Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Image
Cover Image, Volume 50, Issue 9
- Pages: i-ii
- First Published: 27 March 2012

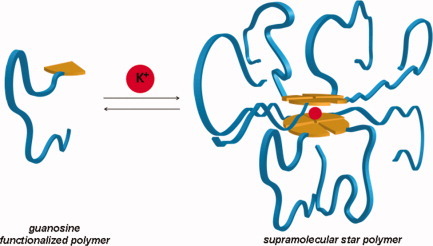
Interaction between a potassium cation and guanosine end-functional polymer chains leads to the formation of a supramolecular star polymer. In the work on page 1844, Anzar Khan and colleagues take a detailed look at this non-covalent synthesis of the polymeric branched architectures. The top part of the image depicts the necessary components for the supramolecular synthesis: a potassium cation (shown as red sphere) and the end-functional polymer chains. The bottom part shows the assembly of eight polymer chains around a central metal cation. The supramolecular star polymer core (the sandwich structure) is stabilized via a combination of hydrogen bonding, π–π stacking, and cation–dipole interactions.
Inside Cover, Volume 50, Issue 9
- Pages: iii-iv
- First Published: 27 March 2012
One-pot synthesis of well-defined molecular brush copolymers by a tandem reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer polymerization (RAFT) and ring-opening metathesis polymerization (ROMP) “grafting-through“ strategy is represented by Karen L. Wooley and colleagues on page 1681. The image depicts the “grafting-through“ synthesis of brush copolymers by end-group polymerization of macromonomers, which are constructed by polymerizing the monomers from chain transfer agents or initiators with norbornenyl groups. In addition, the atomic force microscopy (AFM) 3D-image shows the bottlebrush-like morphologies of brush copolymers on mica surface, caused by densely grafted side chains along the backbone.
Rapid Communications
Soluble reduced graphene oxide functionalized with conjugated polymer for heterojunction solar cells
- Pages: 1663-1671
- First Published: 10 February 2012
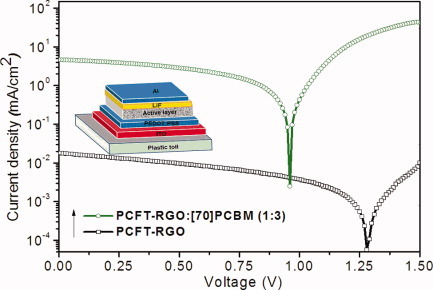
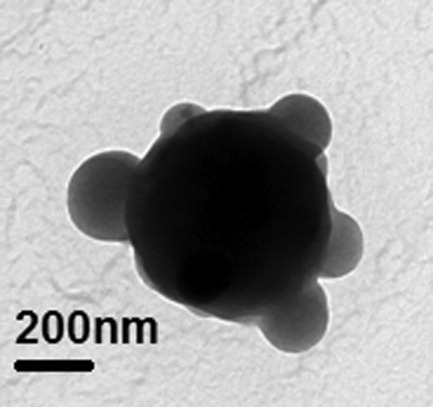
A solution-processable conjugated polymer PCTF-convalently grafted reduced graphene oxide (PCTF-RGO) was synthesized by the 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition of azomethine ylide. The short-circuit current density and power conversion efficiency of a photovoltaic device based on the spin-coated PCTF-RGO/[70]PCBM heterostructure reached 260 and 145 times higher than those of the device without [70]PCBM, respectively.
4-dimethylaminopyridine-based organoactivation: From simple esterification to lactide ring-opening “Living” polymerization
- Pages: 1672-1680
- First Published: 10 February 2012
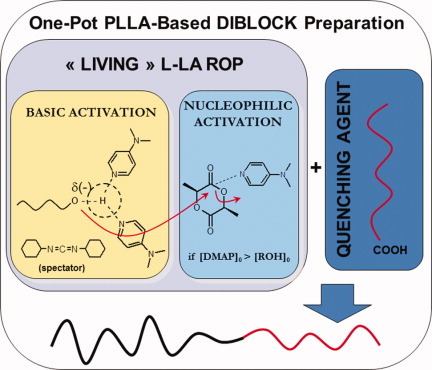
In this research, an equimolar mixture of DCC and DMAP has been used to catalyze the L-LA ROP in DCM at r.t. Kinetically, the mixture has been proved as efficient as the DMAP alone, which has been demonstrated activating both L-LA and free alcohol during the process. The presence of the DCC improves the living character of the process and allows the generation of pure diblock when quenching the L-LA ROP by addition of a stoichiometric amount of PEO-COOH.
