Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION - TABLE OF CONTENTS
Free Access
free
Issue Information - Table of Contents
- Pages: 2527-2529
- First Published: 21 December 2018
REVIEW ARTICLE
Open Access
oa
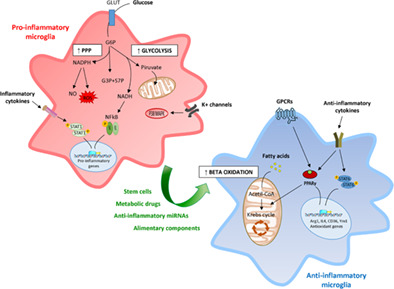
How to reprogram microglia toward beneficial functions
- Pages: 2531-2549
- First Published: 08 September 2018
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Full Access
full
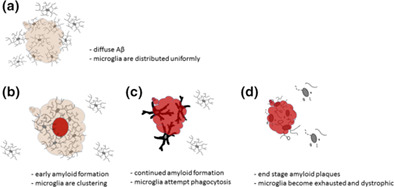
Microglial activation occurs late during preclinical Alzheimer's disease
- Pages: 2550-2562
- First Published: 11 November 2018
Full Access
full
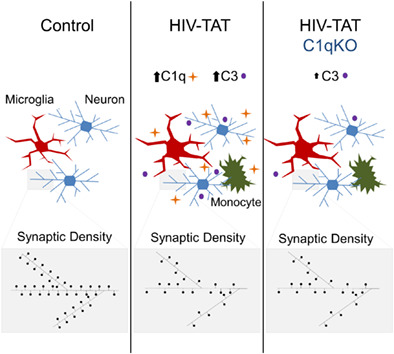
HIV Tat causes synapse loss in a mouse model of HIV-associated neurocognitive disorder that is independent of the classical complement cascade component C1q
- Pages: 2563-2574
- First Published: 16 October 2018
Full Access
full
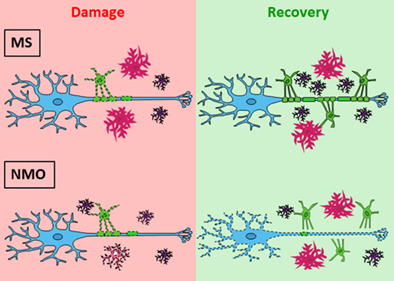
Distinct patterns of glia repair and remyelination in antibody-mediated demyelination models of multiple sclerosis and neuromyelitis optica
- Pages: 2575-2588
- First Published: 21 September 2018
Open Access
oa
Regulatory role of oligodendrocyte gap junctions in inflammatory demyelination
- Pages: 2589-2603
- First Published: 16 October 2018
Main Points
- We induced EAE in WT, Cx32KO and Cx47KO mice.
- EAE scores and pathological findings were exacerbated in Cx47KO more than in Cx32KO mice with dysregulation of several cytokines.
- Loss of oligodendrocyte connexins has pro-inflammatory effects.
Full Access
full
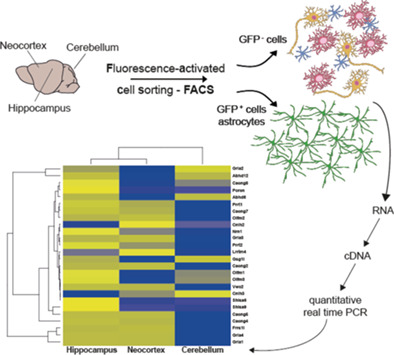
Heterogeneity of the astrocytic AMPA-receptor transcriptome
- Pages: 2604-2616
- First Published: 28 October 2018
Open Access
oa
Olfactory ensheathing cells abutting the embryonic olfactory bulb express Frzb, whose deletion disrupts olfactory axon targeting
- Pages: 2617-2631
- First Published: 26 September 2018
Main Points
- Frzb is expressed by olfactory ensheathing cells abutting the embryonic mouse olfactory bulb.
- Frzb expression requires Sox10. Deletion of Frzb disrupts olfactory receptor neuron maturation, likely reflecting a defect in olfactory axon targeting.
