Polyhydroxyurethanes from Biobased Monomers and CO2: A Bridge between Sustainable Chemistry and CO2 Utilization†
Tharinee Theerathanagorn
VISTEC Advanced Laboratory for Environment-Related Inorganic and Organic Syntheses, Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Vidyasirimedhi Institute of Science and Technology, 21210, Wang Chan, Rayong, Thailand
These authors contributed equally.
Search for more papers by this authorTanika Kessaratikoon
VISTEC Advanced Laboratory for Environment-Related Inorganic and Organic Syntheses, Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Vidyasirimedhi Institute of Science and Technology, 21210, Wang Chan, Rayong, Thailand
These authors contributed equally.
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Hafeez Ur Rehman
Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Vidyasirimedhi Institute of Science and Technology, 21210, Wang Chan, Rayong, Thailand
E-mail: [email protected], [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Valerio D'Elia
VISTEC Advanced Laboratory for Environment-Related Inorganic and Organic Syntheses, Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Vidyasirimedhi Institute of Science and Technology, 21210, Wang Chan, Rayong, Thailand
E-mail: [email protected], [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorDaniel Crespy
Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Vidyasirimedhi Institute of Science and Technology, 21210, Wang Chan, Rayong, Thailand
Search for more papers by this authorTharinee Theerathanagorn
VISTEC Advanced Laboratory for Environment-Related Inorganic and Organic Syntheses, Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Vidyasirimedhi Institute of Science and Technology, 21210, Wang Chan, Rayong, Thailand
These authors contributed equally.
Search for more papers by this authorTanika Kessaratikoon
VISTEC Advanced Laboratory for Environment-Related Inorganic and Organic Syntheses, Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Vidyasirimedhi Institute of Science and Technology, 21210, Wang Chan, Rayong, Thailand
These authors contributed equally.
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Hafeez Ur Rehman
Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Vidyasirimedhi Institute of Science and Technology, 21210, Wang Chan, Rayong, Thailand
E-mail: [email protected], [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Valerio D'Elia
VISTEC Advanced Laboratory for Environment-Related Inorganic and Organic Syntheses, Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Vidyasirimedhi Institute of Science and Technology, 21210, Wang Chan, Rayong, Thailand
E-mail: [email protected], [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorDaniel Crespy
Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Vidyasirimedhi Institute of Science and Technology, 21210, Wang Chan, Rayong, Thailand
Search for more papers by this authorDedicated to the Special Issue of C1 Chemistry.
Comprehensive Summary
Polyhydroxyurethanes (PHUs) have received considerable attention in the last decade as potential alternatives to traditional phosgene-based polyurethanes (PUs). The development of suitable 5CC (five membered-ring cyclic carbonate) precursors bearing multiple carbonate moieties (multi-5CCs) is a key requisite for preparing PHUs by polyaddition reaction with bis- or polyamines. Producing sustainable PHUs from CO2-based five-membered cyclic carbonates (5CCs) obtained from biobased epoxides is a valuable strategy to bridge CO2 utilization and the upcycling of renewable substrates. In this context, while many multi-5CC monomers reported in the literature are oil-based, recent efforts have led to the development of a large variety of multifunctional 5CCs that are produced by the combination of CO2 and renewable resources such as fatty acids and vegetable oils, lignin, terpenes, and sugars. In this work, recent crucial advances (2019—2023) on PHUs prepared from bis- and multi-5CCs produced from CO2 and (partially/potentially) biobased substrates are reviewed with respect to their synthesis, thermal and mechanical properties, and their recent, emerging applications.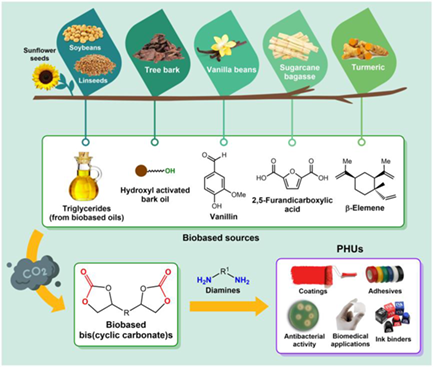
References
- 1 Dabral, S.; Schaub, T. The Use of Carbon Dioxide (CO2) as a Building Block in Organic Synthesis from an Industrial Perspective. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2019, 361, 223–246.
- 2 Artz, J.; Müller, T. E.; Thenert, K.; Kleinekorte, J.; Meys, R.; Sternberg, A.; Bardow, A.; Leitner, W. Sustainable Conversion of Carbon Dioxide: An Integrated Review of Catalysis and Life Cycle Assessment. Chem. Rev. 2017, 118, 434–504.
- 3 Song, Q.-W.; Zhou, Z.-H.; He, L.-N. Efficient, selective and sustainable catalysis of carbon dioxide. Green Chem. 2017, 19, 3707–3728.
- 4
Das, S.; D'Elia, V.; He, L.-N.; Kleij, A. W.; Yamada, T. Carbon dioxide chemistry towards carbon-neutrality. Green Chem. Eng. 2022, 3, 93–95.
10.1016/j.gce.2022.02.002 Google Scholar
- 5 Bui, M.; Adjiman, C. S.; Bardow, A.; Anthony, E. J.; Boston, A.; Brown, S.; Fennell, P. S.; Fuss, S.; Galindo, A.; Hackett, L. A.; et al. Carbon capture and storage (CCS): the way forward. Energy Environ. Sci. 2018, 11, 1062–1176.
- 6 Lenton, T. M.; Xu, C.; Abrams, J. F.; Ghadiali, A.; Loriani, S.; Sakschewski, B.; Zimm, C.; Ebi, K. L.; Dunn, R. R.; Svenning, J.-C.; et al. Quantifying the human cost of global warming. Nat. Sustain. 2023, 6, 1237–1247.
- 7 Chen, L.; Msigwa, G.; Yang, M.; Osman, A. I.; Fawzy, S.; Rooney, D. W.; Yap, P.-S. Strategies to achieve a carbon neutral society: a review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 2277–2310.
- 8 Sun, S.; Sun, H.; Williams, P. T.; Wu, C. Recent advances in integrated CO2capture and utilization: a review. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2021, 5, 4546–4559.
- 9 Cai, S.-F.; Li, H.-R.; He, L.-N. Bifunctionalization of unsaturated bonds via carboxylative cyclization with CO2: a sustainable access to heterocyclic compounds. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 9334–9347.
- 10 He, M.; Sun, Y.; Han, B. Green Carbon Science: Efficient Carbon Resource Processing, Utilization, and Recycling towards Carbon Neutrality. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202112835.
- 11 Bushuyev, O. S.; De Luna, P.; Dinh, C. T.; Tao, L.; Saur, G.; van de Lagemaat, J.; Kelley, S. O.; Sargent, E. H. What Should We Make with CO2 and How Can We Make It? Joule 2018, 2, 825–832.
- 12 Sadeghi, K.; Jeon, Y.; Seo, J. Roadmap to the sustainable synthesis of polymers: From the perspective of CO2 upcycling. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2023, 135, 101103.
- 13 Wu, X.-F.; Dyson, P. J.; Arndtsen, B. A. Achievements in C1 Chemistry for Organic Synthesis. J. Org. Chem. 2023, 88, 4891–4893.
- 14
Xie, W.-H.; Li, H.; Yang, M.; He, L.-N.; Li, H.-R. CO2 capture and utilization with solid waste. Green Chem. Eng. 2022, 3, 199–209.
10.1016/j.gce.2022.01.002 Google Scholar
- 15 Maina, J. W.; Pringle, J. M.; Razal, J. M.; Nunes, S.; Vega, L.; Gallucci, F.; Dumée, L. F. Strategies for Integrated Capture and Conversion of CO2 from Dilute Flue Gases and the Atmosphere. ChemSusChem 2021, 14, 1805–1820.
- 16 Barthel, A.; Saih, Y.; Gimenez, M.; Pelletier, J. D. A.; Kühn, F. E.; D'Elia, V.; Basset, J.-M. Highly integrated CO2 capture and conversion: direct synthesis of cyclic carbonates from industrial flue gas. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 3116–3123.
- 17 Takeda, H.; Cometto, C.; Ishitani, O.; Robert, M. Electrons, Photons, Protons and Earth-Abundant Metal Complexes for Molecular Catalysis of CO2 Reduction. ACS Catal. 2016, 7, 70–88.
- 18 Klankermayer, J.; Wesselbaum, S.; Beydoun, K.; Leitner, W. Selective Catalytic Synthesis Using the Combination of Carbon Dioxide and Hydrogen: Catalytic Chess at the Interface of Energy and Chemistry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 7296–7343.
- 19 Posada-Pérez, S.; Solà, M.; Poater, A. Carbon Dioxide Conversion on Supported Metal Nanoparticles: A Brief Review. Catalysts 2023, 13, 305.
- 20 Qiu, L.-Q.; Chen, K.-H.; Yang, Z.-W.; He, L.-N. A rhenium catalyst with bifunctional pyrene groups boosts natural light-driven CO2 reduction. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 8614–8622.
- 21 Liang, S.; Huang, L.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Q.; Liu, B. Electrochemical Reduction of CO2 to CO over Transition Metal/N-Doped Carbon Catalysts: The Active Sites and Reaction Mechanism. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2102886.
- 22 Moret, S.; Dyson, P. J.; Laurenczy, G. Direct synthesis of formic acid from carbon dioxide by hydrogenation in acidic media. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4017.
- 23 Ye, R.-P.; Ding, J.; Gong, W.; Argyle, M. D.; Zhong, Q.; Wang, Y.; Russell, C. K.; Xu, Z.; Russell, A. G.; Li, Q.; Fan, M.; Yao, Y.-G. CO2 hydrogenation to high-value products via heterogeneous catalysis. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5698.
- 24 Xie, S.; Zhang, W.; Lan, X.; Lin, H. CO2 Reduction to Methanol in the Liquid Phase: A Review. ChemSusChem 2020, 13, 6141–6159.
- 25 Yang, D.; Zhu, Q.; Chen, C.; Liu, H.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, X.; Liu, S.; Han, B. Selective electroreduction of carbon dioxide to methanol on copper selenide nanocatalysts. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 677.
- 26 Song, L.; Jiang, Y.-X.; Zhang, Z.; Gui, Y.-Y.; Zhou, X.-Y.; Yu, D.-G. CO2 = CO + [O]: recent advances in carbonylation of C–H bonds with CO2. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 8355–8367.
- 27 Zhao, Y.; Landfester, K.; Crespy, D. CO2 responsive reversible aggregation of nanoparticles and formation of nanocapsules with an aqueous core. Soft Matt. 2012, 8, 11687–11696.
- 28 Ran, C.-K.; Chen, X.-W.; Gui, Y.-Y.; Liu, J.; Song, L.; Ren, K.; Yu, D.-G. Recent advances in asymmetric synthesis with CO2. Sci. China Chem. 2020, 63, 1336–1351.
- 29 Song, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wu, X. F. Recent Advances in Copper-Catalyzed Carboxylation Reactions with CO2. Asian J. Org. Chem. 2022, 11, e202200237.
- 30 Honda, M.; Tamura, M.; Nakagawa, Y.; Sonehara, S.; Suzuki, K.; Fujimoto, K.; Tomishige, K. Ceria-Catalyzed Conversion of Carbon Dioxide into Dimethyl Carbonate with 2-Cyanopyridine. ChemSusChem 2013, 6, 1341–1344.
- 31 Song, S.; Wei, J.; He, X.; Yan, G.; Jiao, M.; Zeng, W.; Dai, F.; Shi, M. Oxygen vacancies generated by Sn-doped ZrO2 promoting the synthesis of dimethyl carbonate from methanol and CO2. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 35361–35374.
