Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Table of Contents
Salute to the sun: a new dawn in yoga therapy for breast cancer
- First Published: 30 January 2017
An image quality review programme in a population-based mammography screening service
- First Published: 03 June 2021
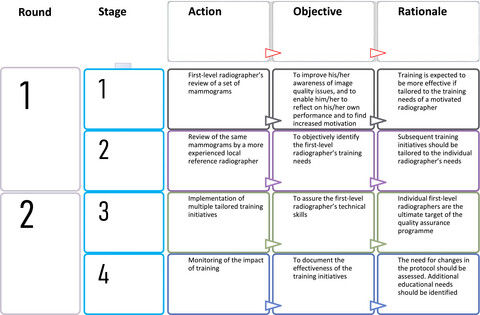
A regional multicentre image quality review programme for mammography was developed consisting of a process of review of a sample of mammograms with image quality classification, independently performed by all first-level radiographers and by more experienced local reference radiographers, followed by a training effort and a monitoring work. The programme places emphasis on motivating and training the radiographers and not on testing them. Its results demonstrate that a successful image quality review initiative for radiographers is one that encourages them to participate with a positive and confident attitude.
The breast cancer patient's experience of making radiation therapy treatment decisions
- First Published: 02 October 2013
The physical and psychological sexual well-being of women with pelvic malignancy: how can we understand and improve our practice?
- First Published: 26 May 2020

How can we better understand and improve our practice around the physical and psychological well-being of women treated with radiation therapy for pelvic malignancy? In this issue, Summerfield et al report the results of a nationwide survey capturing practices around the management of radiation therapy-induced vaginal adhesions and stenosis (RTVAS) across New Zealand. This study highlights the need for oncologists to improve care around a challenging but critically important aspect of women’s health beyond a cancer diagnosis.
Mammographic parenchymal patterns and breast cancer risk in New South Wales North Coast Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander women
- First Published: 25 February 2016
The objective of the study was to document the distribution of mammographic parenchymal patterns (MPP) of Indigenous Australian women and to profile breast cancer risk as it relates to breast density. A quantitative retrospective analysis reviewed 502 screening mammograms against the Tabár I–V MPP classification system. The study demonstrated that no identifiable or unique distribution of MPP was noted in this snapshot of Indigenous women.
The role of volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT) in gynaecological radiation therapy: A dosimetric comparison of intensity modulated radiation therapy versus VMAT
- First Published: 02 November 2018
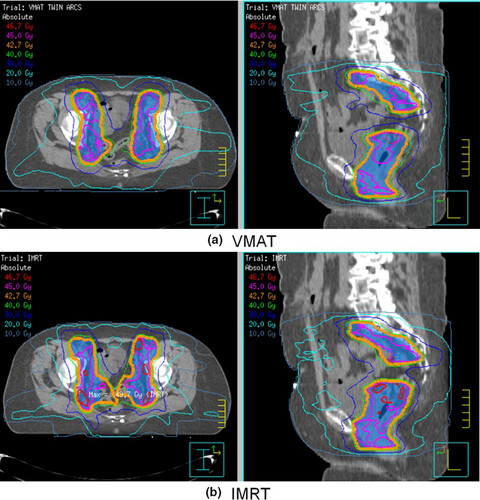
This study developed a twin arc volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT) technique for gynaecological cancer patients. Comparisons between the VMAT and previously implemented 7–9 intensity modulated radiation therapy technique found comparable planning target volume coverage and improved organs at risk sparing.
Feasibility of bone marrow sparing volumetric modulated arc therapy to spare active bone marrow in cervical and vaginal cancer patients: a retrospective dosimetric analysis
- First Published: 19 July 2021
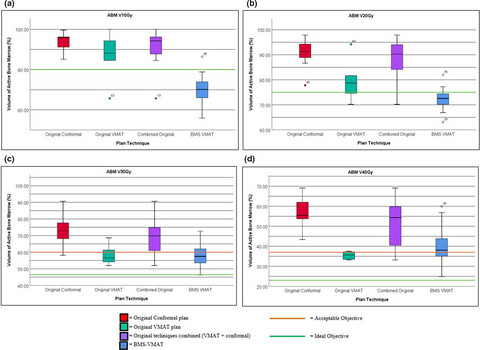
Bone marrow sparing volumetric modulated arc therapy (BMS-VMAT) is a recent technique aimed at reducing haematological toxicity in patients with cervical and vaginal cancer undergoing chemoradiotherapy that could potentially result in treatment interruptions. Our retrospective study found that significant dosimetric sparing in active areas of bone marrow could be achieved, whilst maintaining clinically acceptable target and organ-at-risk doses, comparable to VMAT where BMS was not considered.
Use of magnetic resonance image-guided radiotherapy for breast cancer: a scoping review
- First Published: 15 September 2021
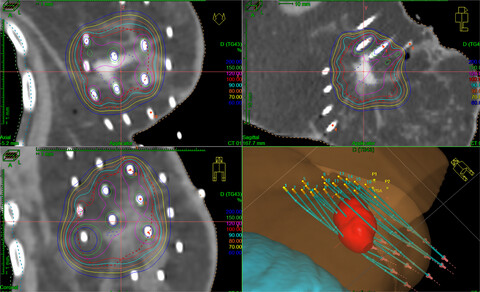
Accelerated partial breast irradiation (APBI) is the most common form of treatment for MRIgRT. The presence of the magnet does not affect target coverage or violate organ at risk (OAR) constraints compared to standard RT methods. Consideration is advised for skin and chestwall (CW) due to the electron return effect (ERE) and areas such as armpit and chin due to the electron stream effect (ESE).
Expanding the indications for MRI in the diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer: what is best practice?
- First Published: 31 January 2015

