Asymmetric Hydrogenation of Phenanthridines with Chiral Boranes
Guangyu Cui
Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Sciences, CAS Key Laboratory of Molecular Recognition and Function, Institute of Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100190 China
University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Xiangqing Feng
Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Sciences, CAS Key Laboratory of Molecular Recognition and Function, Institute of Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100190 China
University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Haifeng Du
Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Sciences, CAS Key Laboratory of Molecular Recognition and Function, Institute of Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100190 China
University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorGuangyu Cui
Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Sciences, CAS Key Laboratory of Molecular Recognition and Function, Institute of Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100190 China
University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Xiangqing Feng
Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Sciences, CAS Key Laboratory of Molecular Recognition and Function, Institute of Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100190 China
University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Haifeng Du
Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Sciences, CAS Key Laboratory of Molecular Recognition and Function, Institute of Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100190 China
University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorComprehensive Summary
The asymmetric hydrogenation of N-heteroarenes provides an efficient method for the synthesis of optically active cyclic secondary amines. In this paper, we described an asymmetric hydrogenation of phenanthridines using a chiral mono-alkene-derived borane. A variety of dihydrophenanthridines were furnished in high yields with up to 93% ee. The current catalytic system was very sensitive for the steric hindrance of phenanthridines. Bulky substituents at one phenyl group of phenanthridines were required to obtain the high enantioselectivity. But large substituents on the carbon of the C=N bonds would diminish the reactivity sharply.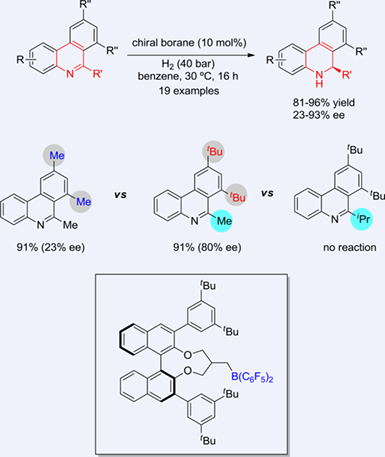
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| cjoc202300588-sup-0001-Supinfo.pdfPDF document, 14.3 MB |
Appendix S1: Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1(a) Stermitz, F. R.; Larson, K. A.; Kim, D. K. Structural Relations among Cytotoxic and Antitumor Benzophenanthridine Alkaloid Derivatives. J. Med. Chem. 1973, 16, 939–940; (b) Chang, Y.-C.; Hsieh, P.-W.; Chang, F.-R.; Wu, R.-R.; Liaw, C.-C.; Lee, K.-H.; Wu, Y.-C. Two New Protopines Argemexicaines A and B and the Anti-HIV Alkaloid 6-Acetonyldihydrochelerythrine from Formosan Argemone Mexicana. Planta Med. 2003, 69, 148–152; (c) Fotie, J.; Bohle, D. S.; Olivier, M.; Gomez, M. A.; Nzimiro, S. Trypanocidal and Antileishmanial Dihydrochelerythrine Derivatives from Garcinia lucida. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 1650–1653; (d) Pegoraro, S.; Lang, M.; Dreker, T.; Kraus, J.; Hamm, S.; Meere, C.; Feurle, J.; Tasler, S.; Prütting, S.; Kuras, Z.; Visan, V.; Grissmer, S. Inhibitors of Potassium Channels KV1.3 and IK-1 as Immunosuppressants. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 2299–2304; (e) Éles, J.; Beke, G.; Vágó, I.; Bozó, É.; Huszár, J.; Tarcsay, Á.; Kolok, S.; Schmidt, É.; Vastag, M.; Hornok, K.; Farkas, S.; Domány, G.; Keserű, G. M. Quinolinyl- and Phenantridinyl-acetamides as Bradykinin B1 Receptor Antagonists. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 3095–3099.
- 2(a) Xiao, K.-J.; Chu, L.; Chen, G.; Yu, J.-Q. Kinetic Resolution of Benzylamines via Palladium(II)-Catalyzed C–H Cross-Coupling. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 7796–7800; (b) Fandrick, D. R.; Hart, C. A.; Okafor, I. S.; Mercadante, M. A.; Sanyal, S.; Masters, J. T.; Sarvestani, M.; Fandrick, K. R.; Stockdill, J. L.; Grinberg, N.; Gonnella, N.; Lee, H.; Senanayake, C. H. Copper-Catalyzed Asymmetric Propargylation of Cyclic Aldimines. Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 6192–6195; (c) Lu, S.-M.; Han, X.-W.; Zhou, Y.-G. Recent Advances in Asymmetric Hydrogenation of Heteroaromatic Compounds. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2005, 25, 634–640.
