Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION - TABLE OF CONTENTS
Free Access
free
Issue Information - Table of Contents
- Pages: 1201-1203
- First Published: 15 June 2017
REVIEW ARTICLES
Open Access
oa
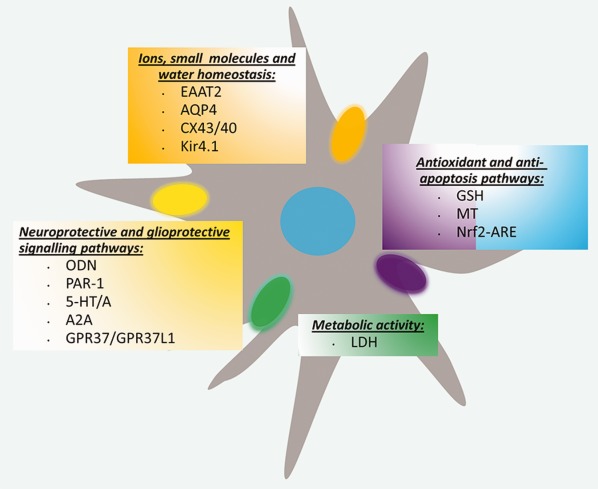
Astroglia as a cellular target for neuroprotection and treatment of neuro-psychiatric disorders
- Pages: 1205-1226
- First Published: 16 March 2017
Full Access
full
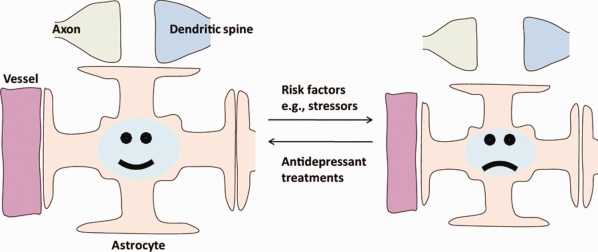
An astroglial basis of major depressive disorder? An overview
- Pages: 1227-1250
- First Published: 20 March 2017
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Open Access
oa
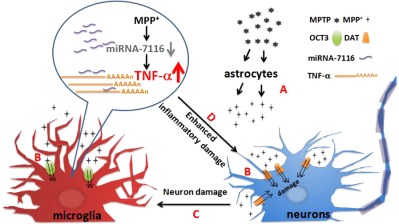
Downregulation of miR-7116-5p in microglia by MPP+ sensitizes TNF-α production to induce dopaminergic neuron damage
- Pages: 1251-1263
- First Published: 22 May 2017
Full Access
full
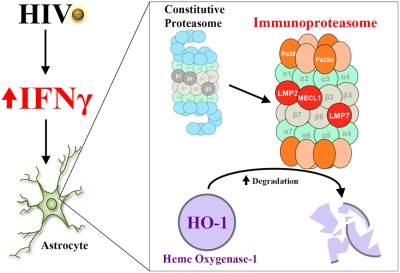
Degradation of heme oxygenase-1 by the immunoproteasome in astrocytes: A potential interferon-γ-dependent mechanism contributing to HIV neuropathogenesis
- Pages: 1264-1277
- First Published: 22 May 2017
Full Access
full
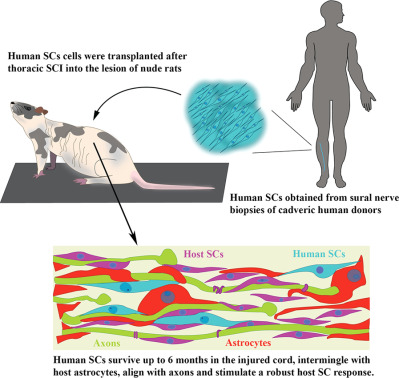
Human Schwann cells exhibit long-term cell survival, are not tumorigenic and promote repair when transplanted into the contused spinal cord
- Pages: 1278-1301
- First Published: 22 May 2017
Main Points
- Human SCs exhibit a safe therapeutic profile with an absence of tumorigenicity long-term in a xenotransplant paradigm of contusive SCI
