Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
FEATURED COVER
Featured Cover
- First Published: 01 June 2021
The cover image is based on the Original Article An adiponectin receptor agonist promote osteogenesis via regulating bone-fat balance by Hanghang Liu et al., https://doi.org/10.1111/cpr.13035.
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEW
The complex roles of neutrophils in APAP-induced liver injury
- First Published: 04 May 2021
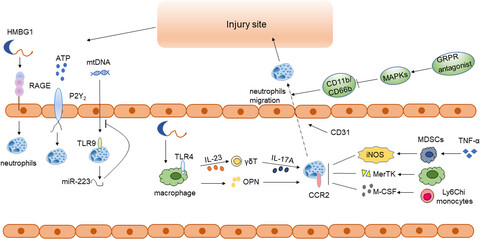
A lot of factors deeply influence the neutrophil's activation, recruitment and migration in APAP-induced liver injury. DAMPs like HMGB1 and ATP are released from damaged hepatocytes, recognized by RAGE, P2Y2 receptors, respectively, inducing the activation and recruitment of neutrophils. But the TLR9 expressed on neutrophils recognize mtDNA and then neutrophils could release miR-223, which inhibits the neutrophil's activation and recruitment. As for other immune cells, they are divided into cells that promote and inhibit the activation and recruitment of neutrophils. Firstly, macrophages express OPN after APAP treatment and then attract neutrophils. Moreover, HMGB1 could recognize TLR4 receptor expressed on macrophages, release IL-23 to induce the release of IL-17A in γδ T cells and finally activate and recruit neutrophils. However, Ly6Chi monocytes inhibit the activation and recruitment of neutrophils via CCR2 and M-CSF pathways. Macrophages could also generate MerTK to inhibit neutrophils. Furthermore, TNF-α/LPS MDSCs could express iNOS to decrease the intrahepatic neutrophils infiltration and induce the apoptosis of activated neutrophil. Activated and recruited neutrophils then migrate to the site of injury to alleviate the inflammation and induce tissue repair. GRPR antagonist could downregulate the expression of CD11b/CD66b via activating MAPKs pathways, which significantly influence the migration of neutrophils to the injury site.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
PTH-induced EndMT via miR-29a-5p/GSAP/Notch1 pathway contributed to valvular calcification in rats with CKD
- First Published: 04 May 2021
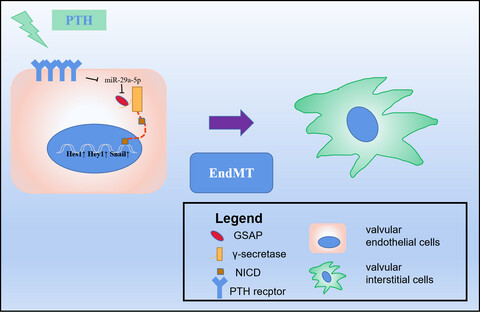
A model depicting how miR-29a-5p regulating VECs EndMT. PTH could trigger a decrease in miR-29a through PTHR1 of VECs, leading to an increase in GSAP at the protein level. GSAP further activated γ-secretase to increase the level of NICD in the cytoplasm, which promoted the increase of HES1 and Snail expression in the nucleus to mediate the activation of Notch1 signal and endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EndMT) which cause VECs transferring to valvular interstitial cells (VICs).
The basic route of nuclear-targeted transport of IGF-1/IGF-1R and potential biological functions in intestinal epithelial cells
- First Published: 01 May 2021
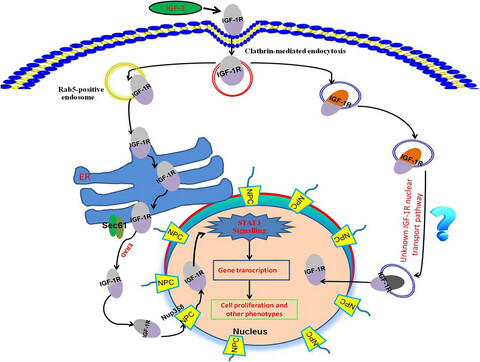
Traditional research believes that IGF-1 only trigger the intracellular signaling on the cell surface. However, in the current research, in intestinal cells, IGF-1R can enter into the nucleus from the cell membrane. Therefore, we first revealed the molecular mechanism of IGF-1R entering into the cell nuclei. On this basis, further studies have revealed that nuclear-localized IGF-1R can Regulate cell proliferation.