One-pot, facile synthesis of well-defined molecular brush copolymers by a tandem RAFT and ROMP, “Grafting-through” strategy
- Pages: 1681-1688
- First Published: 10 February 2012
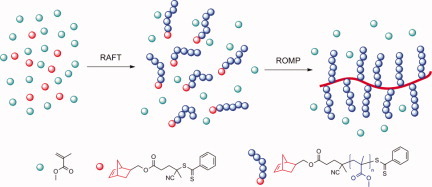
Two well-defined brush copolymers, PNB-g-PMMA, were synthesized by a one-pot, RAFT/ROMP, “grafting-through” method, without intermediate steps of isolation or purification. The controlled dimensions of the brushes were verified by atomic force microscopy. This strategy significantly simplified the synthesis of brush copolymers when compared with conventional methods.
Articles
A novel polymerization approach via thiol-yne addition
- Pages: 1689-1695
- First Published: 10 February 2012
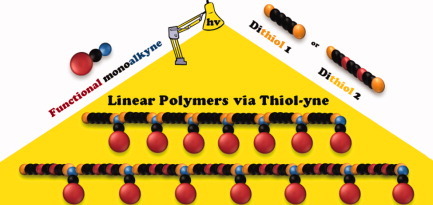
A novel approach to prepare linear polymers with various side chains and functional groups using thiol-yne polymerization is reported. Model reactions and reaction optimization led to the conclusion that a ratio of 2:1 of the reacting thiol and triple bond functional groups leads to linear polymers in a step-growth fashion. Thermal, self-initiated, and photoinitiated routes were investigated revealing that the photoinitiated reactions provided the highest molecular weights and fastest reaction times.
Investigation on dual properties of photosensitive thermotropic liquid-crystalline poly(benzylidene-ether)s containing alkanones and methylene spacers in the main chain
- Pages: 1696-1706
- First Published: 10 February 2012
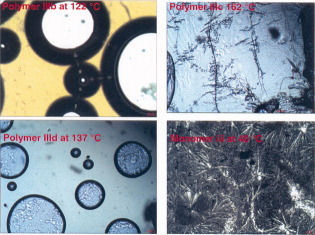
HOPM study showed that cyclohexanone-containing polyethers exhibit nematic threadlike and droplet texture. On increasing length of spacer and presence of methoxy substituent in aromatic rings have significant influence on their absorption and emission. EZ isomeric structure of benzylidene polyethers containing cyclohexanone, giving rise to a nonlinear, semirigid structure, fulfilling the requirement of geometrical anisotropy necessary for molecule to be mesogen to display LC characteristics.
Synthesis of [CH2C(CO2Et)2CH2Ar]n polymers and their unique optical properties by through-space interactions between Ar and CO groups
- Pages: 1707-1716
- First Published: 03 February 2012
![Synthesis of [<span class='icomoon'></span>CH2C(CO2Et)2CH2Ar<span class='icomoon'></span>]n polymers and their unique optical properties by through-space interactions between Ar and CO groups](/cms/asset/e2ed057e-a260-46ec-94ad-84ad57855ea0/mgra001.jpg)
Polymers of type [CH2C(CO2Et)2CH2Ar]n (Ar = 1,4-phenylene, 2,6-naphthylene, 9,10-anthrylene, or 1,4-phenylene-ethynylene-1,4-phenylene) exhibited unexpectedly enhanced UV absorption and strong, broad, bathochromically shifted fluorescence spectra compared with the parent Ar compounds, the origin of which was postulated to be a configuration interaction between the π→π* excitation of the aromatic moiety and the n→π* excitation of the carbonyl moiety on the trimethylene tether via intramolecular charge transfer.
From poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-block-poly(ethylene oxide)-block-poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) triblock copolymer to poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-block-poly(ethylene oxide) hydrogels: Synthesis and rapid deswelling and reswelling behavior of hydrogels
- Pages: 1717-1727
- First Published: 03 February 2012
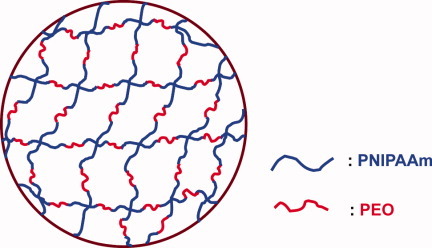
Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-block-poly(ethylene oxide) (PNIPAAm-b-PEO) copolymer networks were preparation via reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer polymerization with macromolecular design via the interchange of xanthate approach. In the PNIPAAm-b-PEO copolymer networks, poly(ethylene oxide) (PEO) chains were blocked into PNIPAAm networks. It was identified that the PNIPAAm-b-PEO hydrogels displayed fast deswelling and reswelling behavior compared with the control PNIPAAm hydrogel. The accelerated deswelling and reswelling behavior has been interpreted based on the formation of PEO microdomains in the PNIPAAm networks, which could act as the hydrophilic tunnels to facilitate the diffusion of water molecules in the PNIPAAm networks.
Synthesis, surface properties, and morphologies of poly[methyl(3,3,3-trifluoropropyl)siloxane]-b-polystyrene-b-poly(tert-butyl acrylate) triblock copolymers by a combination of anionic ROP and ATRP
- Pages: 1728-1739
- First Published: 10 February 2012
![Synthesis, surface properties, and morphologies of poly[methyl(3,3,3-trifluoropropyl)siloxane]-b-polystyrene-b-poly(tert-butyl acrylate) triblock copolymers by a combination of anionic ROP and ATRP](/cms/asset/07b0ea01-303f-48d0-b69e-df047de343ed/mgra001.jpg)
A series of well-defined poly[methyl(3,3,3-trifluoropropyl)siloxane]-b-polystyrene-b-poly(tert-butyl acrylate) (PMTFPS-b-PS-b-PtBA) triblock copolymers were prepared by a combination of anionic ring-opening polymerization and atom transfer radical polymerization. The results of contact angle measurements for the surfaces of PMTFPS-b-PS-b-PtBA triblock copolymers demonstrate that the compositions have an effect on the wetting behavior of the copolymer films. For the copolymer films with different compositions, there may be different microstructures on the outmost layer of the copolymer surfaces. The films with high content of PtBA blocks exhibit almost no ordered microstructures on the outmost layer of surfaces, even though they have microphase-separated structures in bulk.
Effects of salt and temperature on single-chained cationic surfactant/oligodeoxynucleotide vesicle formation
- Pages: 1740-1745
- First Published: 03 February 2012
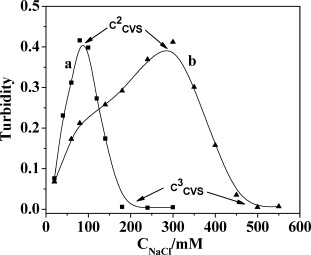
The figure shows the effects of NaCl on the turbidities of different single-chained cationic surfactant/oligodeoxynucleotide systems. A moderate content of NaCl can facilitate vesicle formation in these systems and high content of NaCl makes vesicle degraded. The enhanced hydrophobic interaction between surfactant and oligodeoxynucleotide with NaCl plays a key role for facilitating vesicle formation.
