Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Highlight
The discovery of polymer-clay hybrids
- Pages: 819-824
- First Published: 02 January 2004
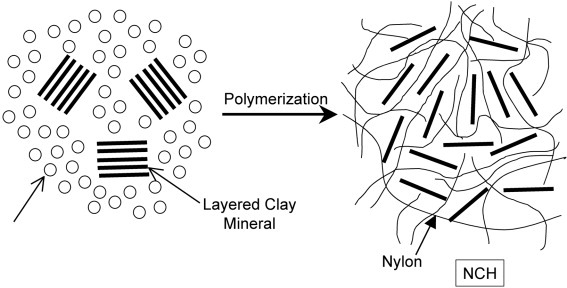
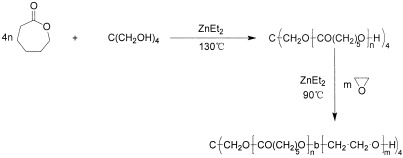
The first successful example of a polymer-clay hybrid was nylon-clay hybrid (NCH), which is a nanometer composite of nylon-6 and 1-nm-thick exfoliated aluminosilicate layers of the clay mineral. NCH was found and developed at Toyota Central Research and Development Laboratories over 17 years ago. NCH containing a few weight percentages of clay exhibits superior properties such as high modulus, high strength, and good gas-barrier properties. The key for NCH's creation was the polymerization of nylon monomer in the interlayer space of the clay. The development of NCH from its discovery to its commercialization is presented.
Articles
Synthesis and characterization of new, soluble polyazomethines bearing fluorene and carbazole units in the backbone and solubility-improving moieties in the side group
- Pages: 825-834
- First Published: 02 January 2004
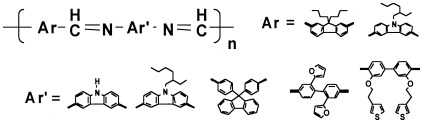
A series of new polyazomethines bearing fluorene and carbazole units on the backbone and solubility-improving moieties on the side group were synthesized. These polymers were thermally stable up to 370–464 °C, were soluble in organic solvents, and gave good-quality films. These solution-processable polyazomethines are potential candidate materials for microelectronic and optoelectronic devices as well as for aerospace parts.
Fully crosslinked poly(styrene-co-divinylbenzene) microspheres by precipitation polymerization and their superior thermal properties
- Pages: 835-845
- First Published: 02 January 2004
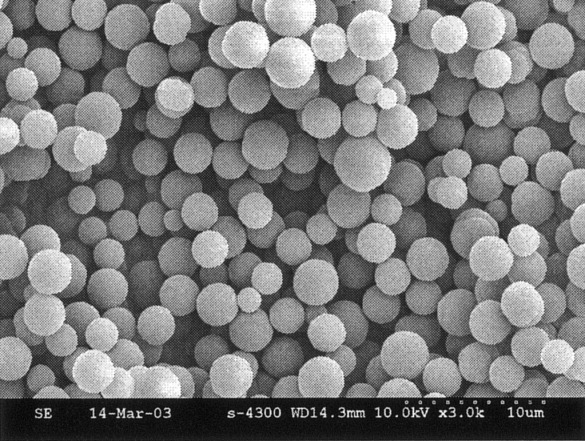

Poly(styrene-co-divinylbenzene) microspheres having a fully crosslinked structure were synthesized by a precipitation polymerization and the characteristics of the resultant polymer beads prepared with various concentrations of divinylbenzene were investigated including the improved thermal properties, particle size and the distribution, yield of polymerization, circularity, surface area, and the chemistry of the sol.
Photoinitiated, inverse emulsion polymerization of acrylamide: Some mechanistic and kinetic aspects
- Pages: 846-852
- First Published: 02 January 2004
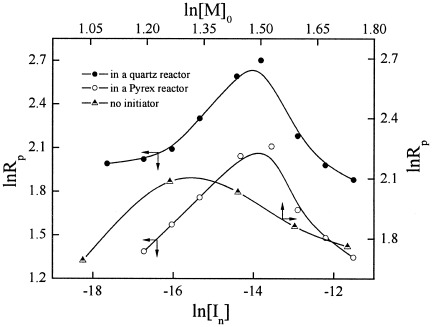
The kinetics of photoinitiated, inverse emulsion polymerization of acrylamide with 2,2-dimethoxy-2-phenylacetophenone as the initiator was investigated under three different situations. The initiator orders were negative at high initiator concentrations. The monomer orders at different initiator concentrations were lower than the first in a quartz reactor but greater than the first in a Pyrex reactor. Monomer participating in initiation and primary radical termination had some influence on the kinetics of polymerization.
