Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Articles
Poly(ester urethane)s with polycaprolactone soft segments: A morphological study
- Pages: 4117-4130
- First Published: 10 October 2002
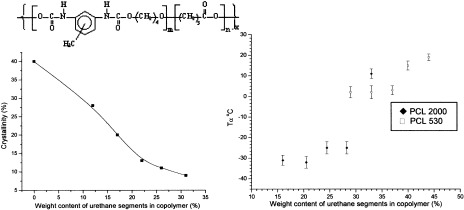
Two series of poly(ester urethane)s were prepared, containing polycaprolactone (PCL) as the soft segment with molecular weights of 530 and 2000. In each series, the soft-segment/hard-segment ratio was varied, and the morphological changes were monitored with differential scanning calorimetry, dynamic mechanical thermal analysis, wide-angle X-ray scattering, and scanning electron microscopy techniques. The polyurethanes with longer PCL segments retained their crystallinity, whereas those with shorter PCL segments did not. A morphological model is proposed, in which a continuous PCL-rich matrix contains both PCL crystallites and domains of urethane hard segments.
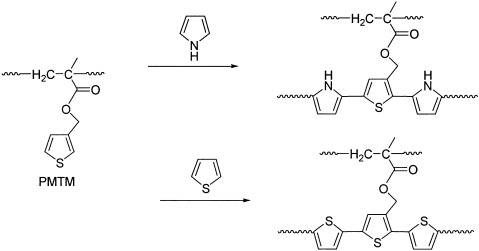
Conducting graft copolymers of poly(3-methylthienyl methacrylate) with pyrrole and thiophene
- Pages: 4131-4140
- First Published: 10 October 2002
Characterization and degradation behavior of poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate)s
- Pages: 4141-4157
- First Published: 14 October 2002
Random copolyesters based on 1,4-butanediol and different ratios between adipic and terephthalic units were synthesized by thermal polycondensation of the appropriate mixture of monomers or by melt transesterification of the mixture of homopolymers. Polymers were characterized and their degradability evaluated under different media.
Synthesis of new hydrolyzable polyurethanes from L-gulonic acid-derived diols and diisocyanates
- Pages: 4158-4166
- First Published: 15 October 2002
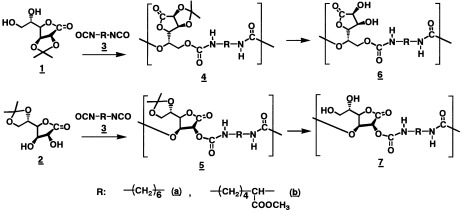
New polyurethanes with lactone groups in the pendants and main chains (4–7) were synthesized by the polyaddition of two kinds of saccharide-derived diols [2,3-O-isopropylidene-L-gulono-1,4-lactone (1) and 5,6-O-isopropylidene-L-gulono-1,4-lactone (2)] with hexamethylene diisocyanate (3a) and methyl (S)-2,6-diisocyanatohexanoate (3b) and by the subsequent deprotection of isopropylidene groups. They were hydrolyzed more quickly than the polyurethane derived from methyl β-D-glucofuranosidurono-6,3-lactone in a phosphate buffer solution, the pH value of which was 8.0, at 27 °C.
Preparations of regioselectively methylated cellulose acetates and their 1H and 13C NMR spectroscopic analyses
- Pages: 4167-4179
- First Published: 15 October 2002
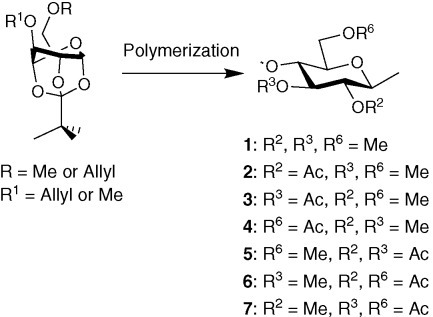
Seven regioselectively methylated cellulose acetates (2,3,6-tri-O-, 3,6-di-O-, 2,6-di-O-, 2,3-di-O-, 6-O-, 3-O-, and 2-O-methyl cellulose acetates) were prepared from cellulose derivatives obtained by the cationic ring-opening polymerization of glucose 1,2,4-orthopivalate derivatives. This is the first report to demonstrate the chemical syntheses of these methyl celluloses.
