Synthesis of Sub-2 nm Iron-Doped NiSe2 Nanowires and Their Surface-Confined Oxidation for Oxygen Evolution Catalysis
Chao Gu
Division of Nanomaterials & Chemistry, Hefei National Research Centre for Physical Sciences at the Microscale, CAS Centre for Excellence in Nanoscience, Collaborative Innovation Centre of Suzhou Nano Science and Technology, Department of Chemistry, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, 230026 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorShaojin Hu
Division of Theoretical and Computational Sciences, Hefei National Research Centre for Physical Sciences at the Microscale, CAS Centre for Excellence and Synergetic Innovation Centre in Quantum Information and Quantum Physics, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, 230026 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Xusheng Zheng
National Synchrotron Radiation Laboratory, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, 230029 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Min-Rui Gao
Division of Nanomaterials & Chemistry, Hefei National Research Centre for Physical Sciences at the Microscale, CAS Centre for Excellence in Nanoscience, Collaborative Innovation Centre of Suzhou Nano Science and Technology, Department of Chemistry, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, 230026 China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Ya-Rong Zheng
Division of Nanomaterials & Chemistry, Hefei National Research Centre for Physical Sciences at the Microscale, CAS Centre for Excellence in Nanoscience, Collaborative Innovation Centre of Suzhou Nano Science and Technology, Department of Chemistry, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, 230026 China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Lei Shi
Division of Nanomaterials & Chemistry, Hefei National Research Centre for Physical Sciences at the Microscale, CAS Centre for Excellence in Nanoscience, Collaborative Innovation Centre of Suzhou Nano Science and Technology, Department of Chemistry, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, 230026 China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Qiang Gao
Division of Nanomaterials & Chemistry, Hefei National Research Centre for Physical Sciences at the Microscale, CAS Centre for Excellence in Nanoscience, Collaborative Innovation Centre of Suzhou Nano Science and Technology, Department of Chemistry, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, 230026 China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Xiao Zheng
Division of Theoretical and Computational Sciences, Hefei National Research Centre for Physical Sciences at the Microscale, CAS Centre for Excellence and Synergetic Innovation Centre in Quantum Information and Quantum Physics, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, 230026 China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Wangsheng Chu
National Synchrotron Radiation Laboratory, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, 230029 China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Hong-Bin Yao
Division of Nanomaterials & Chemistry, Hefei National Research Centre for Physical Sciences at the Microscale, CAS Centre for Excellence in Nanoscience, Collaborative Innovation Centre of Suzhou Nano Science and Technology, Department of Chemistry, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, 230026 China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Junfa Zhu
National Synchrotron Radiation Laboratory, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, 230029 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Shu-Hong Yu
Division of Nanomaterials & Chemistry, Hefei National Research Centre for Physical Sciences at the Microscale, CAS Centre for Excellence in Nanoscience, Collaborative Innovation Centre of Suzhou Nano Science and Technology, Department of Chemistry, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, 230026 China
Search for more papers by this authorChao Gu
Division of Nanomaterials & Chemistry, Hefei National Research Centre for Physical Sciences at the Microscale, CAS Centre for Excellence in Nanoscience, Collaborative Innovation Centre of Suzhou Nano Science and Technology, Department of Chemistry, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, 230026 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorShaojin Hu
Division of Theoretical and Computational Sciences, Hefei National Research Centre for Physical Sciences at the Microscale, CAS Centre for Excellence and Synergetic Innovation Centre in Quantum Information and Quantum Physics, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, 230026 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Xusheng Zheng
National Synchrotron Radiation Laboratory, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, 230029 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Min-Rui Gao
Division of Nanomaterials & Chemistry, Hefei National Research Centre for Physical Sciences at the Microscale, CAS Centre for Excellence in Nanoscience, Collaborative Innovation Centre of Suzhou Nano Science and Technology, Department of Chemistry, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, 230026 China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Ya-Rong Zheng
Division of Nanomaterials & Chemistry, Hefei National Research Centre for Physical Sciences at the Microscale, CAS Centre for Excellence in Nanoscience, Collaborative Innovation Centre of Suzhou Nano Science and Technology, Department of Chemistry, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, 230026 China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Lei Shi
