Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Issue Information - TOC
- Page: 285
- First Published: 03 February 2016
Issue Information - Info Page
- Page: 286
- First Published: 03 February 2016
Special Issue on ‘Novel energy systems for smart grid’
- Page: 287
- First Published: 02 October 2015
Fabrication of PDMS-based triboelectric nanogenerator for self-sustained power source application
- Pages: 288-297
- First Published: 07 August 2015
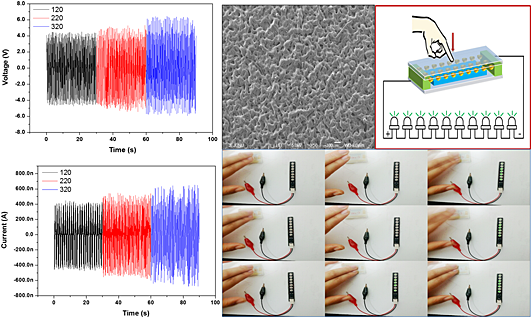
This study presents a simple and effective approach for fabricating PDMS-based triboelectric nanogenerator that can effectively harvesting irregular mechanical energy for driving a small commercial electronic component. The device exhibited the maximum open-circuit voltage and short-circuit current of 6.3 V and 0.635 μA respectively, with maximum output power of 178 nW. The fabricated PDMS-based triboelectric nanogenerator can directly drive 10 commercial LEDs connected in series, when the force is applied to the device through finger. These results demonstrating the potential application of PDMS-based triboelectric nanogenerator for self-powered systems.
Towards a novel quantification approach based on smart grid network vulnerability score
- Pages: 298-312
- First Published: 14 July 2015
An efficient and privacy-preserving scheme for P2P energy exchange among smart microgrids
- Pages: 313-331
- First Published: 14 July 2015
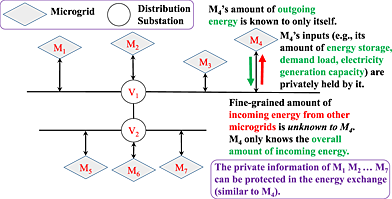
In this paper, we studied the privacy issues in peer-to-peer energy exchange among smart microgrids. To this end, we first formulated several novel energy exchange optimization problems that minimize the energy loss during the exchanges and then developed an efficient and privacy-preserving scheme to them without information disclosure. We also extended the privacy-preserving scheme to a collusion-resistant scheme to resolve a potential collusion-based attack and finally demonstrated the performance of our proposed approaches using experimental results.
Hierarchical reactive power regulation strategies for high-penetration photovoltaic distribution systems
- Pages: 332-342
- First Published: 08 June 2015
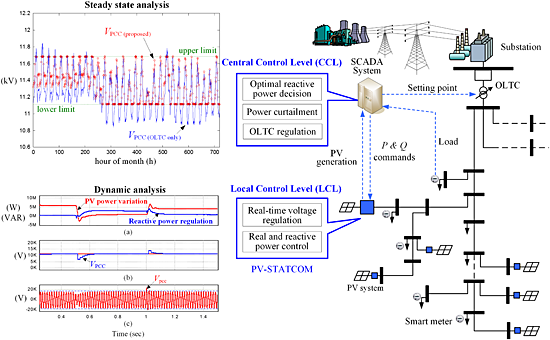
The proposed hierarchical control strategies include central control level (CCL) and local control level to obtain optimal operation point and deal with dynamic problems, respectively. A comprehensive optimization algorithm is proposed for CCL. The photovoltaics static compensator dynamic model and control algorithms coordinated with the CCL are proposed as the local control level. The photovoltaics power curtailment to relive the overvoltage can be greatly reduced without any additional energy storage system. The voltage deviation, line loss, and CO2 emission are also decreased.
Parameter estimation of photovoltaic model via parallel particle swarm optimization algorithm
- Pages: 343-352
- First Published: 22 June 2015
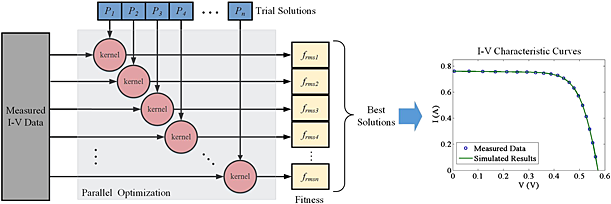
A parallel computing paradigm has been shown to speed up the parameter estimation process for various photovoltaic (PV) models in this work. With the measured current–voltage (I–V) data, the root mean square errors frms can be calculated concurrently in a kernel, which actually is a piece of code executing tasks on a multi-core processor. Experimental and simulation results demonstrate that the proposed method dramatically accelerates the computational speed.
