Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
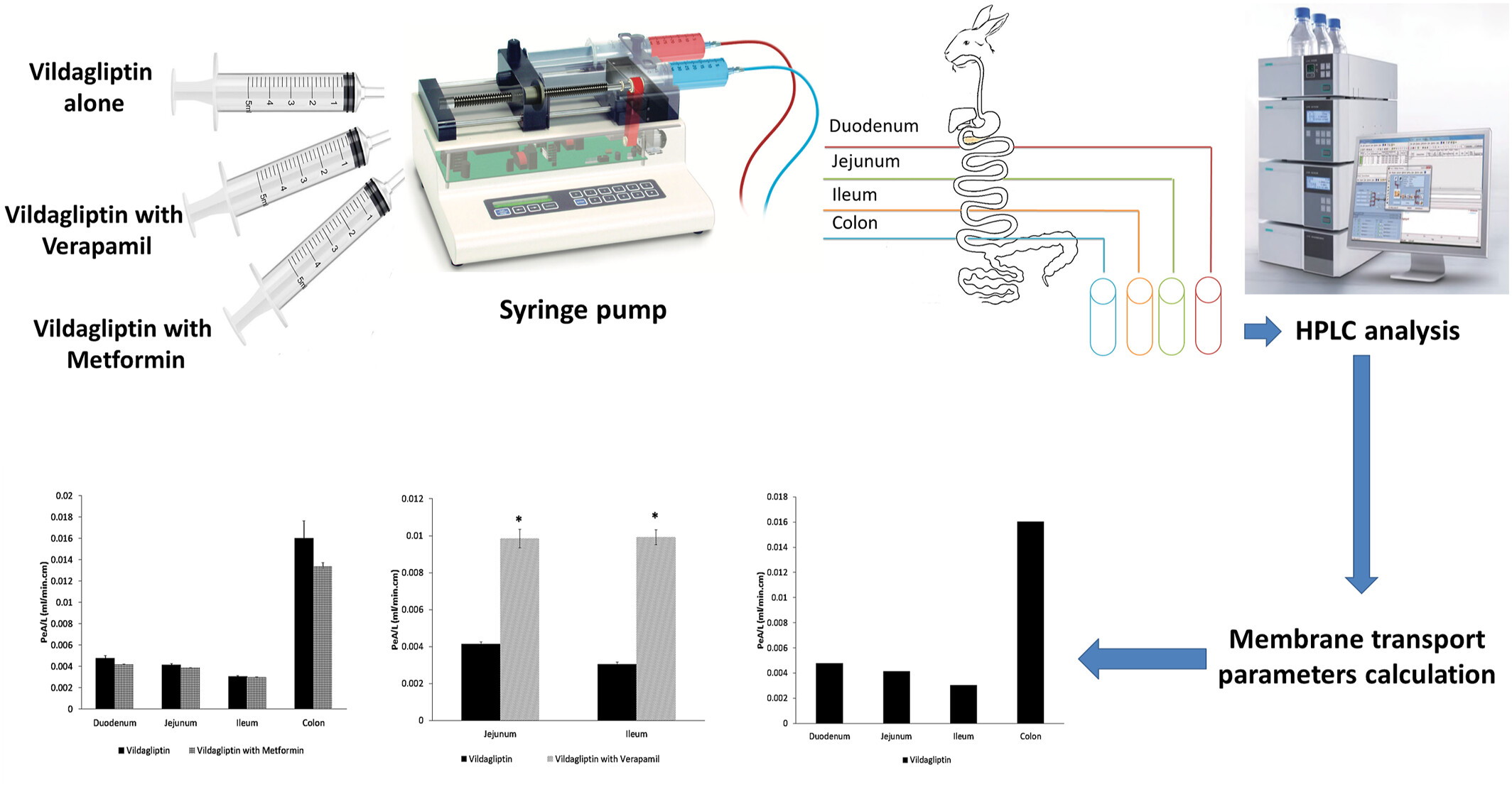
In situ evaluation of the impact of metformin or verapamil coadministration with vildagliptin on its regional absorption from the rabbit’s intestine
- Pages: 71-82
- First Published: 24 February 2024
Characterization of AST-001 non-clinical pharmacokinetics: A novel selective AKR1C3-activated prodrug in mice, rats, and cynomolgus monkeys
- Pages: 83-92
- First Published: 16 March 2024
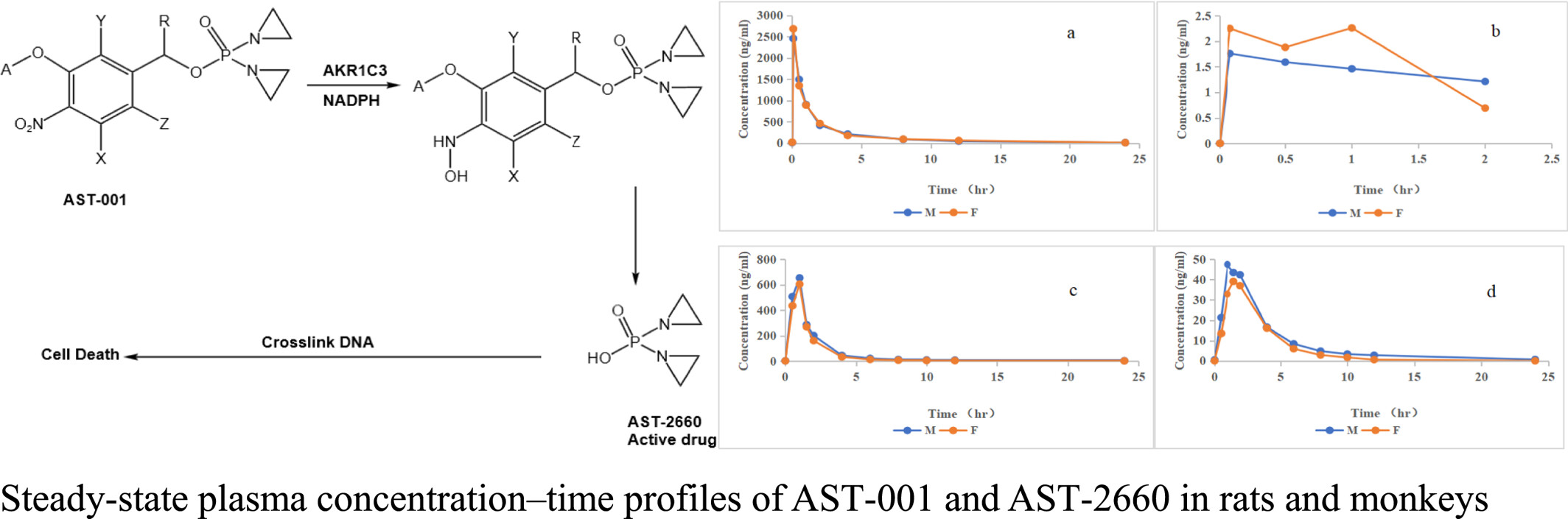
AST-001 is a chemically synthesized inactive nitrogen mustard prodrug that is selectively cleaved to a cytotoxic aziridine (AST-2660) via aldo-keto reductase family 1 member C3 (AKR1C3). The purpose of this study