Reversible addition–fragmentation chain-transfer graft polymerization of styrene: Solid phases for organic and peptide synthesis
- Pages: 4180-4192
- First Published: 15 October 2002
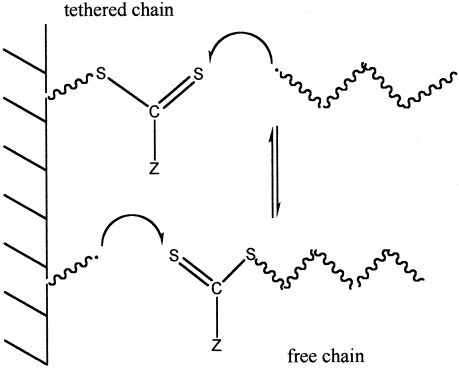
The γ-initiated reversible addition–fragmentation chain-transfer (RAFT)-agent-mediated free-radical graft polymerization of styrene onto a polypropylene solid phase has been performed with cumyl phenyldithioacetate (CPDA). The RAFT graft polymerization is compared with the conventional free-radical graft polymerization of styrene onto polypropylene. Both processes show two distinct regimes of grafting: (1) the grafting layer regime, in which the surface is not yet totally covered with polymer chains, and (2) a regime in which a second polymer layer is formed. The molecular weight of PSfree shows a linear behavior with conversion and has a low polydispersity index.
Structural characterization and gas-transport properties of brominated matrimid polyimide† ‡
- Pages: 4193-4204
- First Published: 15 October 2002
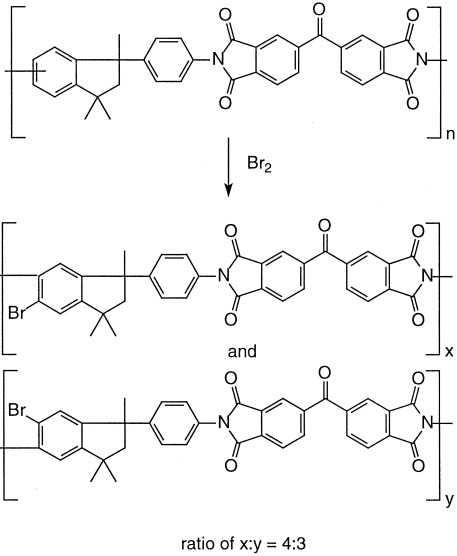
The commercial polyimide Matrimid was modified by bromination for the purpose of improving its membrane-transport properties as a gas-separation material and providing functional group reactivity for further modifications. The unmodified and brominated polymers were characterized in detail by NMR, which revealed that one bromine atom per repeat unit was incorporated onto the indane aromatic ring. The thermal, physical properties, and gas-transport properties of the brominated polyimide were compared with those of the unmodified polymer.
Fluorinated poly(arylene ether ketone)s bearing pentafluorostyrene moieties prepared by a modified polycondensation†
- Pages: 4205-4216
- First Published: 15 October 2002
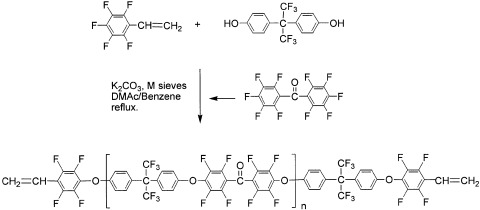
The polycondensation of decafluorobenzophenone with hexafluorobisphenol A was modified with a molecular sieve dehydrating apparatus. This modification enabled the reactions to be conducted in mild conditions and to incorporate pentafluorostyrene moieties into the polymers. The resulting pentaflurodtyrene containing fluorinated poly(arylene ether ketone)s were thermally crosslinked to yield uniform films with a refractive index and birefringence of 1.502 and 2.5 × 10−3, respectively, measured at a wavelength of 1.55 μm.