Crosslinked polynorbornene particles synthesis by ring-opening metathesis polymerization in dispersion
- Pages: 1746-1754
- First Published: 10 February 2012
Synthesis of polyamides from diols and diamines with liberation of H2
- Pages: 1755-1765
- First Published: 10 February 2012
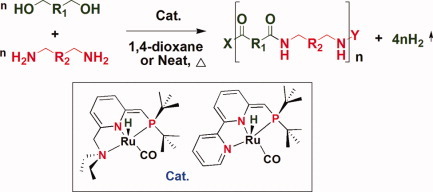
Environmentally benign synthesis of polyamides by dehydrogenative coupling of nonactivated diols with diamines (both aromatic and aliphatic diols and diamines), with Mn up to 26.9 kDa, is catalyzed by dearomatized ruthenium-pincer PNN complexes. This atom-economic process operates under neutral, homogeneous conditions and generates only molecular hydrogen as byproduct. Conditions for polyamidation in the absence of solvent are also reported, representing a “green” reaction. Gel permeation chromatography of the dimethylformamide-soluble polymers, MALDI-TOF, and thermal studies of the polyamides are reported.
Original diols from sunflower and ricin oils: Synthesis, characterization, and use as polyurethane building blocks
- Pages: 1766-1782
- First Published: 13 February 2012
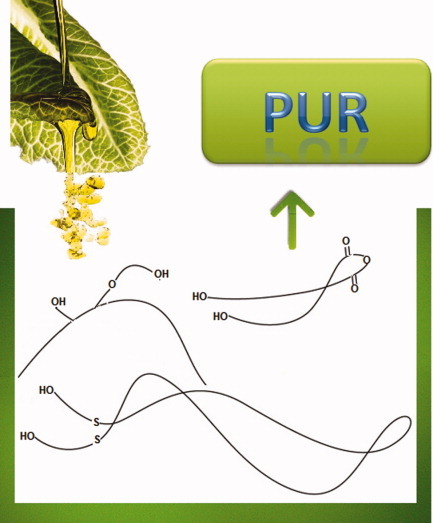
Several new vegetable oil-based diols were designed and synthesized starting from sunflower and ricin oils. Purification and structure determination of these diols were performed by HPLC/GC and NMR spectroscopy. These diols with isophorone diisocyanate were then efficiently used to synthesize well-defined polyurethanes (PUs). The effect of the diol nature and purity on the PU features was investigated. The structural characterization of the different PUs was carried out by means of IRFT, 1H NMR, and 1H DOSY NMR spectroscopy. The thermal and rheological properties of these new PUs were found dependent on the chemical structure and purity of the diol-building blocks.
Poly(ethylene glycol)–poly(L-lactide) star block copolymer hydrogels crosslinked by metal–ligand coordination
- Pages: 1783-1791
- First Published: 10 February 2012
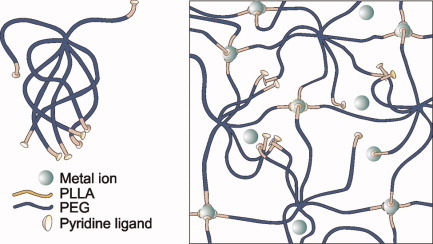
In aqueous solutions, pyridine-end-functionalized poly(ethylene glycol)–poly(L-lactide) star block copolymers self-assemble into micelles and micellar aggregates at low concentrations and form physically crosslinked, thermoreversible hydrogels above a critical gel concentration of 8% w/v. The presence of Mn(II) ions results in increased aggregate dimensions, a larger gel window, and increased in vitro stability due to the coordination of pyridine ligands around the metal centers, thereby introducing additional crosslinks. Importantly, the stabilizing effect of metal–ligand coordination is noticeable at very low, nontoxic metal ion concentrations.
Amphiphilic mesogen-jacketed liquid crystalline polymers: Design, synthesis, and self-assembly behaviors
- Pages: 1792-1800
- First Published: 10 February 2012
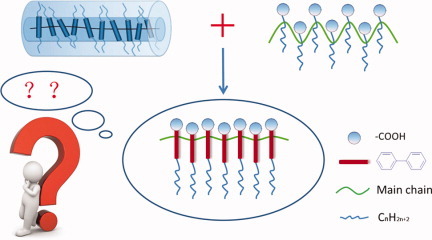
A series of amphiphilic mesogen-jacketed liquid crystalline (LC) polymers with a biphenyl side-chain mesogen containing a carboxylic acid group on one side and an octyloxy group on the other were synthesized. The results revealed that the polymer without any methylene spacer, POBP-0C, did not exhibit LC properties, while POBP-1C (n =1) and POBP-7C (n = 7) formed double layer smectic A (SA) phases. The solution self-assembly behaviors were also preliminarily investigated through the fluorescent probe technique and transmission electron microscopy, and vesicles with uniform sizes were observed.
