Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
Issue Information
- Pages: 2313-2315
- First Published: 02 August 2019

Cover of this issue. A scanning electron microscopic image of MWCNT-7 fi bers phagocytosed by macrophages in the lung. See also Numano et al. (pp. 2485–2492 of this issue).
IN THIS ISSUE
In this Issue : Volume 110, Issue 8, August 2019
- Pages: 2316-2317
- First Published: 02 August 2019
REVIEW ARTICLES
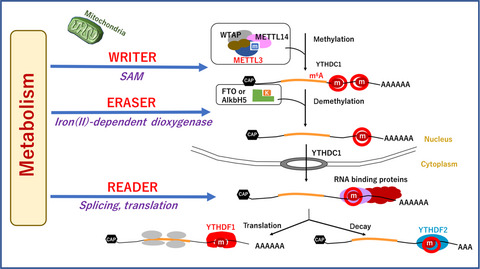
Significant epitranscriptomes in heterogeneous cancer
- Pages: 2318-2327
- First Published: 11 June 2019
Noncoding RNA transcription at enhancers and genome folding in cancer
- Pages: 2328-2336
- First Published: 22 June 2019
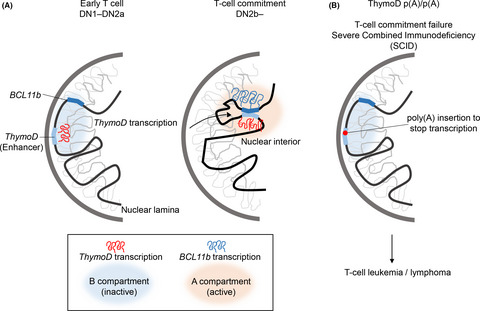
Noncoding RNA ThymoD (thymocyte differentiation factor) transcription at superenhancers is essential for mouse T-cell lineage commitment. The cessation of ThymoD transcription abolishes transcription-mediated demethylation, recruiting looping factors such as the cohesin complex, CTCF, ultimately leading to the phenotype of severe combined immunodeficiency and T-cell leukemia/lymphoma.
Cell volume regulation in cancer cell migration driven by osmotic water flow
- Pages: 2337-2347
- First Published: 23 May 2019
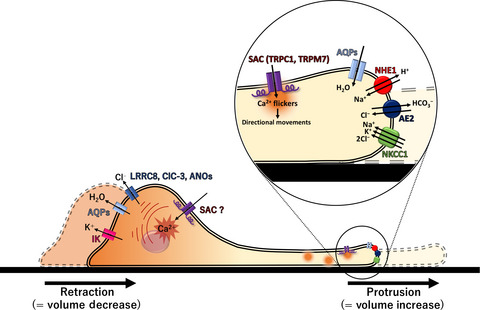
Cell migration is one of the most critical steps of cancer metastasis. Recent studies have revealed that cell volume regulation by osmotic water flow contributes to cell migration. We summarize the role of ion/water transport proteins in cancer cell migration from the point of view of cell volume regulation to provide novel therapeutic targets for cancer metastasis.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
BASIC AND CLINICAL IMMUNOLOGY
The immune response-related mutational signatures and driver genes in non-small-cell lung cancer
- Pages: 2348-2356
- First Published: 21 June 2019
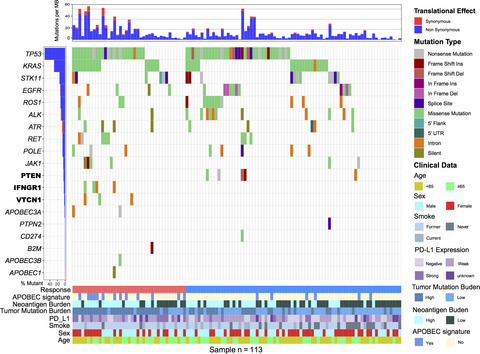
Multivariate analysis of APOBEC mutational signature is strongly associated with objective immune response and progression-free survival in immunotherapy, but not identified in conventional chemotherapy of the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) samples, suggesting the specific predictive effects of ICB treatment. High APOBEC mutational activity samples were enriched for immune checkpoint gene markers and tumor immune lymphocyte infiltration makers. Combined TMB with an APOBEC signature may preferably predict NSCLC immunotherapy responders. Individual genes mutation of IFNGR1 or VTCN1 were only found in responders; however, PTEN was only noticed in non-responders.