An adiponectin receptor agonist promote osteogenesis via regulating bone-fat balance
- First Published: 03 May 2021
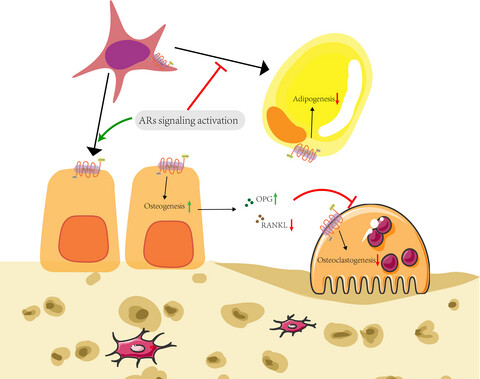
Adiponectin receptors 1 and 2 are expressed early in mesenchymal stem cells lineage and in precursors including pre-osteoblast, pre-osteoclasts and chondrocytes. Using an adiponectin receptor agonist AdipoRon, our study demonstrated a pro-osteogenic, anti-adipogenic and anti-osteoclastogenic effect of adiponectin receptor activation in young mice, which suggested adiponectin receptor signalling was involved in bone regeneration and bone-fat balance regulation.
Oral intake of Lactobacillus plantarum L-14 extract alleviates TLR2- and AMPK-mediated obesity-associated disorders in high-fat-diet-induced obese C57BL/6J mice
- First Published: 08 April 2021
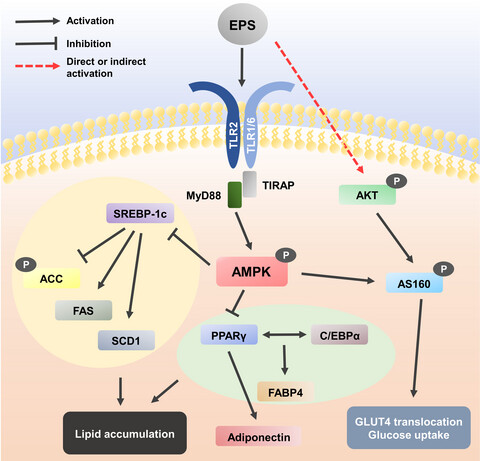
EPS regulates lipid accumulation and glucose uptake via TLR2 and AMPK signalling pathway. When EPS binds to TLR2 in the cell membrane, MyD88, a downstream adaptor protein of TLR, initiating AMPK signalling cascades. The phosphorylated AMPKα inactivates SREBP-1c, ACC, FAS and SCD1 by phosphorylation. In addition, the activated AMPKα inhibits the expression of core adipogenesis markers including PPARγ, C/EBPα and FABP4. The reduced PPARγ expression decreases the expression of adiponectin. These changes eventually reduce lipid accumulation in adipocytes. Also, EPS induces phosphorylation of AKT through a direct or indirect pathway and the activated AKT and AMPKα phosphorylates AS160. The activated AS160 can allow GLUT4 translocation to plasma membrane and subsequently enhance glucose uptake.
