Synthesis of Allylic Phosphate Linked Dinucleotide Phosphoramidite: For the Application of Oligonucleotide Synthesis, Gene Assembly and Protein Expression†
Anzhe Shi
Bioinformatics Center of AMMS, Beijing, 100850 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorYi Xu
Bioinformatics Center of AMMS, Beijing, 100850 China
School of Pharmacy, Yantai University, Yantai, Shandong, 264005 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorXiang Song
Bioinformatics Center of AMMS, Beijing, 100850 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorXinxiu Deng
Bioinformatics Center of AMMS, Beijing, 100850 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Xiaoyang He
Bioinformatics Center of AMMS, Beijing, 100850 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Shengqi Wang
Bioinformatics Center of AMMS, Beijing, 100850 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorAnzhe Shi
Bioinformatics Center of AMMS, Beijing, 100850 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorYi Xu
Bioinformatics Center of AMMS, Beijing, 100850 China
School of Pharmacy, Yantai University, Yantai, Shandong, 264005 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorXiang Song
Bioinformatics Center of AMMS, Beijing, 100850 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorXinxiu Deng
Bioinformatics Center of AMMS, Beijing, 100850 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Xiaoyang He
Bioinformatics Center of AMMS, Beijing, 100850 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Shengqi Wang
Bioinformatics Center of AMMS, Beijing, 100850 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this author† Dedicated to the Special Issue of Nucleic Acid Chemistry.
Comprehensive Summary
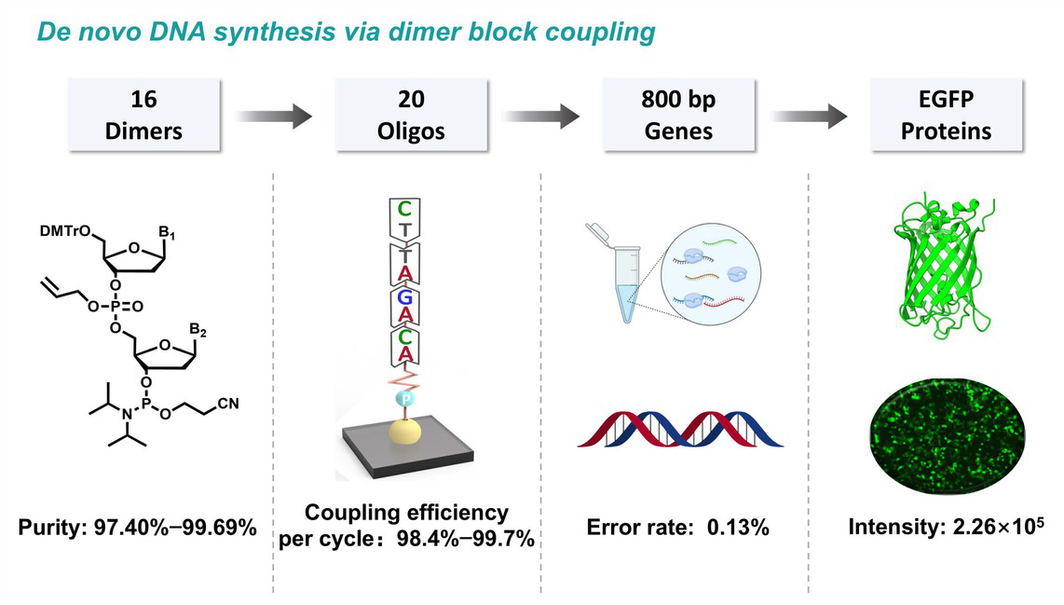
Chain elongation via dinucleotide (dimer) block coupling was considered as an improved chemical technique capable of synthesizing high-quality longer oligonucleotide for de novo DNA synthesis in synthetic biology. However, this dimer block-wise approach was constrained by readily available dimer phosphoramidite with sufficient quality. Herein, through the usage of a one-pot coupling-oxidation-deprotection cascade process for preparing the key precursors 3'-hydroxyl dimers, then condensation with phosphorodiamidite, purification by flash column chromatography and precipation in methyl tert-butyl ether, a rationally designed dimer phosphoramidite bearing an internucleotide allyl phosphate and a β-cyanoethyl phosphoramidite at the 3’-hydroxyl was synthesized. All sixteen allylic dimer phosphoramidites 2a–p were smoothly prepared with overall yields exceeding 50% and HPLC purities ranging from 97.40% to 99.69%. With these allylic reagents, oligonucleotides were successfully synthesized using a modified solid-phase phosphoramidite method and were completely deprotected under normal ammonialysis condition. Our results indicated that these dimer block-wise synthesized oligonucleotides were of sufficient quality for gene assembly and protein expression, thus, the allylic phosphate linked dimer phosphoramidite can serve as a promising dimer reagent that will enable the applications of long oligonucleotides.