Breast magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) now has an accepted place in screening younger women at high risk of breast cancer, and is increasingly used in a number of other settings including assessment of response to neo-adjuvant therapy and local staging of cancer. Although the evidence for its general use in these settings is very limited, in highly selected patients, especially where discordance with conventional measurements occurs, MRI can have a place in assessing the extent of disease, both whether operable and how operable, and guiding surgery. These scenarios and future indications and alternative technologies are explored in this paper.
Extreme hypofractionation in radiation therapy for patients with early breast cancer: what is the optimal technique?
- First Published: 20 April 2022
Many radiation techniques have been employed in the trend of moving towards more hypofractionated regimens in the treatment of early breast cancer. This editorial articulates the advantages of using multi-catheter interstitial brachytherapy when delivering extreme hypofractionation for partial breast radiation.
Imaging dose in breast radiotherapy: does breast size affect the dose to the organs at risk and the risk of secondary cancer to the contralateral breast?
- First Published: 07 January 2015
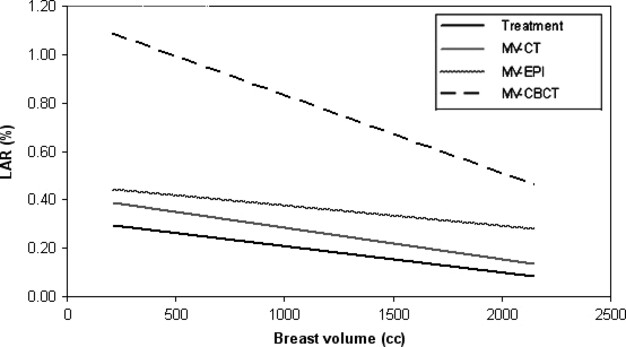
This study investigates the imaging doses related to breast size for three imaging modalities used in breast radiotherapy. The study's main finding was that the primary breast volume inversely correlated with the contralateral breast dose for all three imaging modalities. As the primary breast volume increases, the likelihood of a patient developing a radiation-induced secondary cancer to the contralateral breast decreases.
Artificial intelligence and convolution neural networks assessing mammographic images: a narrative literature review
- First Published: 05 March 2020
Comprehensive nodal breast VMAT: solving the low-dose wash dilemma using an iterative knowledge-based radiotherapy planning solution
- First Published: 12 August 2021

Comprehensive lymph nodal (CLN) radiotherapy can improve the outcomes for advanced breast cancer patients, but it can be particularly challenging to balance target coverage and organ-at-risk sparing without complex beam modification (VMAT avoidance sectors, hybrid IMRT/VMAT fields, other) to limit the low-dose wash and potential second malignancy risk. By presenting the first application of iterative learning to a knowledge-based planning model in CLN-breast radiotherapy, this study demonstrates that a simple and robust ipsilateral VMAT class solution can be applied without increase in low-dose wash compared to benchmark base-tangential IMRT/VMAT methods.










-1693813706.png)