Therapeutic effects of CXCR4+ subpopulation of transgene-free induced cardiosphere-derived cells on experimental myocardial infarction
- First Published: 04 May 2021
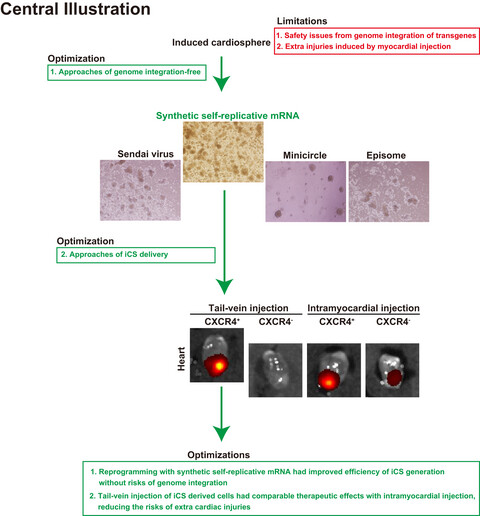
Previously, we and others have successfully reprogrammed mouse fibroblast cells into cardiac progenitor-like cells. However, several issues should be further addressed, including the reprogramming strategy and delivery approach for myocardial infarction (MI) treatment. In the current study, we screened several transgene-free approaches for somatic reprogramming. Our data showed the self-replicative RNA approach produced more iCS, which had cardiomyocyte differentiation ability and therapeutic effects on the mouse model of MI with comparable levels with endogenous cardiospheres and iCS generated with retrovirus. Then, the CXCR4+ (C-X-C chemokine receptor 4) subpopulation of iCS derived cells (iCSDC) delivered by intravenous injection was found to have similar therapeutic effects with intramyocardial injection on the mouse model of MI, representing a more safer delivery approach. Thus, the optimized strategy for iCS generation is much safer and has more therapeutic potentials.
Maternal sevoflurane exposure induces temporary defects in interkinetic nuclear migration of radial glial progenitors in the fetal cerebral cortex through the Notch signalling pathway
- First Published: 06 May 2021
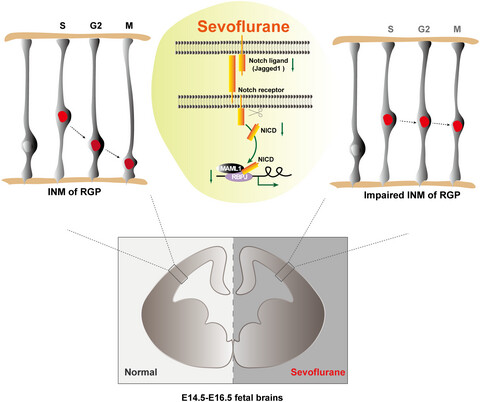
Maternal sevoflurane exposure during the neurogenic period temporarily induced abnormal INM of RGPs by targeting the Notch signalling pathway without inducing long-term effects on RGP progeny cell fate or offspring cognitive behaviors. More importantly, the defects of INM in hESC-derived cerebral organoids provide a novel insight into the effects of general anesthesia on human brain development.
SETD2 epidermal deficiency promotes cutaneous wound healing via activation of AKT/mTOR Signalling
- First Published: 05 May 2021
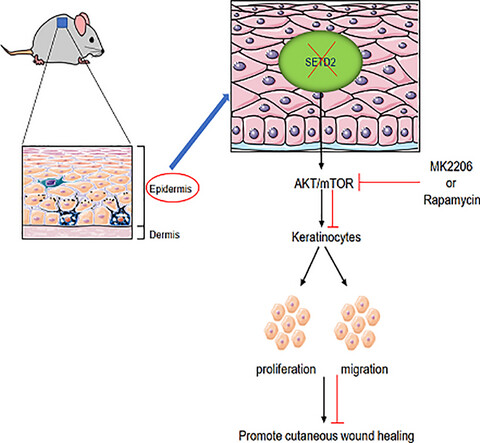
The epidermis-specific Setd2-deficient mice showed accelerated re-epithelialization during cutaneous wound healing by promoting keratinocytes proliferation and migration. Mechanistically, deletion of Setd2 resulted in the activation the AKT/mTOR signalling pathway and pharmacological inhibitions of AKT and mTOR with MK2206 and rapamycin delayed wound closure, respectively.
