Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Highlight
Emulsion polymerization: From fundamental mechanisms to process developments
- Pages: 1025-1041
- First Published: 12 January 2004
The investigations carried out at The University of the Basque Country to develop a knowledge-based strategy to achieve an efficient production of high-quality materials in a consistent, safe, and environmentally friendly way are reviewed. The aim of the research program was to gain insights in fundamental mechanisms to improve process development. Thus, films with superior properties are obtained by avoiding the deleterious effect of surfactant migration through optimal usage of surfmers.
Articles
Glow characterization in direct current plasma polymerization of trimethylsilane
- Pages: 1042-1052
- First Published: 12 January 2004
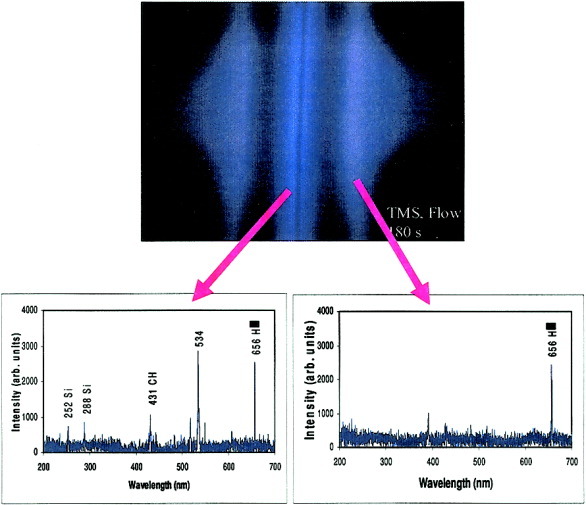
This article reports the dissociation glow found in a direct current glow discharge of trimethylsilane (TMS). Although a secondary negative glow appeared away from the cathode, the primary dissociation glow developed at the cathode surface where the most plasma polymers deposited. The plasma-diagnosis results showed that a dissociation glow mainly consists of polymerizable plasma species, whereas a negative glow contains hydrogen species that do not polymerize.
Very rapid copper-mediated atom transfer radical polymerization of benzyl methacrylate at ambient temperature
- Pages: 1053-1057
- First Published: 12 January 2004
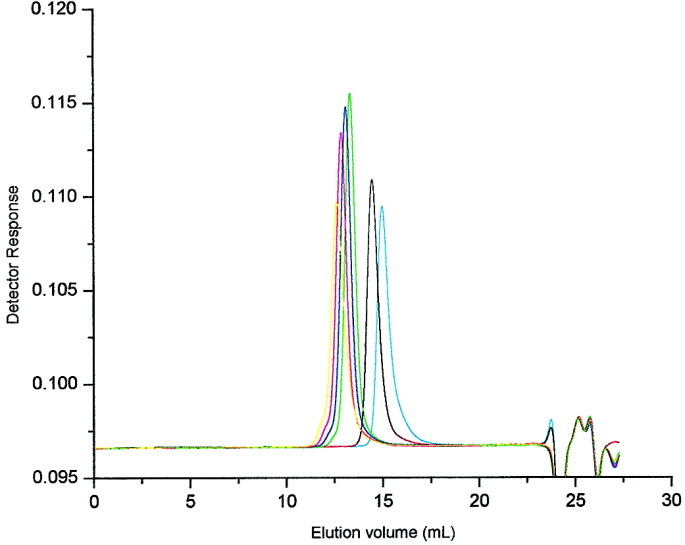
The very rapid bulk ATRP of benzyl methacrylate using CuX/PMDETA complex at room temperature is demonstrated. The experimental conditions required for the synthesis of low and high molecular weight poly(benzyl methacryalte) with low polydispersity are identified. The controlled/living nature of the polymerization is demonstrated through kinetic and chain-extension studies.
