Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
RESEARCH ARTICLE
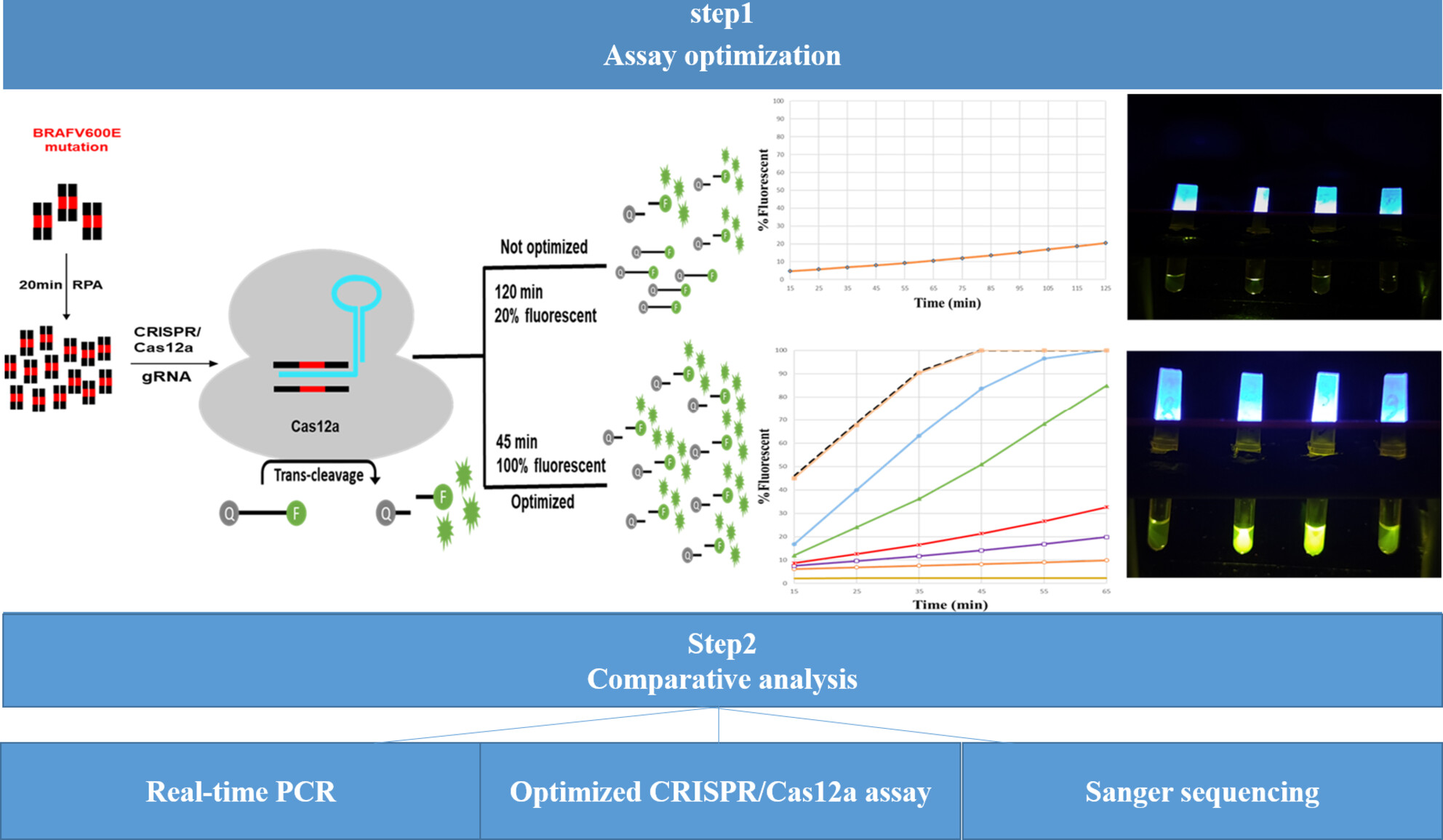
An Optimized CRISPR/Cas12a Assay to Facilitate the BRAF V600E Mutation Detection
- First Published: 24 October 2024
Prognostic Nutritional Index is Related to All-Cause Mortality in Patients With Stage IV Colorectal Cancer Treated With Capecitabine: Single-Center 24-Month Observational Study in Vietnam