Division of Nanomaterials & Chemistry, Hefei National Research Centre for Physical Sciences at the Microscale, CAS Centre for Excellence in Nanoscience, Collaborative Innovation Centre of Suzhou Nano Science and Technology, Department of Chemistry, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, 230026 China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Qiang Gao
Division of Nanomaterials & Chemistry, Hefei National Research Centre for Physical Sciences at the Microscale, CAS Centre for Excellence in Nanoscience, Collaborative Innovation Centre of Suzhou Nano Science and Technology, Department of Chemistry, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, 230026 China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Xiao Zheng
Division of Theoretical and Computational Sciences, Hefei National Research Centre for Physical Sciences at the Microscale, CAS Centre for Excellence and Synergetic Innovation Centre in Quantum Information and Quantum Physics, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, 230026 China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Wangsheng Chu
National Synchrotron Radiation Laboratory, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, 230029 China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Hong-Bin Yao
Division of Nanomaterials & Chemistry, Hefei National Research Centre for Physical Sciences at the Microscale, CAS Centre for Excellence in Nanoscience, Collaborative Innovation Centre of Suzhou Nano Science and Technology, Department of Chemistry, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, 230026 China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Junfa Zhu
National Synchrotron Radiation Laboratory, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, 230029 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Shu-Hong Yu
Division of Nanomaterials & Chemistry, Hefei National Research Centre for Physical Sciences at the Microscale, CAS Centre for Excellence in Nanoscience, Collaborative Innovation Centre of Suzhou Nano Science and Technology, Department of Chemistry, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, 230026 China
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
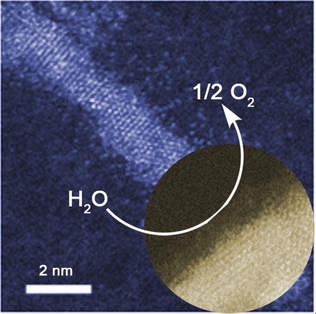
Down to the wire: Colloidal Fe-doped NiSe2 ultrathin nanowires (UNWs) down to 1.7 nm in diameter were synthesized by a binary soft-template strategy. These UNWs yield surface-confined electrochemical oxidation, enabling efficient and robust oxygen evolution catalysis owing to their favorable electronic structures and unsaturated local coordination environments.
Abstract
Ultrathin nanostructures are attractive for diverse applications owing to their unique properties compared to their bulk materials. Transition-metal chalcogenides are promising electrocatalysts, yet it remains difficult to make ultrathin structures (sub-2 nm), and the realization of their chemical doping is even more challenging. Herein we describe a soft-template mediated colloidal synthesis of Fe-doped NiSe2 ultrathin nanowires (UNWs) with diameter down to 1.7 nm. The synergistic interplay between oleylamine and 1-dodecanethiol is crucial to yield these UNWs. The in situ formed amorphous hydroxide layers that is confined to the surface of the ultrathin scaffolds enable efficient oxygen evolution electrocatalysis. The UNWs exhibit a very low overpotential of 268 mV at 10 mA cm−2 in 0.1 m KOH, as well as remarkable long-term stability, representing one of the most efficient noble-metal-free catalysts.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie201800883-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf2.2 MB | Supplementary |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1
- 1aL. Cademartiri, G. A. Ozin, Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 1013–1020;
- 1bS. Hu, X. Wang, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 5577–5594;
- 1cH. Zhang, ACS Nano 2015, 9, 9451–9469;
- 1dM. Nasilowski, B. Mahler, E. Lhuillier, S. Ithurria, B. Dubertret, Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 10934;
- 1eA. C. Berends, C. de Mello Donega, J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2017, 8, 4077–4090.
- 2F. Wang, A. Dong, W. E. Buhro, Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 10888–10933.
- 3
- 3aX. Lu, M. S. Yavuz, H. Y. Tuan, B. A. Korgel, Y. Xia, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 8900–8901;
- 3bZ. Huo, C. K. Tsung, W. Huang, X. Zhang, P. Yang, Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 2041–2044.
- 4
- 4aB. Y. Xia, H. B. Wu, Y. Yan, X. W. Lou, X. Wang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 9480–9485;
- 4bG. Chen, C. Xu, X. Huang, J. Ye, L. Gu, G. Li, Z. Tang, B. Wu, H. Yang, Z. Zhao, Z. Zhou, G. Fu, N. Zheng, Nat. Mater. 2016, 15, 564–569;
- 4cK. Jiang, D. Zhao, S. Guo, X. Zhang, X. Zhu, J. Guo, G. Lu, X. Huang, Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e 1601705.
- 5Z. Wu, Y. Li, J. Liu, Z. Lu, H. Zhang, B. Yang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 12196–12200; Angew. Chem. 2014, 126, 12392–12396.
- 6Z. Huo, C. K. Tsung, W. Huang, M. Fardy, R. Yan, X. Zhang, Y. Li, P. Yang, Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 1260–1264.
- 7G. Xi, S. Ouyang, P. Li, J. Ye, Q. Ma, N. Su, H. Bai, C. Wang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 2395–2399; Angew. Chem. 2012, 124, 2445–2449.