Synthesis of semifluorinated block copolymers by atom transfer radical polymerization
- Pages: 853-861
- First Published: 02 January 2004
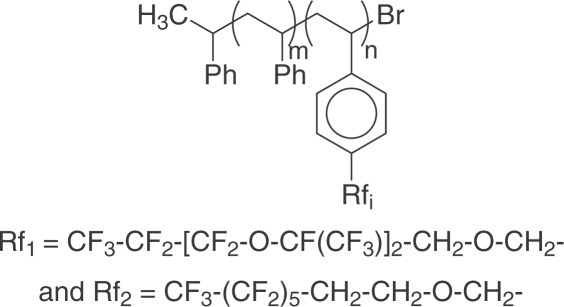
Two sets of styrene-based semifluorinated block copolymers, one with a perfluoroether pendant group and another with a perfluoroalkyl group, were synthesized by atom transfer radical polymerization. Microphase separation of the block copolymers was established by small-angle X-ray scattering and differential scanning calorimetry. The semifluorinated block copolymers possess low surface energies (ca. 13 mJ/m2), and they have potential as low-surface-energy additives or surfactants for supercritical CO2 applications.
Sulfonated naphthalene dianhydride based polyimide copolymers for proton-exchange-membrane fuel cells. I. Monomer and copolymer synthesis
- Pages: 862-874
- First Published: 06 January 2004
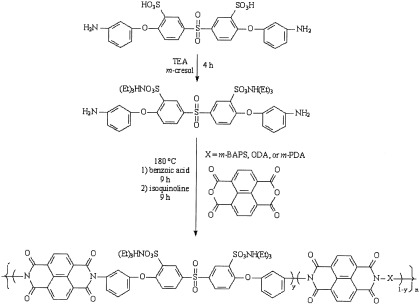
A novel sulfonated diamine, 3,3′-disulfonic acid-bis[4-(3-aminophenoxy)phenyl]sulfone (SA-DADPS), was prepared from m-aminophenol and disodium-3,3′-disulfonate-4,4′-dichlorodiphenylsulfone. The conditions necessary to synthesize and purify SA-DADPS in high yields were investigated in some detail. These materials showed much improved hydrolytic stability with respect to phthalimides. High-molecular-weight film-forming statistical copolymers with controlled degrees of disulfonation were prepared through variations in the stoichiometric ratio of disulfonated diamine (SA-DADPS) in its soluble triethylamine salt form to several unsulfonated diamines. Solution-cast films of the sulfonated copolymers were prepared and afforded tough, ductile membranes with high glass-transition temperatures.
Living anionic polymerization of lauryl methacrylate and synthesis of block copolymers with methyl methacrylate
- Pages: 875-882
- First Published: 02 January 2004
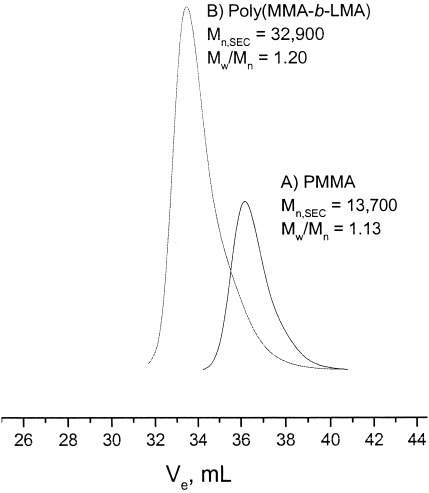
Anionic polymerization of lauryl methyl methacryalte (LMA) in the presence of additives such as dilithium salt of triethylene glycol, LiCl, and LiClO4 results in polymers with narrow molecular weight distribution (MWD) (<1.10). Diblock copolymers of methyl methacrylate and LMA were synthesized using DPHLi as initiator in THI at −40 °C by sequential addition of monomers.