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) impairs the motility and immune function of human mature dendritic cells through the VEGF receptor 2-RhoA-cofilin1 pathway
- Pages: 2357-2367
- First Published: 06 June 2019
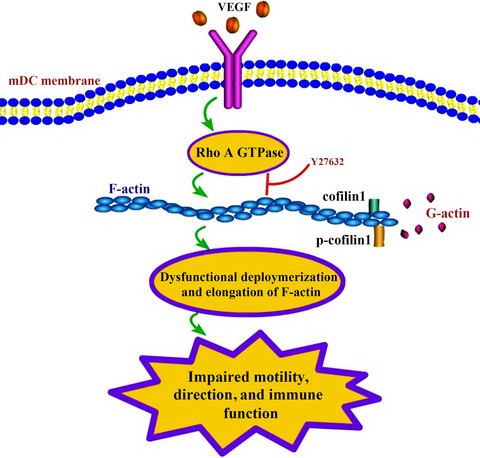
The present study found that vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) could impair the motility and immune function of mature dendritic cells (DCs) through the RhoA-cofilin1 pathway mediated by the receptor 2 of VEGF. It is clinically important to understand the biological behavior of DCs and immune escape mechanisms of tumor as well as how to improve the efficiency of antitumor therapy based on DCs.
Hypoxia decreases macrophage glycolysis and M1 percentage by targeting microRNA-30c and mTOR in human gastric cancer
- Pages: 2368-2377
- First Published: 21 June 2019
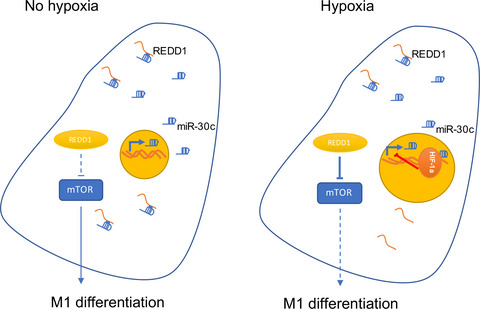
Hypoxia in the human gastric cancer microenvironment suppressed the expression of microRNA-30c, and decreased mTOR activity as well as glycolysis in gastric cancer tumor-associated macrophages, thus inhibiting M1 differentiation and function. These results provide a novel metabolic strategy for tumor microenvironment-based therapy.
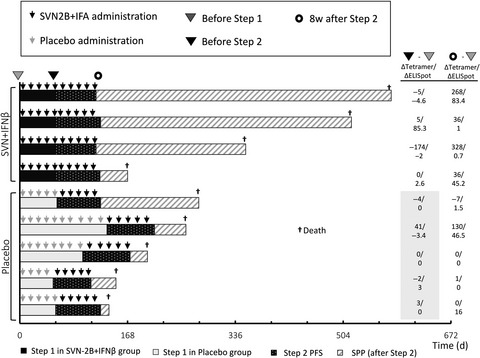
Randomized phase II trial of survivin 2B peptide vaccination for patients with HLA-A24-positive pancreatic adenocarcinoma
- Pages: 2378-2385
- First Published: 20 June 2019
Immunohistological analysis of pancreatic carcinoma after vaccination with survivin 2B peptide: Analysis of an autopsy series
- Pages: 2386-2395
- First Published: 17 June 2019
CARCINOGENESIS
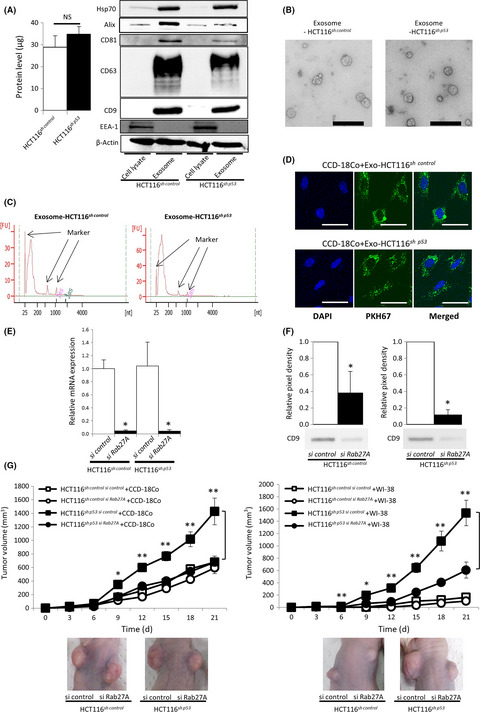
Exosomal microRNAs derived from colon cancer cells promote tumor progression by suppressing fibroblast TP53 expression
- Pages: 2396-2407
- First Published: 31 May 2019
Roles of the hexosamine biosynthetic pathway and pentose phosphate pathway in bile acid-induced cancer development
