Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Image
Issue Information – Table of Contents
Issue Information – Table of Contents
- Pages: 1237-1238
- First Published: 11 April 2017
Commentary
Pain: From genes and proteins to cells in the living organism
- Pages: 1239-1241
- First Published: 22 February 2017
Reviews
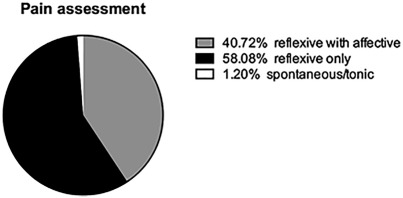
Animal models of chronic pain: Advances and challenges for clinical translation
- Pages: 1242-1256
- First Published: 04 July 2016
Psychological stress in early life as a predisposing factor for the development of chronic pain: Clinical and preclinical evidence and neurobiological mechanisms
- Pages: 1257-1270
- First Published: 12 July 2016
Neuropathic pain following traumatic spinal cord injury: Models, measurement, and mechanisms
- Pages: 1295-1306
- First Published: 12 September 2016
In most animal studies of neuropathic pain following spinal cord injury (SCI), behavioral assessments ignore affect. Consequently, reported pain may be merely SCI-associated hyperreflexia. Clinically, the affective component of pain dominates but is subjective. Additional progress depends on iterations of objective measures in a bench-to-bedside-and-back approach.
Research Article
α5GABAA Receptors Mediate Tonic Inhibition in the Spinal Cord Dorsal Horn and Contribute to the Resolution Of Hyperalgesia
- Pages: 1307-1318
- First Published: 28 October 2016
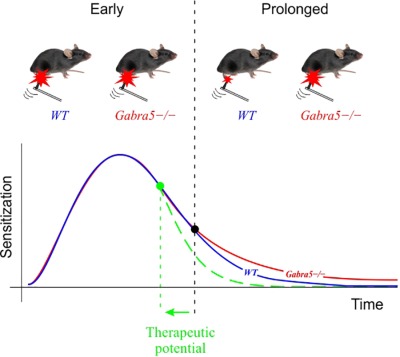
This study reveals that α5GABAARs generate a tonic inhibitory conductance in neurons of the spinal cord dorsal horn and regulate the resolution of hyperalgesia. Gabra5−/− mice show a normal degree of mechanical hypersensitivity immediately after peripheral insult but take longer to return to baseline responsiveness. These findings suggest that enhancing tonic inhibition through α5GABAARs receptors may accelerate recovery after a sensitizing insult.
Review
P2 receptors, microglial cytokines and chemokines, and neuropathic pain
- Pages: 1319-1329
- First Published: 04 July 2016
Research Article
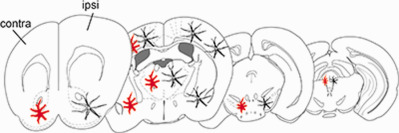
Topography of microglial activation in sensory- and affect-related brain regions in chronic pain
- Pages: 1330-1335
- First Published: 30 August 2016
Review
Systems, Circuits and Microcircuits
The noradrenergic locus coeruleus as a chronic pain generator
- Pages: 1336-1346
- First Published: 29 September 2016
Mini-Review
From blast to bench: A translational mini-review of posttraumatic headache
- Pages: 1347-1354
- First Published: 02 February 2017