Photoluminescent and electrochemical properties of novel copoly(aryl ether)s with isolated fluorophores
- Pages: 883-893
- First Published: 02 January 2004
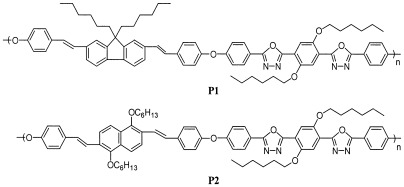
Copoly(aryl ether)s P1 and P2 with electron- and hole-transporting fluorophores were synthesized and characterized. Photoluminescent (PL) and electrochemical properties of copoly(aryl ether)s P1–P5 were investigated. Their PL spectra in the film state showed peaks around 420–498 nm. The emissions of P1 and P2 were compositions of the two isolated fluorophores, and that of P3 was dominated by the fluorophores with a longer emissive wavelength via the energy transfer. The formation of an interchain interaction in P4 and P5 was also observed.
Photopolymerization of acrylates without photoinitiators with short-wavelength UV radiation: A study with real-time fourier transform infrared spectroscopy
- Pages: 894-901
- First Published: 06 January 2004
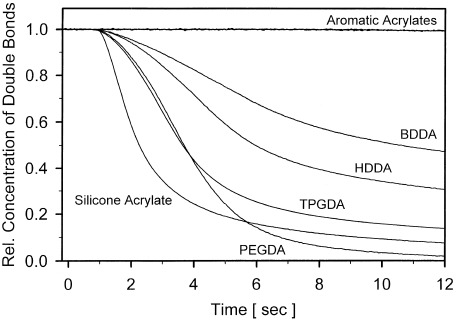
This article reports on the UV photopolymerization of acrylates without photoinitiators. Initiation of the reaction was achieved by direct excitation of the acrylates during irradiation with short-wavelength UV light with the 222-nm emission of a KrCl* excimer lamp. The reactivity of various acrylates was studied by real-time Fourier transform infrared–attenuated total reflection spectroscopy. The rate and the extent of the reaction within the layer were strongly dependent on the depth of penetration of UV light, which was determined by the molar extinction coefficient of the acrylate.
ATRP of methyl methacrylate using a novel binol ester-based bifunctional initiator
- Pages: 902-915
- First Published: 06 January 2004
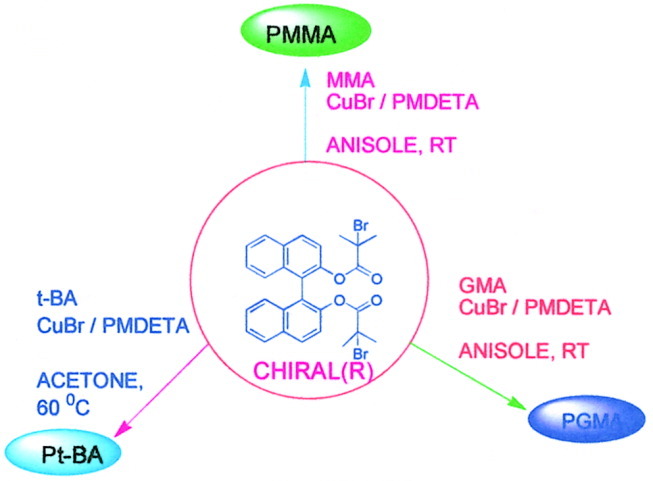
Novel bifunctional initiators obtained from the esterification of bi-2-naphthol were synthesized and used as initiators in atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP) in conjunction with N,N,N′,N′,N″-pentamethyldiethylenetriamine (PMDETA), and copper (I) bromide or copper (I) chloride. A detailed investigation of the ATRP of methyl methacrylate (MMA) in anisole was carried out at 30 °C. Thus MMA polymerization is shown to proceed with first-order kinetics, with predicted molecular weight and narrow polydispersity indices. The synthesis of glycidyl methacrylate (GMA), tert-butyl acrylate (tBA) and the triblock poly(tBA-b-MMA-b-tBA) by ATRP is also discussed.
Polymer–silicate nanocomposites produced by in situ atom transfer radical polymerization
- Pages: 916-924
- First Published: 06 January 2004

Polymer–silicate nanocomposites were synthesized with atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP) from initiator-modified silicates. This yielded homopolymers of styrene, n-butyl acrylate, and methyl methacrylate with predictable molecular weights and low polydispersities, both characteristics of living radical polymerization.
Synthesis and structural characterization of novel, fluorinated poly(phthalazinone ether)s containing perfluorophenylene moieties
- Pages: 925-932
- First Published: 06 January 2004
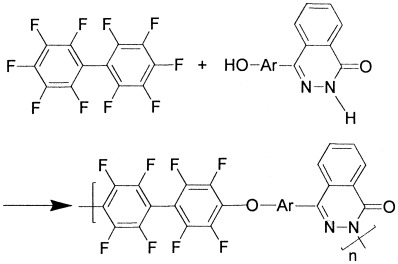
A series of novel, perfluorophenylene-containing poly(phthalazinone ether)s with good thermal stability and excellent solubility were synthesized by nucleophilic substitution polycondensation between perfluorobiphenyl and 4-(4′-hydroxyaryl)phthalazin-1(2H)-ones, and a convenient, efficient synthetic route of the monomers, 4-(4′-hydroxyaryl) phthalazin-1(2H)-ones, was developed.