New blue electroluminescent n-type polyfluorene copolymers with a 1,3,4-oxadiazole unit in the main chain
- Pages: 1058-1068
- First Published: 12 January 2004
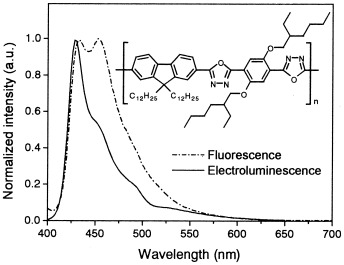
Novel polyfluorene copolymers alternately having 1,3,4-oxadiazole were prepared by simple polyoxadiazole synthetic methods and displayed highly efficient blue photoluminescence, the properties of which were affected by the extent of conjugation and the changes in the electron density by a side chain. They could be used as electron-transport/hole-blocking materials as well as blue emission materials for polymer light-emitting diodes, as determined by cyclic voltammetry.
Thermal behavior of poly(bisphenol A carbonate) in the presence of phosphorus compounds
- Pages: 1069-1074
- First Published: 12 January 2004
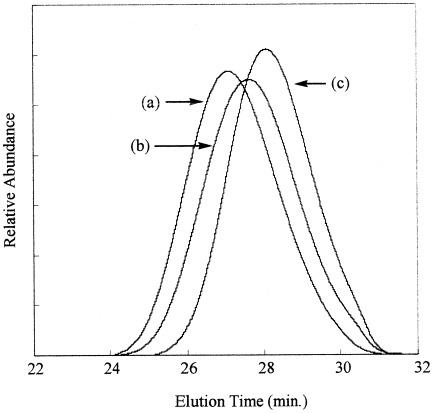
To clarify the interaction between poly(bisphenol A carbonate) and phosphorus compounds such as triphenylphosphine oxide (TPPO) and triphenyl phosphate (TPP), the polymer was heated in the presence of these phosphorus compounds at 240 °C for 2 h. When heated in the presence of TPPO, extensive decomposition of the polymer took place, resulting in a substantial decrease of the molecular weight. In contrast, the thermal treatment in the presence of the phosphates increased the molecular weight. Thermal treatment of PBAC in the presence of both TPPO and TPP allowed us to control the molecular weight with narrower distribution.
Preparation and characterization of chiral polyacrylates end-capped with bornyl groups in the side chains
- Pages: 1075-1092
- First Published: 12 January 2004

Chiral polyacrylates with bornyl end-capped side chains with four kinds of mesogenic moieties (azobenzene, biphenyl, benzoyloxy biphenyl, and phenyl benzoate) were prepared. The phase properties of the polymers were investigated with X-ray diffraction, differential scanning calorimetry, and polarizing optical microscopy. The thermogravimetric characteristics, the glass-transition temperatures and weight-average molecular weights, of the homopolymers were evaluated. The optical properties of the synthesized polymers in diluted solutions and in the thin-film state were also evaluated. The optical behavior of the composite films upon photoirradiation was investigated through the change in the transmittance of the probe light triggered by ultraviolet (365-nm) irradiation. Ultraviolet irradiation and heat treatment caused a reversible intensity change of the probe light at λ = 400 nm. The shrinkage of the photoisomerization of the composite films was also investigated with atomic force microscopy. A spot contraction appeared on the surface when it was irradiated with a laser light spot. The contraction was recovered by heat treatment at 80 °C for 10 min.
