Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Image, Volume 39, Issue 6
- Page: i
- First Published: 16 May 2018
On the cover: This cover image, by Shigeru Nakamura et al., is based on the Brief Report STX2 is a causative gene for nonobstructive azoospermia, Pages 830-833 DOI: 10.1002/humu.23423.
Inferring the effect of genomic variation in the new era of genomics
- Pages: 756-773
- First Published: 06 April 2018
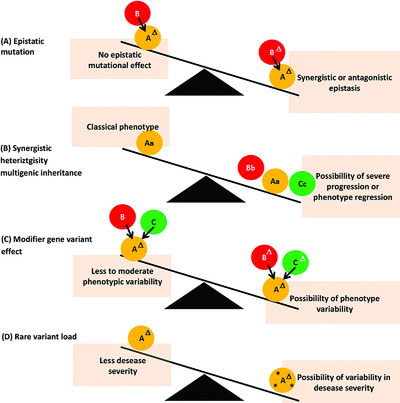
The big challenge in the new genomic era of personalized medicine is to resolve non-Mendelian gene-variant-disease relationship such as in polygenic disorders associated with epistasis, complex inheritance-patterns such as “synergistic heterozygosity”, digenic/multigenic inheritance, modifier gene-variant effect, and rare variant load. Resolving this will lead to novel pharamceuticals such as targeted gene-therapies, biomarkers or clinical-trial enrolments. We describe the newly-emerging functional genomics approaches, large-consortia efforts and novel computational algorithms and the promise of whole genome sequencing in tandem to overcome this.
Tricho-Hepato-Enteric Syndrome mutation update: Mutations spectrum of TTC37 and SKIV2L, clinical analysis and future prospects
- Pages: 774-789
- First Published: 11 March 2018
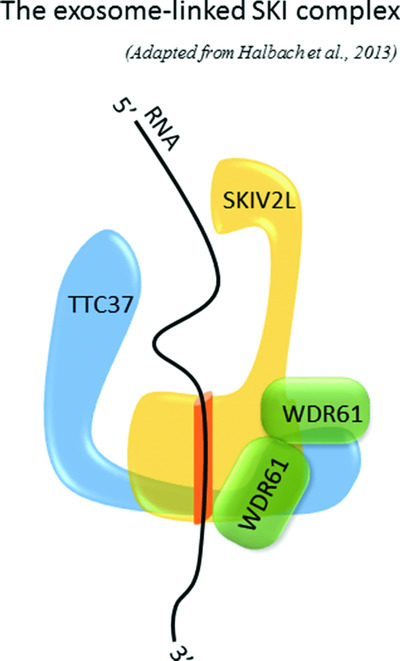
Tricho-Hepato-Enteric Syndrome is a very rare genetic enteropathy that has recently been shown to be caused by mutations of either TTC37 or SKIV2L genes, both coding proteins of the exosome-linked SKI complex. This paper reports an exhaustive phenotype and genotype data analysis from 96 cases worldwide, both from the literature and our in-house diagnostic cohort. Even if there is a remarkable phenotypic homogeneity, we are able to suggest that patients lacking SKIV2L seem more severely affected than those lacking TTC37, in terms of liver damage and prenatal growth impairment.
Mutation update for the GPC3 gene involved in Simpson-Golabi-Behmel syndrome and review of the literature
- Pages: 790-805
- First Published: 10 April 2018
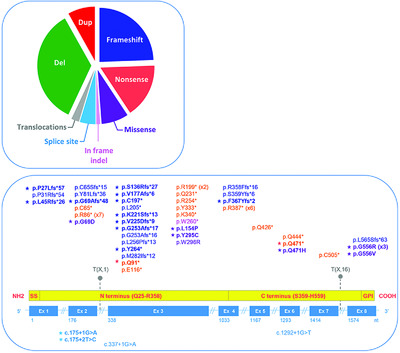
We provide, for the first time, an overview of the mutational spectrum of GPC3, the gene involved in Simpson-Golabi-Behmel syndrome, an X-linked multiple congenital anomalies and overgrowth syndrome, through the description of the 86 distinct mutations, ranging from single nucleotide variations to complex genomic rearrangements, identified until now. The vast majority of these mutations are deletions or truncating mutations (frameshift, nonsense mutations) predicted to result in a loss of function, whereas missense mutations are rare and need functional validation.
MSeqDR mvTool: A mitochondrial DNA Web and API resource for comprehensive variant annotation, universal nomenclature collation, and reference genome conversion
- Pages: 806-810
- First Published: 14 March 2018

MSeqDR is the Mitochondria Disease Sequence Data Resource. The mvTool is developed by the MSeqDR consortium and hosted at MSeqDR (https://www.mseqdr.org) to provide rich annotations for mtDNA variants. The mvTool support all mtDNA nomenclatures and converts variants to standard rCRS- and HGVS-based nomenclatures. In addition to generic annotations, the mvTool provides mtDNA variant allele frequencies in more than 47,000 germline mito-genomes, and disease and pathogenicity classifications from MSeqDR, MitoMap, HmtDB and ClinVar.