- 32 Chapman, A. M.; Keyworth, C.; Kember, M. R.; Lennox, A. J. J.; Williams, C. K. Adding Value to Power Station Captured CO2: Tolerant Zn and Mg Homogeneous Catalysts for Polycarbonate Polyol Production. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 1581–1588.
- 33 Martín, C.; Fiorani, G.; Kleij, A. W. Recent Advances in the Catalytic Preparation of Cyclic Organic Carbonates. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 1353–1370.
- 34 Kamphuis, A. J.; Picchioni, F.; Pescarmona, P. P. CO2-fixation into cyclic and polymeric carbonates: principles and applications. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 406–448.
- 35D’ Elia, V.; Kleij, A. W. Surface science approach to the heterogeneous cycloaddition of CO2 to epoxides catalyzed by site-isolated metal complexes and single atoms: a review. Green Chem. Eng. 2022, 3, 210–227.
- 36 Jaroonwatana, W.; D'Elia, V.; Crespy, D. Hydrophobically-enhanced “on water” cycloaddition of CO2 to long-chain terminal epoxides. Chem. Commun. 2022, 58, 11535–11538.
- 37 Limbach, M. Acrylates from Alkenes and CO2, the Stuff That Dreams Are Made of. Adv. Organomet. Chem. 2015, 63, 175–202.
- 38 Lee, S. Y. T.; Ghani, A. A.; D'Elia, V.; Cokoja, M.; Herrmann, W. A.; Basset, J.-M.; Kühn, F. E. Liberation of methyl acrylate from metallalactone complexes via M–O ring opening (M = Ni, Pd) with methylation agents. New J. Chem. 2013, 37, 3512–3517.
- 39 Manzini, S.; Cadu, A.; Schmidt, A.-C.; Huguet, N.; Trapp, O.; Paciello, R.; Schaub, T. Enhanced Activity and Recyclability of Palladium Complexes in the Catalytic Synthesis of Sodium Acrylate from Carbon Dioxide and Ethylene. ChemCatChem 2017, 9, 2269–2274.
- 40 Della Monica, F.; Kleij, A. W. Mechanistic guidelines in nonreductive conversion of CO2: the case of cyclic carbonates. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2020, 10, 3483–3501.
- 41 Li, N.; Mo, L.; Unluer, C. Emerging CO2 utilization technologies for construction materials: A review. J. CO2 Util. 2022, 65, 102237.
- 42 Li, L.; Liu, Q.; Huang, T.; Peng, W. Mineralization and utilization of CO2 in construction and demolition wastes recycling for building materials: A systematic review of recycled concrete aggregate and recycled hardened cement powder. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 298, 121512.
- 43 Campisciano, V.; Calabrese, C.; Giacalone, F.; Aprile, C.; Lo Meo, P.; Gruttadauria, M. Reconsidering TOF calculation in the transformation of epoxides and CO2 into cyclic carbonates. J. CO2 Util. 2020, 38, 132–140.
- 44 Maeda, C.; Shimonishi, J.; Miyazaki, R.; Hasegawa, J.-y.; Ema, T. Highly Active and Robust Metalloporphyrin Catalysts for the Synthesis of Cyclic Carbonates from a Broad Range of Epoxides and Carbon Dioxide. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 6556–6563.
- 45 Lee, S. E.; Nasirian, A.; Kim, Y. E.; Fard, P. T.; Kim, Y.; Jeong, B.; Kim, S.-J.; Baeg, J.-O.; Kim, J. Visible-Light Photocatalytic Conversion of Carbon Dioxide by Ni(II) Complexes with N4S2 Coordination: Highly Efficient and Selective Production of Formate. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 19142–19149.
- 46 Louis Anandaraj, S. J.; Kang, L.; DeBeer, S.; Bordet, A.; Leitner, W. Catalytic Hydrogenation of CO2 to Formate Using Ruthenium Nanoparticles Immobilized on Supported Ionic Liquid Phases. Small 2023, 19, 2206806.
- 47 Qiu, L.-Q.; Li, H.-R.; He, L.-N. Incorporating Catalytic Units into Nanomaterials: Rational Design of Multipurpose Catalysts for CO2 Valorization. Acc. Chem. Res. 2023, 56, 2225–2240.
- 48 Valluri, S.; Claremboux, V.; Kawatra, S. Opportunities and challenges in CO2 utilization. J. Environ. Sci. 2022, 113, 322–344.
- 49 von der Assen, N.; Jung, J.; Bardow, A. Life-cycle assessment of carbon dioxide capture and utilization: avoiding the pitfalls. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 2721–2734.
- 50 Zhang, S.; Chen, C.; Li, K.; Yu, H.; Li, F. Materials and system design for direct electrochemical CO2 conversion in capture media. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 18785–18792.
- 51 Galimova, T.; Ram, M.; Bogdanov, D.; Fasihi, M.; Khalili, S.; Gulagi, A.; Karjunen, H.; Mensah, T. N. O.; Breyer, C. Global demand analysis for carbon dioxide as raw material from key industrial sources and direct air capture to produce renewable electricity-based fuels and chemicals. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 373, 133920.
- 52 von der Assen, N.; Bardow, A. Life cycle assessment of polyols for polyurethane production using CO2 as feedstock: insights from an industrial case study. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 3272–3280.
- 53 Kuusela, K.; Uusitalo, V.; Ahola, J.; Levänen, J. The transformation of plastics production from net positive greenhouse gas emissions to net negative: An environmental sustainability assessment of CO2-based polypropylene. J. CO2 Util. 2021, 52, 101672.
- 54 Daiyan, R.; MacGill, I.; Amal, R. Opportunities and Challenges for Renewable Power-to-X. ACS Energy Lett. 2020, 5, 3843–3847.
- 55 Zheng, J.; Suh, S. Strategies to reduce the global carbon footprint of plastics. Nat. Clim. Change 2019, 9, 374–378.
- 56 Cabernard, L.; Pfister, S.; Oberschelp, C.; Hellweg, S. Growing environmental footprint of plastics driven by coal combustion. Nat. Sustain. 2021, 5, 139–148.
- 57 Zhang, X.; Fevre, M.; Jones, G. O.; Waymouth, R. M. Catalysis as an Enabling Science for Sustainable Polymers. Chem. Rev. 2017, 118, 839–885.
- 58 Siragusa, F.; Detrembleur, C.; Grignard, B. The advent of recyclable CO2-based polycarbonates. Polym. Chem. 2023, 14, 1164–1183.
- 59 Della Monica, F.; Kleij, A. W. From terpenes to sustainable and functional polymers. Polym. Chem. 2020, 11, 5109–5127.
- 60 Cywar, R. M.; Rorrer, N. A.; Hoyt, C. B.; Beckham, G. T.; Chen, E. Y. X. Bio-based polymers with performance-advantaged properties. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2021, 7, 83–103.
- 61 Sardon, H.; Mecerreyes, D.; Basterretxea, A.; Avérous, L.; Jehanno, C. From Lab to Market: Current Strategies for the Production of Biobased Polyols. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 10664–10677.
- 62 Morales-Cerrada, R.; Molina-Gutierrez, S.; Lacroix-Desmazes, P.; Caillol, S. Eugenol, a Promising Building Block for Biobased Polymers with Cutting-Edge Properties. Biomacromolecules 2021, 22, 3625–3648.
- 63 Otoni, C. G.; Azeredo, H. M. C.; Mattos, B. D.; Beaumont, M.; Correa, D. S.; Rojas, O. J. The Food–Materials Nexus: Next Generation Bioplastics and Advanced Materials from Agri-Food Residues. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2102520.
- 64 Muscat, A.; de Olde, E. M.; de Boer, I. J. M.; Ripoll-Bosch, R. The battle for biomass: A systematic review of food-feed-fuel competition. Glob. Food Sec. 2020, 25, 100330.
- 65
Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, M.; Zhao, J.; Cai, D.; Cao, H. Valorization of lignin for renewable non-isocyanate polyurethanes: a state-of-the- art review. Mater. Today Sustain. 2023, 22, 100367.
10.1016/j.mtsust.2023.100367 Google Scholar
- 66 Rosenboom, J.-G.; Langer, R.; Traverso, G. Bioplastics for a circular economy. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2022, 7, 117–137.
- 67 Zhu, Y.; Romain, C.; Williams, C. K. Sustainable polymers from renewable resources. Nature 2016, 540, 354–362.
- 68 Yates, M. R.; Barlow, C. Y. Life cycle assessments of biodegradable, commercial biopolymers—A critical review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2013, 78, 54–66.
- 69 Shen, L.; Patel, M. K. Life Cycle Assessment of Polysaccharide Materials: A Review. J. Polym. Environ. 2008, 16, 154–167.
- 70 Broeren, M. L. M.; Kuling, L.; Worrell, E.; Shen, L. Environmental impact assessment of six starch plastics focusing on wastewater- derived starch and additives. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2017, 127, 246–255.
- 71 Fahim, I. S.; Chbib, H.; Mahmoud, H. M. The synthesis, production & economic feasibility of manufacturing PLA from agricultural waste. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2019, 12, 100142.
- 72 Tsiropoulos, I.; Faaij, A. P. C.; Lundquist, L.; Schenker, U.; Briois, J. F.; Patel, M. K. Life cycle impact assessment of bio-based plastics from sugarcane ethanol. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 90, 114–127.
- 73 Hottle, T. A.; Bilec, M. M.; Landis, A. E. Biopolymer production and end of life comparisons using life cycle assessment. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2017, 122, 295–306.
- 74 Ali, S. S.; Abdelkarim, E. A.; Elsamahy, T.; Al-Tohamy, R.; Li, F.; Kornaros, M.; Zuorro, A.; Zhu, D.; Sun, J. Bioplastic production in terms of life cycle assessment: A state-of-the-art review. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnol. 2023, 15, 100254.
- 75 Song, B.; Qin, A.; Tang, B. Z. Syntheses, properties, and applications of CO2-based functional polymers. Cell Rep. Phys. Sci. 2022, 3, 100719.
- 76 Liu, Y.; Lu, X.-B. Current Challenges and Perspectives in CO2-Based Polymers. Macromolecules 2023, 56, 1759–1777.
- 77 Yu, Y.; Fang, L.-M.; Liu, Y.; Lu, X.-B. Chemical Synthesis of CO2-Based Polymers with Enhanced Thermal Stability and Unexpected Recyclability from Biosourced Monomers. ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 8349–8357.
- 78 Yadav, N.; Seidi, F.; Crespy, D.; D'Elia, V. Polymers Based on Cyclic Carbonates as Trait d'Union Between Polymer Chemistry and Sustainable CO2 Utilization. ChemSusChem 2019, 12, 724–754.
- 79 Grignard, B.; Gennen, S.; Jérôme, C.; Kleij, A. W.; Detrembleur, C. Advances in the use of CO2 as a renewable feedstock for the synthesis of polymers. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 4466–4514.
- 80 Fukuoka, S.; Kawamura, M.; Komiya, K.; Tojo, M.; Hachiya, H.; Hasegawa, K.; Aminaka, M.; Okamoto, H.; Fukawa, I.; Konno, S. A novel non-phosgene polycarbonate production process using by-product CO2 as starting material. Green Chem. 2003, 5, 497–507.
- 81 Yadav, N.; Seidi, F.; Del Gobbo, S.; D'Elia, V.; Crespy, D. Versatile functionalization of polymer nanoparticles with carbonate groups via hydroxyurethane linkages. Polym. Chem. 2019, 10, 3571–3584.
- 82 Yoshida, Y.; Endo, T. Radical polymerization behavior and thermal properties of vinyl ethylene carbonate derivatives bearing aromatic moieties. Polymer 2016, 102, 167–175.