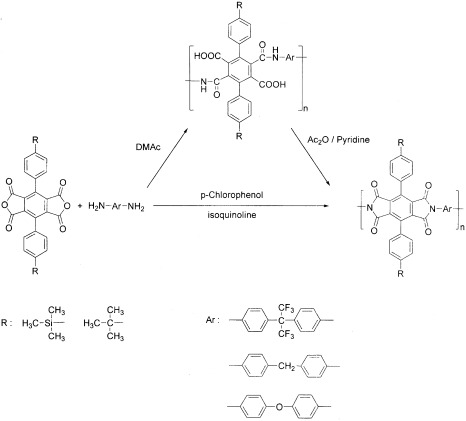
Synthesis and characterization of novel 3,6-di[3′,5′-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]pyromellitic dianhydride for polyimide synthesis
- Pages: 4217-4227
- First Published: 15 October 2002
![Synthesis and characterization of novel 3,6-di[3′,5′-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]pyromellitic dianhydride for polyimide synthesis](/cms/asset/91ebe117-5ed5-4481-88f2-35d6bb02bd55/mgra001.jpg)
A novel dianhydride monomer, 3,6-di[3′,5′-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]pyromellitic dianhydride (12FPMDA), was synthesized via the Suzuki cross-coupling reaction followed by oxidation and cyclodehydration. 12FPMDA was used to prepare polyimides with 1,1-bis(4-aminophenyl)-2,2,2-trifluoroethane and 4,4′-diaminodiphenylether, and the polyimides were designed to have molecular weights of 20,000 g/mol via off-stoichiometry. The resulting polyimides were characterized by Fourier transform infrared, NMR, gel permeation chromatography, differential scanning calorimetry, and thermogravimetric analysis, and their solubility, solution viscosity, water absorption, coefficients of thermal expansion (CTEs), and dielectric constants were also evaluated. The polyimides exhibited excellent solubility even in acetone and toluene, high glass-transition temperatures (>311 °C), good thermal stability (>518 °C in air), and well-controlled molecular weights (19,000–21,000 g/mol). They also provided low CTEs (35–50 ppm/°C), water absorption (1.26–1.35 wt %), and dielectric constants (2.49–2.52).
Thermoresponsive properties of porous poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) hydrogels prepared in the presence of nanosized silica particles and subsequent acid treatment
- Pages: 4228-4235
- First Published: 16 October 2002
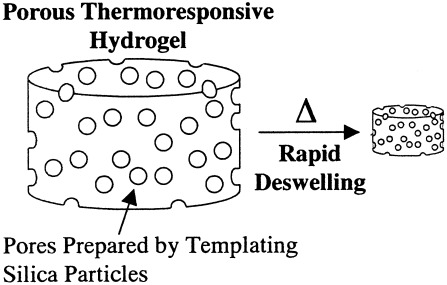
Porous poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) hydrogels were prepared in the presence of spherical silica particles with variable sizes and subsequent acid extraction of silica. The hydrogels showed volume phase-transitions from swelling to deswelling states at approximately 30 °C. Deswelling was facilitated by decreased silica particle size and increased silica content. The deswelling-swelling cycle was repeatable. The mechnical strength of the porous hydrogels was maintained compared to conventional nonporous hydrogels.
Ultraviolet curing of acrylic systems: Real-time Fourier transform infrared, mechanical, and fluorescence studies
- Pages: 4236-4244
- First Published: 16 October 2002
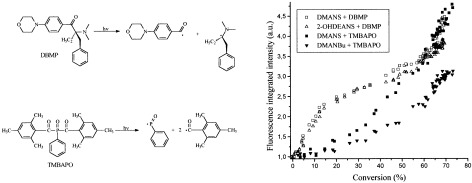
The photopolymerization kinetics of acrylic systems have been studied by Fourier transform infrared and fluorescence in real time. The polymerization rate depends on the square root of the absorbed light intensity when 2-benzyl-2-N,N-dimethylamino-1-(4-morpholinophenyl)-1-butanone (DBMP) is used as a photoinitiator, whereas primary radical termination has been observed with bis(2,4,6-trimethylbenzoyl) phenyl phosphine oxide (TMBAPO) as a photoinitiator. A comparison of the fluorescence emission changes of different fluorescent probes during the ultraviolet curing of an acrylate-based adhesive also shows different behaviors depending on the nature of the photoinitiator. We report for the first time the contribution of the fluorescence probe method to elucidate the mechanism of network formation in a free-radical crosslinking polymerization.
