Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEWS
Advances in single-cell sequencing and its application to musculoskeletal system research
- First Published: 09 December 2021
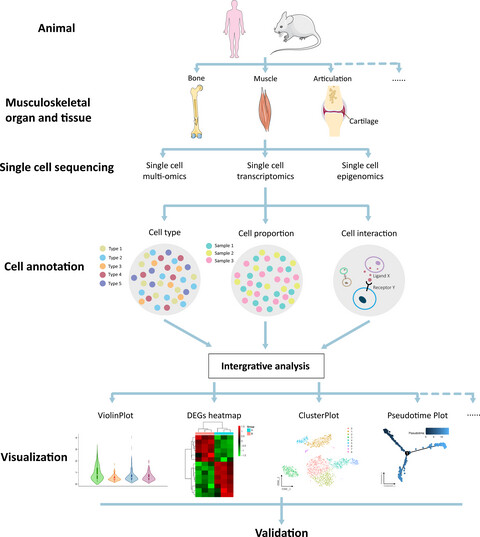
Single cell sequencing (SCS) technologies have superior abilities to analyze cell heterogeneity at a single-cell level, which have elevated omics research to a higher level. Meanwhile, the applications of SCS have enabled many valuable discoveries, and musculoskeletal system offers typical examples. Single cell sequencing of bone, muscle, articulation and cartilage produces a great deal of valuable data. Through integration analysis and visualization, the musculoskeletal system heterogeneity is revealed, which provide new clues for regeneration and disease treatment.
Research progress on the hedgehog signalling pathway in regulating bone formation and homeostasis
- First Published: 16 December 2021
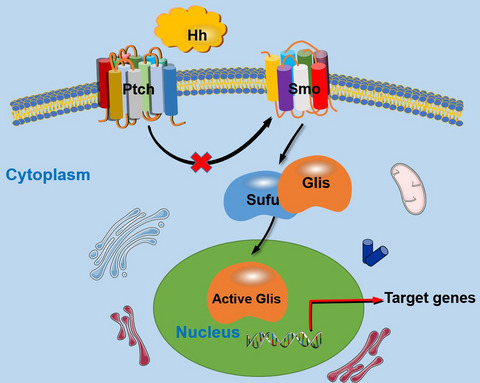
A simplified display of the Hh signalling pathway. In the presence of the Hh protein, the combination of Hh and Ptch abolishes the suppressive effects on Smo delivered by Ptch; then, Hh signalling is activated and the Hh signals are transducted into cells. After that, transcription factors Glis family are dissociated from a suppressive complex containing Sufu and further activated. Subsequently, the Hh signalling downstream target genes that contribute to certain cellular activities are modulated.
Lipid raft involvement in signal transduction in cancer cell survival, cell death and metastasis
- First Published: 22 December 2021
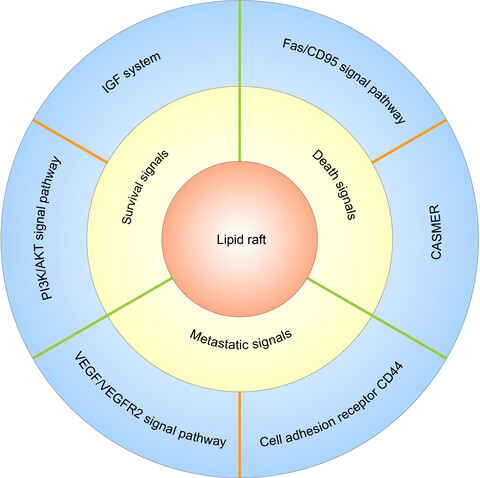
In this review, we focus on the importance of lipid rafts in cancer survival, death and metastasis by describing representative signalling pathways, including the IGF system and the PI3K/AKT, Fas/CD95, VEGF/VEGFR2 and CD44 signalling pathways, and we also discuss the concept of CASMER on the basis of predecessors study. Then, we summarize relevant research progress and suggest that lipid rafts play important roles in the survival, death and metastasis of cancer cells, making them promising targets for cancer therapy.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
YTHDF1 promotes mRNA degradation via YTHDF1-AGO2 interaction and phase separation
- First Published: 25 November 2021
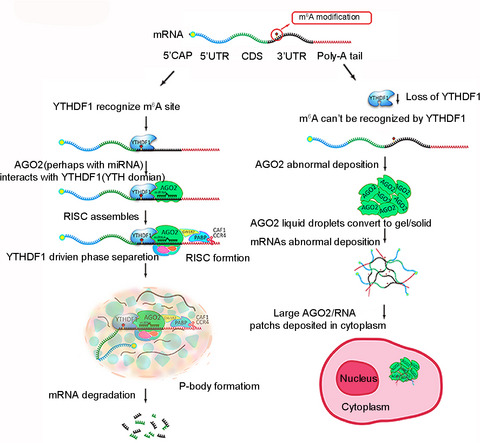
Working model: YTHDF1 interacts with AGO2 (AGO2 perhaps along with miRNA) through YTH domain, then undergoes LLPS to aggregate more components of miRISCs, and leading to P-body formation for mRNA degradation. Deficiency of YTHDF1 disrupts the interaction between YTHDF1 and AGO2, leads to the conversion of AGO2 liquid droplets to gels/solids and substantially increases the mRNA stability.