Open Access
oa
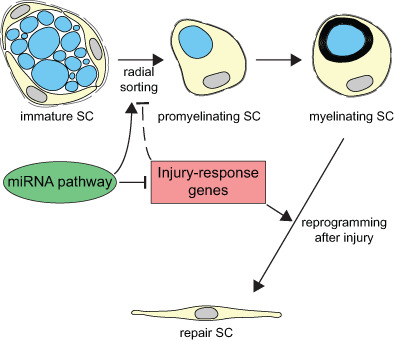
The miRNA biogenesis pathway prevents inappropriate expression of injury response genes in developing and adult Schwann cells
- Pages: 2632-2644
- First Published: 08 October 2018
Open Access
oa
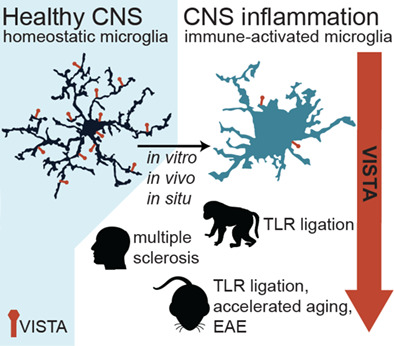
VISTA expression by microglia decreases during inflammation and is differentially regulated in CNS diseases
- Pages: 2645-2658
- First Published: 11 October 2018
Full Access
full
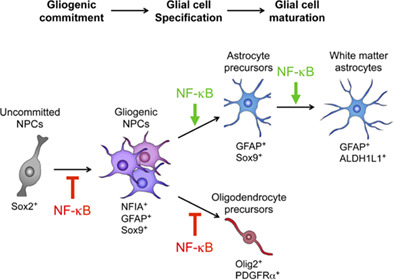
Nuclear factor-kappaB regulates multiple steps of gliogenesis in the developing murine cerebral cortex
- Pages: 2659-2672
- First Published: 19 October 2018
Full Access
full
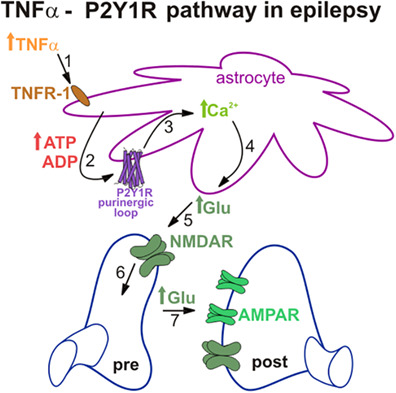
Blocking TNFα-driven astrocyte purinergic signaling restores normal synaptic activity during epileptogenesis
- Pages: 2673-2683
- First Published: 05 November 2018
Full Access
full
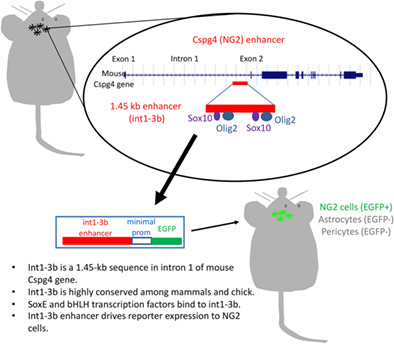
NG2 expression in NG2 glia is regulated by binding of SoxE and bHLH transcription factors to a Cspg4 intronic enhancer
- Pages: 2684-2699
- First Published: 10 October 2018
Full Access
full
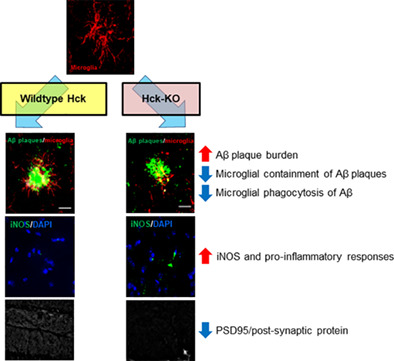
Inhibition of hematopoietic cell kinase dysregulates microglial function and accelerates early stage Alzheimer's disease-like neuropathology
- Pages: 2700-2718
- First Published: 12 September 2018
Full Access
full
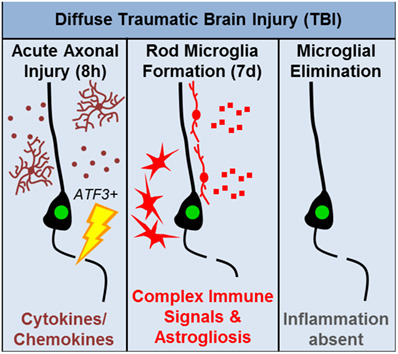
Traumatic brain injury-induced neuronal damage in the somatosensory cortex causes formation of rod-shaped microglia that promote astrogliosis and persistent neuroinflammation
- Pages: 2719-2736
- First Published: 30 October 2018
Full Access
full
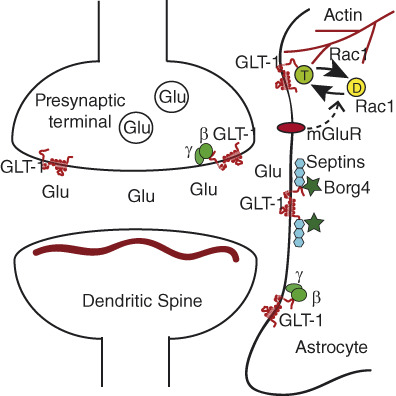
Identification of novel regulatory partners of the glutamate transporter GLT-1
- Pages: 2737-2755
- First Published: 05 November 2018
Full Access
full
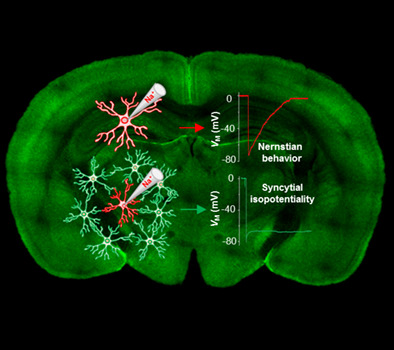
Syncytial isopotentiality: A system-wide electrical feature of astrocytic networks in the brain
- Pages: 2756-2769
- First Published: 12 September 2018