Intrapulmonary distal airway stem cell transplantation repairs lung injury in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- First Published: 07 May 2021
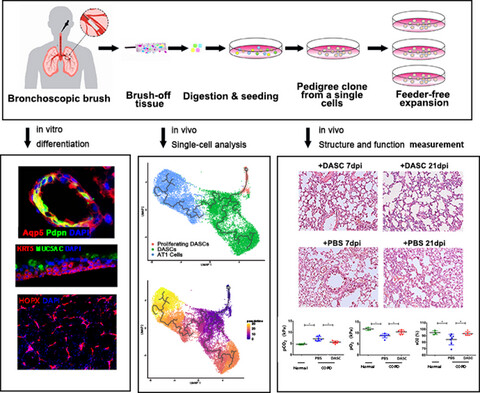
Mouse and human DASCs could be indefinitely expanded and were able to further differentiated into mature alveolar structures during in vitro cultures. Single-cell analysis indicated that the engrafted cells expressed typical cellular markers of type I alveolar cells as well as the specific secreted proteins. Transplantation of human DASCs derived from chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) patients into the lungs of NOD-SCID mice with COPD repaired the tissue damage and improved the pulmonary function.
CircSLC7A2 protects against osteoarthritis through inhibition of the miR-4498/TIMP3 axis
- First Published: 07 May 2021
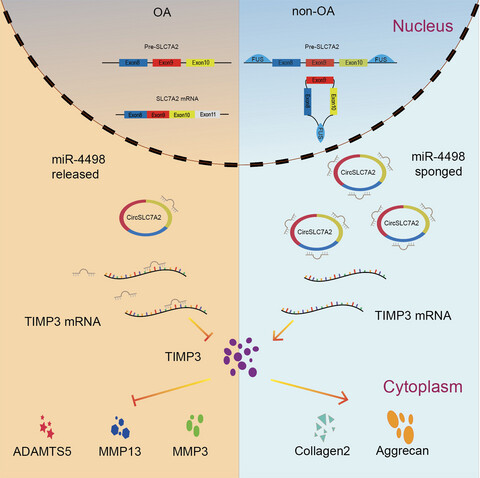
The expression of the novel circular RNA, circSLC7A2, is important for maintaining ECM homeostasis and protecting cartilage against OA progression. CircSLC7A2 is regulated by FUS and functions through miR-4498/TIMP3 axis, which is effective and comprehensive in alleviating inflammation, inhibiting catabolic enzymes, introducing anabolic enzymes and preventing cell apoptosis that resulted in maintaining cartilage ECM, thus preventing or delaying OA progression.
ERK/Drp1-dependent mitochondrial fission contributes to HMGB1-induced autophagy in pulmonary arterial hypertension
- First Published: 04 May 2021
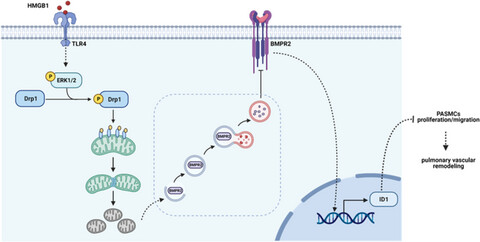
The molecular mechanisms underlying HMGB1-induced pulmonary vascular remodelling in PAH. HMGB1 increases Drp1 phosphorylation and Drp1-dependent mitochondrial fission through activation of ERK1/2 signaling pathway, and subsequently stimulates autophagy activation, which further lead to BMPR2 lysosomal degradation and Id1 downregulation, and ultimately promotes PASMCs proliferation/migration and pulmonary vascular remodeling in PAH.
Retinoic acid induces NELFA-mediated 2C-like state of mouse embryonic stem cells associates with epigenetic modifications and metabolic processes in chemically defined media
- First Published: 07 May 2021
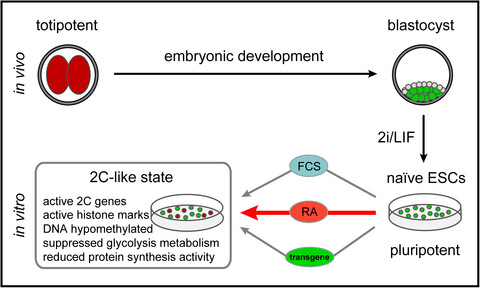
2C-like cells arise spontaneously in ESCs upon serum and leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) containing culture medium and 2C-like cells refers to totipotent. Yet, the establishment of totipotency is poorly understood. Intriguingly, naïve ESCs culture medium fail to induce 2C-like state of ESCs. In this study, we report a robust in vitro induction system, based on retinoic acid (RA) containing chemically defined media, which can efficiently increase 2C-like cells population in culture without any genetic modification and serum. As ever more mechanisms of totipotent cells are unraveled, data of this study will provide new impulses for stem cell research.