- 83 Sánchez-Fontecoba, P.; López del Amo, J. M.; Fernández, N.; Pérez-Villar, S.; Rojo, T.; López, C. M. Combining galvanic displacement and in situ polymerization in a new synthesis: micro-composite materials for Li-based batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 18868–18877.
- 84 Scholten, P. B. V.; Cartigny, G.; Grignard, B.; Debuigne, A.; Cramail, H.; Meier, M. A. R.; Detrembleur, C. Functional Polyethylenes by Organometallic-Mediated Radical Polymerization of Biobased Carbonates. ACS Macro Lett. 2021, 10, 313–320.
- 85 Qiao, C.; Shi, W.; Brandolese, A.; Benet-Buchholz, J.; Escudero-Adán, E. C.; Kleij, A. W. A Novel Catalytic Route to Polymerizable Bicyclic Cyclic Carbonate Monomers from Carbon Dioxide. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202205053.
- 86 Maisonneuve, L.; Lamarzelle, O.; Rix, E.; Grau, E.; Cramail, H. Isocyanate-Free Routes to Polyurethanes and Poly(hydroxy Urethane)s. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 12407–12439.
- 87 Carré, C.; Ecochard, Y.; Caillol, S.; Avérous, L. From the Synthesis of Biobased Cyclic Carbonate to Polyhydroxyurethanes: A Promising Route towards Renewable Non-Isocyanate Polyurethanes. ChemSusChem 2019, 12, 3410–3430.
- 88 Byrne, C. M.; Allen, S. D.; Lobkovsky, E. B.; Coates, G. W. Alternating Copolymerization of Limonene Oxide and Carbon Dioxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 11404–11405.
- 89 Li, C.; Sablong, R. J.; Koning, C. E. Chemoselective Alternating Copolymerization of Limonene Dioxide and Carbon Dioxide: A New Highly Functional Aliphatic Epoxy Polycarbonate. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 11572–11576.
- 90 Peña-Carrodeguas, L.; González-Fabra, J.; Castro-Gómez, F.; Bo, C.; Kleij, A. W. AlIII-Catalysed Formation of Poly(limonene)carbonate: DFT Analysis of the Origin of Stereoregularity. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 6115–6122.
- 91 Blattmann, H.; Lauth, M.; Mülhaupt, R. Flexible and Bio-Based Nonisocyanate Polyurethane (NIPU) Foams. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2016, 301, 944–952.
- 92 Panchireddy, S.; Grignard, B.; Thomassin, J. M.; Jerome, C.; Detrembleur, C. Bio-based poly(hydroxyurethane) glues for metal substrates. Polym. Chem. 2018, 9, 2650–2659.
- 93 Gomez-Lopez, A.; Panchireddy, S.; Grignard, B.; Calvo, I.; Jerome, C.; Detrembleur, C.; Sardon, H. Poly(hydroxyurethane) Adhesives and Coatings: State-of-the-Art and Future Directions. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 9541–9562.
- 94 Liu, G.; Wu, G.; Chen, J.; Kong, Z. Synthesis, modification and properties of rosin-based non-isocyanate polyurethanes coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 2016, 101, 461–467.
- 95 Bizet, B.; Grau, É.; Cramail, H.; Asua, J. M. Water-based non-isocyanate polyurethane-ureas (NIPUUs). Polym. Chem. 2020, 11, 3786–3799.
- 96 Ecochard, Y.; Caillol, S. Hybrid polyhydroxyurethanes: How to overcome limitations and reach cutting edge properties? Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 137, 109915.
- 97 Bizet, B.; Grau, E.; Asua, J. M.; Cramail, H. Hybrid Nonisocyanate Polyurethanes (H-NIPUs): A Pathway towards a Broad Range of Novel Materials. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2022, 223, 2100437.
- 98 Gomez-Lopez, A.; Elizalde, F.; Calvo, I.; Sardon, H. Trends in non-isocyanate polyurethane (NIPU) development. Chem. Commun. 2021, 57, 12254–12265.
- 99 Williams, E. S.; Panko, J.; Paustenbach, D. J. The European Union's REACH regulation: a review of its history and requirements. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2009, 39, 553–575.
- 100 Guo, L.; Lamb, K. J.; North, M. Recent developments in organocatalysed transformations of epoxides and carbon dioxide into cyclic carbonates. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 77–118.
- 101 Büttner, H.; Longwitz, L.; Steinbauer, J.; Wulf, C.; Werner, T. Recent Developments in the Synthesis of Cyclic Carbonates from Epoxides and CO2. Top. Curr. Chem. 2017, 375, 50.
- 102 Whiteoak, C. J.; Kielland, N.; Laserna, V.; Escudero-Adán, E. C.; Martin, E.; Kleij, A. W. A Powerful Aluminum Catalyst for the Synthesis of Highly Functional Organic Carbonates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 1228–1231.
- 103 Maeda, C.; Sasaki, S.; Ema, T. Electronic Tuning of Zinc Porphyrin Catalysts for the Conversion of Epoxides and Carbon Dioxide into Cyclic Carbonates. ChemCatChem 2017, 9, 946–949.
- 104 Yingcharoen, P.; Kongtes, C.; Arayachukiat, S.; Suvarnapunya, K.; Vummaleti, S. V. C.; Wannakao, S.; Cavallo, L.; Poater, A.; D’ Elia, V. Assessing the pKa-Dependent Activity of Hydroxyl Hydrogen Bond Donors in the Organocatalyzed Cycloaddition of Carbon Dioxide to Epoxides: Experimental and Theoretical Study. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2019, 361, 366–373.
- 105 Liu, X.-F.; Song, Q.-W.; Zhang, S.; He, L.-N. Hydrogen bonding- inspired organocatalysts for CO2 fixation with epoxides to cyclic carbonates. Catal. Today 2016, 263, 69–74.
- 106 Kilic, A.; Sobay, B.; Aytar, E.; Söylemez, R. Synthesis and effective catalytic performance in cycloaddition reactions with CO2 of boronate esters versus N-heterocyclic carbene (NHC)-stabilized boronate esters. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2020, 4, 5682–5696.
- 107 Natongchai, W.; Posada-Pérez, S.; Phungpanya, C.; Luque-Urrutia, J. A.; Solà, M.; D'Elia, V.; Poater, A. Enhancing the Catalytic Performance of Group I, II Metal Halides in the Cycloaddition of CO2 to Epoxides under Atmospheric Conditions by Cooperation with Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Highly Nucleophilic Aminopyridines: Experimental and Theoretical Study. J. Org. Chem. 2022, 87, 2873–2886.
- 108 Bayer, U.; Liang, Y.; Anwander, R. Cerium Pyrazolates Grafted onto Mesoporous Silica SBA-15: Reversible CO2 Uptake and Catalytic Cycloaddition of Epoxides and Carbon Dioxide. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 59, 14605–14614.
- 109 Chen, Y.; Luo, R.; Xu, Q.; Jiang, J.; Zhou, X.; Ji, H. Charged Metalloporphyrin Polymers for Cooperative Synthesis of Cyclic Carbonates from CO2 under Ambient Conditions. ChemSusChem 2017, 10, 2534–2541.
- 110 Luo, R.; Chen, M.; Liu, X.; Xu, W.; Li, J.; Liu, B.; Fang, Y. Recent advances in CO2 capture and simultaneous conversion into cyclic carbonates over porous organic polymers having accessible metal sites. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 18408–18424.
- 111 Kessaratikoon, T.; Theerathanagorn, T.; Crespy, D.; D'Elia, V. Organocatalytic Polymers from Affordable and Readily Available Building Blocks for the Cycloaddition of CO2 to Epoxides. J. Org. Chem. 2023, 88, 4894–4924.
- 112 Jose, T.; Cañellas, S.; Pericàs, M. A.; Kleij, A. W. Polystyrene- supported bifunctional resorcinarenes as cheap, metal-free and recyclable catalysts for epoxide/CO2 coupling reactions. Green Chem. 2017, 19, 5488–5493.
- 113 Tudu, G.; Paliwal, K. S.; Ghosh, S.; Biswas, T.; Koppisetti, H. V. S. R. M.; Mitra, A.; Mahalingam, V. para-Aminobenzoic acid-capped hematite as an efficient nanocatalyst for solvent-free CO2 fixation under atmospheric pressure. Dalton Trans. 2022, 51, 1918–1926.
- 114 Metcalfe, I. S.; North, M.; Pasquale, R.; Thursfield, A. An integrated approach to energy and chemicals production. Energy Environ. Sci. 2010, 3, 212–215.
- 115 Kelly, M. J.; Barthel, A.; Maheu, C.; Sodpiban, O.; Dega, F.-B.; Vummaleti, S. V. C.; Abou-Hamad, E.; Pelletier, J. D. A.; Cavallo, L.; D'Elia, V.; et al. Conversion of actual flue gas CO2 via cycloaddition to propylene oxide catalyzed by a single-site, recyclable zirconium catalyst. J. CO2 Util. 2017, 20, 243–252.
- 116 Ma, H.; Liu, S.; Wang, H.; Li, G.; Zhao, K.; Cui, X.; Shi, F. In situ CO2 capture and transformation into cyclic carbonates using flue gas. Green Chem. 2023, 25, 2293–2298.
- 117 Peña Carrodeguas, L.; Cristòfol, À.; Fraile, J. M.; Mayoral, J. A.; Dorado, V.; Herrerías, C. I.; Kleij, A. W. Fatty acid based biocarbonates: Al-mediated stereoselective preparation of mono-, di- and tricarbonates under mild and solvent-less conditions. Green Chem. 2017, 19, 3535–3541.
- 118 Perez-Sena, W. Y.; Eränen, K.; Kumar, N.; Estel, L.; Leveneur, S.; Salmi, T. New insights into the cocatalyst-free carbonation of vegetable oil derivatives using heterogeneous catalysts. J. CO2 Util. 2022, 57, 101879.
- 119 Akhdar, A.; Onida, K.; Vu, N. D.; Grollier, K.; Norsic, S.; Boisson, C.; D'Agosto, F.; Duguet, N. Thermomorphic Polyethylene-Supported Organocatalysts for the Valorization of Vegetable Oils and CO2. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2020, 5, 2000218.
- 120 Natongchai, W.; Pornpraprom, S.; D’ Elia, V. Synthesis of Bio-Based Cyclic Carbonates Using a Bio-Based Hydrogen Bond Donor: Application of Ascorbic Acid to the Cycloaddition of CO2 to Oleochemicals. Asian J. Org. Chem. 2020, 9, 801–810.
- 121 Aomchad, V.; Cristòfol, À.; Della Monica, F.; Limburg, B.; D'Elia, V.; Kleij, A. W. Recent progress in the catalytic transformation of carbon dioxide into biosourced organic carbonates. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 1077–1113.
- 122 Al Maksoud, W.; Saidi, A.; Samantaray, M. K.; Abou-Hamad, E.; Poater, A.; Ould-Chikh, S.; Guo, X.; Guan, E.; Ma, T.; Gates, B. C.; et al. Docking of tetra-methyl zirconium to the surface of silica: a well-defined pre-catalyst for conversion of CO2 to cyclic carbonates. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 3528–3531.
- 123 Mitra, A.; Ghosh, S.; Paliwal, K. S.; Ghosh, S.; Tudu, G.; Chandrasekar, A.; Mahalingam, V. Alumina-Based Bifunctional Catalyst for Efficient CO2 Fixation into Epoxides at Atmospheric Pressure. Inorg. Chem. 2022, 61, 16356–16369.
- 124 Bobbink, F. D.; van Muyden, A. P.; Dyson, P. J. En route to CO2-containing renewable materials: catalytic synthesis of polycarbonates and non-isocyanate polyhydroxyurethanes derived from cyclic carbonates. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 1360–1373.