- First Published: 08 October 2024
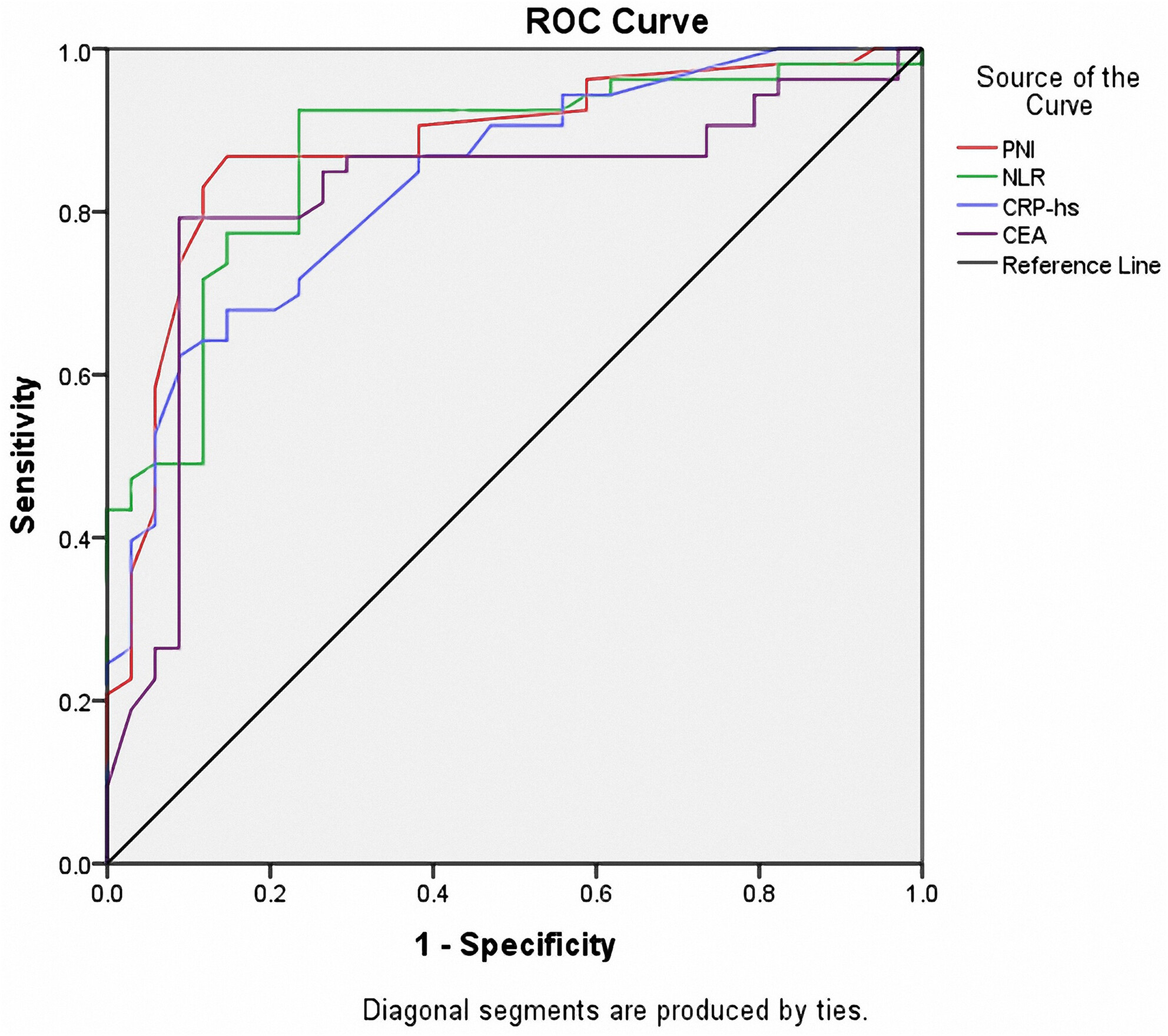
The mortality rate of study subjects was 60.9%. CRP-hs, NLR, and PNI were independent factors associated with 24-month mortality in patients with stage IV colorectal cancer (p < 0.05 to p < 0.01). At a cut-off value of 38.51, PNI was a predictor for mortality, with the area under the curve (AUC) of 0.88 and p < 0.001.