Performance of various activators in ethylene polymerization based on an iron(II) catalyst system
- Pages: 1093-1099
- First Published: 13 January 2004
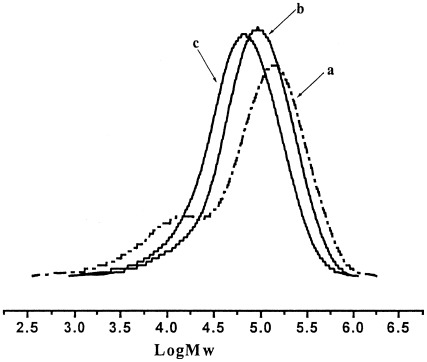
Ethylisobutylaluminoxane (EBAO) and its analogues were synthesized by a reaction between an triethylaluminum (Et3Al)/triisobutylaluminum (i-Bu3Al) mixture and 4-fluorobenzeneboronic acid, phenylboronic acid, or n-butaneboronic acid and subsequent hydrolysis with water. They were used as cocatalysts in ethylene polymerization catalyzed by an iron complex {[(ArNC(Me))2C5H3N]FeCl2, where Ar is 2,6-diisopropylphenyl}. Polyethylene with a high molecular weight and a narrow molecular weight distribution was prepared with modified EBAOs, and the performance of the iron complex at high polymerization temperatures was greatly improved. The activators for the iron complex also affected the polymerization activity and the molecular weight of the resultant polyethylene.
The effect of compositions and combinations of the reactants upon the copolycondensation of isophthalic acid/terephthalic acid with a combination of hydroquinones and bisphenols by tosyl chloride/dimethylformamide/pyridine
- Pages: 1100-1106
- First Published: 12 January 2004
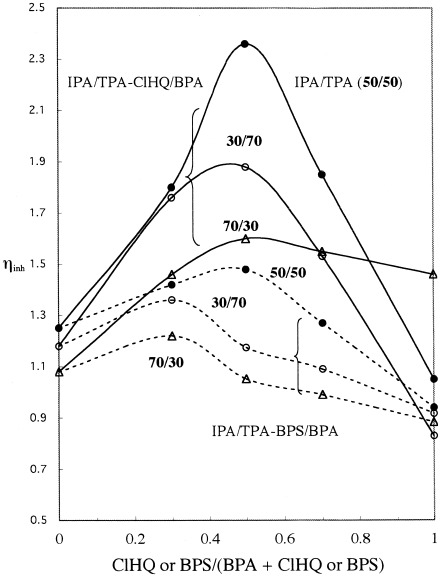
The copolycondensation of a mixture of isophthalic and terephthalic acids with several combinations of aromatic diols was studied from the viewpoint of how the compositions of the acids affected the reaction. The results were discussed by the change in the way the diols reacted with the associates of the activated diacids, which was estimated from sequence distributions of the diols in the resultant copolymers.
Synthesis of ultra-high-molecular-weight poly(α-olefin)s by thiobis(phenoxy)titanium/modified methylaluminoxane system
- Pages: 1107-1111
- First Published: 13 January 2004
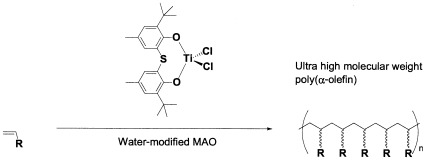
Polymerization of 1-butene with thiobis(phenoxy)titanium dichloride (TBPTiCl2) with modified methylaluminoxane (MMAO) yielded regioirregular and atactic poly(1-butene) with low molecular weight. However, productivity was increased and the structure of the obtained polymer was changed when water-modified MAO (WM-MMAO) was used as a cocatalyst. The molecular weight of obtained polymer with TBPTiCl2/WM-MMAO was dramatically increased and reached over 9 million g/mol. Poly(1-butene) produced by this catalytic system was almost regioregular and slightly isotactic. These results showed that the modified structure of the MMAO cluster by water affects the productivity, molecular weight, regioregularity, and stereoregularity of yielded polyolefins.
Silicone-based impact modifiers for poly(vinyl chloride), engineering resins, and blends
- Pages: 1112-1119
- First Published: 14 January 2004
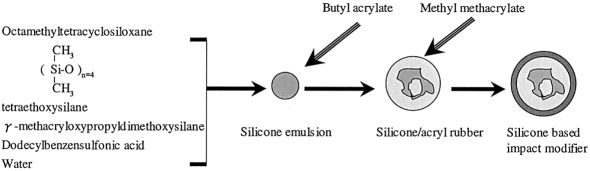
Silicone-based impact modifiers were composed of silicone/acrylic rubber cores and grafted acrylic shells. Through a toughness examination of modified poly(vinyl chloride) (PVC), the best composition of the silicone-based impact modifiers was obtained, and the silicone content in the rubber composition was 25 wt %. The silicone-based impact modifiers were blended with engineering resins such as PVC, polycarbonate (PC), poly(butylene terephthalate) (PBT), and PC/PBT mixtures. The results showed good weatherability and good toughness under low-temperature conditions for the silicone-based impact modifiers.
