Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Cover Picture: Stilbene Ligand-based Metal–Organic Frameworks for Efficient Dye Adsorption and Nitrobenzene Detection (BKCS 6/2023) Jiyun Kim, Chanju Na, Younghu Son, Mani Prabu, Minyoung Yoon
- Page: 449
- First Published: 20 June 2023

Porous metal-organic frameworks (MOF) with fluorescent properties provide a unique platform for the adsorptive removal and sensing harmful chemicals. Herein, the fluorescent sensing of nitro-aromatic explosives was demonstrated by the turn-off of MOF's fluorescent. MOFs' porous properties also allow highly selective dye adsorption towards small cationic dyes (methylene blue). More details are available in the article by Kim et al.
Masthead
Special Issue : Recent Advances in Materials Chemistry
Operando small-angle x-ray scattering for battery research
- Pages: 452-467
- First Published: 04 June 2023
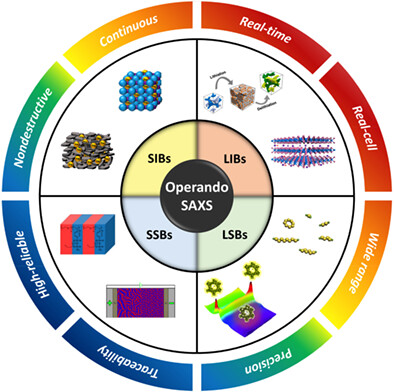
Operando small-angle x-ray scattering (SAXS) for battery research is briefly reviewed, to help in understanding the complex behaviors of nano-scaled electrochemical components such as electrodes and electrolytes in secondary batteries, where this advanced analysis method is expected to play a key role in providing useful information for the design and synthesis of prospective materials in energy-storage fields.
Beyond conventional aqueous electrolytes: Recent developments in Li-free “water-in-salt” electrolytes for supercapacitors
- Pages: 468-482
- First Published: 01 March 2023
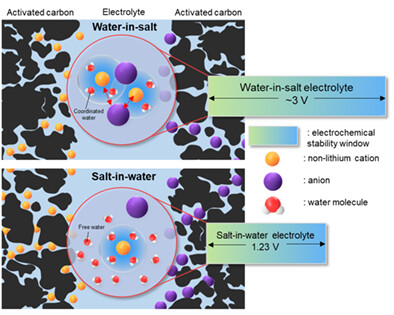
The “Water-in-salt” electrolyte (WiSE) is a promising class of electrolyte because of its unique physicochemical properties. This review highlights the recent progress of WiSE and its application to supercapacitors (SCs). Our discussion is primarily focued on operatig mechanisms of non-Lithium based WiSE and how they affect performance. Current challenges and perspectives are also discussed.
Synthesis of single-crystalline InP tetrapod nanocrystals via addition of ZnCl2
- Pages: 483-487
- First Published: 13 February 2023
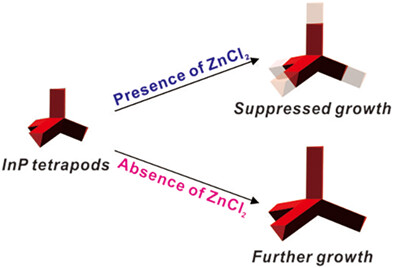
We synthesized indium phosphide (InP) tetrapod NCs with the addition of ZnCl2 and shelling with ZnSe. Consequently, photoluminescence was dramatically enhanced with tetrapodal geometry. Interestingly, we observed suppression of growing arm length and narrower arm length distribution in InP tetrapods with the addition of ZnCl2. This study offers a great platform to study the role of ZnCl2 and exciton behavior in tetrapod NCs.
Multiple-length scale investigation of Pt/C degradation by identical-location transmission electron microscopy
- Pages: 488-494
- First Published: 23 February 2023
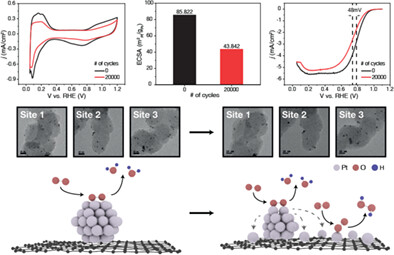
The degradation process of Pt/C was studied using identical-location transmission electron microscopy at multiple-length scales. Various morphological changes in individual Pt nanoparticles were quantitatively analyzed. The formation of Pt single atoms on the carbon support was observed and its effect on the oxygen reduction reaction pathway was studied using rotating ring-disk electrode tests.