- 3(a) Ye, J.; Limouni, A.; Zaichuk, S.; Lautens, M. Synthesis of Enantioenriched 5,6-Dihydrophenanthridine Derivatives through retro-Carbopalladation of Chiral o-Bromobenzylamines. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 3116–3120; (b) Lu, R.; Cao, L.; Guan, H.; Liu, L. Iron-Catalyzed Aerobic Dehydrogenative Kinetic Resolution of Cyclic Secondary Amines. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 6318−6324.
- 4(a) Yang, Z.; Chen, F.; Zhang, S.; He, Y.; Yang, N.; Fan, Q.-H. Ruthenium-Catalyzed Enantioselective Hydrogenation of Phenanthridine Derivatives. Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 1458–1461; (b) Hu, S.-B.; Zhai, X.-Y.; Shen, H.-Q.; Zhou, Y.-G. Iridium-Catalyzed Asymmetric Hydrogenation of Polycyclic Pyrrolo/Indolo[1,2-a]quinoxalines and Phenanthridines. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2018, 360, 1334–1339.
- 5 Welch, G. C.; San Juan, R. R.; Masuda, J. D.; Stephan, D. W. Reversible, Metal-Free Hydrogen Activation. Science 2006, 314, 1124–1126.
- 6(a) Stephan, D. W.; Erker, G. Frustrated Lewis Pairs: Metal-free Hydrogen Activation and More. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 46–76; (b) Soόs, T. Design of Frustrated Lewis Pair Catalysts for Metal-Free and Selective Hydrogenation. Pure Appl. Chem. 2011, 83, 667–675; (c) Erker, G. Frustrated Lewis Pairs: Some Recent Developments. Pure Appl. Chem. 2012, 84, 2203–2217; (d) Paradies, J. Metal-Free Hydrogenation of Unsaturated Hydrocarbons Employing Molecular Hydrogen. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 3552–3557; (e) Stephan, D. W. Frustrated Lewis Pairs: From Concept to Catalysis. Acc. Chem. Res. 2015, 48, 306–316; (f) Stephan, D. W.; Erker, G. Frustrated Lewis Pair Chemistry: Development and Perspectives. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 6400–6441; (g) Stephan, D. W. Frustrated Lewis Pairs. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 10018–10032; (h) Stephan, D. W. The Broadening Reach of Frustrated Lewis Pair Chemistry. Science 2016, 354, aaf7229; (i) Wang, H.; Zheng, Y.; Pan, Z.; Fu, H.; Ling, F.; Zhong, W. Progress of Frustrated Lewis Pairs in Catalytic Hydrogenation. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 37, 301–313; (j) Li, N.; Zhang, W.-X. Frustrated Lewis Pairs: Discovery and Overviews in Catalysis. Chin. J. Chem. 2020, 38, 1360–1370; (k) Lam, J.; Szkop, K. M.; Mosaferi, E.; Stephan, D. W. FLP Catalysis: Main Group Hydrogenations of Organic Unsaturated Substrates. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 3592–3612; (l) Stephan, D. W. Diverse Uses of the Reaction of Frustrated Lewis Pair (FLP) with Hydrogen. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 20002–20014.