Synthesis and properties of novel Schiff base oligomers based on oligo-4-hydroxybenzaldehyde
- Pages: 1120-1125
- First Published: 16 January 2004
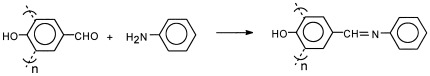
Condensation of oligo-4-hydroxybenzaldehyde with aniline, 2-chloroaniline, 2-aminophenol, 2-aminotoluene, 4-aminotoluene, and 4-nitroaniline gave the corresponding Schiff base oligomers (OFAP, OKAP, OHAP, OOAP, OTAP, and ONAP, respectively). Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) was used to compare the thermal stability of the oligomers, which showed the Schiff base oligomers to be resistant to thermooxidative decomposition. Weight loss of 5% and 50% occurred at temperatures of 122 and 475 °C; for OFAP, at 118 and 453 °C; for OKAP, at 182 and 491 °C; for OHAP, at 150 and 452 °C; for OOAP, at 132 and 401 °C; for OTAP, and at 193 and 414 °C for ONAP.
Effect of the crosslink density on the morphology and properties of reaction-injection-molding poly(urethane urea) elastomers
- Pages: 1126-1131
- First Published: 16 January 2004
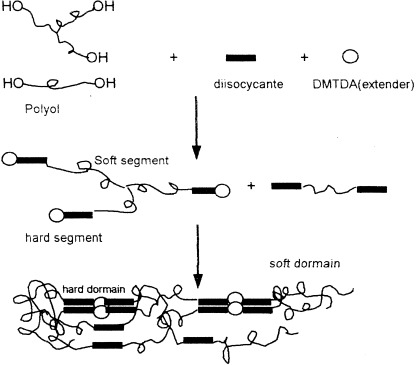
Two types of poly(urethane urea) (PUU) polymers, crosslinked PUU and linear PUU, were prepared by a reaction-injection-molding process. The relationship between the morphology and properties of PUU polymers with different network densities was investigated by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and differential scanning calorimetry, respectively. Because of the presence of covalent crosslinks, a significant difference in the morphology and properties between crosslinked PUU and linear PUU was observed.
Amphiphilic block copolymers of high-molecular-weight poly(ethylene oxide) and either ε-caprolactone or γ-methyl-ε-caprolactone: Synthesis and characterization
- Pages: 1132-1142
- First Published: 20 January 2004

Ethylene oxide (EO) has been block-polymerized with both ε-caprolactone (ε-CL) and γ-methyl-ε-caprolactone (MCL) through the combination of the anionic polymerization of EO and the ring-opening polymerization of ε-CL and MCL. A series of amphiphilic diblock copolymers with poly(ε-caprolactone) (semicrystalline) and poly(γ-methyl-ε-caprolactone) (amorphous) as the hydrophobic blocks have been prepared and characterized with size exclusion chromatography, 1H NMR, IR, and wide-angle X-ray scattering.
Synthesis of optically active polyurethanes by self-polyaddition of tyrosine-based monomers
- Pages: 1143-1153
- First Published: 20 January 2004
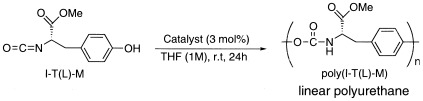
The synthesis and self-polyaddition of the optically active monomers I-T(L)-M and I-T(D)-M bearing both isocyanate and hydroxyl groups were examined. The self-polyaddition of I-T(L)-M and I-T(D)-M proceeded smoothly with triethylamine or tert-butyllithium as the initiator in tetrahydrofuran, affording the optically active linear polyurethanes poly[I-T(L)-M] and poly[I-T(D)-M] with number-average molecular weights in the range of 10,000–20,000 in excellent yields. The optical properties suggested that poly[I-T(L)-M] and poly[I-T(D)-M] have some higher order structures.