Active power control of solar PV generation for large interconnection frequency regulation and oscillation damping
- Pages: 353-361
- First Published: 23 June 2015
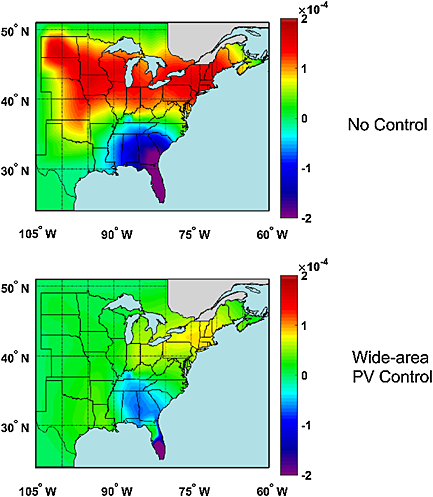
Taking the United States Eastern Interconnection as an example, the impact of solar photovoltaic (PV) penetration on the large interconnected power system frequency response and inter-area oscillation was evaluated in this paper. Despite all those negative impacts, the potential contributions of solar PV generation to the power system frequency regulation and oscillation damping (left figure) were also unveiled. Simulation results confirmed the effectiveness of solar PV active power control in alleviating those negative impacts. This study facilitates the integration of solar PV power into the current electricity generation portfolio.
Wide-area smart grids with new smart units synchronized measurement analysis and control based on cloud computing platform
- Pages: 362-378
- First Published: 08 September 2015
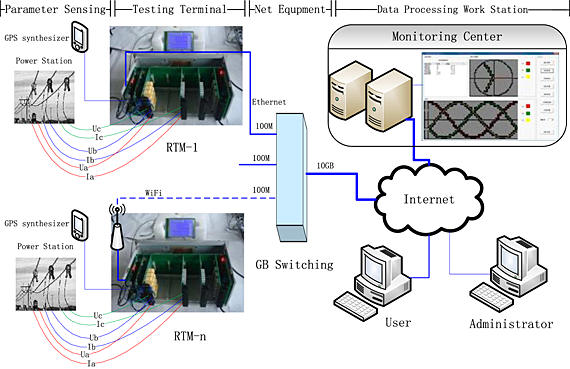
This paper gives a new smart grid with Smart Units, the real-time networks and information web services. The Smart Units with functions of measurement analysis and control include intelligent algorithms of FFT Zoom-FFT Wavelet. The networks working in Synchronous Ticket Strategy are a real-time controlling system. Information web services built on cloud computing platforms provide parallel calculation with S transmit and user application services of power parameters GIS and data accessing.
Li-ion battery performance and degradation in electric vehicles under different usage scenarios
- Pages: 379-392
- First Published: 07 August 2015
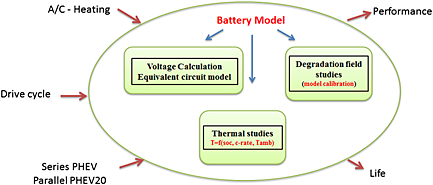
Impact of climate control loads and ambient conditions on the lithium-ion battery performance and vehicle fuel economy is analyzed. A battery model consisting of performance, thermal, and degradation sub-models is developed based on lab and field tests. A series and a parallel plug-in hybrid electric vehicle are used for simulations. It is observed that climate control loads impose a considerable additional load resulting in increased battery degradation and fuel economy. Thermal preconditioning could be used as a means to reduce these effects.
Cathode candidates for zinc-based thermal-electrochemical energy storage
- Pages: 393-399
- First Published: 01 September 2015
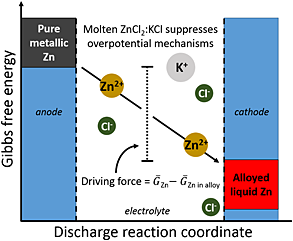
An electrochemical cell utilizing a molten salt eutectic electrolyte is investigated as a new low-cost energy storage technology. Using Zn as the anode, multiple cathode candidates were screened. Cells employing molten metal cathodes that alloy with Zn delivered markedly high current densities independent of their standard reduction potentials and show promise for grid storage.
Development of theoretical model for 3D plasma energy behavior and characteristics
- Pages: 400-407
- First Published: 31 August 2015