- 125 Ghasemlou, M.; Daver, F.; Ivanova, E. P.; Adhikari, B. Bio-based routes to synthesize cyclic carbonates and polyamines precursors of non-isocyanate polyurethanes: A review. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 118, 668–684.
- 126 Decostanzi, M.; Bonneaud, C.; Caillol, S. From hydroxyurethane methacrylates to hybrid nonisocyanate polyurethanes. J. Polym. Sci., Part A: Polym. Chem. 2019, 57, 1224–1232.
- 127
Zhao, Y.; Xia, X.; Zhou, J.; Huang, Z.; Lei, F.; Tan, X.; Yu, D.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, H. Thermoresponsive behavior of non-isocyanate poly(hydroxyl)urethane for biomedical composite materials. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2021, 5, 843–852.
10.1007/s42114-021-00379-x Google Scholar
- 128 Pierrard, A.; Aqil, A.; Detrembleur, C.; Jérôme, C. Thermal and UV Curable Formulations of Poly(propylene glycol)–Poly(hydroxyurethane) Elastomers toward Nozzle-Based 3D Photoprinting. Biomacromolecules 2023, 24, 4375–4384.
- 129 Bourguignon, M.; Thomassin, J.-M.; Grignard, B.; Jerome, C.; Detrembleur, C. Fast and Facile One-Pot One-Step Preparation of Nonisocyanate Polyurethane Hydrogels in Water at Room Temperature. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 12601–12610.
- 130 Gomez-Lopez, A.; Grignard, B.; Calvo, I.; Detrembleur, C.; Sardon, H. Monocomponent Non-isocyanate Polyurethane Adhesives Based on a Sol–Gel Process. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2020, 2, 1839–1847.
- 131 Wołosz, D.; Fage, A. M.; Parzuchowski, P. G.; Świderska, A.; Brüll, R. Reactive Extrusion Synthesis of Biobased Isocyanate-Free Hydrophobically Modified Ethoxylated Urethanes with Pendant Hydrophobic Groups. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 11627–11640.
- 132 Quienne, B.; Pinaud, J.; Caillol, S. Synthesis of hydrophobically modified ethoxylated non-isocyanate urethanes (HENIURs) and their use as rheology additives. Eur. Polym. J. 2022, 175, 111384.
- 133 Wołosz, D.; Fage, A. M.; Parzuchowski, P. G.; Świderska, A.; Brüll, R.; Elsner, P. Sustainable associative thickeners based on hydrophobically modified ethoxylated poly(hydroxy-urethane)s end-capped by long alkyl chains. Prog. Org. Coat. 2023, 179, 107514.
- 134 Cardoso, V.; Correia, D.; Ribeiro, C.; Fernandes, M.; Lanceros-Méndez, S. Fluorinated Polymers as Smart Materials for Advanced Biomedical Applications. Polymers 2018, 10, 161.
- 135 Haydar, L.; El Malti, W.; Ladmiral, V.; Alaaeddine, A.; Ameduri, B. Original Fluorinated Non-Isocyanate Polyhydroxyurethanes. Molecules 2023, 28, 1795.
- 136 Dai, J.; Wu, Z.; Tang, L.; Qu, J. Preparation of five-membered bis(cyclic carbonate)s at atmospheric pressure for polyhydroxyurethane coatings. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 47957.
- 137 Poolwong, J.; Aomchad, V.; Del Gobbo, S.; Kleij, A. W.; D'Elia, V. Simple Halogen-Free, Biobased Organic Salts Convert Glycidol to Glycerol Carbonate under Atmospheric CO2 Pressure. ChemSusChem 2022, 15, e202200765.
- 138 Sonnati, M. O.; Amigoni, S.; Taffin de Givenchy, E. P.; Darmanin, T.; Choulet, O.; Guittard, F. Glycerol carbonate as a versatile building block for tomorrow: synthesis, reactivity, properties and applications. Green Chem. 2013, 15, 283–306.
- 139 Poolwong, J.; Del Gobbo, S.; D'Elia, V. Transesterification of dimethyl carbonate with glycerol by perovskite-based mixed metal oxide nanoparticles for the atom-efficient production of glycerol carbonate. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 104, 43–60.
- 140 Quienne, B.; Kasmi, N.; Dieden, R.; Caillol, S.; Habibi, Y. Isocyanate- Free Fully Biobased Star Polyester-Urethanes: Synthesis and Thermal Properties. Biomacromolecules 2020, 21, 1943–1951.
- 141 Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, J. Epoxy-free synthesis of aromatic dicyclocarbonates and the related strong epoxy hybrid non-isocyanate polyurethanes. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 34, 105263.
- 142 Araujo, M.; Beekman, J. K.; Mapa, M. S. T.; MacMahon, S.; Zhao, Y.; Flynn, T. J.; Flannery, B.; Mossoba, M. E.; Sprando, R. L. Assessment of intestinal absorption/metabolism of 3-chloro-1,2-propanediol (3-MCPD) and three 3-MCPD monoesters by Caco-2 cells. Toxicol. in Vitro 2020, 67, 104887.
- 143 Kaur, J.; Sarma, A. K.; Jha, M. K.; Gera, P. Valorisation of crude glycerol to value-added products: Perspectives of process technology, economics and environmental issues. Biotechnol. Rep. 2020, 27, e00487.
- 144 Hutler Wolkowicz, I. R.; Aronzon, C. M.; Pérez Coll, C. S. Lethal and sublethal toxicity of the industrial chemical epichlorohydrin on Rhinella arenarum (Anura, Bufonidae) embryos and larvae. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 263, 784–791.
- 145 Rokicki, G. Makromol. Chem. 1985, 186, 331–337.
- 146 Wulf, C.; Reckers, M.; Perechodjuk, A.; Werner, T. Catalytic Systems for the Synthesis of Biscarbonates and Their Impact on the Sequential Preparation of Non-Isocyanate Polyurethanes. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2019, 8, 1651–1658.
- 147 Dong, W.; Yoshida, Y.; Endo, T. Synthesis of poly(hydroxyurethane) from 5-membered cyclic carbonate under mild conditions in the presence of bicyclic guanidine and their reaction process. J. Polym. Sci. 2021, 59, 502–509.
- 148 Zhang, C.; Huang, K.-C.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Q. Anti-corrosion non-isocyanate polyurethane polysiloxane organic/inorganic hybrid coatings. Prog. Org Coat. 2020, 148, 105855.
- 149 Mao, H. I.; Chen, C. W.; Yan, H. C.; Rwei, S. P. Synthesis and characteristics of nonisocyanate polyurethane composed of bio-based dimer diamine for supercritical CO2 foaming applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 139, e52841.
- 150 Liu, W.; Ge, W.; Mei, H.; Hang, G.; Li, L.; Zheng, S. Poly(hydroxyurethane-co-thiourethane)s cross-linked with disulfide bonds: Synthesis via isocyanate-free approach, thermomechanical and reprocessing properties. J. Polym. Sci. 2022, 60, 2756–2768.
- 151 Jiang, S.; Liu, L. Novel carbon dioxide based poly(hydroxyurethane- urea)s: Synthesis and properties. Polymer 2022, 244, 124652.
- 152 Hu, S.; Chen, X.; Torkelson, J. M. Isocyanate-free, thermoplastic polyhydroxyurethane elastomers designed for cold temperatures: Influence of PDMS soft-segment chain length and hard-segment content. Polymer 2022, 256, 125251.
- 153 Thoene, M.; Dzika, E.; Gonkowski, S.; Wojtkiewicz, J. Bisphenol S in Food Causes Hormonal and Obesogenic Effects Comparable to or Worse than Bisphenol A: A Literature Review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 532.
- 154 Escrivá, L.; Hanberg, A.; Zilliacus, J.; Beronius, A. Assessment of the endocrine disrupting properties of Bisphenol AF according to the EU criteria and ECHA/EFSA guidance. EFSA J. 2019, 17, e170914.
- 155 Wu, Z.; Tang, L.; Dai, J.; Qu, J. Synthesis and properties of fluorinated non-isocyanate polyurethanes coatings with good hydrophobic and oleophobic properties. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2019, 16, 1233–1241.
- 156 Yin, X.; Liu, H.; Lin, R.; Liu, X.; Huang, Z.; Du, J.; Gu, Y.; Lin, X.; Lin, W.; Yi, G. Synthesis and properties of semicrystalline non-isocyanate polyurethane with tunable triple shape memory properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2023, 140, e53705.
- 157 Ou, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Tao, L.; Wang, T.; Wang, Q.; Chen, S. High strength, recyclable and shape memory polyhydroxyurethanes with intrinsic fluorescent properties. J. Polym. Sci. 2023, 61, 1360–1371.
- 158 Xu, W.; Ding, Y.; You, S.; Chao, C.; Wu, B.; Chen, F. Customized thermoplastic polyhydroxyurethanes synthesized from ene-containing cyclic carbonates, dithiols and diamines: design, mechanical properties and applications in adhesives. Polym. Chem. 2023, 14, 2220–2228.
- 159 Villa, R.; Porcar, R.; Nieto, S.; Donaire, A.; Garcia-Verdugo, E.; Luis, S. V.; Lozano, P. Sustainable chemo-enzymatic synthesis of glycerol carbonate (meth)acrylate from glycidol and carbon dioxide enabled by ionic liquid technologies. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 4191–4200.
- 160 Morales-Cerrada, R.; Boutevin, B.; Caillol, S. Glycerol carbonate methacrylate: A cross-linking agent for hydroxyurethane-acrylate coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 2021, 151, 106078.
- 161 Schimpf, V.; Asmacher, A.; Fuchs, A.; Bruchmann, B.; Mülhaupt, R. Polyfunctional Acrylic Non-isocyanate Hydroxyurethanes as Photocurable Thermosets for 3D Printing. Macromolecules 2019, 52, 3288–3297.
- 162 Hu, S.; Chen, X.; Bin Rusayyis, M. A.; Purwanto, N. S.; Torkelson, J. M. Reprocessable polyhydroxyurethane networks reinforced with reactive polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxanes (POSS) and exhibiting excellent elevated temperature creep resistance. Polymer 2022, 252, 124971.
- 163 Li, L.; Ge, W.; Zhao, B.; Adeel, M.; Mei, H.; Zheng, S. Polyhydroxyurethane thermosets from novolac epoxide: Synthesis and its nanostructured blends with poly(trifluoroethylacrylate)-block- poly(N-vinylpyrrolidone) diblock copolymer. Polymer 2021, 213, 123314.
- 164 Ge, W.; Zhao, B.; Li, L.; Nie, K.; Zheng, S. Nanocomposites of polyhydroxyurethane with nanocrystalline cellulose: Synthesis, thermomechanical and reprocessing properties. Eur. Polym. J. 2021, 149, 110287.
- 165 Ngassam Tounzoua, C.; Grignard, B.; Detrembleur, C. Exovinylene Cyclic Carbonates: Multifaceted CO2-Based Building Blocks for Modern Chemistry and Polymer Science. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202116066.
- 166 Gennen, S.; Grignard, B.; Tassaing, T.; Jérôme, C.; Detrembleur, C. CO2-Sourced α-Alkylidene Cyclic Carbonates: A Step Forward in the Quest for Functional Regioregular Poly(urethane)s and Poly(carbonate)s. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 10394–10398.
- 167 Zhu, Y.; Yang, J.; Mei, F.; Li, X.; Zhao, C. Bio-based 1,4-butanediol and tetrahydrofuran synthesis: perspective. Green Chem. 2022, 24, 6450–6466.