Synthesis of polybutadiene-based particles via dispersion ring-opening metathesis polymerization
- Pages: 1154-1163
- First Published: 20 January 2004
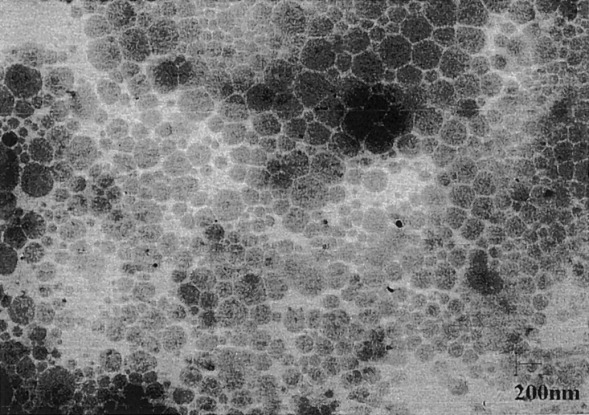
Latex particles based on 1,4-polybutadiene were synthesized via dispersion ring-opening metathesis copolymerization of 1,5-cyclooctadiene with a α-norbornenyl poly(ethylene oxide) macromonomer. Stable but polydisperse colloidal dispersions in the 50 nm to 10 μm size range were obtained. In this work, particular attention was paid to the effects of the kinetics of copolymerization on the structure of the graft copolymers formed and on the onset of turbidity. Strategies to prepare monodisperse polybutadiene particles were also designed through the growth of a polybutadiene shell from a well-defined polynorbornene seed.
Effects of tris(pentafluorophenyl)borane on the activation of a metal alkyl-free Ni-based catalyst in the polymerization of 1,3-butadiene
- Pages: 1164-1173
- First Published: 20 January 2004
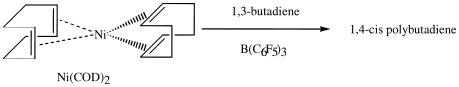
The activation of a metal alkyl-free Ni-based catalyst with B(C6F5)3 was investigated in the polymerization of 1,3-butadiene. It was found that a catalyst of bis(1,5-cyclooctadiene)nickel (Ni(COD)2)/B(C6F5)3 has a high catalytic activity and 1,4-cis stereoregularity, and provides polybutadiene having a molecular weight (Mw) of up to 117,000, even in the absence of AlR3 and MAO.
Dendritic homopolymers and block copolymers: Tuning the morphology and properties
- Pages: 1174-1188
- First Published: 20 January 2004
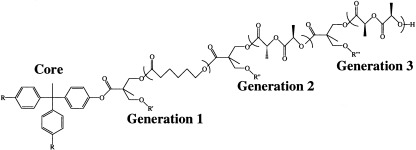
Dendritic block copolymers are described by a radial geometry in which different generations or layers consist of a high-molecular-weight polymer emanating from a central core. The use of either L-lactide or D,L-lactide in different combinations with other cyclic esters has provided a means of tuning the properties and morphology through stereochemistry. Optical rotation, NMR, and size exclusion chromatography measurements have been used to characterize the polymers.
Properties of double-hydrophilic graft copolymers with a polyacetal backbone
- Pages: 1189-1197
- First Published: 20 January 2004

Graft copolymers consisting of the polyacetal backbone substituted with COO− groups and poly(oxyethylene) side chains in different proportions were synthesized, and their efficiency as modifiers of the processes occurring at the interphase between inorganic particles and the surrounding aqueous phase was studied. Measurements of the elektrokinetic (zeta) potential, the stability of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) suspensions as well as the size and shape of the CaCO3 crystals formed in the presence of graft copolymers allowed us to draw some conclusions concerning the effect of the structure of those double-hydrophilic graft copolymers on their efficiency.