A detailed surface analytical study of degradation processes in (meth)acrylic polymers
- Pages: 1801-1811
- First Published: 10 February 2012
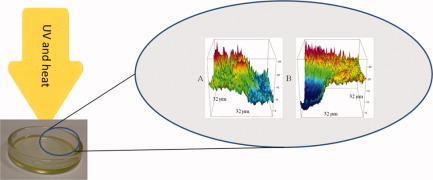
The study investigates the degradation behavior of various high molecular weight acrylic polymers namely poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA), poly(n-butyl methacrylate) (PBMA), poly(n-butyl acrylate) (PBA) and poly(lauryl methacrylate) (PLMA) under extreme environmental conditions via X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and high resolution FTIR microscopy imaging.
Alternating copolymers with degradability and quantitatively controlled thermosensitivity
- Pages: 1812-1818
- First Published: 10 February 2012
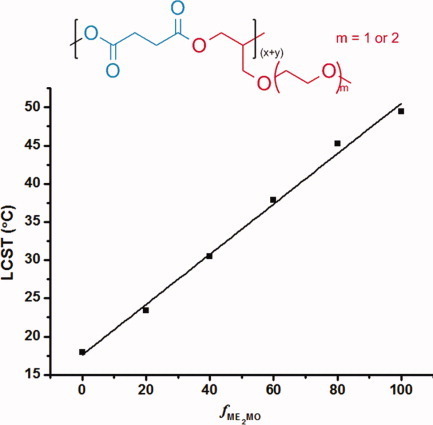
By introducing degradability to thermoresponsive polymers, the P(MEMO/ME2MO-alt-SA) thermoresponsive polyesters were designed and prepared. The lower critical solution temperature of the copolymers could be precisely and quantitatively controlled within a temperature range covering physiological temperature by a linear equation. And the thermal properties of P(MEMO/ME2MO-alt-SA) copolymers also exhibited very interesting composition dependence. More importantly, the polyester backbone of P(MEMO/ME2MO-alt-SA)s endows them with degradability and appropriate degradable periods in vitro.
Synthesis of arborescent styrene homopolymers and copolymers from epoxidized substrates
- Pages: 1819-1826
- First Published: 10 February 2012
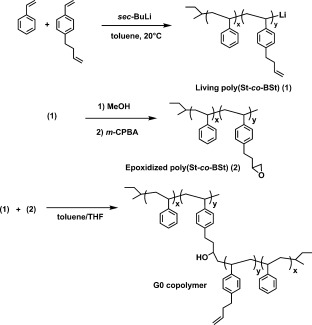
Arborescent styrenic homopolymers and copolymers were obtained by anionic polymerization and grafting. Styrene and p-(3-butenyl)styrene were first copolymerized using sec-butyllithium in toluene and epoxidized with m-chloroperbenzoic acid. A comb-branched copolymer structure was obtained by coupling the linear epoxidized substrate with living styrene-p-(3-butenyl)styrene copolymer chains in toluene/THF. Further cycles of epoxidation and coupling reactions yielded arborescent copolymers of generations G1–G3. Arborescent styrene homopolymers were also obtained by grafting polystyrene side chains onto the linear and G0–G2 copolymer substrates. The graft polymers have low polydispersity indices (Mw/Mn = 1.02–1.15) and molecular weights increasing geometrically over successive generations.