Mutations in the fourth β-propeller domain of LRP4 are associated with isolated syndactyly with fusion of the third and fourth fingers
- Pages: 811-815
- First Published: 10 March 2018
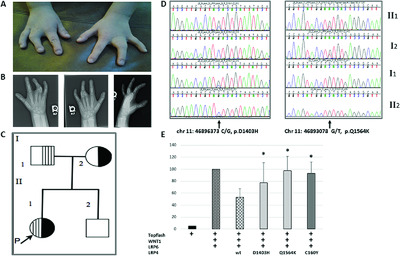
We report a child with isolated syndactyly of the third and fourth fingers with compound heterozygote non-synonymous variants (p.D1403H and p.Q1564K) in LRP4. Variants in LRP4 have been associated with syndactyly in Cenani-Lenz syndactyly syndrome and Sclerosteosis 2, but not with isolated syndactyly. These variants are located within the fourth β-propeller of the extracellular protein domain that has yet to be associated with disease. Functional analyses of these variants show that they significantly decrease LRP4's inhibition of Wnt signaling.
Neurofibromin (NF1) genetic variant structure–function analyses using a full-length mouse cDNA
- Pages: 816-821
- First Published: 09 March 2018
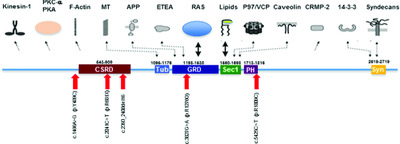
We established a heterologous cell culture expression system that allows structure-function analyses of predicted NF1 patient mutations and variants of unknown significance using a full-length mouse Nf1 cDNA and human cell lines. When the mNf1 cDNA is transiently transfected into HEK293 cells, neurofibromin is expressed in both NF1 replete (NF1+/+) and deficient (NF1−/−) cells. Re-expression of wild-type mNf1 cDNAs, but not mutants, produces neurofibromin that suppresses elevated pERK seen in the NF1−/− HEK293 cells.
A homozygous variant disrupting the PIGH start-codon is associated with developmental delay, epilepsy, and microcephaly
- Pages: 822-826
- First Published: 23 March 2018
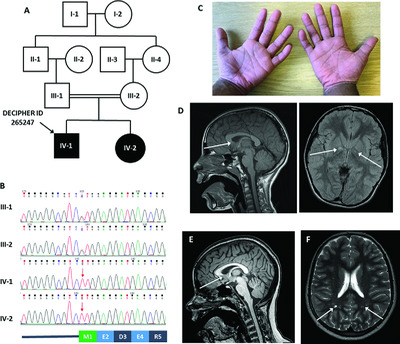
Although defective GPI-anchor biogenesis is known to cause a spectrum of predominantly neurological conditions, there are 8 genes critical to this biological process for which disease associations are not yet reported. Analysis of this set of genes in exomes from 9625 patients with developmental delay identified a homozygous PIGH start codon variant in siblings with epilepsy, microcephaly, and behavioral difficulties. FACS analysis of PIGH-deficient CHO cells indicated that cDNAs with c.1A > T could not efficiently restore expression of GPI-APs.
A PIGH mutation leading to GPI deficiency is associated with developmental delay and autism
- Pages: 827-829
- First Published: 30 March 2018
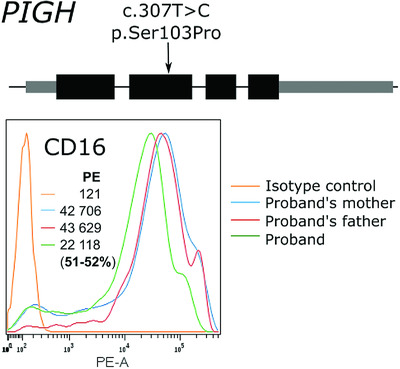
An individual with a homozygous missense variant (p.Ser103Pro) in PIGH had hypotonia, moderate developmental delay, and autism. This gene is key for the biosynthesis of the glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchor added to several neuronal proteins. Upon analysis of the surface expression of GPI-anchored proteins on granulocytes, he was demonstrated to have GPI deficiency. This suggest that PIGH mutations may cause a syndrome with developmental delay and autism, but without epilepsy.