Knowledge-based choice of the initiator type for monomer removal by postpolymerization
- Pages: 4245-4249
- First Published: 16 October 2002
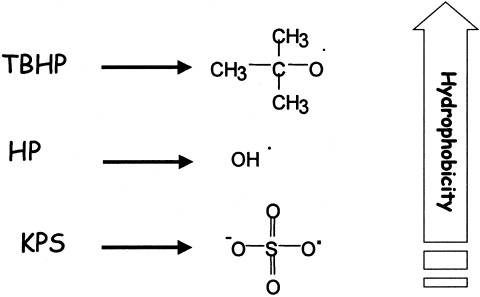
The mechanisms involved in monomer removal by postpolymerization were investigated. Three redox systems yielding radicals of different hydrophobicities were studied. Efficiency in monomer removal by postpolymerization increased with the hydrophobicity of the radical formed from the initiator system. This result was independent of the water solubility of the residual monomer.
Luminescent polymeric ruthenium complexes with polystyrene-b-poly(methyl methacrylate) macroligands: The sequential activation of initiator sites for blocks generated by parallel polymerization mechanisms
- Pages: 4250-4255
- First Published: 21 October 2002
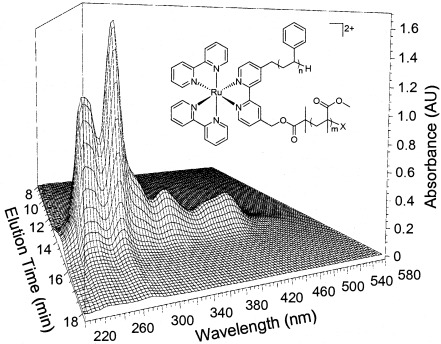
Polystyrene-b-poly(methyl methacrylate) diblock copolymers with a luminescent Ru(bpy)3 complex at the block junction were synthesized. The macroligand precursor, bpy(PS–H)(PMMA), was generated via the atom transfer radical polymerization of styrene and methyl methacrylate from two independent, sequentially activated initiating sites. Subsequent reactions with Ru(bpy)2Cl2 in the presence of Ag+ generated the ruthenium tris(bipyridine)-centered diblock, which is of interest for the imaging of block copolymer microstructures and for incorporation into new photonic materials.
Effect of introduction mode of hydroxyl functionality on morphology and film properties of cycloaliphatic diepoxide crosslinkable core-shell latex†
- Pages: 4256-4265
- First Published: 17 October 2002
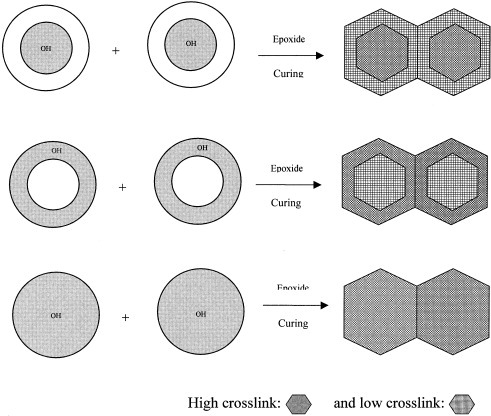
Three series of core-shell hydroxyl functionalized latexes were synthesized and then crosslinked with a cycloaliphatic diepoxide. The same amont of hydroxyl functional monomer was added during the core stage, shell stage, or partitioned equally between the core and shell. The introduction of hydroxyl groups during the shell polymerization resulted in a higher crosslinking density but a lower Tukon hardness and tensile properties. Not surprisingly, distribution of hydroxyl groups in both core and shell polymerization provided lowest water adsorption and impact resistance as well as highest tensile elongation.
Perfluoropolyether alkyl diesters: Structure effects of the alkyl group on the kinetics of the hydrolysis reactions
- Pages: 4266-4280
- First Published: 18 October 2002
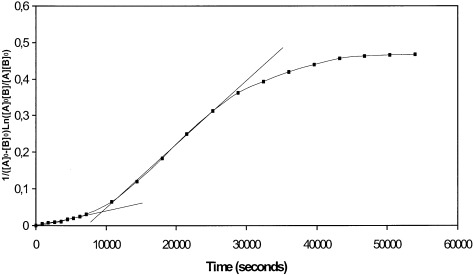
Kinetics of the neutral ester hydrolysis for a series of perfluoropolyether bis-carboxylic esters was examined by 19F NMR and 1H NMR spectroscopy. The investigated esters showed a much higher reactivity than a fully hydrogenated ester having a closely related structure. Two distinctive kinetic regimes were observed, depending on the spontaneous pH variation of the solution during reaction. These two sequential regimes, active at higher and lower pH, corresponded to BAC2 and AAC2 mechanisms, respectively. Steric and polar contributions to the hydrolysis rate are discussed with thermodynamic parameters.
