Practical stability for switched affine systems via time-dependent switching function
Funding information: National Natural Science Foundation of China, 61803001; 61971100
Abstract
In this article, the stability analysis of both continuous-time switched affine systems discrete-time switched affine systems is addressed via dwell time switching. Since the information of system states is difficult to obtain in the state-dependent switching function, the time-dependent switching function is considered to stabilize the switched affine system. The purpose of this article is to design a time-dependent switching function assuring the state trajectories are globally attracted to an attractive set containing the desired equilibrium point (which is selected from a set of attainable equilibrium points). By constructing discretized Lyapunov function, a set of conditions in the framework of dwell time are designed to guarantee practical stability of the state trajectories. At last, some numerical examples are given to illustrate our method and compare it with the existing results.
Open Research
DATA AVAILABILITY STATEMENT
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
No conflict of interest exists in the submission of this manuscript, and the manuscript is approved by all authors for publication. I would like to declare on behalf of my coauthors that the work described was original research that has not been published previously, and not under consideration for publication elsewhere, in whole or in part. All the authors listed have approved the manuscript that is enclosed.



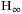 switching control techniques for switched nonlinear systems with application to urban traffic control
switching control techniques for switched nonlinear systems with application to urban traffic control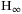 control design of continuous-time switched affine systems
control design of continuous-time switched affine systems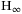 control of continuous-time switched affine systems
control of continuous-time switched affine systems