Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Image
Cover Image, Volume 56, Issue 12
- Pages: i-ii
- First Published: 03 May 2018

Nonwoven fabrics are popular in a wide range of products for both consumer and industrial use. In their work described on page 947, Koviljka A. Asanovic, Dragana D. Cerovic, Mirjana M. Kostic, Slavica B. Maletic, and Ana D. Kramar specifically examined the sorption and dielectric properties of viscose/polypropylene multi-purpose nonwoven fabrics. The cover shows an SEM microphotograph of one nowoven fabric investigated in this paper, an 80%/20% viscose/polypropylene nonwoven. The changes of the water absorptive capacity, height of capillary rise, and water retention value are a function of viscose fiber content, total porosity, pore size, and web bonding process. Effective dielectric permeability and AC specific electrical conductivity are dependent on viscose fiber content, web bonding process, frequency of electric field, and bulk free water content. (DOI: 10.1002/polb.24611)
Issue Information
Full Papers
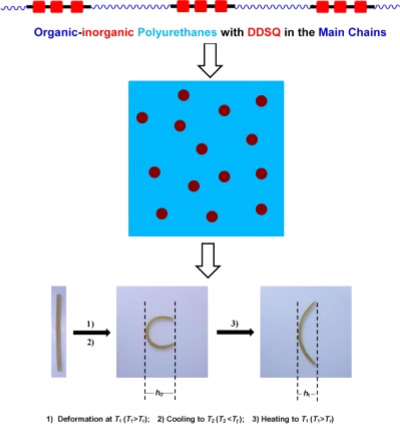
Organic–inorganic polyurethanes with double decker silsesquioxanes in the main chains: Morphologies, surface hydrophobicity, and shape memory properties
- Pages: 893-906
- First Published: 15 March 2018
Dielectric and rheological study of the molecular dynamics during the cure of an epoxy resin
- Pages: 907-913
- First Published: 23 March 2018

The market for carbon fiber-reinforced plastics (CFRP) is a promising and fast growing market, for example, in the automotive industry. However, the lack of process monitoring and control equipment is one of the main challenges that prevent the penetration of high-volume markets. The solution for a successful breakthrough of CFRPs into markets, such as the automotive industry, is as follows: A significant decrease in manufacturing costs by fast and robust processes via the combination of in-mold sensors and a powerful data management enabling closed-loop controlled processes. Therefore, the sensors have to be fully integrated into the superordinate machine control to enable in-mold quality assurance.
Deep insights into the hydrolysis of N,N-dialkylaminoethyl methacrylates in aqueous solution with 1H NMR spectroscopy
- Pages: 914-923
- First Published: 31 March 2018
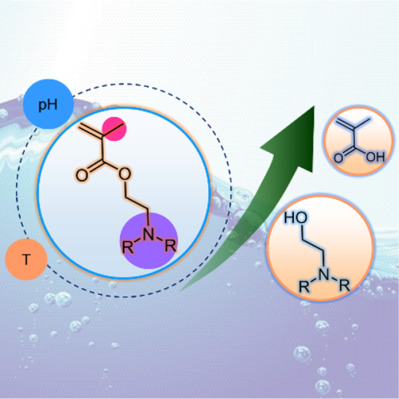
N,N-dialkylaminoethyl methacrylate (DAEA) monomers face a high risk of hydrolysis in their ester groups when polymerized in water-containing media. In this work, based on NMR spectroscopy, the relationship between hydrolysis behavior and solubility of a series of DAEA monomers is developed. The influences of several factors, including molecular structure (changes in terminal alkylamino group and the methyl group adjacent to CC), pH, and temperature on hydrolysis are separately examined. These efforts will serve as a guide map for the precise synthesis of well-defined DAEA copolymers in aqueous media.
Polyelectrolyte micelles in salt-free solutions: Micelle size and electrostatic potential
- Pages: 924-934
- First Published: 10 April 2018
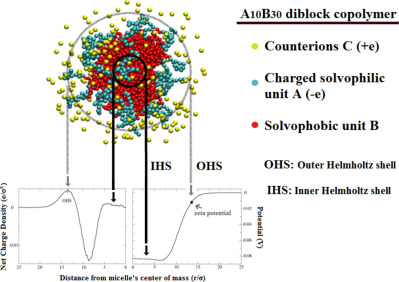
Diblock copolymers with short charged blocks form polyelectrolyte micelles with multimodal mass distribution. Micelles of different sizes coexist when their charge content differs slightly. The electrostatic potential of spherical micelles was calculated by solving the Poisson equation. The resulting zeta potential of the micelle increases with the molecular weight of the charged block if the ratio between the percentages of the confined counterions is less than 1.11.
Dynamic postpolymerization of 3D-printed photopolymer nanocomposites: Effect of cellulose nanocrystal and postcure temperature
- Pages: 935-946
- First Published: 17 April 2018
Cellulose nanocrystal (CNC) reinforced methacrylate (MA) nanocomposites are 3D printed by stereolithography technology. CNC retards the polymerization of MA polymer during 3D printing; however, it promotes the postpolymerization of MA nanocomposites in the postcure. The printed nanocomposites obtain optimal mechanical properties with addition of 0.5–1% CNC and at a postcure temperature between 120 and 140 °C.
Multipurpose nonwoven viscose/polypropylene fabrics: Effect of fabric characteristics on sorption and dielectric properties
- Pages: 947-957
- First Published: 17 April 2018
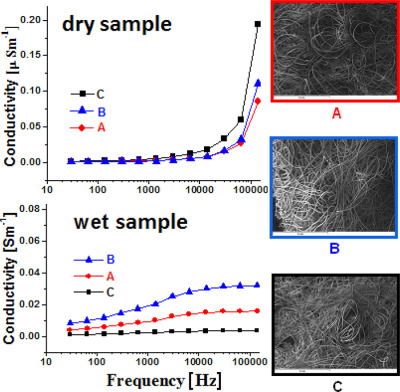
Viscose fiber content, porosity, pore size, and web bonding process have a dominant influence on the sorption properties of viscose/polypropylene nonwoven fabrics. Changes in dielectric properties are a function of viscose fiber content, web bonding process, frequency of electric field, and water adsorbed in material. Increase in effective dielectric permeability and AC specific electrical conductivity by several orders of magnitude in wet samples as compared to dry samples is influenced by bulk free water in the samples.