was to investigate the pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution of the prodrug, AST-001, and its active metabolite, AST-2660, in mice, rats and monkeys. AST-001 has an acceptable pharmacokinetic profile, desirable efficacy and safety profile, as well as potential clinical efficacy, and is therefore currently well underway in clinical studies.
Aging and brain free cholesterol concentration on amyloid-β peptide accumulation in guinea pigs
- Pages: 93-106
- First Published: 15 March 2024
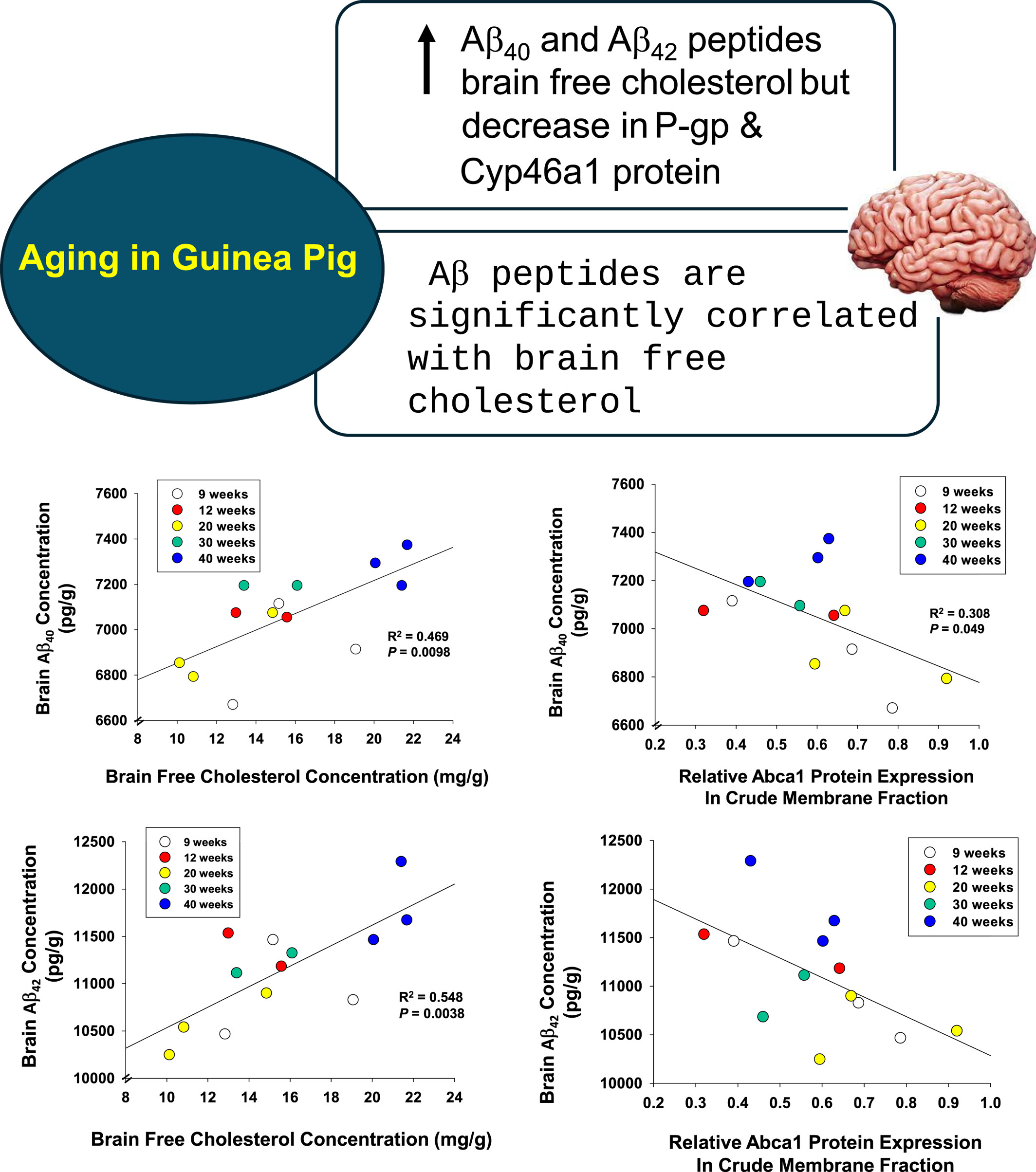
We described aging effects on the brain Aβ40 and Aβ42 peptide load and demonstrated that accumulation of the peptides in guinea pig (GP), whose genetic makeup and handling of Aβ peptides