Special Issue : Emerging Investigator
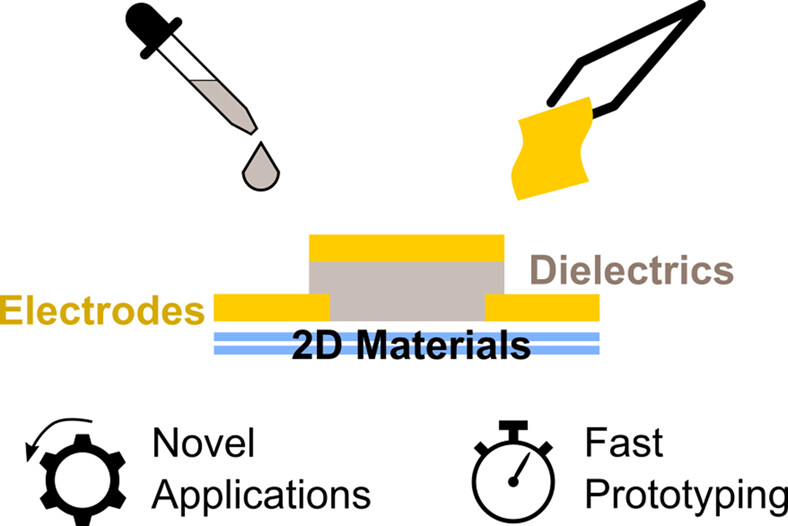
Novel electrodes and gate dielectrics for field-effect transistors based on two-dimensional materials
- Pages: 495-506
- First Published: 01 March 2023
Stilbene ligand-based metal–organic frameworks for efficient dye adsorption and nitrobenzene detection
- Pages: 507-515
- First Published: 17 April 2023
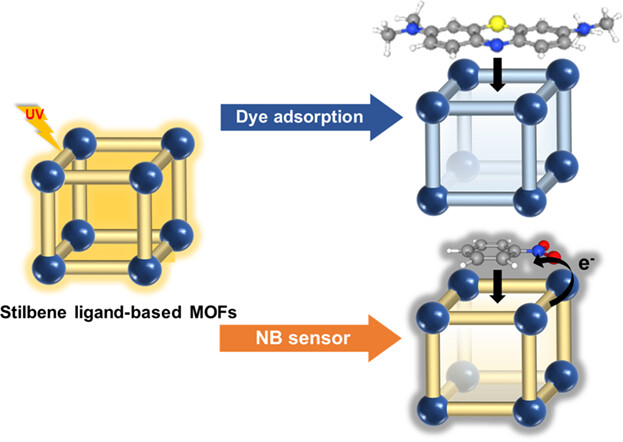
The stilbene ligand-based metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) were used for dye adsorption and nitrobenzene sensing. Despite the low adsorption capacity, the MOFs showed unique selectivity in dye adsorption. In addition, the MOFs also show fluorescence-based sensing ability toward organic analytes. Depending on the structure of MOFs, the MOF shows different selectivity and sensitivity as a sensor.
Communication
A rational design of AIE-active fluorophore for the fingerprint optical detection
- Pages: 516-522
- First Published: 25 January 2023
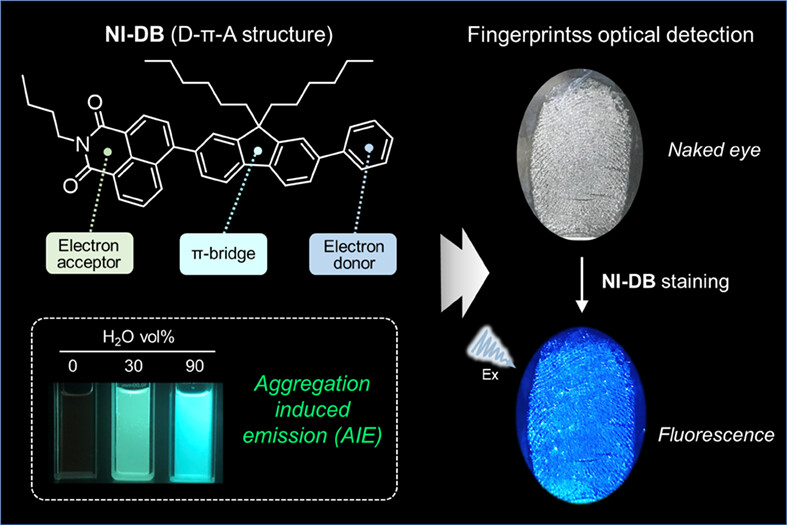
Herein, a novel AIE-active fluorophore (NI-DB) with electron donor-π bridge-electron acceptor (D-π-A) structure based on the 1,8-naphthalimide was developed. Significantly, after fingerprints fixed by cyanoacrylate glue fuming, NI-DB is capable of detecting and imaging latent fingerprints (LFPs) via its intrinsic fluorescence emission. Accordingly, such an AIE-active fluorophore is expected to be an ideal material that would reach the reliable optical detection and imaging of LFPs.
