Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEWS
Essential functions of miR-125b in cancer
- First Published: 17 December 2020
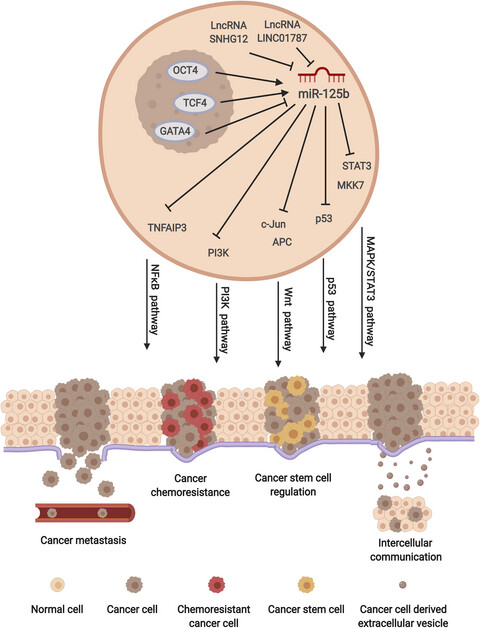
miR-125b is an important microRNA in cancer. It is deregulated in different types of cancer where it acts as an oncogene and/or a tumour suppressor in a context-dependent manner. miR-125b interacts with multiple upstream regulators and downstream targets, which are involved in a variety of signalling pathways and cellular processes during tumourigenesis and cancer progression. It also exerts as a key regulator with regards to the response of cancer cells to chemotherapy. miR-125b holds a great potential in clinical cancer diagnosis, prognosis and therapies. Created with BioRender.com.
Activation of nuclear factor-κB in the angiogenesis of glioma: Insights into the associated molecular mechanisms and targeted therapies
- First Published: 10 December 2020

Growing evidence suggests that there is a correlation between the activation of nuclear factor (NF)-κB and the angiogenesis of glioma. Herein, we sought to discuss the current understanding of the molecular mechanisms of NF-κB in diverse glioma microenvironments such as hypoxia, inflammation, and oxidative stress, and its function as a therapeutic target for antiangiogenic strategies aimed at glioma.
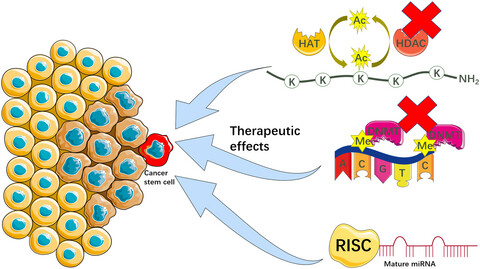
Beyond regulations at DNA levels: A review of epigenetic therapeutics targeting cancer stem cells
- First Published: 13 December 2020
The long non-coding RNA landscape in triple-negative breast cancer
- First Published: 13 December 2020
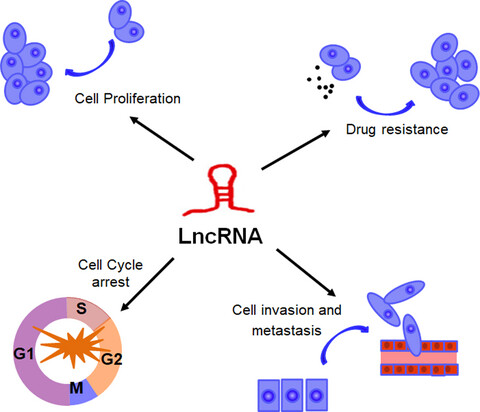
In current review, we accumulated literature to the understanding of lncRNAs biogenesis and function, as well as the latest findings of novel lncRNAs-based therapeutics in TNBC. We also present the current state of knowledge concerning the expression and regulation of lncRNAs in TNBC, and discuss the future development of lncRNA-based strategies for clinical TNBC patients.