bear similarity to humans, was highly correlated with brain free cholesterol concentrations. With aging, brain Aβ peptides and free cholesterol concentrations were higher whereas protein expression levels of P-gp, Lrp1 and Cyp46a1 for Aβ peptide efflux and cholesterol metabolism, respectively, were reduced. Additionally, protein expression of Abca1 for cholesterol efflux was highly correlated to free cholesterol levels. These data suggest that the higher brain free cholesterol and reduced P-gp and Lrp1 play a role in Aβ peptide accumulation for the guinea pig.
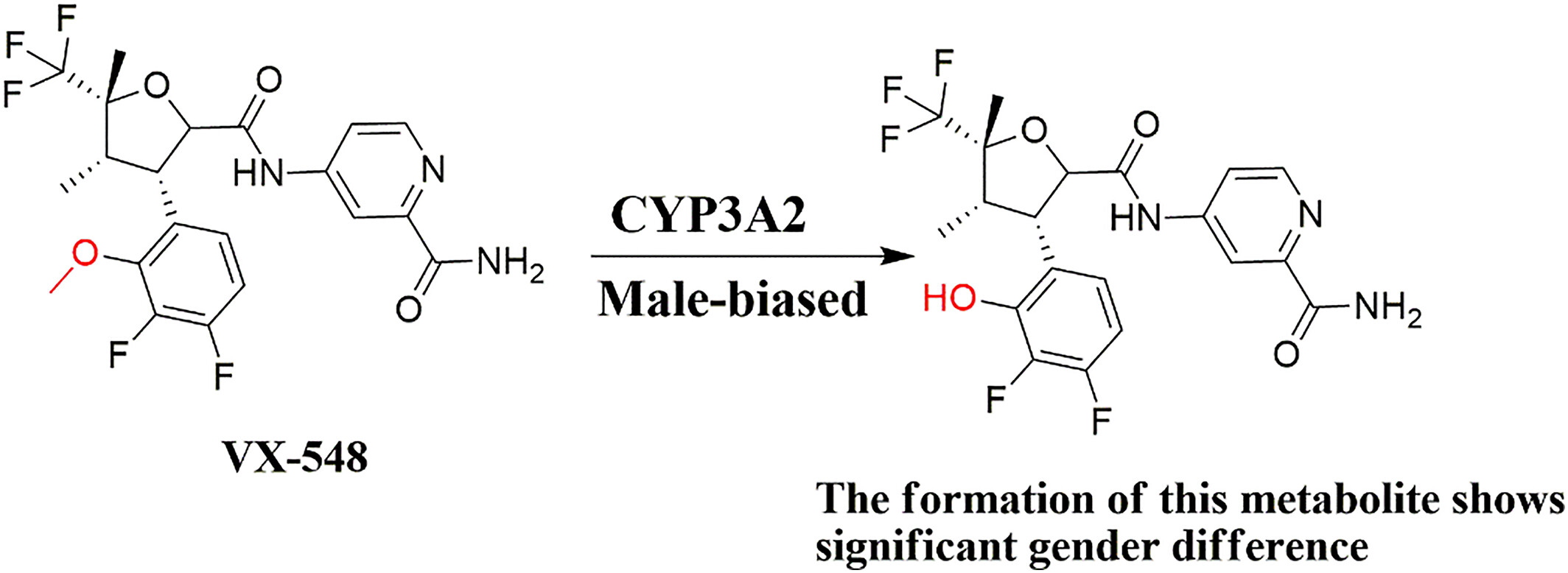
Gender difference in the pharmacokinetics and metabolism of VX-548 in rats
- Pages: 107-114
- First Published: 04 April 2024