- Pages: 2408-2420
- First Published: 19 June 2019
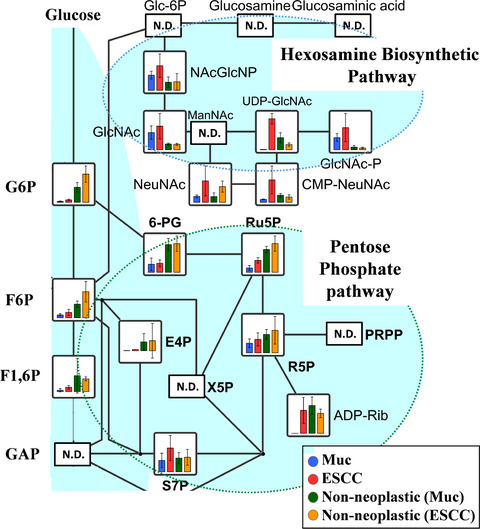
Glucose metabolism is upregulated in both esophageal cancer tissue and cell lines, and the hexosamine biosynthetic pathway (HBP) is activated in the former. The cell line-based experiments demonstrated that upregulation of the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP) at higher degrees of malignancy. While bile acids are not mutagenic, chronic exposure seems to trigger G6PD overexpression and NF-κB(p65) activation, potentially inducing genetic mutations as well as facilitating carcinogenesis and cancer progression.
Cysteine-rich protein 61 regulates the chemosensitivity of chronic myeloid leukemia to imatinib mesylate through the nuclear factor kappa B/Bcl-2 pathway
- Pages: 2421-2430
- First Published: 30 May 2019
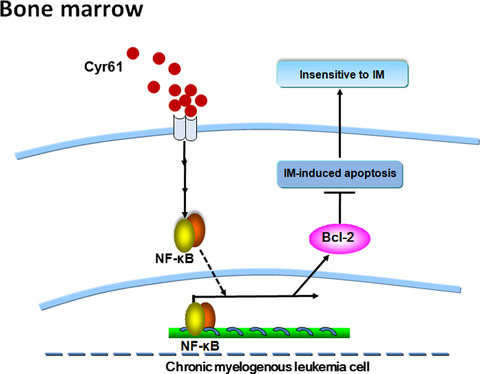
Cyr61 levels were upregulated in the plasma and BM of patients with CML as well as in K562 cells. This upregulation of Cyr61 significantly decreased IM-induced cellular apoptosis of CML cells. Thus, our results suggest that selectively targeting Cyr61 directly or its relevant effector pathways may provide potential value in improving the clinical response of patients with CML to IM treatment.
Carcinogen-induced tumors in SFN-transgenic mice harbor a characteristic mutation spectrum of human lung adenocarcinoma
- Pages: 2431-2441
- First Published: 29 May 2019
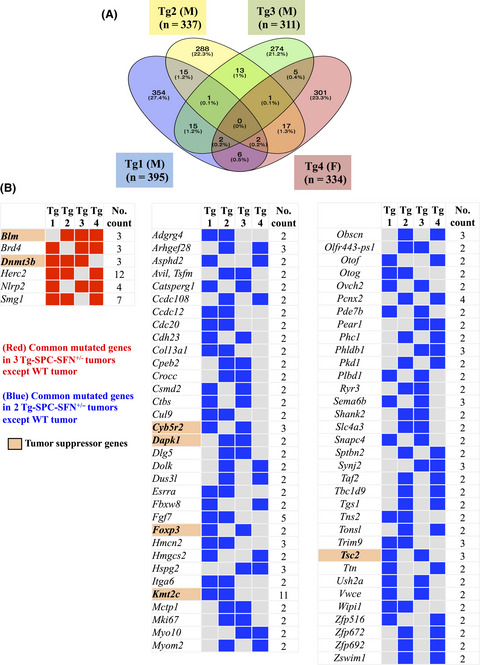
In this study, we identified 73 common mutated genes among 4 Tg-SPC-SFN+/− tumors, which were predicted to be associated with tumorigenesis. The expression levels of some of these genes were significantly associated with the clinical outcome of lung adenocarcinoma patients. Therefore, we suggest that Tg-SPC-SFN+/− tumors recapitulate key features of major human lung adenocarcinoma.