Super enhancers—Functional cores under the 3D genome
- First Published: 17 December 2020
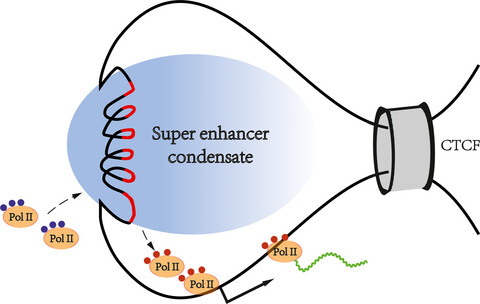
As a regulatory element on the genome, the formation of super enhancers depends on specific chromatin states and spatial structures. A large number of regulatory molecules gather in the chromatin regions where the super enhancers are located. The molecules in these regions are very dense, forming huge transcriptional activation complexes, which interact with each other to construct phase-separated condensates. Super enhancer-mediated transcriptional activation depends on spatial proximity rather than a rigid bridge. There are molecular exchanges between the super enhancer-associated condensate and the surroundings. Inactive Pol II is recruited and phosphorylated Pol II is excreted. Therefore, we propose a super enhancer-mediated transcription mode to pave the way for future research.
STAT3 and its targeting inhibitors in osteosarcoma
- First Published: 31 December 2020
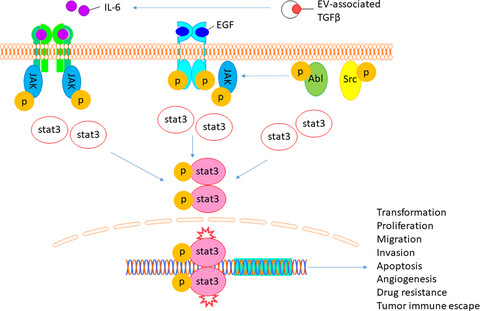
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) is a member of the STAT protein family, vitally important for eukaryotic cells. We review the molecular structure and function of STAT3 and its isoforms, highlighting signalling pathways for the regulation of gene transcription. A critical appraisal of STAT3 in cancers, such as osteosarcoma, is provided emphasizing potential therapeutic approaches targeting STAT3 and its inhibitors
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma–associated IL-33 rewires macrophage polarization towards M2 via activating ornithine decarboxylase
- First Published: 10 December 2020
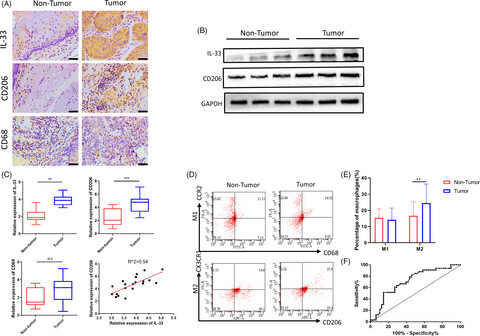
M2 macrophage infiltration and IL-33 production are enhanced with close correlation in ESCC. (A) Representative images of IL-33+ cell, CD206+ cell and CD68+ cell in non-tumour and tumour tissue (scale bar = 50 μm). (B) Western blot analysis of IL-33 and CD206 expression in non-tumour and tumour tissues, and GAPDH was used as a reference control. (C) IL-33, CD206 and CD68 were measured by RT-PCR in non-tumour and tumour tissues; the correlation of CD206 and IL-33 in ESCC tissues; N = 20, R2 = .54, P < .01. (D) M1 (CD68+ CCR2+) and M2 (CD206+ CX3CR1+) populations in peripheral blood from those with ESCC (n = 48) and healthy controls (n = 33), as measured by flow cytometry. The difference in M1/M2 ratio between two groups was analyzed. (E) The population of M2-like monocytes subset in peripheral blood between ESCC patients and healthy controls showed significant difference instead of M1-like monocytes. (F) ROC curve was used to analyse to assess the diagnostic value in ESCC. *P < .05; **P < .01; ***P < .001. Bars indicate mean and SEM of triplicate experiments and show a representative experiment of at least 3 independent experiments performed for each panel.
