Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Image
Cover Image, Volume 52, Issue 5
- Pages: i-ii
- First Published: 25 January 2014

On page 596, Sanghun Han and Yong-beom Lim report on the development of polyacrylamide gel stabilization electrophoresis (PASE) technology to covalently capture, physically constrain, and stabilize biologically active α-helical peptides (green) into a polyacrylamide hydrogel network (white). They synthesized a bioactive RNA-binding helical peptide with acryloyl groups at both ends of the peptide, covalently captured in its bioactive helical conformation into the polyacrylamide network via radical polymerization, and investigated whether the peptide can specifically recognize its target RNA molecule. This newly developed technology has the potential to be applied in many applications in which specific biomacromolecular recognition is necessary within a polymer hydrogel network.
Cover Image, Volume 52, Issue 5
- Pages: iii-iv
- First Published: 25 January 2014
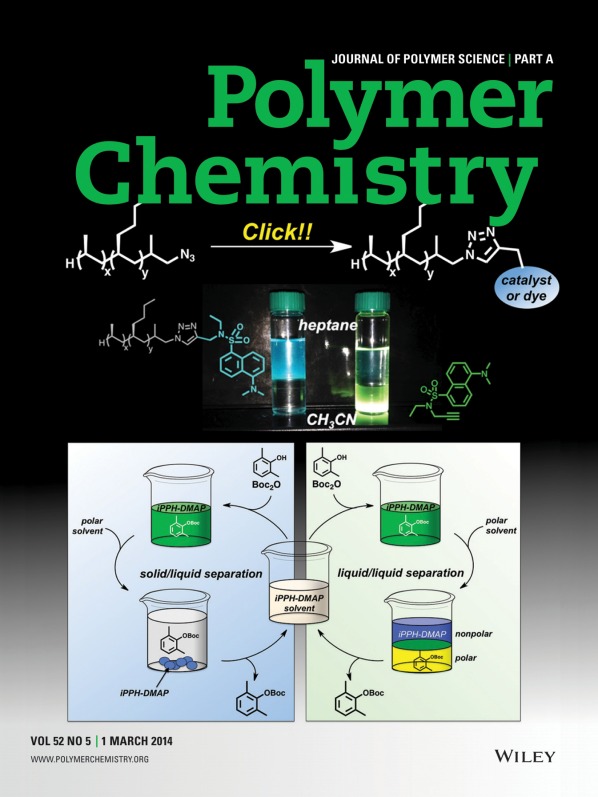
Various functionalities could be installed on the terminus of commercially-available isotactic-poly(propylene-co-hexene) (iPPH) using standard organic transformations, as presented by Abbey Hicks, Binhong Lin, Philip L. Osburn, and Christopher E. Hobbs on page 600. An atom-economical, copper-catalyzed click reaction could also be utilized to prepare useful iPPH-supported species that exhibited high phase-selective solubility (>98%) for nonpolar solvents over their polar counterparts. This feature allowed for the liquid/liquid recovery and reuse of an iPPH-supported DMAP organocatalyst. Furthermore, the semi-crystalline nature of this support permitted its recovery as a solid upon precipitation into a polar solvent. The ability to easily use more than one recovery technique makes iPPH an attractive, versatile support.
Rapid Communications
Cis/Cis-2,5-dipropenylthiophene monomers for high-molecular-weight poly(2,5-thienylene vinylene)s through acyclic diene metathesis polymerization
- Pages: 591-595
- First Published: 07 December 2013
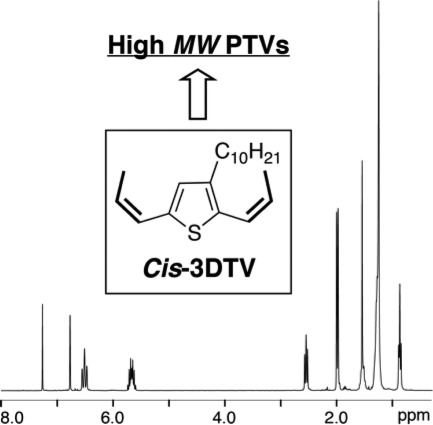
The synthesis of the 2,5-dipropenylthiophene monomer possessing exclusively cis-double bond configurations through the reduction of a dipropynylthiophene precursor is reported. Lindlar's catalyst is found to be completely ineffective, while a dissolving metal method involving activated zinc is successful in alkyne reduction to cis-alkenes with high yields and excellent selectivity. The acyclic diene metathesis polymerization of the monomer affords the poly(2,5-thienylene vinylene) polymer of a high molecular weight.