Synthesis and properties of amine-containing poly(arylene ether sulfone) as an anion-exchange matrix
- Pages: 4281-4287
- First Published: 17 October 2002
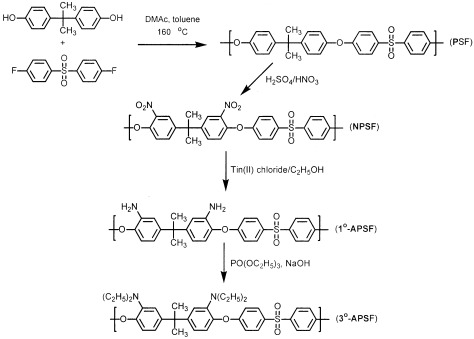
Poly(arylene ether sulfone) (PSF) was synthesized by the condensation polymerization between bisphenol A and 4,4′-dichlorodiphenylsulfone as an anion-exchange matrix. 1°-Amine-containing poly(arylene ether sulfone) (1°-APSF) was synthesized by the reduction reaction of a nitrated PSF. Then, it was transferred to 3°-amine-containing poly(arylene ether sulfone) (3°-APSF) by the alkylation of the amine of 1°-APSF. 1°-APSF and 3°-APSF showed good thermal stability and excellent mechanical properties. The ion-exchange capacities of 1°-APSF and 3°-APSF were studied.
Synthesis and characterization of new organosoluble and gas-permeable polyimides from bulky substituted pyromellitic dianhydrides†
- Pages: 4288-4296
- First Published: 17 October 2002
Thermally stable nonlinear optical polyurea functionalized by multiple charge-transfer chromophore
- Pages: 4297-4301
- First Published: 17 October 2002
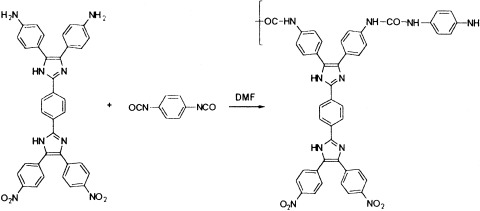
Second-order nonlinear optical polyurea was prepared from novel multiple charge-transfer chromophore and 1,4-phenylene diisocyanate. Simultaneous poling and polymerization and the in situ second-harmonic generation measurement technique was carried out to evaluate the thermal stability of the poling-induced orientation. The polyurea exhibited a high glass-transition temperature and an extraordinary orientation to thermal stability.
Anionic polymerization of methyl methacrylate initiated with molybdenum and tungsten chloride/organolithium/triisobutylaluminum systems
- Pages: 4302-4315
- First Published: 18 October 2002
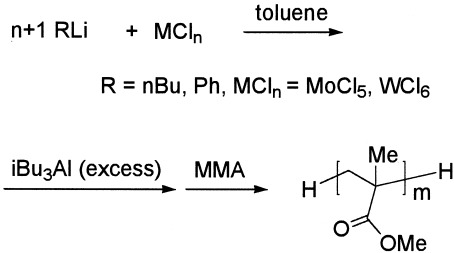
Molybdenum chloride (MoCl5) and tungsten chloride (WCl6)/phenyllithium/triisobutylaluminum (iBu3Al) systems were found to be quite effective for controlling the anionic polymerization of methyl methacrylate (MMA), affording high molecular weight poly(methyl methacrylate)s (PMMAs; number-average molecular weight > 100,000) with narrow molecular weight distributions (weight-average molecular weight/number-average molecular weight < 1.25) quantitatively at 0 °C for 1 h in toluene. Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry analyses of PMMAs obtained with the MoCl5 and WCl6/RLi (R = nBu or Ph)/iBu3Al systems revealed that the initiation of MMA with the systems occurred by a nucleophilic attack of H− to the monomer, and the polymerization was terminated by the introduction of H+ to the propagating chain end.