Sorafenib attenuates liver fibrosis by triggering hepatic stellate cell ferroptosis via HIF-1α/SLC7A11 pathway
- First Published: 22 November 2021
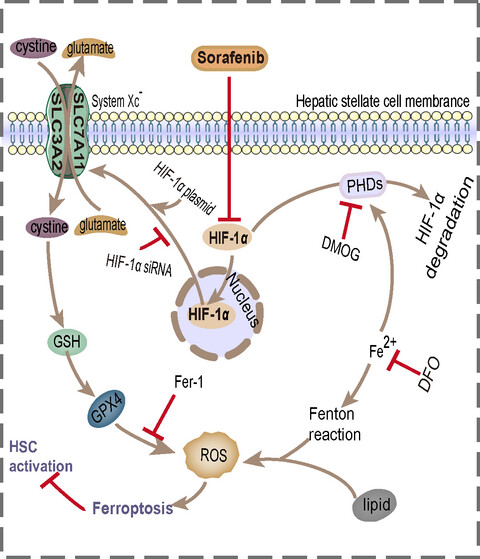
Sorafenib triggers hepatic stellate cell ferroptosis by inhibiting the HIF-1α/SLC7A11 pathway to attenuate liver fibrosis. Treatment with sorafenib induces a decrease of HIF-1α, which in turn reduces SLC7A11 expression in HSCs. Then leads to GPX4, GSH depletion and ROS excess, and ultimately induces HSC ferroptosis and ECM reduction.
Comprehensive analysis of human chorionic membrane extracts regulating mesenchymal stem cells during osteogenesis
- First Published: 28 November 2021

Go et al. report the therapeutic effects of human chorionic membrane extract during bone regeneration and its mechanism studies via in vitro/in vivo osteogenesis model and multi-omics approaches. Their findings provide new insight into natural biomaterial and indicate the feasibility of placental tissue application for bone healing in regenerative medicine.
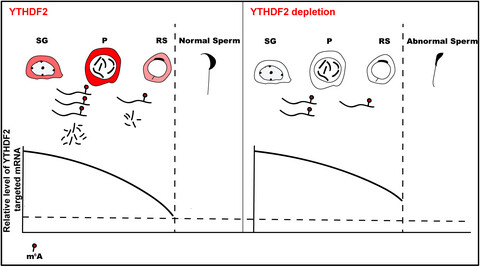
m6A reader protein YTHDF2 regulates spermatogenesis by timely clearance of phase-specific transcripts
- First Published: 30 November 2021
Glycomics reveal that ST6GAL1-mediated sialylation regulates uterine lumen closure during implantation
- First Published: 27 December 2021

Effect of α2,6-sialylation mediated by ST6GAL1 on regulation of pig endometrial folds extending during implantation. The ST6GAL1 mediated α2,6-sialylation of cell adhesion molecular, such as E-cadherin, alters the stability of the cell-cell adherens junction, participates in activation of Rac1/WAVE1 signal pathway to regulate the collective migration of uterine LE and leads to the extending of endometrial folds during implantation.
Understanding of mouse and human bladder at single-cell resolution: integrated analysis of trajectory and cell-cell interactive networks based on multiple scRNA-seq datasets
- First Published: 23 December 2021
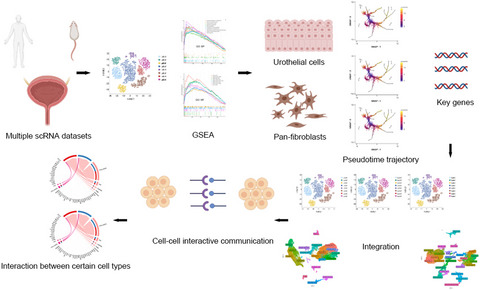
Multiple scRNA-seq datasets of normal mouse and human bladder were collected. Through standard workflow of Seurat R package, we identified cell clusters in bladder tissue. After initial exploration of differentially expressed gene and gene set enrichment analysis, we performed trajectory analysis for pan-fibroblasts and urothelial cells and identified common pseudotime genes across datasets and species. Then, we integrated multiple datasets to create, to date, the largest cell map of mouse and human bladder, respectively. We further explored the details of signaling pathways between certain cell types and the communication networks of specific pathways.