Covalent capture of α-helical peptides in polymer hydrogel network for polyacrylamide gel stabilization electrophoresis
- Pages: 596-599
- First Published: 16 December 2013
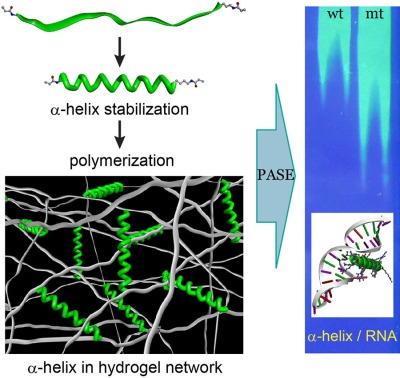
A strategy to incorporate, physically constrain, and stabilize biologically active α-helical peptides into the polyacrylamide hydrogel network is developed. A bioactive RNA-binding helical peptide with polymerizable acryloyl groups at both ends of the peptide is synthesized and covalently captured in its bioactive helical conformation into the polyacrylamide network via radical polymerization. The usefulness of this approach is demonstrated by the specific recognition of RNAs in the polyacrylamide gel stabilization electrophoresis (PASE) system.
Articles
Use of an isotactic-propylene/hexene copolymer as a new, versatile, soluble support
- Pages: 600-605
- First Published: 26 November 2013
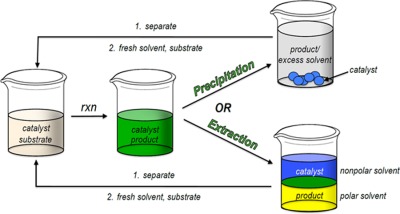
A new isotactic-poly(propylene-co-hexene) (iPPH)-supported catalyst is described. Soluble polymer-supports are typically used for catalyst recovery and reuse using either one of two methods (solid/liquid or liquid/liquid), depending on the polymer's solubility. The need for robust, versatile supports that can be used for more than one type of recovery is evident. The iPPH-supported DMAP catalyst can be used in both liquid/liquid and liquid/solid recovery techniques, which allow for its recovery and reuse.
Spotlight Article
Bifunctional 2-(alkoxycarbonothioylthio)acetic acids for the synthesis of TiO2-poly(vinyl acetate) nanocomposites via RAFT polymerization
- Pages: 606-618
- First Published: 14 January 2014
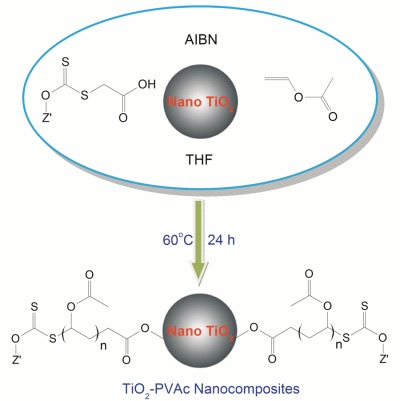
Reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) polymerization of vinyl acetate (VAc) is challenging, requiring special chain-transfer agents (CTAs) such as xanthate esters. However, bifunctional CTAs suitable for coordination to metal oxide nanoparticles and RAFT polymerization are not available. Herein, four bifunctional RAFT CTAs with –COOH functionalities containing methoxy, ethoxy, isopropoxy, and octyloxy groups, respectively, are synthesized. Polymerizations of VAc using these CTAs exhibit living behavior. A one-pot process is developed to show the functionality of this approach.
Investigation of sequence isomer effects in AB-polybenzimidazole polymers
- Pages: 619-628
- First Published: 30 November 2013
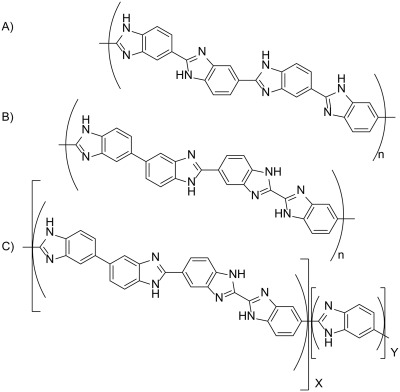
A unique series of random polybenzimidazole (PBI) copolymers consisting of the recently reported novel isomeric AB-PBI (i-AB-PBI) and the well-known AB-PBI are synthesized. The r-AB-PBI system introduces disorder through random isomerism in polymer sequences when compared with the ordered structures of both AB-PBI and i-ABPBI. Random copolymers varying in composition at 10 mol % increments are synthesized to evaluate the effects of sequence isomerism. The disrupted regularity of the sequence in the polymer main chain is found to affect fundamental polymer properties, such as chain packing, solubility, glass transition temperatures (Tg), and membrane properties for high-temperature fuel cell applications.