Solvent effect on chain-growth polycondensation for aromatic polyethers
- Pages: 1198-1207
- First Published: 21 January 2004
Tropone-containing π-conjugated polymers: Annulation of tropone onto benzene ring in the conjugated polymer
- Pages: 1208-1215
- First Published: 20 January 2004
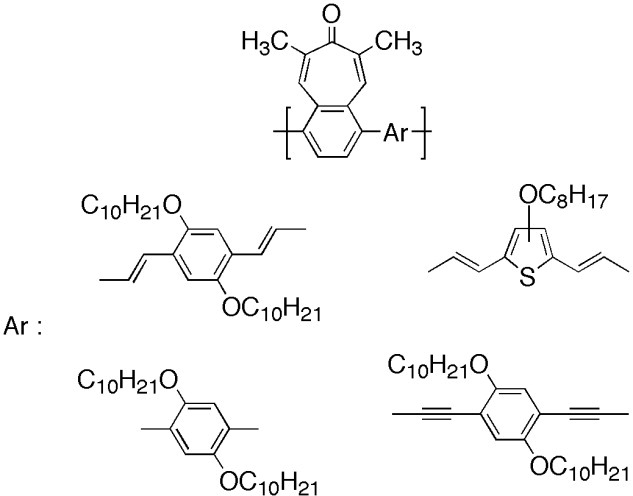
π-Conjugated polymers decorated with tropone were synthesized by the transition-metal-catalyzed coupling reaction and were characterized by NMR, IR, ultraviolet–visible, and photoluminescence measurements. The effects of the aromatic ring and the linking pattern were carefully investigated. The electron spectroscopies of the polymers were compared with the corresponding model compounds.
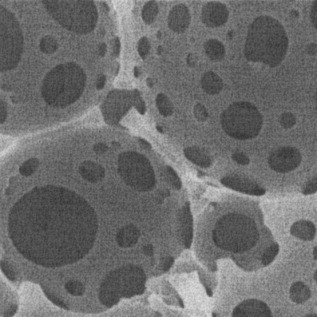
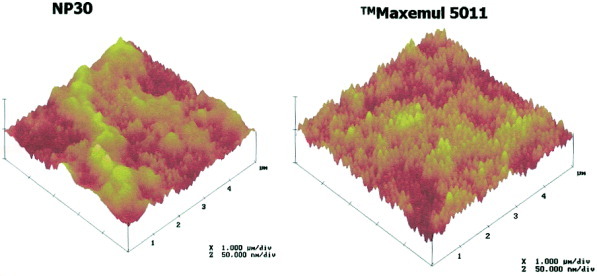
Copper-mediated radical polymerization on a microcellular monolith surface
- Pages: 1216-1226
- First Published: 21 January 2004
Fluorescent probes for monitoring the pulsed-laser-induced photocuring of poly(urethane acrylate)-based adhesives
- Pages: 1227-1238
- First Published: 21 January 2004
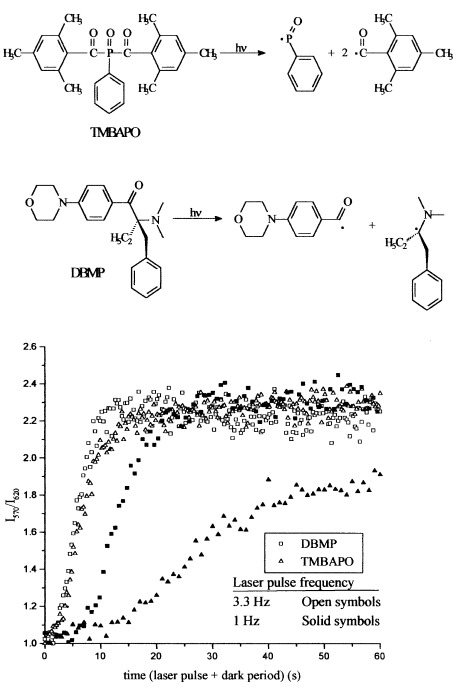
Fluorescent probes were used to study the kinetics and microstructural aspects of the curing of acrylic adhesives exposed to a 355-nm pulsed emission from an Nd-YAG laser. Special features of pulsed-laser-induced polymerization were treated in detail, such as the influence of the laser pulse frequency and the incident laser beam intensity. The inhibition period due to oxygen quenching was observed, and it was highly dependent on the laser repetition rate and the nature of the photoinitiator. The degree of cure improved as the polymerization rate increased as a result of a faster crosslinking, rather than relaxation volume kinetics. Moreover, a saturation rate effect occurred that depended on the photoinitiator. The different behaviors of the two photoinitiators in the curing of the same acrylic formulation was explained on the basis of primary radical termination.