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| cjoc202500117-sup-0001-supinfo.pdfPDF document, 5.3 MB |
Appendix S1: Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1 Hoose, A.; Vellacott, R.; Storch, M.; Freemont, P. S.; Ryadnov, M. G. DNA synthesis technologies to close the gene writing gap. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2023, 7, 144–161.
- 2 Boeke, J. D.; Church, G.; Hessel, A.; Kelley, N. J.; Arkin, A.; Cai, Y.; Carlson, R.; Chakravarti, A.; Cornish, V. W.; Holt, L.; Isaacs, F. J.; Kuiken, T.; Lajoie, M.; Lessor, T.; Lunshof, J.; Maurano, M. T.; Mitchell, L. A.; Rine, J.; Rosser, S.; Sanjana, N. E.; Silver, P. A.; Valle, D.; Wang, H.; Way, J. C.; Yang, L. GENOME ENGINEERING. The Genome Project- Write. Science 2016, 353, 126–127.
- 3 Dong, Y.; Sun, F.; Ping, Z.; Ouyang, Q.; Qian, L. DNA storage: research landscape and future prospects. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2020, 7, 1092–1107.
- 4 Xu, C.; Zhao, C.; Ma, B.; Liu, H. Uncertainties in synthetic DNA-based data storage. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 5451–5469.
- 5 Yu, M.; Tang, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, W.; Wang, S.; Li, M.; Yu, Q.; Xie, S.; Zuo, X.; Chen, C. High-throughput DNA synthesis for data storage. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2024, 53, 4463–4489.
- 6 Hughes, R. A.; Ellington, A. D. Synthetic DNA Synthesis and Assembly: Putting the Synthetic in Synthetic Biology. Cold Spring Harbor Perspect. Biol. 2017, 9, a023812.
- 7 Ostrov, N.; Beal, J.; Ellis, T.; Gordon, D. B.; Karas, B. J.; Lee, H. H.; Lenaghan, S. C.; Schloss, J. A.; Stracquadanio, G.; Trefzer, A.; Bader, J. S.; Church, G. M.; Coelho, C. M.; Efcavitch, J. W.; Güell, M.; Mitchell, L. A.; Nielsen, A. A. K.; Peck, B.; Smith, A. C.; Stewart, C. N.; Tekotte, H. Technological challenges and milestones for writing genomes. Science 2019, 366, 310–312.
- 8 Song, L. F.; Deng, Z. H.; Gong, Z. Y.; Li, L. L.; Li, B. Z. Large-Scale de novo Oligonucleotide Synthesis for Whole-Genome Synthesis and Data Storage: Challenges and Opportunities. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 689797.
- 9 Beaucage, S. L.; Iyer, R. P. Advances in the Synthesis of Oligonucleotides by the Phosphoramidite Approach. Tetrahedron 1992, 48, 2223–2311.
- 10 Beaucage, S. L.; Caruthers, M. H. Deoxynucleoside phosphoramidites—A new class of key intermediates for deoxypolynucleotide synthesis. Tetrahedron Lett. 1981, 22, 1859–1862.
- 11 Quan, J.; Saaem, I.; Tang, N.; Ma, S.; Negre, N.; Gong, H.; White, K. P.; Tian, J. Parallel on-chip gene synthesis and application to optimization of protein expression. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 449–452.
- 12 LeProust, E. M.; Peck, B. J.; Spirin, K.; McCuen, H. B.; Moore, B.; Namsaraev, E.; Caruthers, M. H. Synthesis of high-quality libraries of long (150mer) oligonucleotides by a novel depurination controlled process. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, 2522–2540.
- 13
Efcavitch, J. W.; Heiner, C. R. Depurination as a Yield Decreasing Mechanism in Oligodeoxynucleotide Synthesis. Nucleosides, Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 1985, 4, 267–267.
10.1080/07328318508077883 Google Scholar
- 14 Jensen, M. A.; Davis, R. W. Template-Independent Enzymatic Oligonucleotide Synthesis (TiEOS): Its History, Prospects, and Challenges. Biochemistry 2018, 57, 1821–1832.