- 168 Martínez de Sarasa Buchaca, M.; de la Cruz-Martínez, F.; Francés-Poveda, E.; Fernández-Baeza, J.; Sánchez-Barba, L. F.; Garcés, A.; Castro-Osma, J. A.; Lara-Sánchez, A. Synthesis of Nonisocyanate Poly(hydroxy)urethanes from Bis(cyclic carbonates) and Polyamines. Polymers 2022, 14, 2719.
- 169 Castro-Osma, J. A.; Martínez, J.; de la Cruz-Martínez, F.; Caballero, M. P.; Fernández-Baeza, J.; Rodríguez-López, J.; Otero, A.; Lara-Sánchez, A.; Tejeda, J. Development of hydroxy-containing imidazole organocatalysts for CO2 fixation into cyclic carbonates. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2018, 8, 1981–1987.
- 170 Hansen, C. A.; Frost, J. W. Deoxygenation of Polyhydroxybenzenes: An Alternative Strategy for the Benzene-Free Synthesis of Aromatic Chemicals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 5926–5927.
- 171 Gioia, C.; Banella, M. B.; Vannini, M.; Celli, A.; Colonna, M.; Caretti, D. Resorcinol: A potentially bio-based building block for the preparation of sustainable polyesters. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 73, 38–49.
- 172 Sessini, V.; Thai, C. N.; Amorín, H.; Jiménez, R.; Samuel, C.; Caillol, S.; Cornil, J.; Hoyas, S.; Barrau, S.; Dubois, P.; et al. Solvent-Free Design of Biobased Non-isocyanate Polyurethanes with Ferroelectric Properties. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 14946–14958.
- 173 Schimpf, V.; Max, J. B.; Stolz, B.; Heck, B.; Mülhaupt, R. Semicrystalline Non-Isocyanate Polyhydroxyurethanes as Thermoplastics and Thermoplastic Elastomers and Their Use in 3D Printing by Fused Filament Fabrication. Macromolecules 2018, 52, 320–331.
- 174 Gomez-Lopez, A.; Ayensa, N.; Grignard, B.; Irusta, L.; Calvo, I.; Müller, A. J.; Detrembleur, C.; Sardon, H. Enhanced and Reusable Poly(hydroxy urethane)-Based Low Temperature Hot-Melt Adhesives. ACS Polym. Au 2022, 2, 194–207.
- 175 Główka, M.; Krawczyk, T. New Trends and Perspectives in Production of 1,2-Propanediol. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 7274–7287.
- 176 Ju, J.-H.; Wang, D.; Heo, S.-Y.; Kim, M.-S.; Seo, J.-W.; Kim, Y.-M.; Kim, D.-H.; Kang, S.-A.; Kim, C.-H.; Oh, B.-R. Enhancement of 1,3-propanediol production from industrial by-product by Lactobacillus reuteri CH53. Microb. Cell Fact. 2020, 19, 6.
- 177 Harmer, M. A.; Confer, D. C.; Hoffman, C. K.; Jackson, S. C.; Liauw, A. Y.; Minter, A. R.; Murphy, E. R.; Spence, R. E.; Sunkara, H. B. Renewably sourced polytrimethylene ether glycol by superacid catalyzed condensation of 1,3-propanediol. Green Chem. 2010, 12, 1410–1416.
- 178 Błażek, K.; Kasprzyk, P.; Datta, J. Diamine derivatives of dimerized fatty acids and bio-based polyether polyol as sustainable platforms for the synthesis of non-isocyanate polyurethanes. Polymer 2020, 205, 122768.
- 179 Viklund, C.; Pontén, E.; Glad, B.; Irgum, K.; Hörstedt, P.; Svec, F. “Molded” Macroporous Poly(glycidyl methacrylate-co-trimethylolpropane trimethacrylate) Materials with Fine Controlled Porous Properties: Preparation of Monoliths Using Photoinitiated Polymerization. Chem. Mater. 1997, 9, 463–471.
- 180 Wei, F.; Zhang, J.; Wu, C.; Luo, M.; Ye, B.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Miao, M.; Li, T.; Zhang, D. Closed-Loop Recycling of Tough and Flame- Retardant Epoxy Resins. Macromolecules 2023, 56, 5290–5305.
- 181 Groce, B. R.; Lane, E. E.; Gary, D. P.; Ngo, D. T.; Ngo, D. T.; Shaon, F.; Belgodere, J. A.; Pojman, J. A. Kinetic and Chemical Effects of Clays and Other Fillers in the Preparation of Epoxy–Vinyl Ether Composites Using Radical-Induced Cationic Frontal Polymerization. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 19403–19413.
- 182
Fantoni, A.; Koch, T.; Baudis, S.; Liska, R. Synthesis and Characterization of Homogeneous Epoxy Networks: Development of a Sustainable Material Platform Using Epoxy-Alcohol Polyaddition. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2022, 5, 731–742.
10.1021/acsapm.2c01728 Google Scholar
- 183 Webster, D. C. Cyclic carbonate functional polymers and their applications. Prog. Org. Coat. 2003, 47, 77–86.
- 184 Panchireddy, S.; Thomassin, J. M.; Grignard, B.; Damblon, C.; Tatton, A.; Jerome, C.; Detrembleur, C. Reinforced poly(hydroxyurethane) thermosets as high performance adhesives for aluminum substrates. Polym. Chem. 2017, 8, 5897–5909.
- 185 Rantakylä, T.-K.; Salmi, T.; Aumo, J.; Mäki-Arvela, P.; Sjöholm, R.; Ollonqvist, T.; Väyrynen, J.; Lindfors, L. P. Hydrogenation Kinetics of 2,2-Dimethylol-1-butanal to Trimethylolpropane over a Supported Nickel Catalyst. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2000, 39, 2876–2882.
- 186 Khan, Y.; Kilpiö, T.; Marin, M.; Russo, V.; Lehtonen, J.; Karinen, R.; Salmi, T. Modelling of a microreactor for the partial oxidation of 1-butanol on a titania supported gold catalyst. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2020, 221, 115695.
- 187 Ndaba, B.; Chiyanzu, I.; Marx, S. n-Butanol derived from biochemical and chemical routes: A review. Biotechnol. Rep. 2015, 8, 1–9.
- 188 Bahmanpour, A. M.; Hoadley, A.; Tanksale, A. Critical review and exergy analysis of formaldehyde production processes. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2014, 30, 583–604.
- 189 Fleischer, M.; Blattmann, H.; Mülhaupt, R. Glycerol-, pentaerythritol- and trimethylolpropane-based polyurethanes and their cellulose carbonate composites prepared via the non-isocyanate route with catalytic carbon dioxide fixation. Green Chem. 2013, 15, 934–942.
- 190 Woelk, H. U. Stärke als Chemierohstoff — Möglichkeiten und Grenzen. Starch - Stärke 1981, 33, 397–408.
- 191 White, W. C. Butadiene production process overview. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2007, 166, 10–14.
- 192 Cespi, D.; Passarini, F.; Vassura, I.; Cavani, F. Butadiene from biomass, a life cycle perspective to address sustainability in the chemical industry. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 1625–1638.
- 193 Makshina, E. V.; Dusselier, M.; Janssens, W.; Degrève, J.; Jacobs, P. A.; Sels, B. F. Review of old chemistry and new catalytic advances in the on-purpose synthesis of butadiene. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 7917–7953.
- 194 Dechent, S.-E.; Kleij, A. W.; Luinstra, G. A. Fully bio-derived CO2 polymers for non-isocyanate based polyurethane synthesis. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 969–978.
- 195 Monie, F.; Grignard, B.; Thomassin, J. M.; Mereau, R.; Tassaing, T.; Jerome, C.; Detrembleur, C. Chemo- and Regioselective Additions of Nucleophiles to Cyclic Carbonates for the Preparation of Self-Blowing Non-Isocyanate Polyurethane Foams. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 17033–17041.
- 196 Bourguignon, M.; Grignard, B.; Detrembleur, C. Water-Induced Self-Blown Non-Isocyanate Polyurethane Foams. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202213422.
- 197 Monie, F.; Grignard, B.; Detrembleur, C. Divergent Aminolysis Approach for Constructing Recyclable Self-Blown Nonisocyanate Polyurethane Foams. ACS Macro Lett. 2022, 11, 236–242.
- 198 Purwanto, N. S.; Chen, Y.; Wang, T.; Torkelson, J. M. Rapidly synthesized, self-blowing, non-isocyanate polyurethane network foams with reprocessing to bulk networks via hydroxyurethane dynamic chemistry. Polymer 2023, 272, 125858.
- 199 Coste, G.; Negrell, C.; Caillol, S. Cascade (Dithio)carbonate Ring Opening Reactions for Self-Blowing Polyhydroxythiourethane Foams. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2022, 43, 2100833.
- 200 Pronoitis, C.; Hakkarainen, M.; Odelius, K. Structurally Diverse and Recyclable Isocyanate-Free Polyurethane Networks from CO2- Derived Cyclic Carbonates. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 2522–2531.
- 201 Capar, Ö.; Tabatabai, M.; Klee, J. E.; Worm, M.; Hartmann, L.; Ritter, H. Fast curing of polyhydroxyurethanes via ring opening polyaddition of low viscosity cyclic carbonates and amines. Polym. Chem. 2020, 11, 6964–6970.
- 202 Pössel, B.; Mülhaupt, R. Lysine-Functionalized Gibbsite Nanoplatelet Dispersions for Nonisocyanate Polyhydroxyurethane Nanocomposites and Translucent Coatings. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2020, 305, 2000217.
- 203 Gomez-Lopez, A.; Grignard, B.; Calvo, I.; Detrembleur, C.; Sardon, H. Synergetic Effect of Dopamine and Alkoxysilanes in Sustainable Non-Isocyanate Polyurethane Adhesives. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2020, 42, 2000538.
- 204 Fiorani, G.; Perosa, A.; Selva, M. Dimethyl carbonate: a versatile reagent for a sustainable valorization of renewables. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 288–322.
- 205 Shi, D.; Heyte, S.; Capron, M.; Paul, S. Catalytic processes for the direct synthesis of dimethyl carbonate from CO2 and methanol: a review. Green Chem. 2022, 24, 1067–1089.
- 206 Zhang, M.; Xu, Y.; Williams, B. L.; Xiao, M.; Wang, S.; Han, D.; Sun, L.; Meng, Y. Catalytic materials for direct synthesis of dimethyl carbonate (DMC) from CO2. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 279, 123344.
- 207 Kontou, V.; Grimekis, D.; Braimakis, K.; Karellas, S. Techno-economic assessment of dimethyl carbonate production based on carbon capture and utilization and power-to-fuel technology. Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev. 2022, 157, 112006.
- 208 Tryznowski, M.; Świderska, A.; Żołek-Tryznowska, Z.; Gołofit, T.; Parzuchowski, P. G. Facile route to multigram synthesis of environmentally friendly non-isocyanate polyurethanes. Polymer 2015, 80, 228–236.
- 209 Martin, A.; Richter, M. Oligomerization of glycerol – a critical review. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2010, 113, 100–117.
- 210 Younes, G. R.; Kamel, M.; Titi, H. M.; Farkhondehnia, M.; Marić, M. Sugar-Based Thermoplastic Polyhydroxyurethanes: Effects of Sorbitol and Mannitol Diastereomers on Polymer Properties and Applications in Melt Blending. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2022, 4, 5161–5172.
- 211 Younes, G. R.; Marić, M. Bio-based Thermoplastic Polyhydroxyurethanes Synthesized from the Terpolymerization of a Dicarbonate and Two Diamines: Design, Rheology, and Application in Melt Blending. Macromolecules 2021, 54, 10189–10202.