- 8
- 8aL. Cademartiri, R. Malakooti, P. G. O'Brien, A. Migliori, S. Petrov, N. P. Kherani, G. A. Ozin, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 3814–3817; Angew. Chem. 2008, 120, 3874–3877;
- 8bY. Du, Z. Yin, J. Zhu, X. Huang, X. J. Wu, Z. Zeng, Q. Yan, H. Zhang, Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 1177.
- 9
- 9aZ. Deng, H. Yan, Y. Liu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 8695–8698; Angew. Chem. 2010, 122, 8877–8880;
- 9bG. Zhu, S. Zhang, Z. Xu, J. Ma, X. Shen, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 15605–15612.
- 10Y. P. Du, Y. W. Zhang, Z. G. Yan, L. D. Sun, C. H. Yan, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 16364–16365.
- 11S. Hu, H. Liu, P. Wang, X. Wang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 11115–11124.
- 12
- 12aM. R. Gao, W. T. Yao, H. B. Yao, S. H. Yu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 7486–7487;
- 12bH. Li, S. Chen, H. Lin, X. Xu, H. Yang, L. Song, X. Wang, Small 2017, 13, 1701487.
- 13
- 13aY. Du, G. Cheng, W. Luo, Nanoscale 2017, 9, 6821–6825;
- 13bY. Du, G. Cheng, W. Luo, Catal. Sci. Technol. 2017, 7, 4604–4608.
- 14
- 14aM. R. Gao, Y. F. Xu, J. Jiang, S. H. Yu, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 2986–3017;
- 14bM. R. Gao, Y. R. Zheng, J. Jiang, S. H. Yu, Acc. Chem. Res. 2017, 50, 2194–2204;
- 14cM. S. Faber, S. Jin, Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 3519–3542.
- 15M. Gong, H. Dai, Nano Res. 2014, 8, 23–39.
- 16S. Jin, ACS Energy Lett. 2017, 2, 1937–1938.
- 17
- 17aC. Tang, N. Cheng, Z. Pu, W. Xing, X. Sun, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 9351–9355; Angew. Chem. 2015, 127, 9483–9487;
- 17bK. Xu, H. Ding, K. Jia, X. Lu, P. Chen, T. Zhou, H. Cheng, S. Liu, C. Wu, Y. Xie, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 1710–1713; Angew. Chem. 2016, 128, 1742–1745.
- 18X. Xu, F. Song, X. Hu, Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12324.
- 19
- 19aW. Chen, H. Wang, Y. Li, Y. Liu, J. Sun, S. Lee, J. S. Lee, Y. Cui, ACS Cent. Sci. 2015, 1, 244–251;
- 19bW. Chen, Y. Liu, Y. Li, J. Sun, Y. Qiu, C. Liu, G. Zhou, Y. Cui, Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 7588–7596.
- 20S. Zhao, Y. Wang, J. Dong, C.-T. He, H. Yin, P. An, K. Zhao, X. Zhang, C. Gao, L. Zhang, J. Lv, J. Wang, J. Zhang, A. M. Khattak, N. A. Khan, Z. Wei, J. Zhang, S. Liu, H. Zhao, Z. Tang, Nat. Energy 2016, 1, 16184.
- 21J. Yang, G.-H. Cheng, J.-H. Zeng, S.-H. Yu, X.-M. Liu, Y.-T. Qian, Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 848–853.
- 22F. Wang, Y. Li, T. A. Shifa, K. Liu, F. Wang, Z. Wang, P. Xu, Q. Wang, J. He, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 6919–6924; Angew. Chem. 2016, 128, 7033–7038.
- 23Y. Zhang, H. Xu, Q. Wang, Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 8941–8943.
- 24X. G. Peng, J. Wickham, A. P. Alivisatos, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 5343–5344.
- 25I. H. Kwak, H. S. Im, D. M. Jang, Y. W. Kim, K. Park, Y. R. Lim, E. H. Cha, J. Park, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 5327–5334.
- 26D. Y. Wang, M. Gong, H. L. Chou, C. J. Pan, H. A. Chen, Y. Wu, M. C. Lin, M. Guan, J. Yang, C. W. Chen, Y. L. Wang, B. J. Hwang, C. C. Chen, H. Dai, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 1587–1592.
- 27M. W. Louie, A. T. Bell, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 12329–12337.
- 28M. Gao, W. Sheng, Z. Zhuang, Q. Fang, S. Gu, J. Jiang, Y. Yan, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 7077–7084.
- 29L. Trotochaud, J. K. Ranney, K. N. Williams, S. W. Boettcher, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 17253–17261.
- 30R. D. Smith, M. S. Prevot, R. D. Fagan, S. Trudel, C. P. Berlinguette, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 11580–11586.