Generation of highly stable amidate anion in anionic polymerization of 3-(triethylsilyl)propyl isocyanate
- Pages: 933-940
- First Published: 06 January 2004
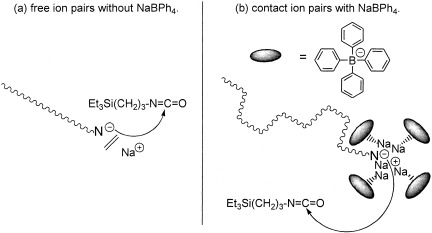
A highly stabilized amidate anion for anionic polymerization of isocyanate from 3-(triethylsilyl)propyl isocyanate (TEtSPI) was generated for the first time with the combined effect of the bulky substituent and the shielding action of the additive sodium tetraphenylborate (NaBPh4), extending the living character at least up to 120 min at −98 °C. Even the anion could exist at −78 °C for 10 min.
Synthesis and characterization of polyethylene/clay–silica nanocomposites: A montmorillonite/silica-hybrid-supported catalyst and in situ polymerization
- Pages: 941-949
- First Published: 06 January 2004
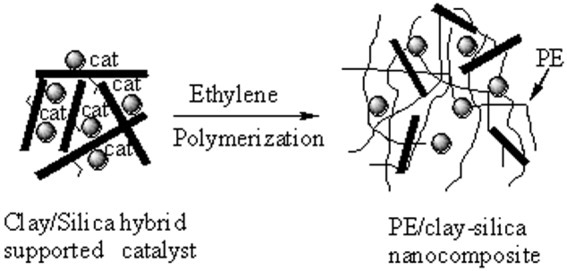
A novel approach to the preparation of polyethylene (PE) nanocomposites through insitu polymerization with montmorillonite/silica-hybrid-supported catalyst was developed. After ethylene polymerization, two classes of nanofillers (clay layers and silica nanoparticles) were dispersed concurrently in the PE matrix and PE/clay–silica nanocomposites were obtained.
Synthesis of four-armed poly(ε-caprolactone)-block-poly(ethylene oxide) by diethylzinc catalyst
- Pages: 950-959
- First Published: 06 January 2004
Controlled, radical reversible addition–fragmentation chain-transfer polymerization in high-surfactant-concentration ionic miniemulsions
- Pages: 960-974
- First Published: 06 January 2004
Living free-radical polymerization of methacrylate and styrenic monomers with ionic surfactants was carried out with reversible addition–fragmentation chain transfer in miniemulsion with different surfactant types and concentrations. The previously reported problem of phase separation was found to be insignificant at higher surfactant concentrations, and control of the molar-mass and polydispersity index was superior to that of published miniemulsion systems. Cationic and anionic surfactants were used to examine the validity of the argument that ionic surfactants interfere with transfer agents. Ionic surfactants were suitable for miniemulsion polymerization under certain conditions. The colloidal stability of the miniemulsions was consistent with the predictions of a specific model. The living character of the polymer that comprised the latex material was shown by its transformation into block copolymers.
A polymeric photobase generator containing oxime–urethane groups: Crosslinking reaction and application to negative photoresist
- Pages: 975-984
- First Published: 08 January 2004
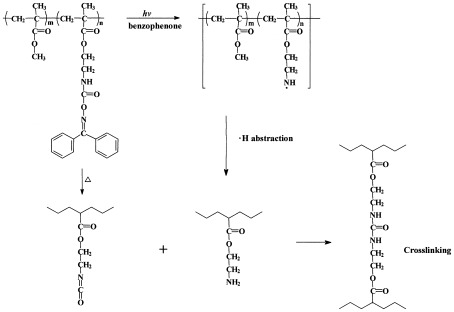
Photo-crosslinking and thermal crosslinking reaction of a polymeric photobase generator containing oxime–urethane groups after postexposure baking (PEB) were examined, with this crosslinking reaction was applied to a negative photoresist. Studies of a model reaction indicate that this thermal crosslinking reaction after PEB is due to the formation of urea-type chemical bonds between photochemically produced amino groups and thermally produced isocyanate groups from the oxime–urethane moieties.