Targeting PIN1 exerts potent antitumor activity in pancreatic ductal carcinoma via inhibiting tumor metastasis
- Pages: 2442-2455
- First Published: 31 May 2019
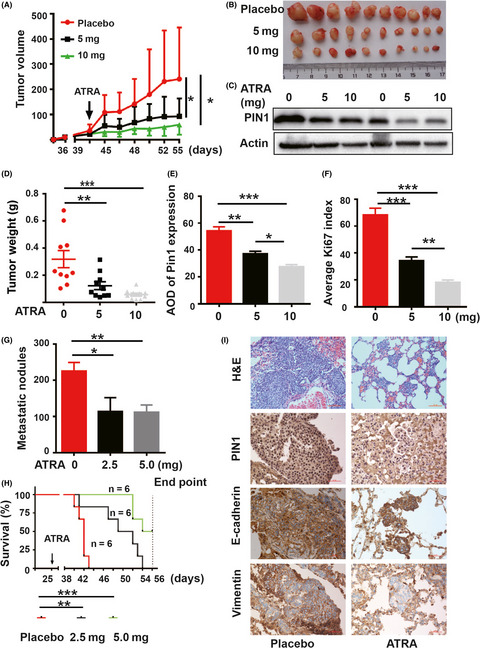
PIN1 was highly expressed in pancreatic cancer and metastatic tissues. PIN1 high expression is significantly associated with lymph node metastasis. PIN1 ablation dramatically decreased migration and invasion in vitro and inhibited the tumorigenesis and metastatic spread of PDAC cells in vivo through regulating the key molecules of multiple cancer-driving pathways.
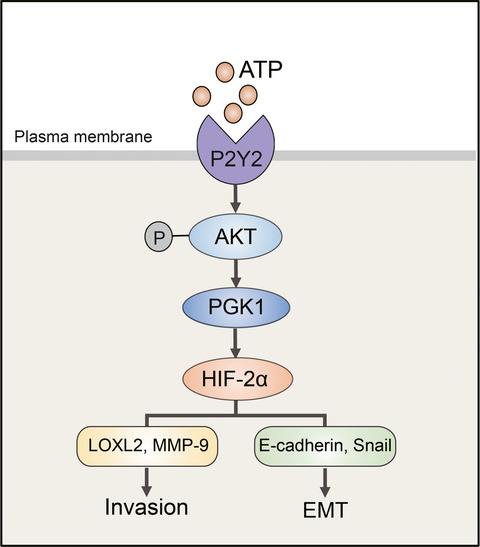
Extracellular ATP promotes breast cancer invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition via hypoxia-inducible factor 2α signaling
- Pages: 2456-2470
- First Published: 31 May 2019
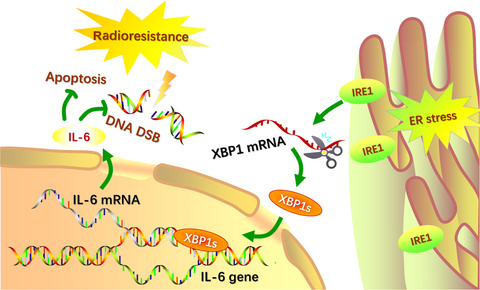
Interleukin-6 production mediated by the IRE1-XBP1 pathway confers radioresistance in human papillomavirus-negative oropharyngeal carcinoma
- Pages: 2471-2484
- First Published: 11 June 2019
MWCNT-7 administered to the lung by intratracheal instillation induces development of pleural mesothelioma in F344 rats
- Pages: 2485-2492
- First Published: 02 July 2019
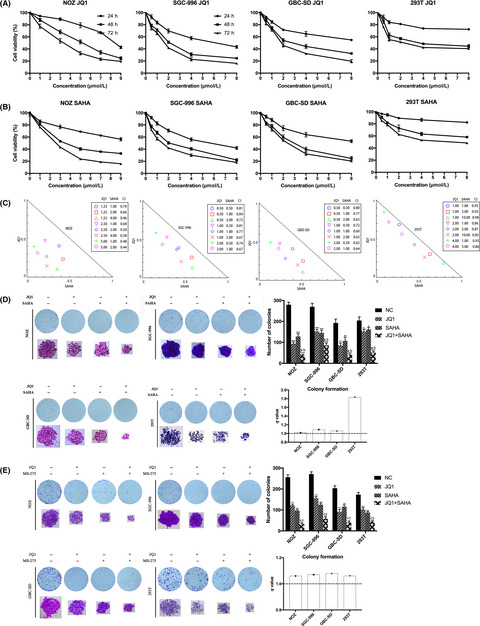
BRD4 inhibitor and histone deacetylase inhibitor synergistically inhibit the proliferation of gallbladder cancer in vitro and in vivo
- Pages: 2493-2506
- First Published: 19 June 2019
Interaction of transforming growth factor-β-Smads/microRNA-362-3p/CD82 mediated by M2 macrophages promotes the process of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma cells
- Pages: 2507-2519
- First Published: 19 June 2019
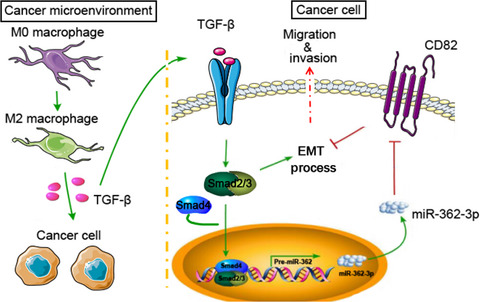
In this work, we found that microRNA-362-3p can serve as a core factor mediating cross-talk between the transforming growth factor-β pathway in tumor-associated macrophages and tetraspanins in tumor cells, and thus facilitate the epithelial-mesenchymal transition process. This finding provides a rationale for antagonizing macrophage-directed polarization to inhibit hepatocellular carcinoma.