Higher content of microcystin-leucine-arginine promotes the survival of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma cells via regulating SET resulting in the poorer prognosis of patients
- First Published: 25 November 2020
Kcnh2 mediates FAK/AKT-FOXO3A pathway to attenuate sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction
- First Published: 02 December 2020
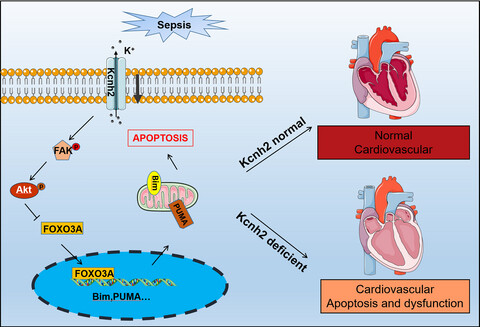
Schematic representation shows the mechanisms of Kcnh2-modulated cardiac dysfunction following sepsis stimulus. Sepsis-induced decrease of Kcnh2 resulted in inhibition of AKT in cardiomyocytes. Attenuation of AKT of cardiomyocytes mediated by Kcnh2 upregulated FOXO3A expression, which initiated the transcription of BIM/PUMA genes. Finally, enhanced BIM/PUMA caused the cardiomyocytes apoptosis, leading to cardiac dysfunction.
20-HETE synthesis inhibition attenuates traumatic brain injury–induced mitochondrial dysfunction and neuronal apoptosis via the SIRT1/PGC-1α pathway: A translational study
- First Published: 13 December 2020
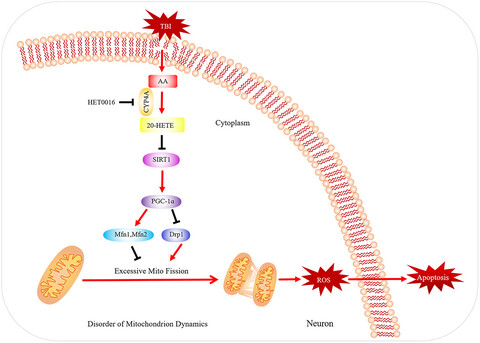
The mechanism on 20-HETE–induced alterations of mitochondrial dynamics in neurons. 20-HETE is synthesized from AA by CYP4A, which is inhibited by HET0016. The alterations of mitochondrial dynamics induced by 20-HETE activate oxidative stress and subsequently result in neuronal apoptosis mediated by inhibition of the Sirt1/PGC-1α signalling pathway.
The epidermal growth factor receptor variant type III mutation frequently found in gliomas induces astrogenesis in human cerebral organoids
- First Published: 06 December 2020
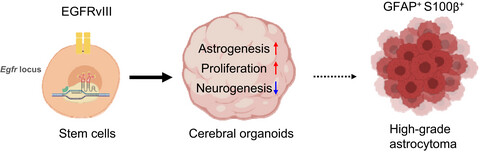
The epidermal growth factor receptor variant type III (EGFRvIII) mutation mostly found in high-grade astrocytoma in the brain, suggesting connection of EGFRvIII to astrogenesis. Using human brain organoids, we demonstrated that EGFRvIII mutation facilitated astrogenesis at the expense of neurogenesis and cell proliferation. In summary, this study shows for the first time the close connection between EGFRvIII mutation and gliogenesis in human system.
Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals heterogeneity and differential expression of decidual tissues during the peripartum period
- First Published: 09 December 2020
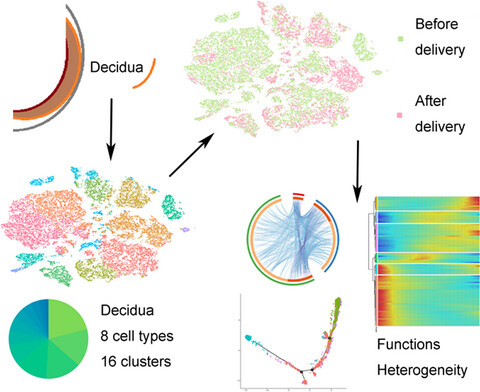
Single-cell RNA sequencing was used to characterize the transcriptomes of decidua before and after delivery. Eight major cell types and sixteen clusters were identified and found to have various functions. The activation of various cell subtypes to different degrees was observed after delivery. These reveal the heterogeneity of peripartum decidual cells at single-cell resolution
Systemic transcriptome comparison between early- And late-onset pre-eclampsia shows distinct pathology and novel biomarkers
- First Published: 17 December 2020
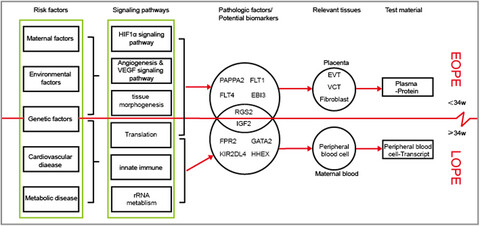
The schematic diagram shows the distinct pathogenesis between early- (EOPE) and late-onset pre-eclampsia (LOPE). The difference between EOPE and LOPE is demonstrated at several layers, such as risk factors, signalling pathways and disease affected/causing tissues. Based on divergence of EOPE and LOPE pathogenesis, specific biomarkers can be identified and used to distinguish both diseases by testing placental secreted proteins or maternal blood cell transcripts.