Hydrogen bonding and hydrophobic interactions between [60]fullerenated poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) and poly(1-vinylimidazole) or poly(4-vinylpyridine)
- Pages: 4316-4327
- First Published: 18 October 2002
![Hydrogen bonding and hydrophobic interactions between [60]fullerenated poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) and poly(1-vinylimidazole) or poly(4-vinylpyridine)](/cms/asset/ff732583-9818-4cbb-b587-fe98535f53b4/mgra001.jpg)
Poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) (PHEMA) forms miscible blends with poly(1-vinylimidazole) (PVI) and poly(4-vinylpyridine) (P4VPy). The incorporation of a small amount of C60 into PHEMA leads to hydrophobic interactions and enhanced hydrogen bonding with PVI and P4VPy, as shown by calorimetry and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy studies.
Rapid Communication
Synthesis of well-defined poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) by the anionic polymerization of N-methoxymethyl-N-isopropylacrylamide
- Pages: 4328-4332
- First Published: 18 October 2002
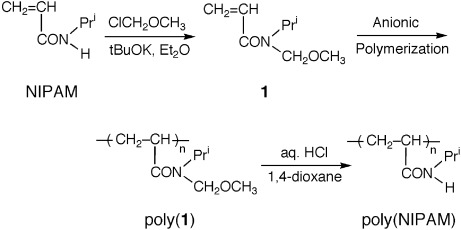
The anionic polymerization of N-methoxymethyl-N-isopropylacrylamide (1) was carried out with diphenylmethylpotassium in the presence of Et2Zn in tetrahydrofuran at −78 °C for 20 h. Poly(1)s, having predicted molecular weights and narrow molecular weight distributions (weight-average molecular weight/number-average molecular weight < 1.1), were obtained in quantitative yields. The methoxymethyl protecting group of the resultant poly(1)s was completely removed, and this yielded poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) possessing well-defined chain structures because of treatment with aqueous hydrochloric acid in 1,4-dioxane at room temperature for 20 h.
Articles
Synthesis and polymerization of 5-(methacrylamido)tetrazole, a water-soluble acidic monomer
- Pages: 4333-4343
- First Published: 21 October 2002
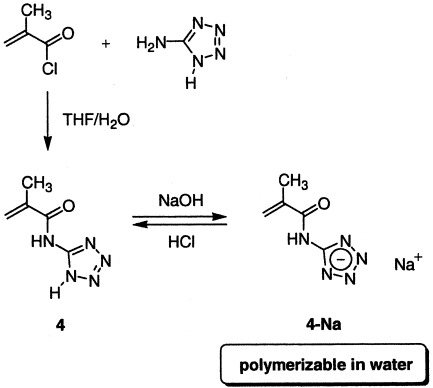
The weakly acidic monomer 4 (pKa 4.50 ± 0.01) is readily available from methacryloyl chloride and 5-aminotetrazole. Radical polymerization proceeded smoothly in DMF or, after conversion of monomer 4 into sodium salt 4-Na, even in water. A superabsorbent polymer gel was obtained by copolymerization of 4-Na and 0.08 mol % N,N′-methylenebisacrylamide. The copolymerization of 4-Na and acrylamide (as a model compound for the crosslinker) at 57 °C in D2O was followed by 1H NMR spectroscopy, and revealed that 4-Na was consumed slightly more rapidly than acrylamide. The reactivity ratios were determined for this monomer pair.
Synthesis and crosslinking of a series of dimeric liquid-crystalline diglycidylester compounds containing imine groups
- Pages: 4344-4356
- First Published: 21 October 2002
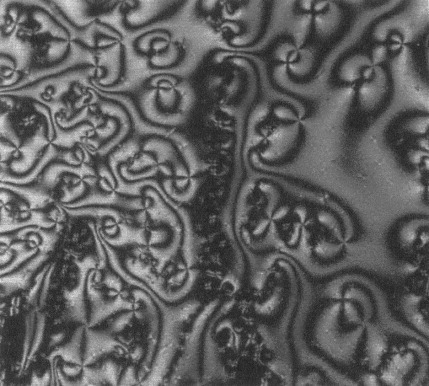
We synthesized a series of aromatic imine mesogenic diglycidylester dimeric compounds. Their liquid-crystalline behavior was examined by differential scanning calorimetry, hot-stage polarized optical microscopy (POM), and wide-angle X-ray scattering. We obtained liquid-crystalline thermosets (LCTs) with several primary aromatic diamines in stoichiometric ratios or a tertiary amine as a catalyst. The ordered character of the LCTs was confirmed by POM and WAXS. Finally, the mechanical characterization of the LCTs was measured by dynamic mechanical thermal analysis.