Stromal iodothyronine deiodinase 2 (DIO2) promotes the growth of intestinal tumors in ApcΔ716 mutant mice
- Pages: 2520-2528
- First Published: 18 June 2019
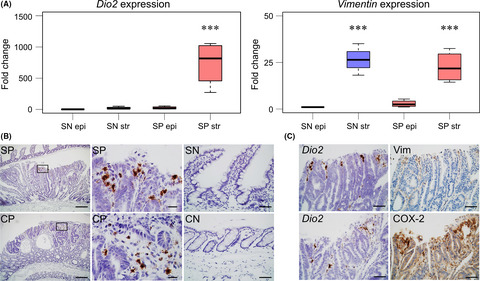
Iodothyronine deiodinase 2 (DIO2) converts the prohormone thyroxine (T4) to bioactive T3 in peripheral tissues and thereby regulates local thyroid hormone levels. Here we show that stromal DIO2 promotes the growth of intestinal tumors in ApcΔ716 mutant mice, a mouse model of familial adenomatous polyposis and early stage sporadic colorectal cancer (CRC). Analysis of The Cancer Genome Atlas data also indicated significant upregulation of DIO2 expression in colorectal cancer and a close association of its expression pattern with the stromal component of CRC.
CELL, MOLECULAR, AND STEM CELL BIOLOGY
In vivo effects of chemotherapy on oncogenic pathways in colorectal cancer
- Pages: 2529-2539
- First Published: 22 May 2019
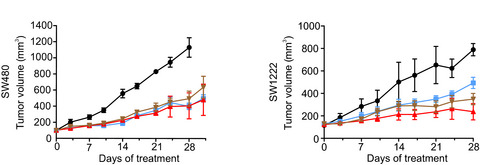
Patients with advanced colorectal cancer often are treated with systemic cytotoxic therapy using fluorouracil, oxaliplatin, irinotecan, and FOLFOX or FOLFIRI combination protocols. Herein, we examined whether chemotherapy impacts on WNT, MAPK and NOTCH signaling pathways in xenograft models of colon cancer. Furthermore, we tested whether combining chemotherapy with MAPK and NOTCH inhibition has superior therapeutic effects.
Induced miR-31 by 5-fluorouracil exposure contributes to the resistance in colorectal tumors
- Pages: 2540-2548
- First Published: 04 June 2019
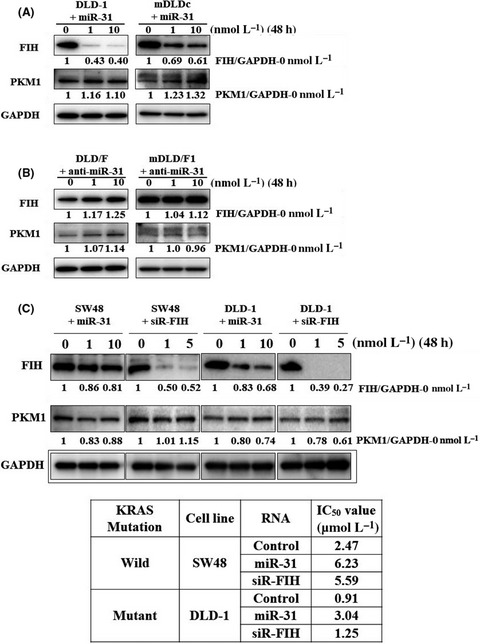
In this study, we mainly analyzed the relationship between 5-FU resistance and the miRNA profile of colorectal tumors. Moreover, the expression level of miR-31 was higher in carcinomas invading submucosa and advanced cancer than in carcinomas in situ and adenomas. These data might suggest that the increased expression level of miR-31 caused 5-FU resistance in colorectal cancer through maintenance of the Warburg effect.