Effects and mechanisms of basic fibroblast growth factor on the proliferation and regenerative profiles of cryopreserved dental pulp stem cells
- First Published: 17 December 2020
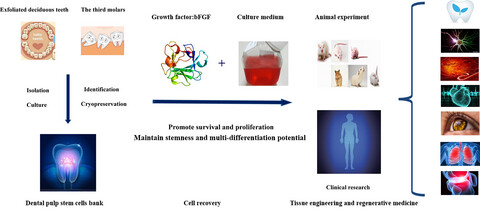
The graphical abstract demonstrated that short-term application of bFGF in the early stage post-thawing could rescue cellular viability without shifting their pluripotency, unexpectedly, this proliferative superiority could prolong to the succeeding passage, so the usage time of bFGF for post-thawed cell culture should be addressed. This study illustrated a safe and feasible cell culture technique to rapidly amplify post-thawed DPSCs with robust regenerative potency, which brightening the future of stem cells banking and tissue engineering.
Ski promotes proliferation and inhibits apoptosis in fibroblasts under high-glucose conditions via the FoxO1 pathway
- First Published: 21 December 2020
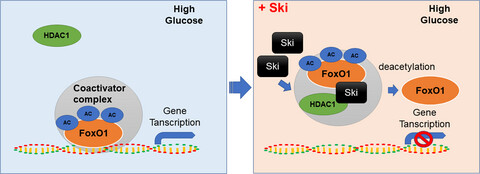
Under HG conditions, FoxO1 acetylation level was increased. As a transcription factor, FoxO1 involved in the induction of a special subset of genes that regulate cellular proliferation or apoptosis, etc Increased Ski protein increased the binding of Ski to FoxO1, which mediated deacetylation through Ski binding with HDAC1 and resulted in a reduction in FoxO1 acetylation level. Therefore, the role of FoxO1 transcription factor was inhibited.
NLRP3 regulates alveolar bone loss in ligature-induced periodontitis by promoting osteoclastic differentiation
- First Published: 31 December 2020
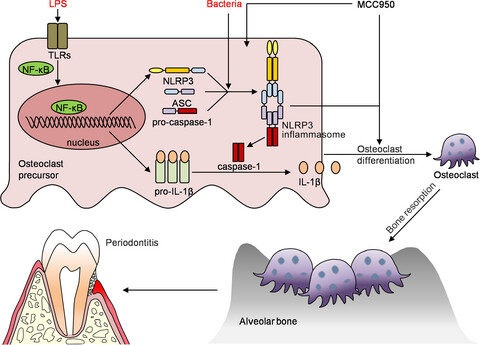
NLRP3 Regulates Alveolar Bone Loss in Ligature-induced Periodontitis by Promoting Osteoclastic Differentiation. Bacterial infection in periodontal tissues leads to the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome in osteoclast precursor cells, which promotes osteoclast differentiation and alveolar bone resorption. Thus, NLRP3 inflammasome contribute significantly to the pathologic bone loss in periodontitis. MCC950, a specific inhibitor of the NLRP3 inflammasome, inhibits osteoclast differentiation, thereby reduces alveolar bone loss in periodontitis.