Articles
Effects of the protonation and the polar solvation on the molecular properties of methyl orange: A density functional theory study
- Pages: 523-527
- First Published: 16 February 2023
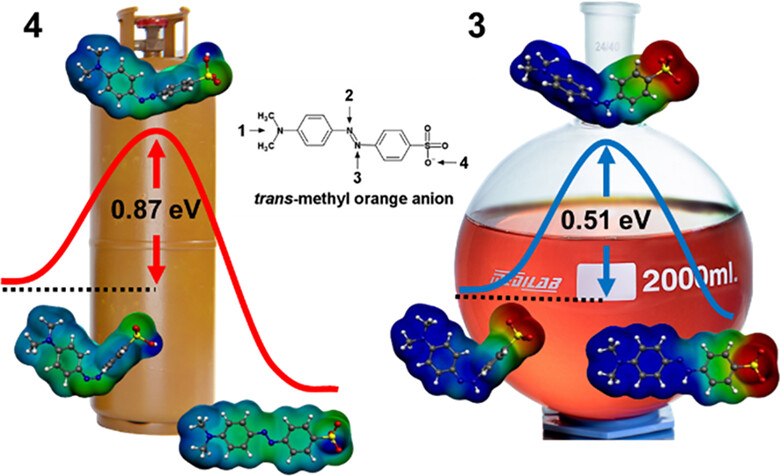
A density functional theory (DFT) study was carried out to unveil the effect of the protonation and the solvation on the molecular properties of methyl orange (MO) anion. In the gas phase, the sulfonate is the strongest proton acceptor and shows the least energy barrier for the cis-to-trans isomerization, while the protonation at azo N atom is the most stable in both the equilibrium and transition states in the aqueous solution.
Preparation of nanopillar array electrode of iridium oxide for high performance of pH sensor and its real-time sweat monitoring
- Pages: 528-535
- First Published: 22 February 2023
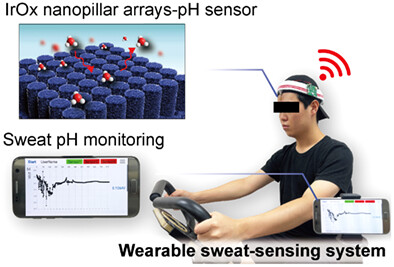
A flexible iridium oxide-based nanopillar array pH sensor is fabricated using soft-lithography and electrochemical deposition steps, resulting in high sensitivity, a fast response time, good repeatability, and selectivity. A wearable sweat-sensing system is designed by integrating the pH sensor with a wireless electronic module, demonstrating real-time monitoring of pH dynamics in the sweat of a volunteer during an indoor cycling exercise.
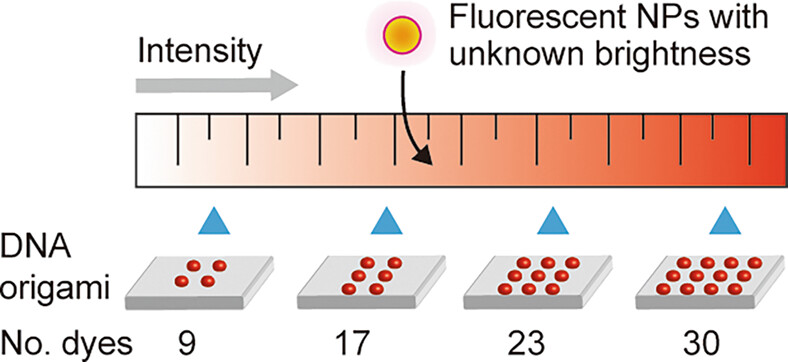
Quantitative evaluation of brightness of fluorescent nanoparticles using DNA origami standards
- Pages: 536-541
- First Published: 09 March 2023