Acquired resistance mechanisms to afatinib in HER2-amplified gastric cancer cells
- Pages: 2549-2557
- First Published: 04 June 2019
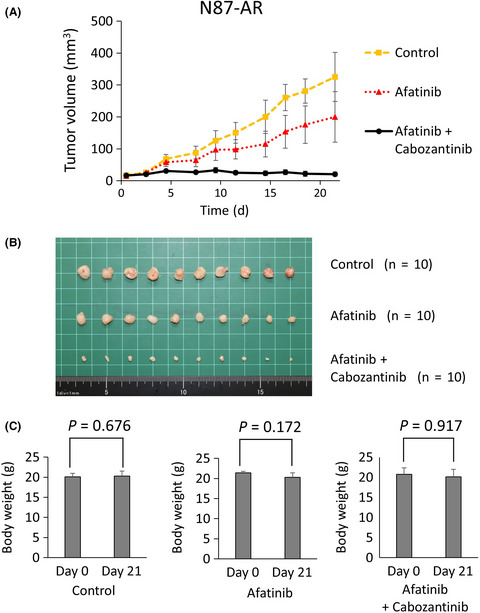
The purpose of this study was to identify the mechanisms of acquired afatinib resistance and to investigate the treatment strategies for HER2-amplified gastric cancer cells. We identified MET and AXL activation in addition to YES1 activation as novel mechanisms of afatinib resistance in HER2-driven gastric cancer. Treatment strategies targeting individual mechanisms of resistance are key to overcoming such resistance.
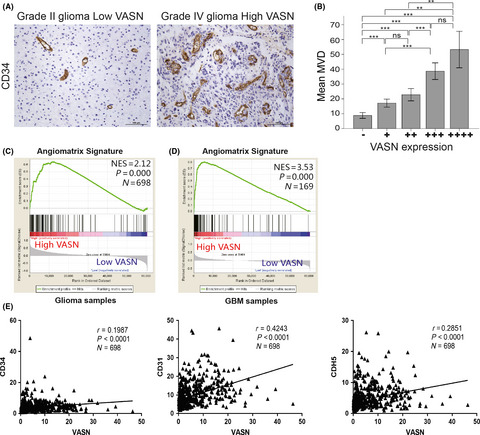
Vasorin stimulates malignant progression and angiogenesis in glioma
- Pages: 2558-2572
- First Published: 19 June 2019
CLINICAL RESEARCH
Clinical significance of the LacdiNAc-glycosylated prostate-specific antigen assay for prostate cancer detection
- Pages: 2573-2589
- First Published: 30 May 2019
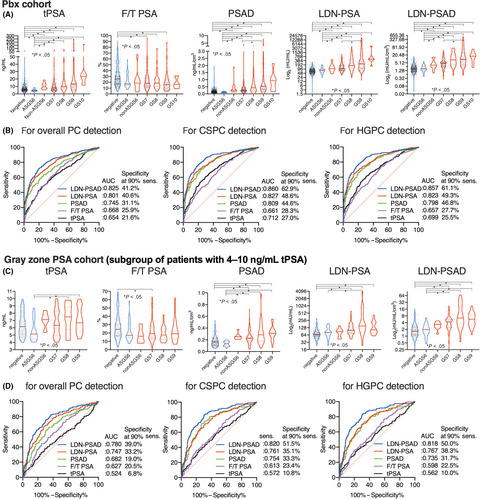
We evaluated the clinical significance of LacdiNAc-glycosylated prostate-specific antigen (LDN-PSA) and LDN-PSA normalized by prostate volume (LDN-PSAD). We retrospectively measured LDN-PSA, PSA, and free PSA/total PSA (F/T) PSA values using 718 men who had prostate biopsy in 3 academic urology sites (Japan and Canada) and 174 prostate cancer patients who underwent radical prostatectomy in Australia. It was observed that inclusion of LDN-PSA and LDN-PSAD to the base diagnostic model (age, digital rectal examination status, tPSA, and F/T PSA) permitted avoidance of even more biopsies without missing clinically significant prostate cancer, indicating that LDN-PSA and LDN-PSAD are significantly better than the conventional PSA test in identifying patients with clinically significant prostate cancer.