Substrate stiffness regulates the differentiation profile and functions of osteoclasts via cytoskeletal arrangement
- First Published: 24 December 2021
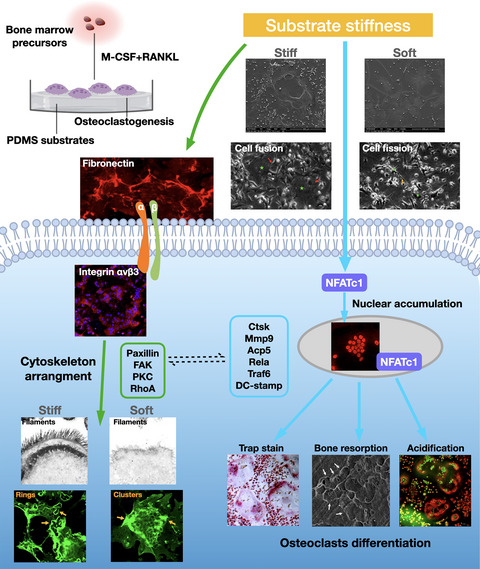
We fabricated a mechanical model of PDMS substrates that mimic physiologically mechanical properties of extracellular microenvironment, with varied stiffness for cell culture. Osteoclasts respond to stiffness variations in cell morphology, fusion/fission activity, osteoclast differentiation profile (Nfatc1, Acp5, Ctsk, Camk2a, Mmp9, Rela, Traf6, and DC-stamp) and resorption functions. The potential regulatory mechanism with the involvement of cytoskeletons adhesion molecules: cytoskeletons adhesion molecules, including fibronectin-integrin αvβ3 activation and following biochemical signaling cascades of paxillin, FAK, PKC, and RhoA were altered in response to stiffness signals. Bioinformatics proposed strong connection between cytoskeleton adhesion and osteoclast differentiation.
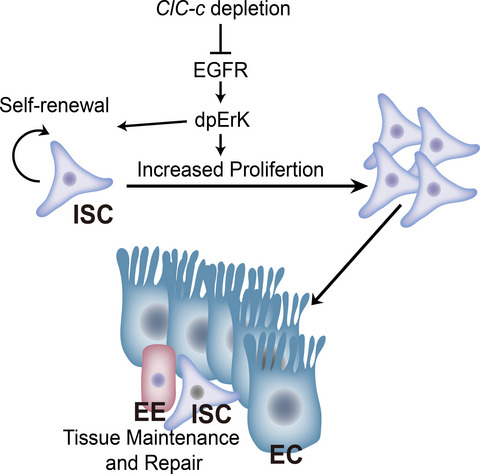
ClC-c regulates the proliferation of intestinal stem cells via the EGFR signalling pathway in Drosophila
- First Published: 24 December 2021
LncRNA-AK137033 inhibits the osteogenic potential of adipose-derived stem cells in diabetic osteoporosis by regulating Wnt signaling pathway via DNA methylation
- First Published: 24 December 2021
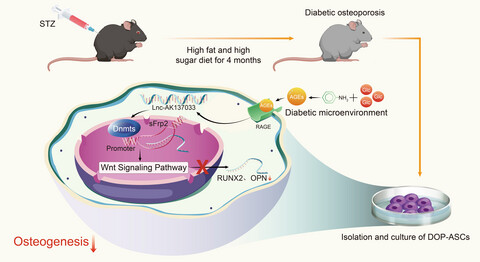
In this work, the diabetic osteoporosis (DOP) animal model was successfully constructed. DOP-ASCs were successfully isolated and cultured from DOP mice. In vitro and in vivo studies have demonstrated that LncRNA-AK137033 regulates the osteogenic potential of DOP-ASCs by modulating the Wnt signaling pathway via DNA methylation in the sFrp2 promoter region.
LETTER TO THE EDITOR
Enhancing targeted transgene knock-in by donor recruitment
- First Published: 02 December 2021