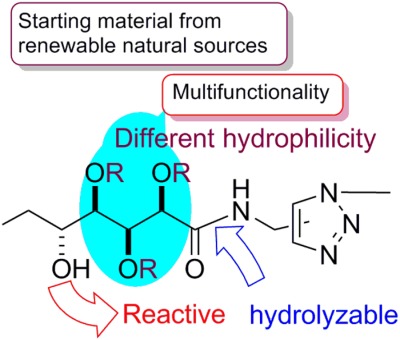
Linear poly(amide triazole)s derived from d-glucose
- Pages: 629-638
- First Published: 03 December 2013
Spotlight Article
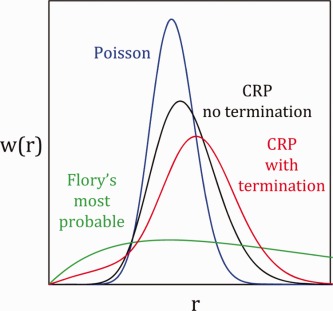
Modeling molecular weight distribution and effect of termination in controlled radical polymerization: A novel and transformative approach
- Pages: 639-651
- First Published: 17 December 2013
Synthesis, characterization, and applications in photovoltaic cells of oxetane-functionalized P3HT derivatives
- Pages: 652-663
- First Published: 07 December 2013
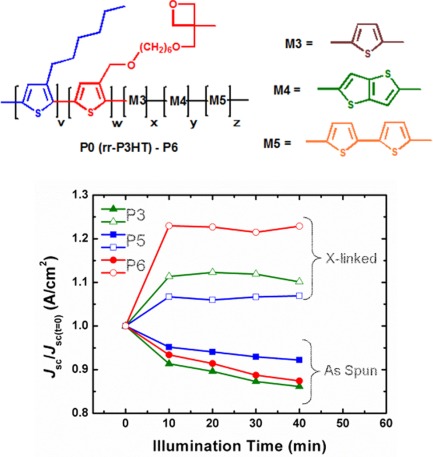
A series of new crosslinkable conjugated polymers, derivatives of region-regular poly(3-hexylthiophene), are synthesized and investigated in organic photovoltaic devices. The individual effect of the conditions employed in the crosslinking is investigated, and an overall beneficial effect upon crosslinking on the device stability is shown.
Spotlight Article
Ring-opening polymerization of cyclic ethers initiated by benzazaphosphole-W(CO)5/silver hexafluoroantimonate
- Pages: 664-670
- First Published: 18 December 2013
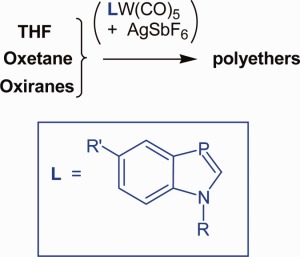
LM(CO)5 complexes 1a–e of benzazaphospholes, π-excess aromatic PC ligands, react with AgSbF6 to highly reactive species, which act as efficient initiators of the ring-opening polymerization of cyclic ethers like tetrahydrofuran (even at −30 °C), oxetane, or epoxides and likewise start copolymerizations of these ethers. In other solvents, such as dichloromethane or toluene, they trap traces of OH nucleophiles by addition at the PC bond, for example, MeOH to 2a, characterized by crystal structure analysis; although without AgSbF6 the complexes 1a–e or the respective ligands L are stable to nucleophiles, including OH compounds.
Side chain impacts on pH- and thermo-responsiveness of tertiary amine functionalized polypeptides
- Pages: 671-679
- First Published: 22 December 2013
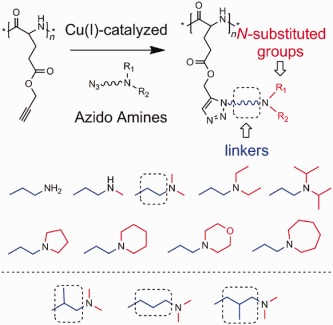
A series of tertiary amine functionalized poly(L-glutamate)s (TA-PGs) are synthesized by the copper-catalyzed azide-alkyne cycloaddition (CuAAC) click reaction of azido tertiary amines with poly(γ-propargyl-L-glutamate) (PPLG). The pH- and thermo-responsiveness of the resulting TA-PGs are tested and found to be dependent on the structures of Nsubstituted groups and “linkers” in the side chains.
Synthesis and characterization of polyurethane ionomers with trimellitic anhydride and dimethylol propionic acid for waterborne self-emulsifying dispersions
- Pages: 680-690
- First Published: 16 December 2013
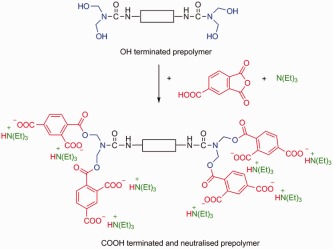
Polyurethane ionomers with terminal COOH groups are synthesized by using trimellitic anhydride (TMA). The neutralization with triethyl amine (TEA) enables the dispersibility into water. The benefit of COOH groups located at the polymer chain end are pH values in the range of 6.7–6.9. Additionally, ionomers are developed with a combined stabilization with TMA and dimethylol propionic acid. Mechanical properties and thermal behaviors of the films can be controlled through the incorporation of these ionic building blocks.