- 7(a) Liu, Y.; Du, H. Frustrated Lewis Pair Catalyzed Asymmetric Hydrogenation. Acta Chim. Sinica 2014, 72, 771−777; (b) Feng, X.; Du, H. Metal-Free Asymmetric Hydrogenation and Hydrosilylation Catalyzed by Frustrated Lewis Pairs. Tetrahedron Lett. 2014, 55, 6959−6964; (c) Shi, L.; Zhou, Y.-G. Enantioselective Metal-Free Hydrogenation Catalyzed by Chiral Frustrated Lewis Pairs. ChemCatChem 2015, 7, 54−56; (d) Wilkins, L. C.; Melen, R. L. Enantioselective Main Group Catalysis: Modern Catalysts for Organic Transformations. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2016, 324, 123−129; (e) Paradies, J. Chiral Borane-Based Lewis Acids for Metal Free Hydrogenations. Top. Organomet. Chem. 2017, 62, 193−216; (f) Meng, W.; Feng, X.; Du, H. Lewis Pairs Catalyzed Asymmetric Metal-Free Hydrogenations and Hydrosilylations. Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 191−201; (g) Feng, X.; Meng, W.; Du, H. Frustrated Lewis Pair Catalyzed Asymmetric Reactions. In Frustrated Lewis Pairs, Molecular Catalysis, Vol. 2, Eds.: Slootweg, J. C.; Jupp, A. R., Springer Nature Switzerland AG, Cham, Switzerland, 2020, pp. 29−86; (h) Feng, X.; Meng, W.; Du, H. Chiral Dienes: From Ligands to FLP Catalysts. Chin. J. Chem. 2022, 40, 1109−1116.
- 8(a) Chen, D.; Klankermayer, J. Metal-Free Catalytic Hydrogenation of Imines with Tris(perfluorophenyl)borane. Chem. Commun. 2008, 2130−2131; (b) Chen, D.; Wang, Y.; Klankermayer, J. Enantioselective Hydrogenation with Chiral Frustrated Lewis Pairs. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 9475−9478; (c) Ghattas, G.; Chen, D.; Pan, F.; Klankermayer, J. Asymmetric Hydrogenation of Imines with a Recyclable Chiral Frustrated Lewis Pair Catalyst. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 9026−9028; (d) Liu, Y.; Du, H. Chiral Dienes as “Ligands” for Borane-Catalyzed Metal-Free Asymmetric Hydrogenation of Imines. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 6810−6813; (e) Wei, S.; Du, H. A Highly Enantioselective Hydrogenation of Silyl Enol Esters Catalyzed by Chiral Frustrated Lewis Pairs. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 12261−12264; (f) Ren, X.; Li, G.; Wei, S.; Du, H. Facile Development of Chiral Alkenylboranes from Chiral Diynes for Asymmetric Hydrogenation of Silyl Enol Ethers. Org. Lett. 2015, 17, 990−993; (g) Lindqvist, M.; Borre, K.; Axenov, K.; Kótai, B.; Nieger, M.; Leskelä, M.; Pápai, I.; Repo, T. Chiral Molecular Tweezers: Synthesis and Reactivity in Asymmetric Hydrogenation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 4038–4041; (h) Ye, K.-Y.; Wang, X.; Daniliuc, C. G.; Kehr, G.; Erker, G. A Ferrocene-Based Phosphane/Borane Frustrated Lewis Pair for Asymmetric Imine Reduction. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 368–371; (i) Tu, X.-S.; Zeng, N.-N.; Li, R.-Y.; Zhao, Y.-Q.; Xie, D.-Z.; Peng, Q.; Wang, X.-C. C2-Symmetric Bicyclic Bisborane Catalysts: Kinetic or Thermodynamic Products of a Reversible Hydroboration of Dienes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 15096–15100; (j) Gao, B.; Feng, X.; Meng, W.; Du, H. Asymmetric Hydrogenations of Ketones and Enones with Chiral Lewis Base Derived Frustrated Lewis Pairs. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 4498−4504.
- 9(a) Zhang, Z.; Du, H. cis-Selective and Highly Enantioselective Hydrogenation of 2,3,4-Trisubstituted Quinolines. Org. Lett. 2015, 17, 2816−2819; (b) Zhang, Z.; Du, H. Enantioselective Metal-Free Hydrogenations of Disubstituted Quinolines. Org. Lett. 2015, 17, 6266−6269; (c) Li, X.; Tian, J.-J.; Liu, N.; Tu, X.-S.; Zeng, N.-N.; Wang, X.-C. Spiro-Bicyclic Bisborane Catalysts for Metal-Free Chemoselective and Enantioselective Hydrogenation of Quinolines. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 4664−4668.
- 10 Zhang, Z.; Du, H. A Highly cis-Selective and Enantioselective Metal-Free Hydrogenation of 2,3-Disubstituted Quinoxalines. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 623−626.
- 11CCDC 2297370 ESI.