Radiochemical aging of ethylene–propylene–diene monomer elastomers. I. Mechanism of degradation under inert atmosphere
- Pages: 1239-1248
- First Published: 21 January 2004
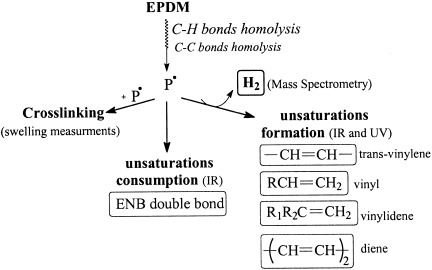
This study concerns electron-beam-induced degradation under argon atmosphere of an ethylene–propylene–diene monomer (EPDM, based on 5-ethylidene 2-norbornene) and an ethylene–propylene rubber (EPR) containing the same molar ratio of ethylene/propylene. Irradiation of EPDM and EPR induced the creation of trans-vinylene, vinyl, vinylidene, and dienic-type unsaturations. The radiochemical yields for unsaturation formations in EPDM and EPR were similar. Degradation also involved crosslinking and the production of dihydrogen. The comparison between EPDM and EPR showed that the diene (in which a double bond is consumed with a high radiochemical yield) increases the rate and the density of reticulation. This comparative study of EPDM and EPR under electron beams in inert atmosphere allows us to propose a general mechanism.
Preparation and properties of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)/poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) interpenetrating polymer networks for drug delivery
- Pages: 1249-1254
- First Published: 21 January 2004
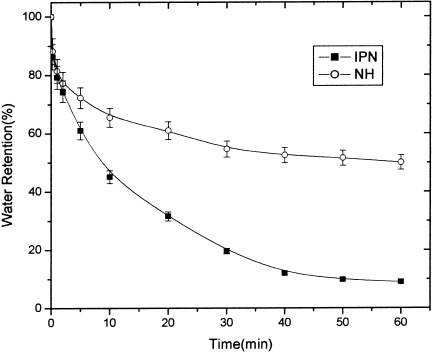
Novel poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)/poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) interpenetrating polymer network (IPN) hydrogel was synthesized and characterized. The response property of IPN hydrogel to temperature change was improved by the introduction of another PNIPA network into conventional PNIPA hydrogel. IPN hydrogel had a better mechanical strength due to the higher crosslinking density and polymer volume fraction.
Synthesis and properties of soluble trifluoromethyl-substituted polyimides containing laterally attached p-Terphenyls
- Pages: 1255-1271
- First Published: 21 January 2004
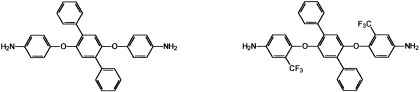
A new fluorinated diamine monomer, 2′,5′-bis(4-amino-2-trifluoromethylphenoxy)-p-terphenyl, was synthesized from the chloro-displacement of 2-chloro-5-nitrobenzotrifluoride with the potassium phenolate of 2,5-diphenylhydroquinone, followed by hydrazine palladium-(on-charcoal)-catalyzed reduction. Trifluoromethyl-substituted polyimides containing flexible ether linkages and laterally attached p-terphenyls were synthesized from the diamine with various aromatic dianhydrides via a conventional two-step process. The basic properties of these fluorinated polyimides were examined and compared with those of nonfluorinated counterparts based on 2′,5′-bis(4-aminophenoxy)-p-terphenyl.
