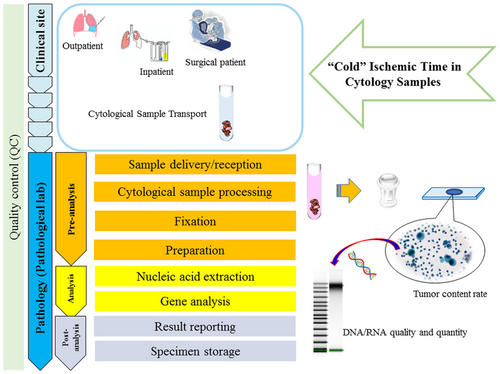
Impact of Cold Ischemic Time on Nucleic Acid Quality in Cytology Samples for Cancer Gene Analysis
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work.
ABSTRACT
Objective
Despite the growing attention on the use of cytology samples for genetic analysis, the impact of the time from sample collection to fixation, referred to as ‘cold’ ischemic time, has not been sufficiently studied. Therefore, we investigated the quality of nucleic acids prior to fixation in body cavity fluid samples, focusing on the benign/malignant status, differences in collection methods and tumour cell content.
Methods
We analysed 49 body cavity fluid samples collected using different methods: aspiration (n = 21), drainage (n = 5), and surgery (n = 15). The samples were collected from 26 malignant and 23 benign cases. DNA and RNA were extracted from all samples, and their yield and quality were assessed using Agilent TapeStation. Tumour cell content was calculated as the ratio of malignant to benign cells.
Results
DNA and RNA yields were significantly higher in malignant than in benign cases (p < 0.05). Regarding nucleic acid quality, there was a significant difference in RNA quality between malignant and benign cases, but no significant difference in DNA quality. Among the 26 malignant cases, there were significant differences in integrity number (RIN) and RNA percentage of nucleic acid fragments with > 200 nucleotides (DV200) between samples collected via aspiration and surgery (p < 0.05). Tumour cell content (median, 36%; range, 20%–72%) showed no correlation with nucleic acid yield or quality.
Conclusions
This study's findings suggest that DNA extracted from cytology samples is highly stable, while RNA is affected by cold ischemic time. Thus, prompt fixation after collection is necessary to maintain RNA quality.
Graphical Abstract
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
Research data are not shared.