Synthesis and characterization of a novel, fluoride-releasing dimethacrylate monomer and its dental composite
- Pages: 985-998
- First Published: 06 January 2004
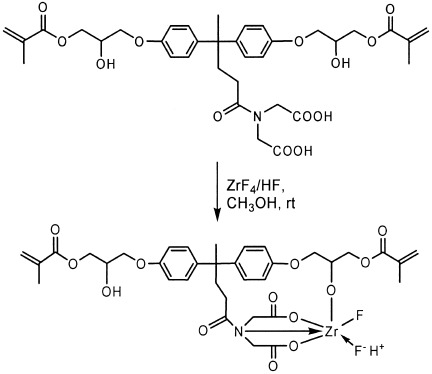
A novel, fluoride-releasing dimethacrylate monomer containing zirconium(IV) fluoride chelate was synthesized by an efficient four-step procedure starting from 4,4-bis-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-pentanoic acid and was characterized by electrospray mass spectrometry, Fourier transform infrared, and 1H and 13C NMR spectroscopies. The synthesized monomer was photopolymerized with camphorquinone and 1-phenyl-1,2-propane-dione as initiators and N,N-dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate as an accelerator. The experimental dental composite containing 13.7 wt % of the synthesized monomer showed significantly higher fluoride release and fluoride recharge capabilities than some commercial flowable composites.
Polymerization of 1,3-dienes with functional groups. III. Free-radical polymerization of N,N-diethyl-2-methylene-3-butenamide
- Pages: 999-1007
- First Published: 06 January 2004
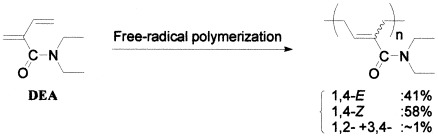
The free-radical homopolymerization and copolymerization behaviors of N,N-diethyl-2-methylene-3-butenamide (DEA) were investigated. The polymerization rate (Rp) equation was Rp ∝ [DEA]1.1[AIBN]0.51, and the overall activation energy of polymerization was 84.1 kJ/mol. The microstructure of the resulting polymer was exclusively a 1,4-structure where both the 1,4-E and 1,4-Z structures were included. From the product analysis of the telomerization with tert-butylmercaptan as a telogen, the modes of monomer addition were estimated both 1,4- and 4,1-addition. The copolymerization with styrene as a comonomer was carried out in benzene solution at 60 °C. The monomer reactivity ratios obtained were r1 = 5.8 and r2 = 0.05, and the Q and e values were Q = 8.4 and e = 0.33, respectively.
Synthesis and characterization of soluble polyimides derived from 2′,5′-bis(3,4-dicarboxyphenoxy)-p-terphenyl dianhydride
- Pages: 1008-1017
- First Published: 08 January 2004
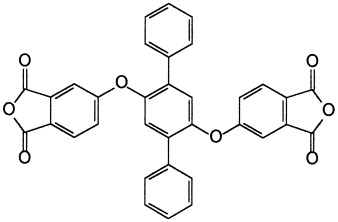
A series of new poly(ether imide)s containing laterally attached p-terphenyls was prepared from 2′,5′-bis(3,4-dicarboxyphenoxy)-p-terphenyl dianhydride and various aromatic diamines. These poly(ether imide)s were characterized by high solubility, good film-forming ability and mechanical properties, and high thermal stability.
Micron-granula polyolefin with self-immobilized nickel and iron diimine catalysts bearing one or two allyl groups
- Pages: 1018-1024
- First Published: 08 January 2004
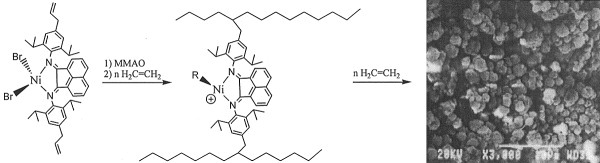
Nickel and iron diimine catalysts bearing one or two allyl groups can be used as catalysts for ethylene polymerization with high catalytic activities in the presence of modified methylaluminoxane (MMAO). The allyl substituents induced self-immobilization of the originally homogeneous catalysis and produced the micron-granula particles of polyethylene. The molecular structure of nickel catalyst [o,o′-bis(4-allyl-2,6-diisopropylphenyl-imino)acenaphthene] nickel(II) dibromide was characterized by crystallographic analysis.