- 212 Zhang, P.; Zhang, G.; Pan, J.; Ma, C.; Zhang, G. Non-isocyanate Polyurethane Coating with High Hardness, Superior Flexibility, and Strong Substrate Adhesion. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 5998–6004.
- 213 Yin, Q.; Xu, B.; Qin, Y.; Zhao, J.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, J. Biobased Linear and Crystallizable Polyhydroxy(amide-urethane)s from Diglycerol Bis(cyclic carbonate) and the Polyamides of Dimer Fatty Acids. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2022, 4, 2116–2131.
- 214 Bossion, A.; Olazabal, I.; Aguirresarobe, R. H.; Marina, S.; Martín, J.; Irusta, L.; Taton, D.; Sardon, H. Synthesis of self-healable waterborne isocyanate-free poly(hydroxyurethane)-based supramolecular networks by ionic interactions. Polym. Chem. 2019, 10, 2723–2733.
- 215 Zhang, C.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Q. Waterborne isocyanate-free polyurethane epoxy hybrid coatings synthesized from sustainable fatty acid diamine. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 1329–1337.
- 216 Pronoitis, C.; Hakkarainen, M.; Odelius, K. Solubility-governed architectural design of polyhydroxyurethane-graft-poly(ε-caprolactone) copolymers. Polym. Chem. 2021, 12, 196–208.
- 217 Bowman, L. P.; Younes, G. R.; Marić, M. Effects of Poly(propylene glycol)-Based Triamine on the Sol/Gel Curing and Properties of Hybrid Non-Isocyanate Polyurethanes. Macromol. React. Eng. 2022, 16, 2100055.
- 218 Younes, G. R.; Price, G.; Dandurand, Y.; Maric, M. Study of Moisture- Curable Hybrid NIPUs Based on Glycerol with Various Diamines: Emergent Advantages of PDMS Diamines. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 30657–30670.
- 219 Younes, G. R.; Maric, M. Increasing the Hydrophobicity of Hybrid Poly(propylene glycol)-Based Polyhydroxyurethanes by Capping with Hydrophobic Diamine. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 8159–8171.
- 220 Mirończuk, A. M.; Rakicka, M.; Biegalska, A.; Rymowicz, W.; Dobrowolski, A. A two-stage fermentation process of erythritol production by yeast Y. lipolytica from molasses and glycerol. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 198, 445–455.
- 221 Dannecker, P.-K.; Meier, M. A. R. Facile and Sustainable Synthesis of Erythritol bis(carbonate), a Valuable Monomer for Non-Isocyanate Polyurethanes (NIPUs). Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9858.
- 222 Salvado, V.; Dolatkhani, M.; Grau, É.; Vidil, T.; Cramail, H. Sequence- Controlled Polyhydroxyurethanes with Tunable Regioregularity Obtained from Sugar-Based Vicinal Bis-cyclic Carbonates. Macromolecules 2022, 55, 7249–7264.
- 223 Le Goupil, F.; Salvado, V.; Rothan, V.; Vidil, T.; Fleury, G.; Cramail, H.; Grau, E. Bio-Based Poly(hydroxy urethane)s for Efficient Organic High-Power Energy Storage. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 4583–4588.
- 224 Furtwengler, P.; Avérous, L. From D-sorbitol to five-membered bis(cyclo-carbonate) as a platform molecule for the synthesis of different original biobased chemicals and polymers. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9134.
- 225 Younes, G. R.; Maric, M. Moisture Curable Hybrid Polyhydroxyurethanes from Sugar-Derived Dicarbonates. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2021, 306, 2000715.
- 226 Oilseeds and oilseed products. In OECD-FAO Agricultural Outlook 2018–2027, OECD Publishing, 2018, pp. 127–138.
- 227 Biermann, U.; Bornscheuer, U.; Meier, M. A. R.; Metzger, J. O.; Schäfer, H. J. Oils and Fats as Renewable Raw Materials in Chemistry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 3854–3871.
- 228 Alam, M.; Akram, D.; Sharmin, E.; Zafar, F.; Ahmad, S. Vegetable oil based eco-friendly coating materials: A review article. Arabian J. Chem. 2014, 7, 469–479.
- 229 Sierra-Cantor, J. F.; Guerrero-Fajardo, C. A. Methods for improving the cold flow properties of biodiesel with high saturated fatty acids content: A review. Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev. 2017, 72, 774–790.
- 230 Tudge, S. J.; Purvis, A.; De Palma, A. The impacts of biofuel crops on local biodiversity: a global synthesis. Biodivers. Conserv. 2021, 30, 2863–2883.
- 231 Orjuela, A.; Clark, J. Green chemicals from used cooking oils: Trends, challenges, and opportunities. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2020, 26, 100369.
- 232 Laprise, C. M.; Hawboldt, K. A.; Kerton, F. M.; Kozak, C. M. Synthesis of a Renewable, Waste-Derived Nonisocyanate Polyurethane from Fish Processing Discards and Cashew Nutshell-Derived Amines. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2020, 42, 2000339.
- 233 Fridrihsone, A.; Romagnoli, F.; Kirsanovs, V.; Cabulis, U. Life Cycle Assessment of vegetable oil based polyols for polyurethane production. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 266, 121403.
- 234 Moretti, C.; Junginger, M.; Shen, L. Environmental life cycle assessment of polypropylene made from used cooking oil. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 157, 104750.
- 235 Nayab, R.; Imran, M.; Ramzan, M.; Tariq, M.; Taj, M. B.; Akhtar, M. N.; Iqbal, H. M. N. Sustainable biodiesel production via catalytic and non-catalytic transesterification of feedstock materials – A review. Fuel 2022, 328, 125254.
- 236 Nitbani, F. O.; Tjitda, P. J. P.; Nurohmah, B. A.; Wogo, H. E. Preparation of Fatty Acid and Monoglyceride from Vegetable Oil. J. Oleo Sci. 2020, 69, 277–295.
- 237 Boyer, A.; Cloutet, E.; Tassaing, T.; Gadenne, B.; Alfos, C.; Cramail, H. Solubility in CO2 and carbonation studies of epoxidized fatty acid diesters: towards novel precursors for polyurethane synthesis. Green Chem. 2010, 12, 2205–2213.
- 238 Van der Steen, M.; Stevens, C. V. Undecylenic Acid: A Valuable and Physiologically Active Renewable Building Block from Castor Oil. ChemSusChem 2009, 2, 692–713.
- 239 Bigot, S.; Daghrir, M.; Mhanna, A.; Boni, G.; Pourchet, S.; Lecamp, L.; Plasseraud, L. Undecylenic acid: A tunable bio-based synthon for materials applications. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 74, 26–37.
- 240 Lamarzelle, O.; Durand, P.-L.; Wirotius, A.-L.; Chollet, G.; Grau, E.; Cramail, H. Activated lipidic cyclic carbonates for non-isocyanate polyurethane synthesis. Polym. Chem. 2016, 7, 1439–1451.
- 241 Yu, S.; Cui, J.; Zhong, C.; Meng, J.; Xue, T. Green Process without Thinning Agents for Preparing Sebacic Acid via Solid-Phase Cleavage. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 6697–6702.
- 242 Yu, S.; Cui, J.; Wang, X.; Zhong, C.; Li, Y.; Yao, J. Preparation of Sebacic Acid via Alkali Fusion of Castor Oil and its Several Derivatives. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2020, 97, 663–670.
- 243 Biermann, U.; Bornscheuer, U. T.; Feussner, I.; Meier, M. A. R.; Metzger, J. O. Fatty Acids and their Derivatives as Renewable Platform Molecules for the Chemical Industry. Ang. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 20144–20165.
- 244 Rix, E.; Grau, E.; Chollet, G.; Cramail, H. Synthesis of fatty acid-based non-isocyanate polyurethanes, NIPUs, in bulk and mini-emulsion. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 84, 863–872.
- 245 Carré, C.; Bonnet, L.; Avérous, L. Solvent- and catalyst-free synthesis of fully biobased nonisocyanate polyurethanes with different macromolecular architectures. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 100390–100400.
- 246 Froidevaux, V.; Negrell, C.; Caillol, S.; Pascault, J.-P.; Boutevin, B. Biobased Amines: From Synthesis to Polymers; Present and Future. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 14181–14224.
- 247 Włoch, M.; Datta, J.; Błażek, K. The Effect of High Molecular Weight Bio-based Diamine Derivative of Dimerized Fatty Acids Obtained from Vegetable Oils on the Structure, Morphology and Selected Properties of Poly(ether-urethane-urea)s. J. Polym. Environ. 2018, 26, 1592–1604.
- 248 Hablot, E.; Donnio, B.; Bouquey, M.; Avérous, L. Dimer acid-based thermoplastic bio-polyamides: Reaction kinetics, properties and structure. Polymer 2010, 51, 5895–5902.
- 249 Wai, P. T.; Jiang, P.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, P.; Gu, Q.; Leng, Y. Catalytic developments in the epoxidation of vegetable oils and the analysis methods of epoxidized products. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 38119–38136.
- 250 Cai, X.; Zheng, J. L.; Wärnå, J.; Salmi, T.; Taouk, B.; Leveneur, S. Influence of gas-liquid mass transfer on kinetic modeling: Carbonation of epoxidized vegetable oils. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 313, 1168–1183.
- 251 Poussard, L.; Mariage, J.; Grignard, B.; Detrembleur, C.; Jérôme, C.; Calberg, C.; Heinrichs, B.; De Winter, J.; Gerbaux, P.; Raquez, J. M.; et al. Non-Isocyanate Polyurethanes from Carbonated Soybean Oil Using Monomeric or Oligomeric Diamines To Achieve Thermosets or Thermoplastics. Macromolecules 2016, 49, 2162–2171.
- 252 Tamami, B.; Sohn, S.; Wilkes, G. L. Incorporation of carbon dioxide into soybean oil and subsequent preparation and studies of nonisocyanate polyurethane networks. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 92, 883–891.
- 253 Fortman, D. J.; Brutman, J. P.; Cramer, C. J.; Hillmyer, M. A.; Dichtel, W. R. Mechanically Activated, Catalyst-Free Polyhydroxyurethane Vitrimers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 14019–14022.
- 254 Chen, X.; Li, L.; Jin, K.; Torkelson, J. M. Reprocessable polyhydroxyurethane networks exhibiting full property recovery and concurrent associative and dissociative dynamic chemistry via transcarbamoylation and reversible cyclic carbonate aminolysis. Polym. Chem. 2017, 8, 6349–6355.
- 255 Helberg, J.; Ampßler, T.; Zipse, H. Pyridinyl Amide Ion Pairs as Lewis Base Organocatalysts. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 85, 5390–5402.
- 256 D'Elia, V.; Liu, Y.; Zipse, H. Immobilized DMAP Derivatives Rivaling Homogeneous DMAP. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2011, 1527–1533.
- 257 Hu, S.; Chen, X.; Torkelson, J. M. Biobased Reprocessable Polyhydroxyurethane Networks: Full Recovery of Crosslink Density with Three Concurrent Dynamic Chemistries. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 10025–10034.
- 258 Schmidt, S.; Göppert, N. E.; Bruchmann, B.; Mülhaupt, R. Liquid sorbitol ether carbonate as intermediate for rigid and segmented non-isocyanate polyhydroxyurethane thermosets. Eur. Polym. J. 2017, 94, 136–142.
- 259 Wang, S.; Urban, M. W. Self-healing polymers. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2020, 5, 562–583.
- 260 Li, X.; Yu, R.; He, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhao, X.; Huang, W. Self-Healing Polyurethane Elastomers Based on a Disulfide Bond by Digital Light Processing 3D Printing. ACS Macro Lett. 2019, 8, 1511–1516.