- Introduction of human SCs into the injured cord produced an environment conducive to cyst reduction, enhanced white matter preservation, axon growth and myelination
Full Access
full
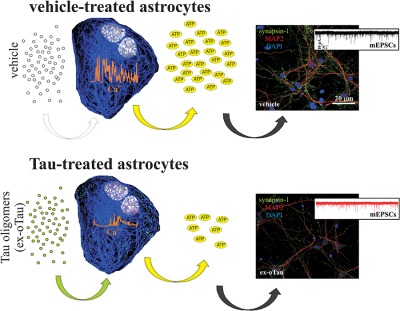
Reduced gliotransmitter release from astrocytes mediates tau-induced synaptic dysfunction in cultured hippocampal neurons
- Pages: 1302-1316
- First Published: 18 May 2017
Full Access
full
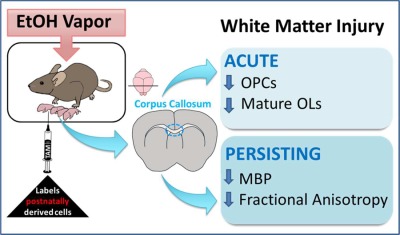
Acute oligodendrocyte loss with persistent white matter injury in a third trimester equivalent mouse model of fetal alcohol spectrum disorder
- Pages: 1317-1332
- First Published: 18 May 2017
Full Access
full
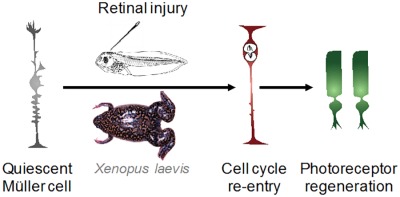
Müller glial cell reactivation in Xenopus models of retinal degeneration
- Pages: 1333-1349
- First Published: 26 May 2017
Open Access
oa
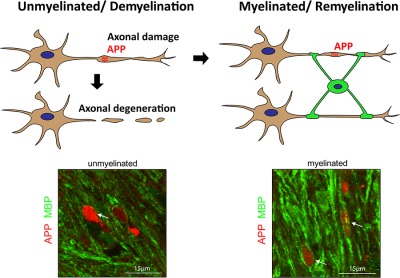
Acutely damaged axons are remyelinated in multiple sclerosis and experimental models of demyelination
- Pages: 1350-1360
- First Published: 31 May 2017
Open Access
oa
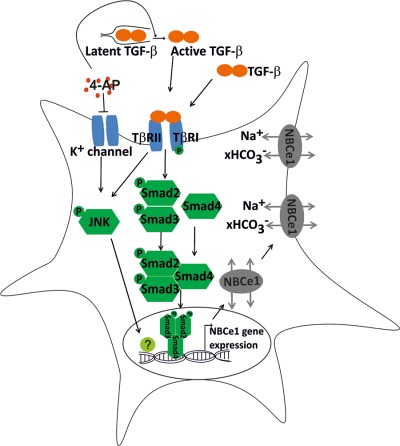
TGF-β signaling directly regulates transcription and functional expression of the electrogenic sodium bicarbonate cotransporter 1, NBCe1 (SLC4A4), via Smad4 in mouse astrocytes
- Pages: 1361-1375
- First Published: 01 June 2017
Full Access
full
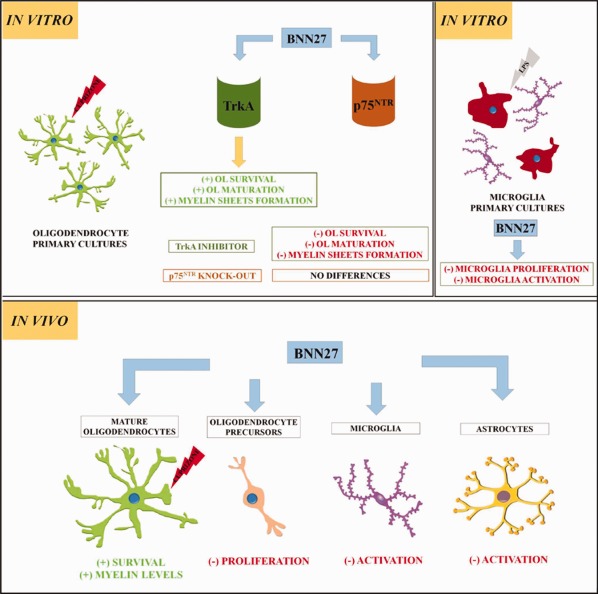
The novel synthetic microneurotrophin BNN27 protects mature oligodendrocytes against cuprizone-induced death, through the NGF receptor TrkA
- Pages: 1376-1394
- First Published: 01 June 2017