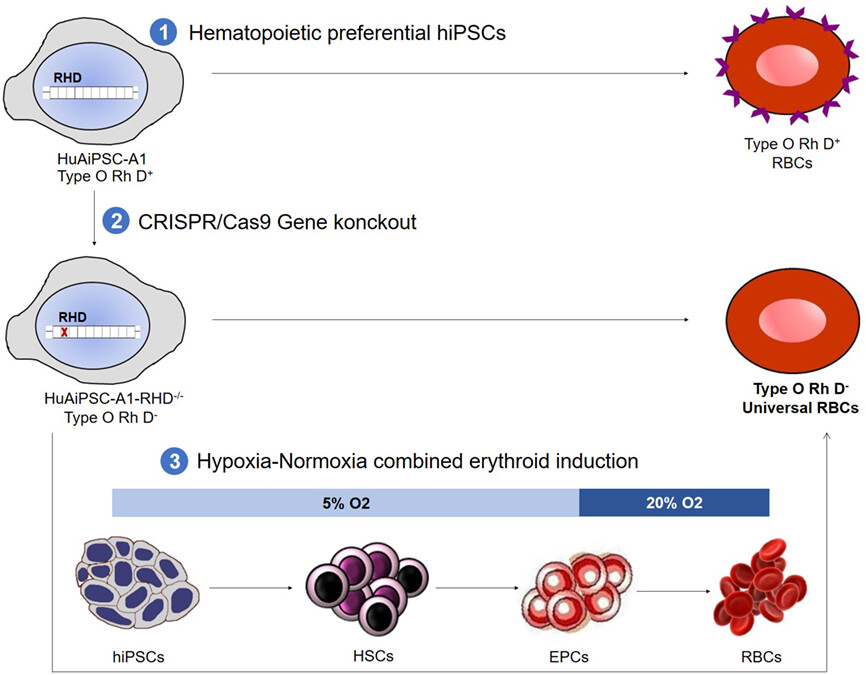
To generate O-type Rh D-negative universal RBCs, an hiPSC line, HuAiPSC, which was derived from human umbilical arterial endothelial cells and showed haematopoietic development preference, was genetic modified to knockout RHD gene with CRISPR/Cas9. The modified seed cells, HuAiPSC-A1-RHD−/− cells were induced towards erythroid cells with optimized protocol, which combined hypoxia and normoxia conditions for better erythrocyte outcome. Consequently, O-type Rh D-negative universal RBCs were efficiently generated, holding great potential in clinic applications.
Generation of stable integration-free pig induced pluripotent stem cells under chemically defined culture condition
- First Published: 15 May 2023
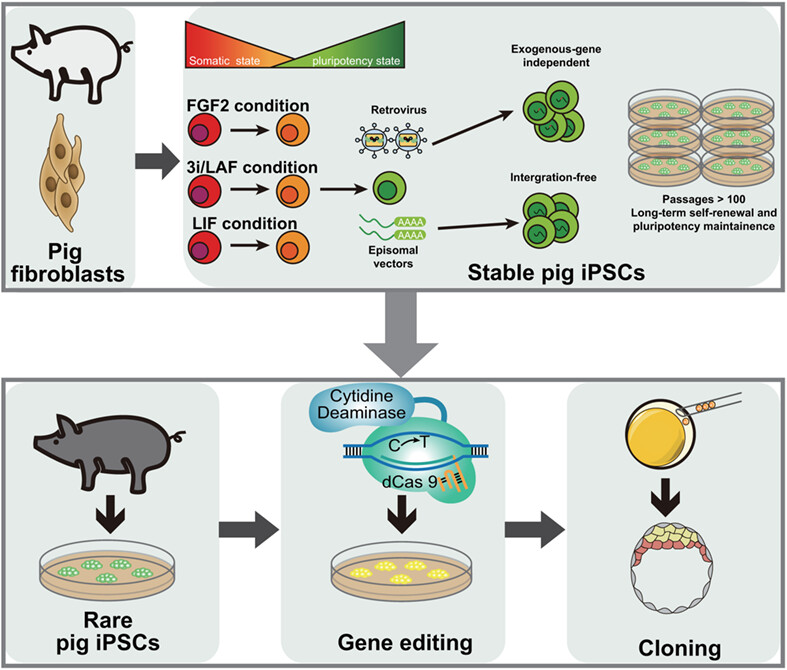
An overview of model presented by this study. Pig induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) reprogrammed using retrovirus or episomal vectors under the 3i/LAF culture medium could maintain long-term self-renewal and pluripotency without exogenous genes. Using episomal reprogramming system, rare pig integration-free iPSCs could be generated, which could be gene-edited and served as donor cells for cloning.