New polymer syntheses. CXI. Aliphatic polyesters by the ring-opening polycondensation of glutaric anhydride with ethylene or trimethylene carbonate
- Pages: 4357-4367
- First Published: 21 October 2002
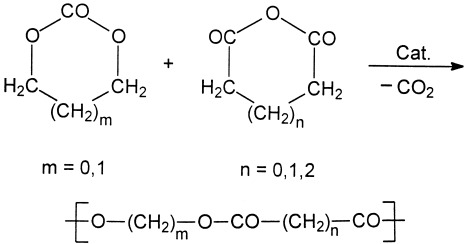
Several polycondensations of ethylene carbonate with succinic anhydride or glutaric anhydride (GA) were conducted in bulk. Low molar mass polyesters were obtained with pyridine-type catalysts and GA. Analogous polycondensations of trimethylene carbonate (TMC) and GA were successful when quinoline, 4-(N,N-dimethylamino)pyridine, or BF3 · OEt2 was used as a catalyst. Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectra revealed the formation of cyclic oligoesters and polyesters by backbiting degradation. Monomer mixtures containing an excess of TMC yielded copoly(ester carbonate)s with number-average molecular weights up to 16,000 Da.
Synthesis of highly crosslinked monodisperse polymer particles: Effect of reaction parameters on the size and size distribution
- Pages: 4368-4377
- First Published: 21 October 2002
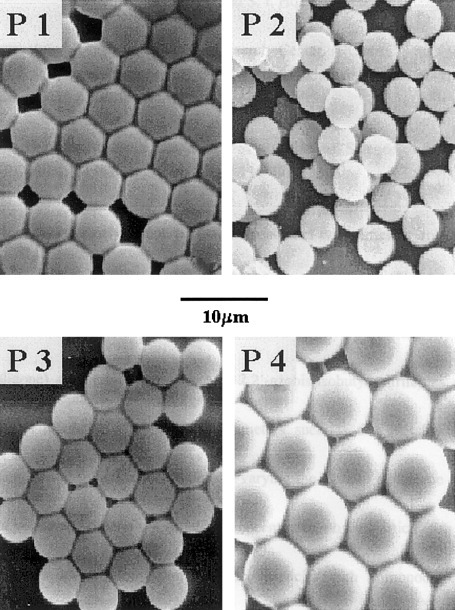
Monodisperse polystyrene particles crosslinked with different concentrations of divinylbenzene were synthesized in the 3.2–9.1 μm size range by dispersion polymerization. The effects of the reaction parameters such as the crosslinking agent concentration, media solvency, the initiator concentration, and the stabilizer concentration on the particle size and size distribution were investigated with reference particles with a monodisperse size distribution and crosslinked by 1.5 wt % divinylbenzene. The results showed that only specific sets of conditions produce particles with a monodisperse size distribution. The glass-transition temperatures of the particles increased with increasing divinylbenzene concentration.
Novel elastomeric polyurethanes with pendant epoxy groups as highly reactive auxiliary groups for further derivatizations
- Pages: 4378-4385
- First Published: 21 October 2002
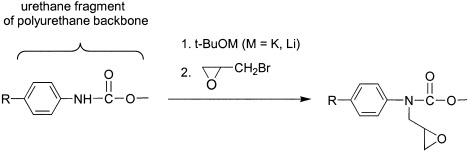
Glycidyl groups were attached in amounts of 0.30–0.44 mmol/g to the hard segments of model polyurethanes via a one-step, base-induced glycidylation of urethane NH sites in the polymeric backbone with an excess of epibromohydrin. Two types of aromatic polyurethanes, represented by a poly(ether urethane) and a poly(urethane urea), were found to be equally suitable for the epoxy derivatization. No side reactions and no degradation of the polymer backbone were noticed in the course of the modification. These materials are useful for the further covalent attachment of active compounds (stabilizers or biocompatibility enhancers) to polyurethane macromolecules.