Synthesis of well-defined poly(dimethylsiloxane) telechelics having nitrobenzoxadiazole fluorescent chain-ends via thiol-ene coupling
- Pages: 1827-1833
- First Published: 13 February 2012

Well-defined fluorescent PDMS telechelics having NBD fluorescent probes at both chain-ends were prepared by thiol-ene coupling of 6-mercapto-1-hexanol to divinyl-terminated PDMS and further esterification of the hydroxymethyl chain-ends with 6-(7-nitrobenzofurazan-4-ylamino)hexanoic acid. In order to get ultra-low molar mass distributions, the polymer samples were fractionated after the thiol-ene coupling step. The resulting well-defined NBD-tagged fluorescent PDMS telechelics (Mn = 96–152 kDa and Đ < 1.2) were characterized by SEC, 1H NMR, UV–visible, and fluorescence spectroscopies.
Synthesis, conformation transition, liquid crystal phase, and self-assembled morphology of thermosensitive homopolypeptide
- Pages: 1834-1843
- First Published: 13 February 2012
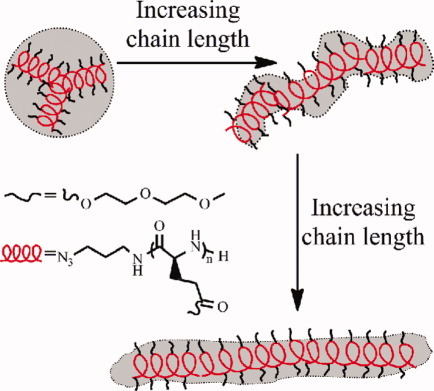
Thermosensitive poly-L-EG2-Glu homopolypeptide was synthesized via the ROP of EG2-Glu-NCA in DMF solution at 50 °C. In solid state, poly-L-EG2-Glu transformed from α-helix to β-sheet with increasing MW at room temperature, while it mainly assumed an α-helix in aqueous solution. Poly-L-EG2-Glu showed an irreversible LC phase transition in solid state, while it gave a reversible LCST behavior in aqueous solution. The self-assembled nanostructures changed from spheres to worm, then to fiber micelles with increasing MW.
Supramolecular star polymers with compositional heterogeneity
- Pages: 1844-1850
- First Published: 13 February 2012
Synthesis of poly(oligoaniline)s with structures controlled over three different oxidation states
- Pages: 1851-1860
- First Published: 10 February 2012
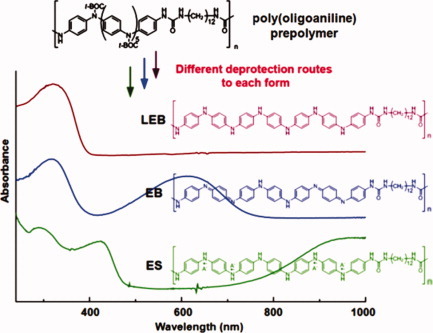
Poly(oligoaniline)s consisting of oligoaniline units linked by alkane spacers are synthesized with their structures controlled over three different oxidation forms. Each of the LEB, EB, and ES forms of the poly(oligoaniline)s is isolated by using distinct methods for deprotection of a t-BOC-protected prepolymer, enabling to exploit the crystalline structure, electrochemical activity, or conductivity as well as thin-film processability of oligoaniline-based materials.
3,6-Dialkylthieno[3,2-b]thiophene moiety as a soluble and electron donating unit preserving the coplanarity of photovoltaic low band gap copolymers
- Pages: 1861-1868
- First Published: 10 February 2012
![3,6-Dialkylthieno[3,2-b]thiophene moiety as a soluble and electron donating unit preserving the coplanarity of photovoltaic low band gap copolymers](/cms/asset/129be4d0-c6a3-4a01-8d1d-e986b2770a82/mgra001.jpg)
A new low band gap polymer including the unusual 3,6-dihexylthieno[3,2-b]thiophene unit as electron donating and coplanar moiety has been designed after theoretical calculations and successfully synthesized. The comparison with a less planar copolymer with an identical conjugated backbone pointed out the major impact of alkyl side chains anchoring position. The new polymer exhibits an extended absorption spectrum with a smaller band gap of 1.6 eV and a higher charge carrier mobility. A power conversion efficiency of 2.6% has been reached with this new polymer in classical bulk heterojunction devices.