Suppression of the gut microbiota–bile acid–FGF19 axis in patients with atrial fibrillation
- First Published: 26 April 2023
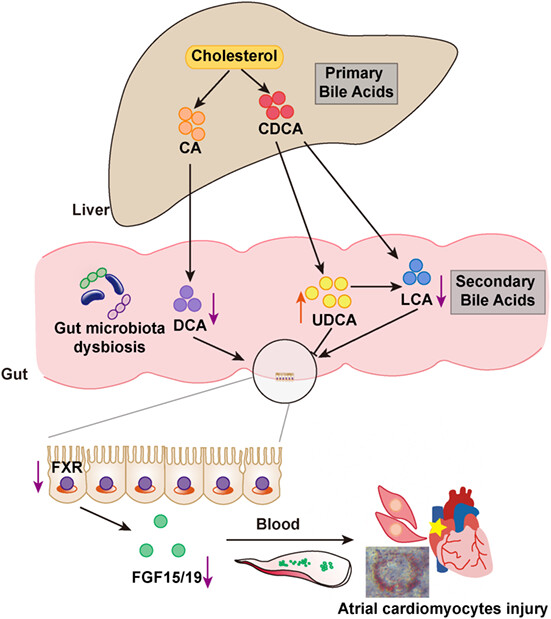
In the current study, the BA synthesis-related microbial signatures based on metagenome, the composition of the intestinal BAs pools based on metabolome, and the circulating FGF 19 level via ELISA were detected to characterize the profile of GM–BAs–FGF19 axis in patients with AF. Subsequently, the protective effect of FGF19 on palmitic acid-stimulated HL-1 cells in vitro was explored by evaluating the levels of lipid droplet accumulation, phosphorylated Yes-associated protein (YAP) and Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinases II (CaMKII) and secretion of interleukin-1 β (IL-1β) was revealed.
Lin−PU.1dimGATA-1− defines haematopoietic stem cells with long-term multilineage reconstitution activity
- First Published: 05 May 2023
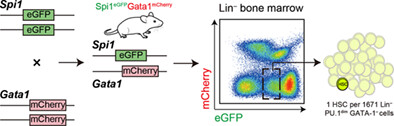
Haematopoietic stem cells (HSC) population in mouse bone marrow can be defined by the distinct expression levels of Spi1 and Gata1. By using a double fluorescence knock-in mouse model, PGdKI, in which the expression levels of PU.1 and GATA-1 are indicated by the expression of GFP and mCherry respectively, we uncover that the HSCs with lymphoid and myeloid repopulating activity are specifically enriched in a Lin−PU.1dimGATA-1− (LPG) cell subset. In vivo competitive repopulation assays demonstrate that bone marrow cells gated by LPG exhibit haematopoietic reconstitution activity which is comparable to that of classical Lin−Sca1+c-kit+ (LSK). The integrated analysis of single-cell RNA sequence data from LPG and LSK gated cells reveals that a transcriptional network governed by core TFs contributes to regulation of HSC multipotency.
Expression and correlation of the Pi3k/Akt pathway and VEGF in oral submucous fibrosis
- First Published: 08 May 2023
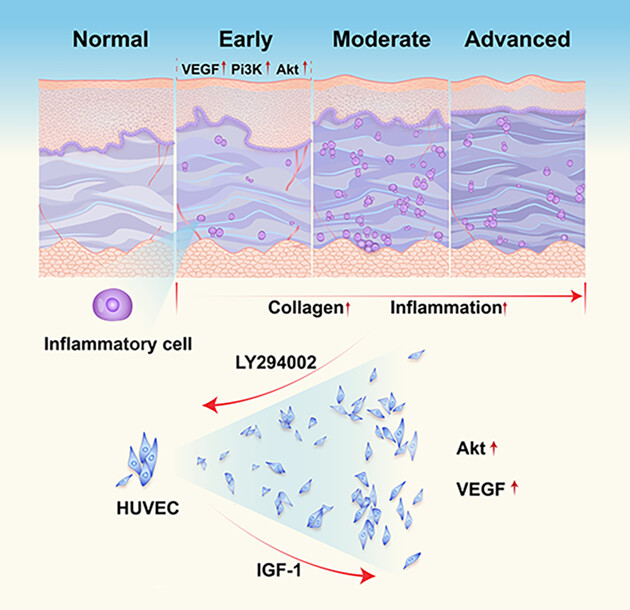
With the process of oral submucous fibrosis, the expression level of Collagen increased with rising inflammatory response. In vitro experiments also demonstrate that IGF-1, the activator of Pi3k/Akt pathway promoted proliferation and migration of huvecs while LY294004, the inhibitor, exhibited the opposite function.
Subvacuum environment-enhanced cell migration promotes wound healing without increasing hypertrophic scars caused by excessive cell proliferation
- First Published: 01 May 2023
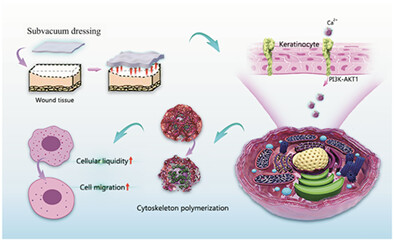
A subvacuum dressing can create a subvacuum environment in the area of the wound, and then calcium influx due to the opening of the mechanical calcium channel. Calcium influx leads to cytoskeleton depolymerisation through AKT1/PI3K signalling pathway. After cytoskeleton disaggregation, cells have stronger migration ability, thus promoting wound healing.