- 261 Yimyai, T.; Phakkeeree, T.; Crespy, D. Tattooing Plastics with Reversible and Irreversible Encryption. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 1903785.
- 262 Yimyai, T.; Pena-Francesch, A.; Crespy, D. Transparent and Self-Healing Elastomers for Reconfigurable 3D Materials. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2022, 43, 2200554.
- 263 Dong, J.; Liu, B.; Ding, H.; Shi, J.; Liu, N.; Dai, B.; Kim, I. Bio-based healable non-isocyanate polyurethanes driven by the cooperation of disulfide and hydrogen bonds. Polym. Chem. 2020, 11, 7524–7532.
- 264 Yang, X.; Wang, S.; Liu, X.; Huang, Z.; Huang, X.; Xu, X.; Liu, H.; Wang, D.; Shang, S. Preparation of non-isocyanate polyurethanes from epoxy soybean oil: dual dynamic networks to realize self-healing and reprocessing under mild conditions. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 6349–6355.
- 265 Yang, X.; Ren, C.; Liu, X.; Sun, P.; Xu, X.; Liu, H.; Shen, M.; Shang, S.; Song, Z. Recyclable non-isocyanate polyurethanes containing a dynamic covalent network derived from epoxy soybean oil and CO2. Mater. Chem. Front. 2021, 5, 6160–6170.
- 266 Wang, T.; Deng, H.; Li, N.; Xie, F.; Shi, H.; Wu, M.; Zhang, C. Mechanically strong non-isocyanate polyurethane thermosets from cyclic carbonate linseed oil. Green Chem. 2022, 24, 8355–8366.
- 267 Tenhumberg, N.; Büttner, H.; Schäffner, B.; Kruse, D.; Blumenstein, M.; Werner, T. Cooperative catalyst system for the synthesis of oleochemical cyclic carbonates from CO2 and renewables. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 3775–3788.
- 268 Javni, I.; Hong, D. P.; Petrović, Z. S. Soy-based polyurethanes by nonisocyanate route. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 108, 3867–3875.
- 269 Helbling, P.; Hermant, F.; Petit, M.; Tassaing, T.; Vidil, T.; Cramail, H. Unveiling the reactivity of epoxides in carbonated epoxidized soybean oil and application in the stepwise synthesis of hybrid poly(hydroxyurethane) thermosets. Polym. Chem. 2023, 14, 500–513.
- 270 Catalá, J.; Guerra, I.; García-Vargas, J. M.; Ramos, M. J.; García, M. T.; Rodríguez, J. F. Tailor-Made Bio-Based Non-Isocyanate Polyurethanes (NIPUs). Polymers 2023, 15, 1589.
- 271 Mokhtari, C.; Malek, F.; Manseri, A.; Caillol, S.; Negrell, C. Reactive jojoba and castor oils-based cyclic carbonates for biobased polyhydroxyurethanes. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 113, 18–28.
- 272 Gholami, H.; Yeganeh, H. Soybean oil-derived non-isocyanate polyurethanes containing azetidinium groups as antibacterial wound dressing membranes. Eur. Polym. J. 2021, 142, 110142.
- 273 Zhang, W.; Wang, T.; Zheng, Z.; Quirino, R. L.; Xie, F.; Li, Y.; Zhang, C. Plant oil-based non-isocyanate waterborne poly(hydroxyl urethane)s. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 452, 138965.
- 274 Bizet, B.; Grau, E.; Cramail, H.; Asua, J. M. Volatile Organic Compound-Free Synthesis of Waterborne Poly(hydroxy urethane)–(Meth)acrylic Hybrids by Miniemulsion Polymerization. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2020, 2, 4016–4025.
- 275 Dong, T.; Dheressa, E.; Wiatrowski, M.; Pereira, A. P.; Zeller, A.; Laurens, L. M. L.; Pienkos, P. T. Assessment of Plant and Microalgal Oil-Derived Nonisocyanate Polyurethane Products for Potential Commercialization. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 12858–12869.
- 276 Schmidt, S.; Gatti, F. J.; Luitz, M.; Ritter, B. S.; Bruchmann, B.; Mülhaupt, R. Erythritol Dicarbonate as Intermediate for Solvent- and Isocyanate-Free Tailoring of Bio-Based Polyhydroxyurethane Thermoplastics and Thermoplastic Elastomers. Macromolecules 2017, 50, 2296–2303.
- 277 Gharibi, R.; Yeganeh, H.; Kazemi, S. Green and non-leaching anti- bacterial and cytocompatible coating with build-in quaternary ammonium salt derived from methoxysilane functionalized soybean oil. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 99, 887–899.
- 278 Gholami, H.; Yeganeh, H. Vegetable oil-based polyurethanes as antimicrobial wound dressings: in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Biomed. Mater. 2020, 15, 045001.
- 279 Ochiai, B.; Nakayama, J.-i.; Mashiko, M.; Kaneko, Y.; Nagasawa, T.; Endo, T. Synthesis and crosslinking reaction of poly(hydroxyurethane) bearing a secondary amine structure in the main chain. J. Polym. Sci. Part A: Polym. Chem. 2005, 43, 5899–5905.
- 280 Lamarzelle, O.; Hibert, G.; Lecommandoux, S.; Grau, E.; Cramail, H. A thioglycerol route to bio-based bis-cyclic carbonates: poly(hydroxyurethane) preparation and post-functionalization. Polym. Chem. 2017, 8, 3438–3447.
- 281 Ogunniyi, D. Castor oil: A vital industrial raw material. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 1086–1091.
- 282 Magliozzi, F.; Chollet, G.; Grau, E.; Cramail, H. Benefit of the Reactive Extrusion in the Course of Polyhydroxyurethanes Synthesis by Aminolysis of Cyclic Carbonates. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 17282–17292.
- 283 Maisonneuve, L.; More, A. S.; Foltran, S.; Alfos, C.; Robert, F.; Landais, Y.; Tassaing, T.; Grau, E.; Cramail, H. Novel green fatty acid-based bis-cyclic carbonates for the synthesis of isocyanate-free poly(hydroxyurethane amide)s. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 25795–25803.
- 284 Martínez, J.; Cruz-Martínez, F.; Martínez de Sarasa Buchaca, M.; Fernández-Baeza, J.; Sánchez-Barba, L. F.; North, M.; Castro-Osma, J. A.; Lara-Sánchez, A. Efficient Synthesis of Cyclic Carbonates from Unsaturated Acids and Carbon Dioxide and their Application in the Synthesis of Biobased Polyurethanes. ChemPlusChem 2021, 86, 460–468.
- 285 Ren, F.-Y.; You, F.; Gao, S.; Xie, W.-H.; He, L.-N.; Li, H.-R. Oligomeric ricinoleic acid synthesis with a recyclable catalyst and application to preparing non-isocyanate polyhydroxyurethane. Eur. Polym. J. 2021, 153, 110501.
- 286 Li, H.; Ren, F. Y.; Li, H. R.; He, L. N. Modification of ricinoleic acid based nonisocyanate polyurethane using polyamine containing polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2023, 63, 1507–1515.
- 287 Theerathanagorn, T.; Vidal-López, A.; Comas-Vives, A.; Poater, A.; D′ Elia, V. Cycloaddition of CO2 to epoxides “around water”: a strategy to apply and recycle efficient water-soluble bio-based organocatalysts in biphasic media. Green Chem. 2023, 25, 4336–4349.
- 288 Steinbauer, J.; Spannenberg, A.; Werner, T. An in situ formed Ca2+–crown ether complex and its use in CO2-fixation reactions with terminal and internal epoxides. Green Chem. 2017, 19, 3769–3779.
- 289 Quienne, B.; Poli, R.; Pinaud, J.; Caillol, S. Enhanced aminolysis of cyclic carbonates by β-hydroxylamines for the production of fully biobased polyhydroxyurethanes. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 1678–1690.
- 290 Mora, A.-S.; Tayouo, R.; Boutevin, B.; David, G.; Caillol, S. Vanillin-derived amines for bio-based thermosets. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 4075–4084.
- 291 Tomita, H.; Sanda, F.; Endo, T. Model reaction for the synthesis of polyhydroxyurethanes from cyclic carbonates with amines: Substituent effect on the reactivity and selectivity of ring-opening direction in the reaction of five-membered cyclic carbonates with amine. J. Polym. Sci. Part A: Polym. Chem. 2001, 39, 3678–3685.
- 292 Quérette, T.; Fleury, E.; Sintes-Zydowicz, N. Non-isocyanate polyurethane nanoparticles prepared by nanoprecipitation. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 114, 434–445.
- 293 Ganachaud, F.; Katz, J. L. Nanoparticles and Nanocapsules Created Using the Ouzo Effect: Spontaneous Emulsification as an Alternative to Ultrasonic and High-Shear Devices. ChemPhysChem 2005, 6, 209–216.
- 294 Zhao, Y.; Berger, R.; Landfester, K.; Crespy, D. Double Redox-Responsive Release of Encoded and Encapsulated Molecules from Patchy Nanocapsules. Small 2015, 11, 2995–2999.
- 295 Mehravar, S.; Ballard, N.; Tomovska, R.; Asua, J. M. Polyurethane/ Acrylic Hybrid Waterborne Dispersions: Synthesis, Properties and Applications. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 20902–20922.
- 296 Danish, M.; Ahmad, T. A review on utilization of wood biomass as a sustainable precursor for activated carbon production and application. Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev. 2018, 87, 1–21.
- 297 Zikeli, F.; Vinciguerra, V.; D'Annibale, A.; Capitani, D.; Romagnoli, M.; Scarascia Mugnozza, G. Preparation of Lignin Nanoparticles from Wood Waste for Wood Surface Treatment. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 281.
- 298 Tardy, B. L.; Lizundia, E.; Guizani, C.; Hakkarainen, M.; Sipponen, M. H. Prospects for the integration of lignin materials into the circular economy. Mater. Today 2023, 65, 122–132.
- 299 Upton, B. M.; Kasko, A. M. Strategies for the Conversion of Lignin to High-Value Polymeric Materials: Review and Perspective. Chem. Rev. 2015, 116, 2275–2306.
- 300 Jaroonwatana, W.; Theerathanagorn, T.; Theerasilp, M.; Del Gobbo, S.; Yiamsawas, D.; D'Elia, V.; Crespy, D. Nanoparticles of aromatic biopolymers catalyze CO2 cycloaddition to epoxides under atmospheric conditions. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2021, 5, 5431–5444.
- 301 Quinsaat, J. E. Q.; Feghali, E.; van de Pas, D. J.; Vendamme, R.; Torr, K. M. Preparation of Biobased Nonisocyanate Polyurethane/Epoxy Thermoset Materials Using Depolymerized Native Lignin. Biomacromolecules 2022, 23, 4562–4573.
- 302 Ma, Y.; Hummel, M.; Määttänen, M.; Särkilahti, A.; Harlin, A.; Sixta, H. Upcycling of waste paper and cardboard to textiles. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 858–866.
- 303 Bernier, E.; Lavigne, C.; Robidoux, P. Y. Life cycle assessment of kraft lignin for polymer applications. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2012, 18, 520–528.
- 304 Manzardo, A.; Marson, A.; Roso, M.; Boaretti, C.; Modesti, M.; Scipioni, A.; Lorenzetti, A. Life Cycle Assessment Framework to Support the Design of Biobased Rigid Polyurethane Foams. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 14114–14123.
- 305 Chen, H.; Chauhan, P.; Yan, N. “Barking” up the right tree: biorefinery from waste stream to cyclic carbonate with immobilization of CO2 for non-isocyanate polyurethanes. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 6874–6888.