Preparation and characterization of solution processable phthalocyanine-containing polymers via a combination of RAFT polymerization and post-polymerization modification techniques
- Pages: 691-698
- First Published: 17 December 2013
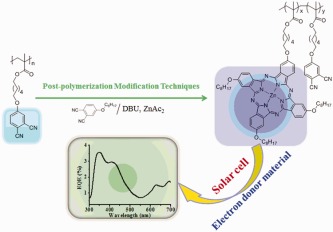
Polymers with benzendinitrile side chains are synthesized via reversible additionfragmentation chain transfer. Soluble Zn(II) phthalocyanine (Pc)-containing (ZnPc) polymers are achieved by post-polymerization modification of the obtained polymers. The potential application of this ZnPc-functionalized polymer as an electron donor material in a bulk heterojunction organic solar cell is studied.
Synthesis of methacrylate polymer bearing cyanate groups and its chemoselective reaction with amines
- Pages: 699-706
- First Published: 16 December 2013
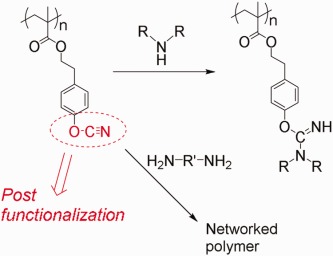
A novel cyanate-containing reactive polymer, poly[2-(4-cyanatophenyl)ethyl methacrylate] (PCPMA), is designed and synthesized for post-functionalization at the cyanate ester moiety. The model reaction reveals that the cyanate ester shows chemoselective reactivity with aliphatic amines. The post-functionalization of PCPMA is achieved by the reaction with a secondary aliphatic amine or by the crosslinking with aliphatic diamines.
Spotlight Article
Novel 9,9′-(1,3-phenylene)bis-9H-carbazole-containing copolymers as hole-transporting and host materials for blue phosphorescent polymer light-emitting diodes
- Pages: 707-718
- First Published: 17 December 2013
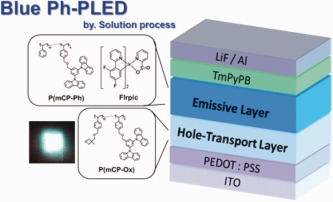
Novel photo-crosslinkable hole-transport and host materials incorporated into multilayer blue phosphorescent polymer light-emitting diodes (Ph-PLEDs) are demonstrated. The oxetane-containing copolymers, which function as hole-transport layers, could be cured by UV irradiation in the presence of a cationic photoinitiator. The blue Ph-PLEDs made of a new hole-transporting polymer exhibit a maximum external quantum efficiency of 2.55% and a luminous efficiency of 8.75 cd A−1.
Electrolytes for quasi solid-state dye-sensitized solar cells based on block copolymers
- Pages: 719-727
- First Published: 22 December 2013
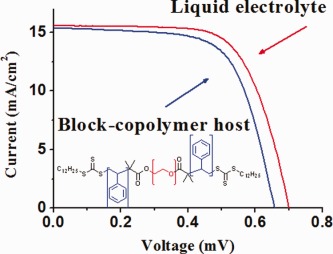
For the first time, block-copolymers are used as polymeric hosts for electrolytes in quasi solid-state dye-sensitized solar cells. The use of block-copolymers allows the tuning of properties and morphologies that, in turn, affect device performances. For the optimal ratio of polystyrene:poly(ethylene oxide), overall power conversion efficiencies comparable to that of conventional liquid solar cells are obtained.
Obtaining of hybrid nanocomposites by simultaneous photopolymerization of some urethane monomers and photoinduced formation of gold nanoparticles
- Pages: 728-738
- First Published: 18 December 2013
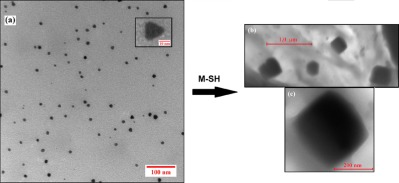
Photopolymerized composites containing in situ photogenerated gold nanoparticles are synthesized, and the degree of conversion of double bonds from urethane dimethacrylates is greater than 70% (after 5 min of UV irradiation). These nanoparticles present a resonance plasmon band at 535 nm and emit fluorescence at 575 nm. X-ray spectroscopy, transmission electron microscopy, and small angle X-ray scattering technique analyses demonstrate their homogeneous distribution in the matrix. The addition of thiol methacrylate controls the size and shape of gold nanoparticles.