Monitoring of cancer patients via next-generation sequencing of patient-derived circulating tumor cells and tumor DNA
- Pages: 2590-2599
- First Published: 06 June 2019
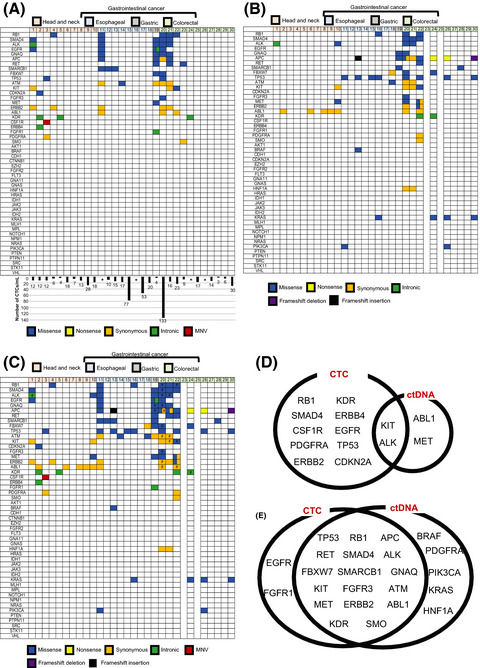
In summary, we optimized the efficiency of a platform for capturing circulating tumor cells (CTC) using a label-free inertial microfluidics approach and revealed the importance of both CTC and circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) as diagnostic tools. In addition, our data suggest that both CTC and ctDNA can be used to closely monitor the emergence of molecular changes in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer.
Immunohistochemistry for identification of CCND1, NSD2, and MAF gene rearrangements in plasma cell myeloma
- Pages: 2600-2606
- First Published: 20 June 2019
DRUG DISCOVERY AND DELIVERY
Proximity proteomics identifies cancer cell membrane cis-molecular complex as a potential cancer target
- Pages: 2607-2619
- First Published: 22 June 2019
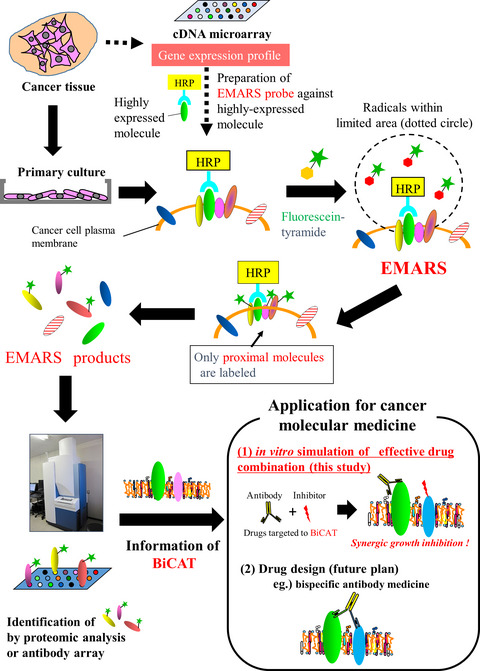
Here, we examined the cancer cell membrane-resident “cis-bimolecular complex” as a possible cancer target (cis-bimolecular cancer target: BiCAT) using proximity proteomics, a technique that has attracted attention in the last 10 years. BiCAT has the potential to contribute to several molecular targeted strategies in future.
GENETICS, GENOMICS, AND PROTEOMICS
Mutational burden and signatures in 4000 Japanese cancers provide insights into tumorigenesis and response to therapy
- Pages: 2620-2628
- First Published: 01 June 2019
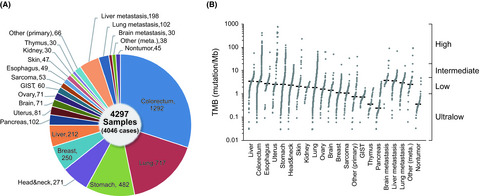
By applying whole-exome sequencing and microarray technologies for high-throughput genomic and transcriptional analysis, this study investigates the mutational burden and signatures in a large cohort of tumor samples of different histology from Japanese patients. The contribution ratio of Signature 16, which is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma in drinkers, was increased in hypopharynx cancer. Furthermore, based on microarray analysis, tumors with predominant signatures were classified into 2 subgroups depending on the expression of immune-related genes, reflecting differences in the immune context of the tumor microenvironment.