Clustering Based on Laboratory Data in Patients With Heart Failure Admitted to the Intensive Care Unit
- First Published: 04 October 2024
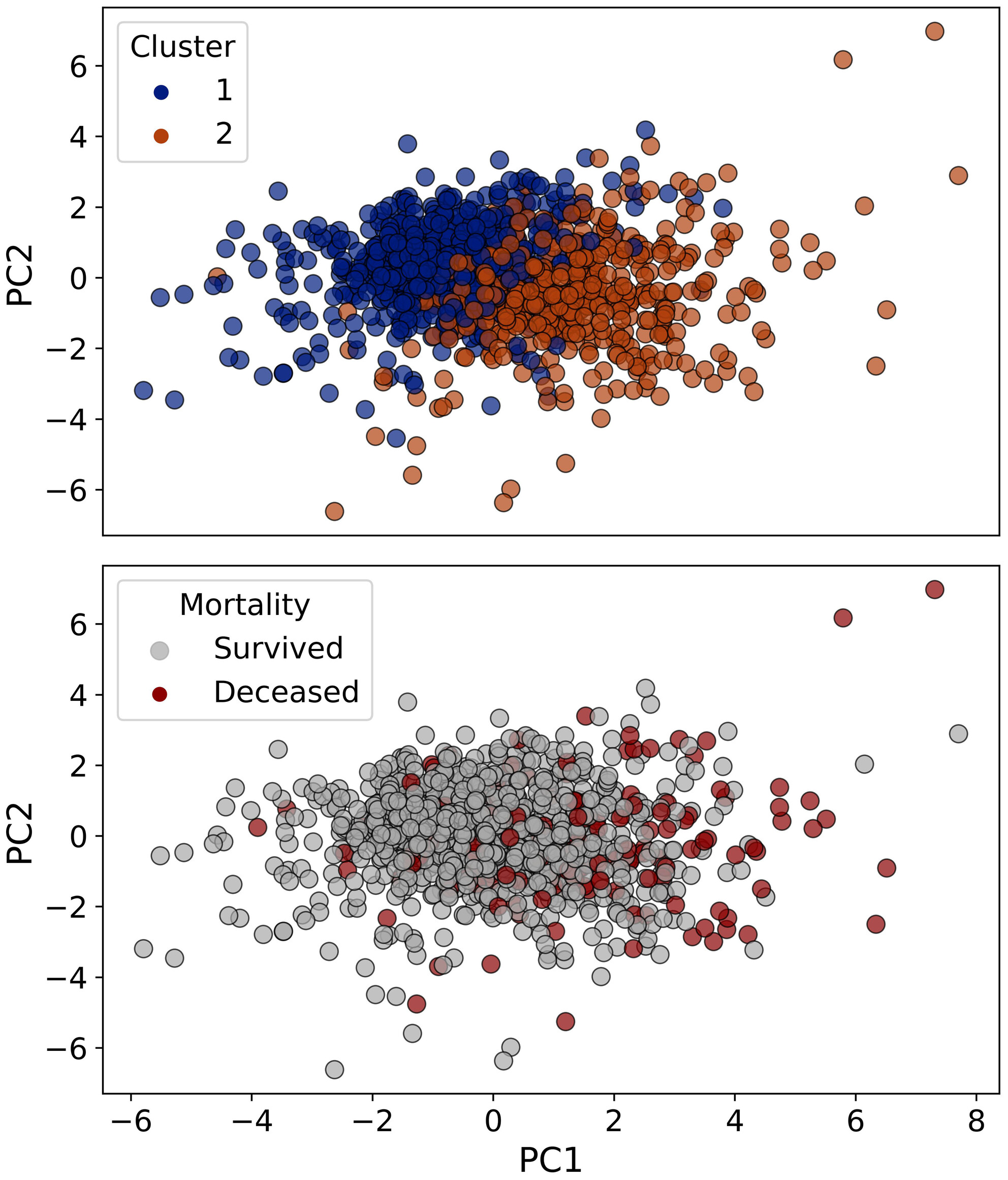
Heart failure is a common condition that imposes a significant burden on healthcare systems. We aimed to identify subgroups of patients with heart failure admitted to the ICU using routinely measured laboratory biomarkers. Laboratory data revealed two phenotypes of ICU-admitted patients with heart failure. The two phenotypes are of prognostic importance in term of mortality rate. They can be differentiated using blood cell count, kidney function status, and serum electrolytes concentrations.