Poly(phenylene vinylene)-based copolymers containing 3,7-phenothiazylene and 2,6-pyridylene chromophores: Fluorescence sensors for acids, metal ions, and oxidation
- Pages: 1272-1284
- First Published: 21 January 2004
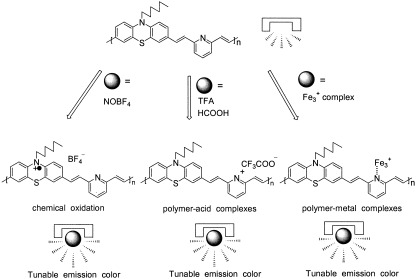
Three iminodibenzyl-containing and phenothiazylene-containing poly(arylene vinylene)s were prepared successfully by Wittig polymerization. The variations in the absorption and photoluminescence spectra of poly(N-hexyl-3,7-phenothiazylene-1,2-ethenylene-2,6-pyridylene-1,2-ethenylene) (P3) were easily manipulated by protonation, metal chelation, and chemical oxidation. P3 displayed significant bathochromic shifts when protonated with trifluoroacetic acid in chloroform. The complexation of P3 with Fe3+ led to a significant absorption change and fluorescence quenching, and this implied the coordination of ferric ions to the 2,6-pyridylene groups in the backbone. Both 3,7-phenothiazylene-containing poly(N-hexyl-3,7-phenothiazylene-1,2-ethenylene-1,3-phenylene-1,2-ethenylene) and P3 showed conspicuous photoluminescence quenching with a slight redshift when oxidized with NOBF4.
Measurement of the dissolved oxygen concentration in acrylate monomers with a novel photochemical method
- Pages: 1285-1292
- First Published: 21 January 2004
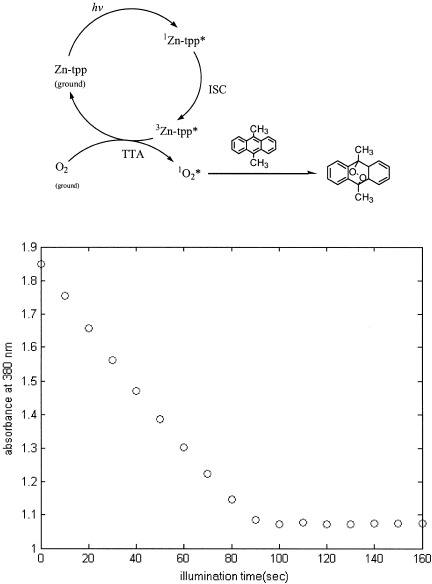
The deleterious effects of diffused oxygen in a polymerization system result in both a reduced polymerization rate and the loss of surface properties of the polymer. However, reliable data for the oxygen concentration in acrylate monomers are relatively scarce because of the experimental and instrumental limitations of the commercially available techniques. In this study, a photochemical method was developed and was used to obtain the dissolved oxygen concentration in seven acrylate monomers. The principle of the method was to convert ground-state molecular oxygen dissolved in monomer to the excited, singlet-state oxygen and then react the singlet oxygen with a third compound (singlet oxygen trapper). By monitoring the concentration of this singlet oxygen trapper spectrophotometrically, the concentration of dissolved oxygen can be obtained with the established stoichiometry for the reaction between singlet oxygen and trapper. The singlet oxygen concentrations in the acrylate monomers varied from 0.59 to 2.07 × 10−3 mol/L, depending on the monomer structure. The strategies and considerations for generalizing the method to other systems, including highly oxygenated organics, are discussed.