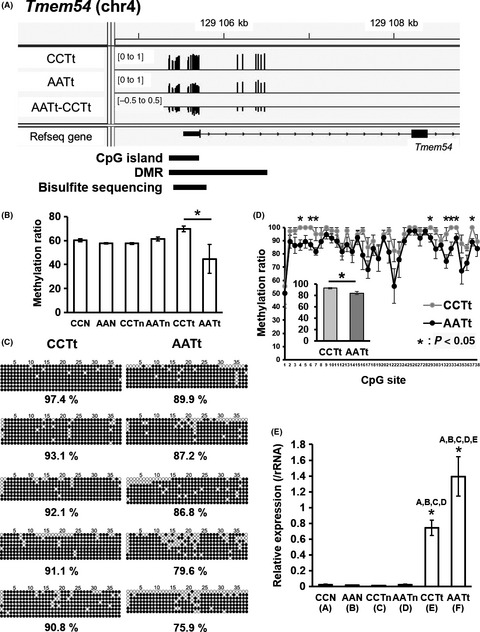
DNA methylation changes involved in the tumor increase in F2 males born to gestationally arsenite-exposed F1 male mice
- Pages: 2629-2642
- First Published: 19 June 2019
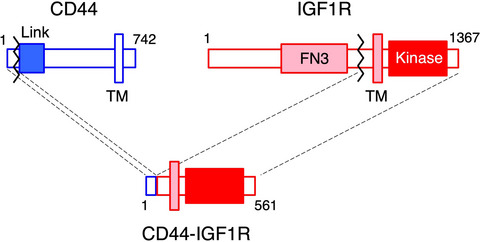
Identification of candidates for driver oncogenes in scirrhous-type gastric cancer cell lines
- Pages: 2643-2651
- First Published: 21 June 2019
Small lung tumor biopsy samples are feasible for high quality targeted next generation sequencing
- Pages: 2652-2657
- First Published: 21 June 2019
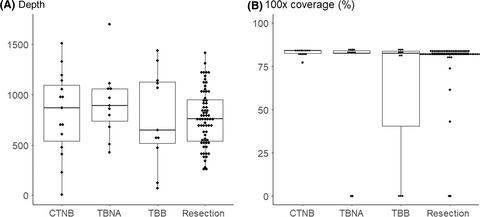
CT-guided needle biospy, endobronchial ultrasound-needle aspiration, and transbronchial biopsy mostly resulted in adequate DNA and RNA quality, which enalbled high-quality targeted next generation sequencing (NGS) analysis. Our results indicate that small biopsies may be feasible for targeted NGS in general.
PATHOLOGY
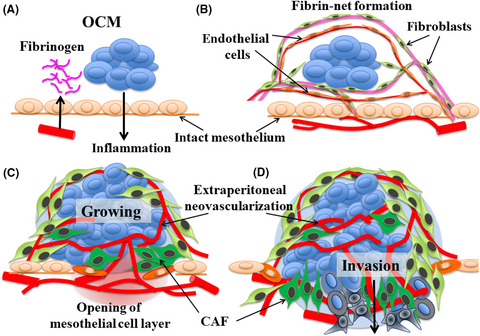
Novel strategy of ovarian cancer implantation: Pre-invasive growth of fibrin-anchored cells with neovascularization
- Pages: 2658-2666
- First Published: 14 June 2019
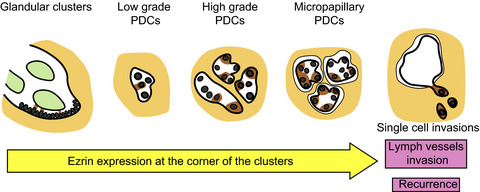
Clinicopathological significance of heterogeneic ezrin expression in poorly differentiated clusters of colorectal cancers
- Pages: 2667-2675
- First Published: 07 June 2019
REPORT
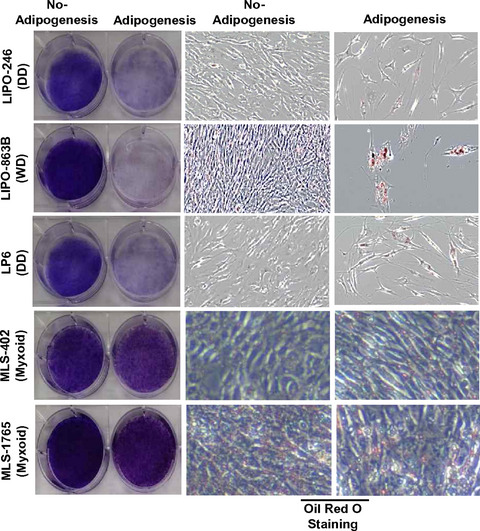
Adipogenesis induces growth inhibition of dedifferentiated liposarcoma
- Pages: 2676-2683
- First Published: 08 May 2019