STX2 is a causative gene for nonobstructive azoospermia
- Pages: 830-833
- First Published: 23 March 2018
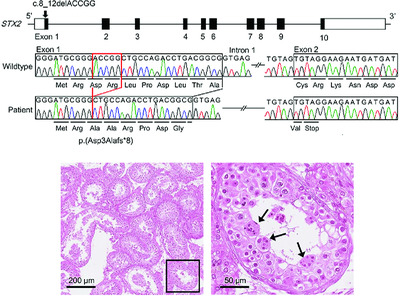
We identified a homozygous frameshift variant of STX2 in one of 131 Japanese men with nonobstructive azoospermia. Testicular histology of the variant-positive patient showed universal maturation arrest and multinucleated spermatocytes, which have also been observed in mice lacking Stx2. Our results indicate that STX2 nullizygosity results in maturation arrest with multinucleated spermatocytes, and accounts for a small fraction of cases with nonobstructive azoospermia.
Compound heterozygosity for loss-of-function FARSB variants in a patient with classic features of recessive aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase-related disease
- Pages: 834-840
- First Published: 23 March 2018
ABCA3 missense mutations causing surfactant dysfunction disorders have distinct cellular phenotypes
- Pages: 841-850
- First Published: 05 March 2018
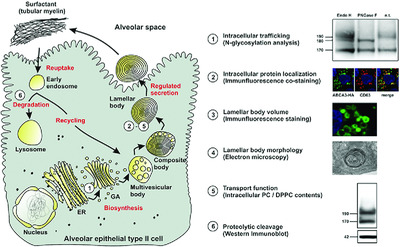
We found that our investigated missense mutations within the ABCA3 gene affect surfactant homeostasis in different ways: first by disrupting intracellular ABCA3 protein localization, second by impairing the lipid transport of ABCA3 protein, and third by yet undetermined mechanisms predisposing for the development of interstitial lung diseases despite correct localization and normal lipid transport of the variant ABCA3 protein.
Novel approach to functional SNPs discovery from genome-wide data reveals promising variants for colon cancer risk
- Pages: 851-859
- First Published: 23 March 2018

We combined available ChIP-Seq, ChIA-PET and RNA-Seq data and assessed 1476 regulatory SNPs (rSNPs) in the human genome with their gene targets. We further revealed twenty-seven rSNPs that exhibited a link with a risk of malignancy based on GWAS datasets and thirty – with a risk of colorectal cancer (CRC) based on the comparative minor allele frequency analysis (using ICGC RNA-Seq and dbSNP datasets). Our findings suggest that aberrant splicing is one of the key mechanisms in CRC and provide a subset of promising candidates for functional studies.
Genotype-specific progression of hereditary medullary thyroid cancer
- Pages: 860-869
- First Published: 14 April 2018
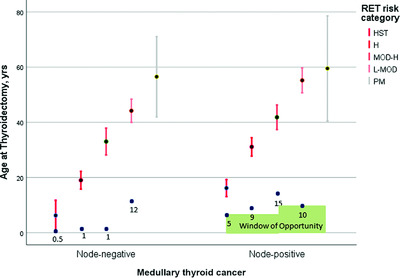
When 32 unique RET sequence variants (29 mutations, 3 polymorphisms), dispersed over 567 gene carriers, were grouped by mutational risk (highest; high; moderate–high; low–moderate; polymorphism), the age-related progression of medullary thyroid cancer (MTC) was significant for all categories of RET mutations, which differed significantly across and within the histopathological groups (normal thyroid/C-cell hyperplasia; node-negative MTC; node-positive MTC). This finding argues in favor of splitting the American Thyroid Association's moderate-risk category into moderate–high and low–moderate risk categories.
Robust identification of deletions in exome and genome sequence data based on clustering of Mendelian errors
- Pages: 870-881
- First Published: 11 March 2018
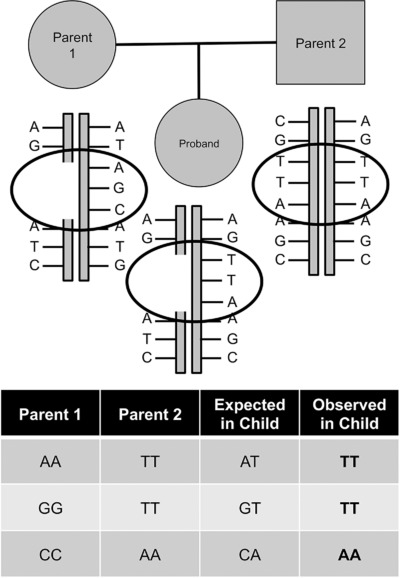
Here, we introduce the Mendelian Error Method (MEM), a novel tool to identify deletion CNVs based on the clustering of Mendelian errors (MEs) in whole exome and genome sequencing data from of trios. We show MEM deletion calls achieve validation rates of 88–97%, and can identify additional de novo deletions that are missed by read-depth based methods such as XHMM. In addition, MEM is able to robustly identify cases of uniparental disomy, sample switches, and DNA contamination.