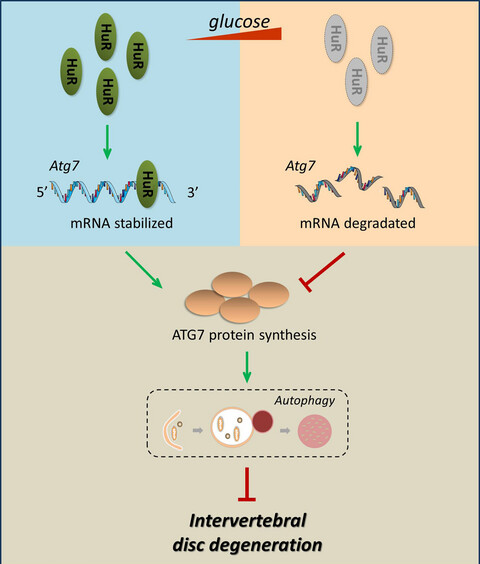
RNA-binding protein HuR suppresses senescence through Atg7 mediated autophagy activation in diabetic intervertebral disc degeneration
- First Published: 28 December 2020
Endometrial extracellular matrix rigidity and IFNτ ensure the establishment of early pregnancy through activation of YAP
- First Published: 04 January 2021
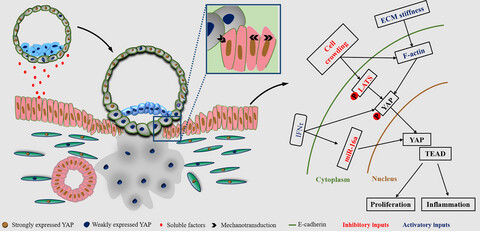
In the endometrium of pregnant mammals, YAP activation promoted endometrial cell proliferation, induced EMT progression and supplied a weak inflammation benefit for uterus to receive the embryo. Mechanistically, expression levels of YAP were double regulated by upstream biochemical and mechanical signals in bEECs and partially dependent on the Hippo signalling pathway.
lnc-RHL, a novel long non-coding RNA required for the differentiation of hepatocytes from human bipotent progenitor cells
- First Published: 04 January 2021
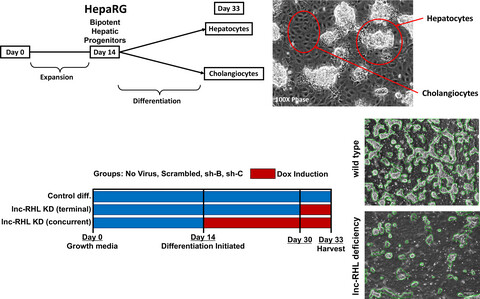
HepaRG cells serve as a useful model of hepatic differentiation. A novel lncRNA (lnc-RHL) is induced when bipotent hepatic progenitor cells are induced to differentiate. Using inducible knockdown approaches, we show that lnc-RHL regulates the final stage of liver development in which hepatocytes and cholangiocytes are formed from bipotent progenitor cells. Deficiency for lnc-RHL alters the balance of hepatocytes and cholangiocytes over the course of differentiation.
The distinct roles of myosin IIA and IIB under compression stress in nucleus pulposus cells
- First Published: 07 January 2021
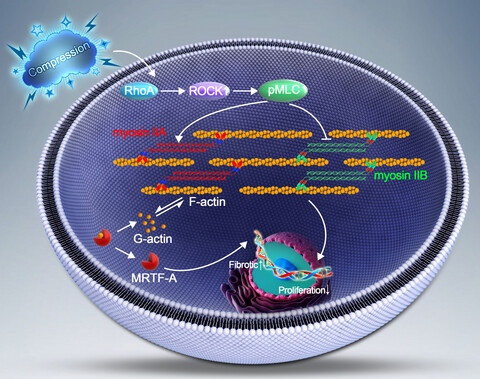
Compression stress induced the RhoA/ROCK1 pathway activation, which regulated the interaction of myosin IIA and IIB with actin. The actomyosin cytoskeleton remodelling was involved in the compression stress-induced fibrotic phenotype mediated by MRTF-A nuclear translocation and inhibition of proliferation in human NP cells.