Transplantation of tauroursodeoxycholic acid–inducing M2-phenotype macrophages promotes an anti-neuroinflammatory effect and functional recovery after spinal cord injury in rats
- First Published: 07 May 2021
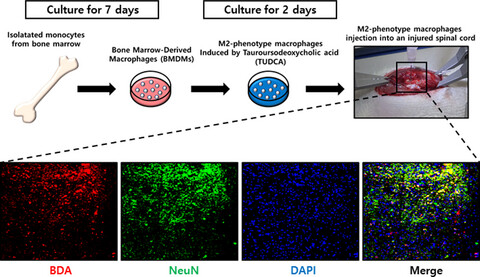
Bone marrow–derived monocytes were differentiated into M2-phenotype (M2) macrophages using tauroursodeoxycholic acid (TUDCA). TUDCA-induced M2 macrophages were directly transplanted to a lesion in an injured spinal cord. The pro-inflammatory cytokine levels were significantly decreased in the TUDCA-induced M2 group. We suggest that the transplantation of TUDCA-induced M2 macrophages represents a possible alternative cell therapy for SCI.
Carbon monoxide alleviates senescence in diabetic nephropathy by improving autophagy
- First Published: 07 May 2021
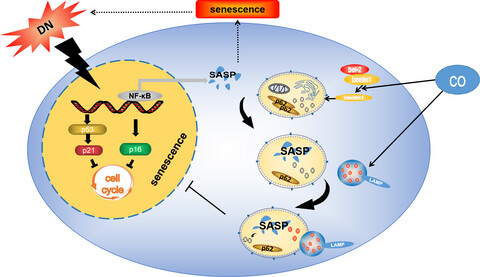
In diabetic nephropathy, senescent cells were accumulated, which may accelerate disease progression through senescence-related secretory phenotype (SASP). Carbon monoxide activated autophagy by dissociating Beclin-1-Bcl-2 complexe, and restore lysosomal function to improve autophagy flow, enabling autophagosomes to encapsulate some SASP and deliver it to lysosome for degradation. Thus, the reversion of SASP from secretion to degradation prevented senescence and subsequently improved DN.
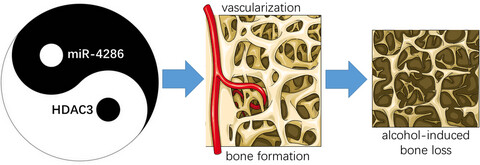
miR-4286 functions in osteogenesis and angiogenesis via targeting histone deacetylase 3 and alleviates alcohol-induced bone loss in mice
- First Published: 10 May 2021
Activated mesangial cells induce glomerular endothelial cells proliferation in rat anti-Thy-1 nephritis through VEGFA/VEGFR2 and Angpt2/Tie2 pathway
- First Published: 13 May 2021
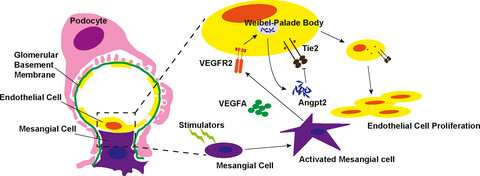
The underlying mechanism of glomerular ECs proliferation. Normally, Angpt2 was stored in the Weibel-Palade bodies in ECs. When MCs were stimulated, they produced VEGFA which acted on the ECs surface receptor VEGFR2 to promote Angpt2 expression. Angpt2 acted on Tie2 through autocrine which inhibited Tie2 phosphorylation and caused ECs proliferation. ECs, endothelial cells. MCs, mesangial cells. VEGFA, vascular endothelial growth factor A. VEGFR2, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor2. Angpt2, angiopoietin2. Tie2, TEK tyrosine kinase.