The Neutrophil Percentage-to-Albumin Ratio as a Biomarker for All-Cause and Diabetes-Cause Mortality Among Diabetes Patients: Evidence From the NHANES 1988–2018
- First Published: 10 October 2024
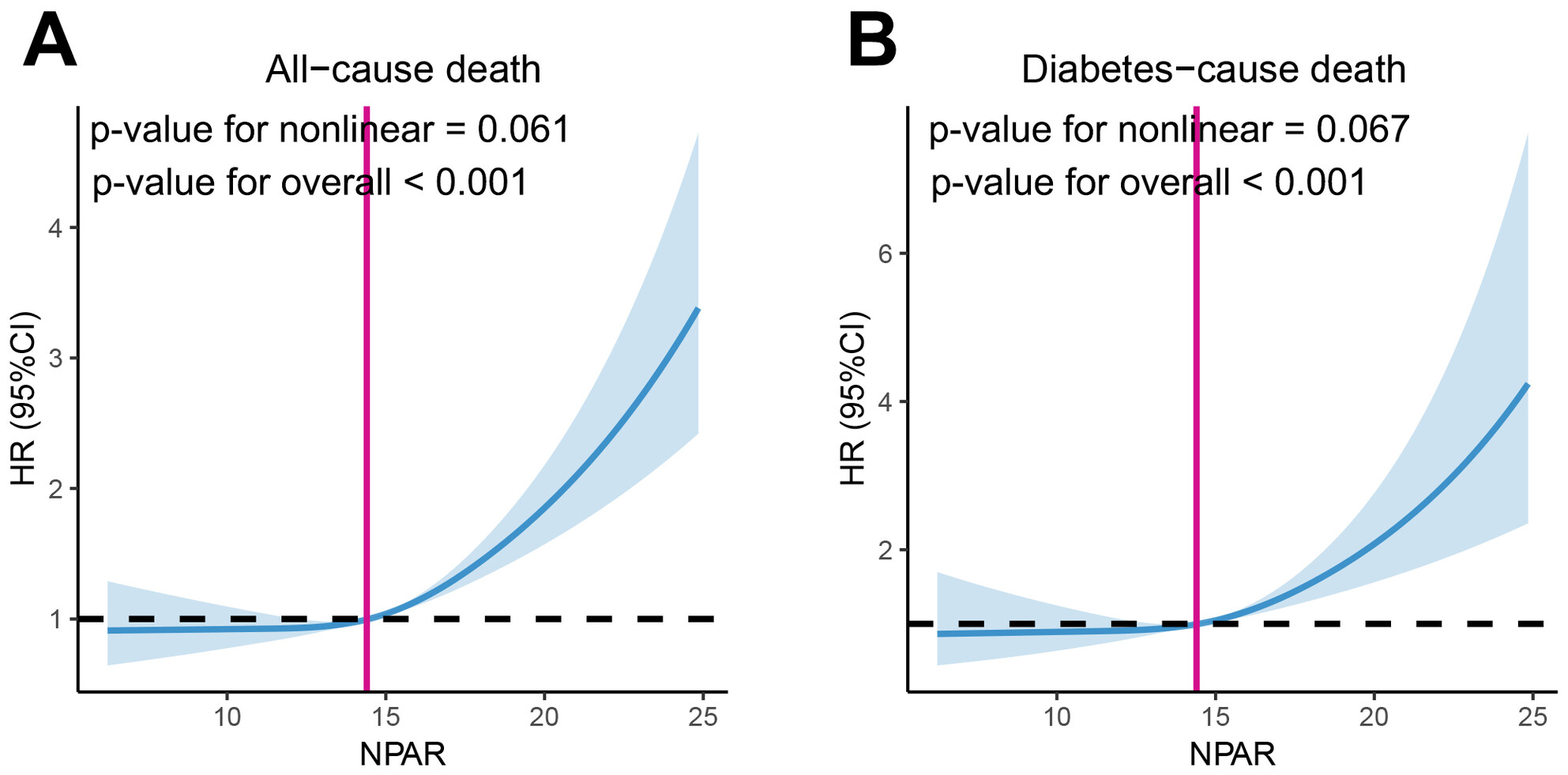
The RCS regression analysis showed a positive linear association between the NPAR and all-cause and diabetes-cause mortality. High NPAR group had a significantly higher risk of all-cause and diabetes-cause mortality in univariate and multivariate analysis. Compared with low NPAR group, high NPAR group had a low survival rate of diabetes cases in all-cause death and diabetes-cause mortality with area under the curve of the 3-year, 5-year, and 10-year ROC curve being 0.725, 0.739, and 0.734 for all-cause mortality.
CORRECTION
Correction to “Global distribution of treatment resistance gene markers for leishmaniasis”
- First Published: 31 October 2024