- 15 Eisenstein, M. Enzymatic DNA synthesis enters new phase. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 1113–1115.
- 16 Palluk, S.; Arlow, D. H.; de Rond, T.; Barthel, S.; Kang, J. S.; Bector, R.; Baghdassarian, H. M.; Truong, A. N.; Kim, P. W.; Singh, A. K.; Hillson, N. J.; Keasling, J. D. De novo DNA synthesis using polymerase-nucleotide conjugates. Nat. Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 645–650.
- 17 Verardo, D.; Adelizzi, B.; Rodriguez-Pinzon, D. A.; Moghaddam, N.; Thomée, E.; Loman, T.; Godron, X.; Horgan, A. Multiplex enzymatic synthesis of DNA with single-base resolution. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadi0263.
- 18 Lu, X.; Li, J.; Li, C.; Lou, Q.; Peng, K.; Cai, B.; Liu, Y.; Yao, Y.; Lu, L.; Tian, Z.; Ma, H.; Wang, W.; Cheng, J.; Guo, X.; Jiang, H.; Ma, Y. Enzymatic DNA Synthesis by Engineering Terminal Deoxynucleotidyl Transferase. ACS Catal. 2022, 12, 2988–2997.
- 19 Perkel, J. M. The race for enzymatic DNA synthesis heats up. Nature 2019, 566, 565–565.
- 20 Simmons, B. L.; McDonald, N. D.; Robinett, N. G. Assessment of enzymatically synthesized DNA for gene assembly. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1208784.
- 21 Yin, Y.; Arneson, R.; Apostle, A.; Eriyagama, A.; Chillar, K.; Burke, E.; Jahfetson, M.; Yuan, Y.; Fang, S. Long oligodeoxynucleotides: chemical synthesis, isolation via catching-by-polymerization, verification via sequencing, and gene expression demonstration. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1957–1965.
- 22 Krotz, A. H.; Klopchin, P.; Cole, D. L.; Ravikumar, V. T. Phosphorothioate oligonucleotides: Largely reduced (N-1)-mer and phosphodiester content through the use of dimeric phosphoramidite synthons. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1997, 7, 73–78.
- 23 Kumar, G.; Poonian, M. S. Improvements in oligodeoxyribonucleotide synthesis: methyl N,N-dialkylphosphoramidite dimer units for solid support phosphite methodology. J. Org. Chem. 1984, 49, 4905–4912.
- 24 Shi, A.; Liu, L.; Wang, F.; Deng, X.; He, X.; Wang, S. A practical dinucleotide phosphoramidite chemistry for de novo DNA synthesis via block coupling. Tetrahedron Lett. 2024, 142, 155106.
- 25 Umemoto, T.; Wada, T. Nitromethane as a scavenger of acrylonitrile in the deprotection of synthetic oligonucleotides. Tetrahedron Lett. 2005, 46, 4251–4253.
- 26
Hayakawa, Y. Toward an Ideal Synthesis of Oligonucleotides: Development of a Novel Phosphoramidite Method with High Capability. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2002, 74, 1547–1565.
10.1246/bcsj.74.1547 Google Scholar
- 27 Manoharan, M.; Lu, Y.; Casper, M. D.; Just, G. Allyl group as a protecting group for internucleotide phosphate and thiophosphate linkages in oligonucleotide synthesis: facile oxidation and deprotection conditions. Org. Lett. 2000, 2, 243–246.
- 28 Bergmann, F.; Kueng, E.; Laiza, P.; Bannwarth, W. Allyl as internucleotide protecting group in DNA synthesis to be cleaved off by ammonia. Tetrahedron 1995, 51, 6971–6976.
- 29 Westman, E.; Strömberg, R. Removal of t-butyldimethylsilyl protection in RNA-synthesis. Triethylamine trihydrofluoride (TEA, 3HF) is a more reliable alternative to tetrabutylammonium fluoride (TBAF). Nucleic Acids Res. 1994, 22, 2430–2431.
- 30 Janczyk, M.; Appel, B.; Springstubbe, D.; Fritz, H. J.; Müller, S. A new and convenient approach for the preparation of β-cyanoethyl protected trinucleotide phosphoramidites. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2012, 10, 1510–1513.
- 31 Masaki, Y.; Onishi, Y.; Seio, K. Quantification of synthetic errors during chemical synthesis of DNA and its suppression by non-canonical nucleosides. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 12095.