- 306 Fache, M.; Boutevin, B.; Caillol, S. Vanillin Production from Lignin and Its Use as a Renewable Chemical. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2015, 4, 35–46.
- 307 Fache, M.; Boutevin, B.; Caillol, S. Vanillin, a key-intermediate of biobased polymers. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 68, 488–502.
- 308 Fanjul-Mosteirín, N.; Fonseca, L. P.; Dove, A. P.; Sardon, H. Bio-based non-isocyanate poly(hydroxy urethane)s (PHU) derived from vanillin and CO2. Mater. Adv. 2023, 4, 2437–2448.
- 309 Caes, B. R.; Teixeira, R. E.; Knapp, K. G.; Raines, R. T. Biomass to Furanics: Renewable Routes to Chemicals and Fuels. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 2591–2605.
- 310 Hu, L.; Zhao, G.; Hao, W.; Tang, X.; Sun, Y.; Lin, L.; Liu, S. Catalytic conversion of biomass-derived carbohydrates into fuels and chemicals via furanic aldehydes. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 11184–11206.
- 311 Choudhary, V.; Sandler, S. I.; Vlachos, D. G. Conversion of Xylose to Furfural Using Lewis and Brønsted Acid Catalysts in Aqueous Media. ACS Catal. 2012, 2, 2022–2028.
- 312 Toftgaard Pedersen, A.; Ringborg, R.; Grotkjær, T.; Pedersen, S.; Woodley, J. M. Synthesis of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) by acid catalyzed dehydration of glucose–fructose mixtures. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 273, 455–464.
- 313 Gandini, A.; M. Lacerda, T. Furan Polymers: State of the Art and Perspectives. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2022, 307, 2100902.
- 314 García González, M. N.; Börjesson, P.; Levi, M.; Turri, S. Development and Life Cycle Assessment of Polyester Binders Containing 2,5-Furandicarboxylic Acid and Their Polyurethane Coatings. J. Polym. Environ. 2018, 26, 3626–3637.
- 315 Dolci, E.; Froidevaux, V.; Michaud, G.; Simon, F.; Auvergne, R.; Fouquay, S.; Caillol, S. Thermoresponsive crosslinked isocyanate-free polyurethanes by Diels-Alder polymerization. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 44408.
- 316 Dolci, E.; Michaud, G.; Simon, F.; Boutevin, B.; Fouquay, S.; Caillol, S. Remendable thermosetting polymers for isocyanate-free adhesives: a preliminary study. Polym. Chem. 2015, 6, 7851–7861.
- 317 Wu, P.; Cheng, H.; Wang, X.; Shi, R.; Zhang, C.; Arai, M.; Zhao, F. A self-healing and recyclable polyurethane-urea Diels–Alder adduct synthesized from carbon dioxide and furfuryl amine. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 552–560.
- 318 Choong, P. S.; Chong, N. X.; Wai Tam, E. K.; Seayad, A. M.; Seayad, J.; Jana, S. Biobased Nonisocyanate Polyurethanes as Recyclable and Intrinsic Self-Healing Coating with Triple Healing Sites. ACS Macro Lett. 2021, 10, 635–641.
- 319 Monteiro, J. L. F.; Veloso, C. O. Catalytic Conversion of Terpenes into Fine Chemicals. Top. Catal. 2004, 27, 169–180.
- 320 Masyita, A.; Mustika Sari, R.; Dwi Astuti, A.; Yasir, B.; Rahma Rumata, N.; Emran, T. B.; Nainu, F.; Simal-Gandara, J. Terpenes and terpenoids as main bioactive compounds of essential oils, their roles in human health and potential application as natural food preservatives. Food Chem.: X 2022, 13, 100217.
- 321 Ye, M.; Gao, J.; Zhou, Y. J. Global metabolic rewiring of the nonconventional yeast Ogataea polymorpha for biosynthesis of the sesquiterpenoid β-elemene. Metab. Eng. 2023, 76, 225–231.
- 322 Lamparelli, D. H.; Paradiso, V.; Monica, F. D.; Proto, A.; Guerra, S.; Giannini, L.; Capacchione, C. Toward More Sustainable Elastomers: Stereoselective Copolymerization of Linear Terpenes with Butadiene. Macromolecules 2020, 53, 1665–1673.
- 323 Winnacker, M.; Rieger, B. Recent Progress in Sustainable Polymers Obtained from Cyclic Terpenes: Synthesis, Properties, and Application Potential. ChemSusChem 2015, 8, 2455–2471.
- 324 Peña Carrodeguas, L.; Martín, C.; Kleij, A. W. Semiaromatic Polyesters Derived from Renewable Terpene Oxides with High Glass Transitions. Macromolecules 2017, 50, 5337–5345.
- 325 Bähr, M.; Bitto, A.; Mülhaupt, R. Cyclic limonene dicarbonate as a new monomer for non-isocyanate oligo- and polyurethanes (NIPU) based upon terpenes. Green Chem. 2012, 14, 1447–1454.
- 326 Schimpf, V.; Ritter, B. S.; Weis, P.; Parison, K.; Mülhaupt, R. High Purity Limonene Dicarbonate as Versatile Building Block for Sustainable Non-Isocyanate Polyhydroxyurethane Thermosets and Thermoplastics. Macromolecules 2017, 50, 944–955.
- 327 Rehman, A.; Russell, E.; Saleem, F.; Mahmood, K.; Abbas, A.; Eze, V. C.; Harvey, A. A Stereoselective Route to R-(+)-Limonene-Based Non-isocyanate Poly(hydroxyurethanes). J. Polym. Environ. 2022, 30, 4452–4462.
- 328 Rehman, A.; López Fernández, A. M.; Gunam Resul, M. F. M.; Harvey, A. Highly selective, sustainable synthesis of limonene cyclic carbonate from bio-based limonene oxide and CO2: A kinetic study. J. CO2 Util. 2019, 29, 126–133.
- 329 Maquilón, C.; Brandolese, A.; Alter, C.; Hövelmann, C. H.; Della Monica, F.; Kleij, A. W. Renewable Beta-Elemene Based Cyclic Carbonates for the Preparation of Oligo(hydroxyurethane)s. ChemSusChem 2022, 15, e202201123.
- 330 Melchionna, M.; Fornasiero, P.; Prato, M. The Rise of Hydrogen Peroxide as the Main Product by Metal-Free Catalysis in Oxygen Reductions. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1802920.
- 331 van Velthoven, J. L.; Gootjes, L.; van Es, D. S.; Noordover, B. A.; Meuldijk, J. Poly (hydroxy urethane)s based on renewable diglycerol dicarbonate. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 70, 125–135.
- 332 Leitsch, E. K.; Heath, W. H.; Torkelson, J. M. Polyurethane/polyhydroxyurethane hybrid polymers and their applications as adhesive bonding agents. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2016, 64, 1–8.
- 333 Ketata, N.; Sanglar, C.; Waton, H.; Alamercery, S.; Delolme, F.; Raffin, G.; Grenier-Loustalot, M. F. Thermal Degradation of Polyurethane Bicomponent Systems in Controlled Atmospheres. Polym. Polym. Comp. 2005, 13, 1–26.
- 334 Farhadian, A.; Ahmadi, A.; Omrani, I.; Miyardan, A. B.; Varfolomeev, M. A.; Nabid, M. R. Synthesis of fully bio-based and solvent free non-isocyanate poly (ester amide/urethane) networks with improved thermal stability on the basis of vegetable oils. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2018, 155, 111–121.
- 335 Yao, Y.; Xiao, M.; Liu, W. A short review on self-healing thermoplastic polyurethanes. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2021, 222, 2100002.
- 336 Besse, V.; Camara, F.; Méchin, F.; Fleury, E.; Caillol, S.; Pascault, J.-P.; Boutevin, B. How to explain low molar masses in Polyhydroxyurethanes (PHUs). Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 71, 1–11.
- 337 Chen, W.; Li, T.; Du, S.; Chen, H.; Wang, Q. Microalgal polyunsaturated fatty acids: Hotspots and production techniques. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1146881.
- 338 Mora, A.-S.; Tayouo, R.; Boutevin, B.; David, G.; Caillol, S. Synthesis of biobased reactive hydroxyl amines by amination reaction of cardanol-based epoxy monomers. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 118, 429–436.
- 339 Ip, Y. K.; Chew, S. F.; Randall, D. J. Ammonia toxicity, tolerance, and excretion. Fish Physiol. 2001, 20, 109–148.
- 340 Tandon, R.; Unzner, T.; Nigst, T. A.; De Rycke, N.; Mayer, P.; Wendt, B.; David, O. R. P.; Zipse, H. Annelated Pyridines as Highly Nucleophilic and Lewis Basic Catalysts for Acylation Reactions. Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 6435–6442.
- 341 Sahu, P.; Bhowmick, A. K.; Kali, G. Terpene Based Elastomers: Synthesis, Properties, and Applications. Processes 2020, 8, 553.
- 342 Behr, A.; Johnen, L. Myrcene as a Natural Base Chemical in Sustainable Chemistry: A Critical Review. ChemSusChem 2009, 2, 1072–1095.
- 343 Farkhondehnia, M.; Younes, G. R.; Maric, M. Development of Myrcene-Based Resins with Amine Ended Poly(Propylene Glycol) Side Chains Bonded Through Hydroxyurethane Linkages. Macromol. React. Eng. 2022, 17, 2200054.
- 344 Wang, X.; Gao, S.; Wang, J.; Xu, S.; Li, H.; Chen, K.; Ouyang, P. The production of biobased diamines from renewable carbon sources: Current advances and perspectives. Chinese J. Chem. Eng. 2021, 30, 4–13.
- 345 Jens, C. M.; Müller, L.; Leonhard, K.; Bardow, A. To Integrate or Not to Integrate—Techno-Economic and Life Cycle Assessment of CO2 Capture and Conversion to Methyl Formate Using Methanol. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 12270–12280.
- 346 Alassmy, Y. A.; Pescarmona, P. P. The Role of Water Revisited and Enhanced: A Sustainable Catalytic System for the Conversion of CO2 into Cyclic Carbonates under Mild Conditions. ChemSusChem 2019, 12, 3856–3863.
- 347 Alassmy, Y. A.; Sebakhy, K. O.; Picchioni, F.; Pescarmona, P. P. Novel non-ionic surfactants synthesised through the reaction of CO2 with long alkyl chain epoxides. J. CO2 Util. 2021, 50, 101577.
- 348 Fiorani, G.; Stuck, M.; Martín, C.; Belmonte, M. M.; Martin, E.; Escudero-Adán, E. C.; Kleij, A. W. Catalytic Coupling of Carbon Dioxide with Terpene Scaffolds: Access to Challenging Bio-Based Organic Carbonates. ChemSusChem 2016, 9, 1304–1311.
- 349 Kato, S.; Jung, J.; Suenobu, T.; Fukuzumi, S. Production of hydrogen peroxide as a sustainable solar fuel from water and dioxygen. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 3756–3764.
- 350 Cao, P.; Quan, X.; Nie, X.; Zhao, K.; Liu, Y.; Chen, S.; Yu, H.; Chen, J. G. Metal single-site catalyst design for electrocatalytic production of hydrogen peroxide at industrial-relevant currents. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 172.
- 351 Beier, M. J.; Kleist, W.; Wharmby, M. T.; Kissner, R.; Kimmerle, B.; Wright, P. A.; Grunwaldt, J.-D.; Baiker, A. Aerobic Epoxidation of Olefins Catalyzed by the Cobalt-Based Metal-Organic Framework STA-12(Co). Chem. Eur. J. 2012, 18, 887–898.
- 352 Madadi, S.; Charbonneau, L.; Bergeron, J.-Y.; Kaliaguine, S. Aerobic epoxidation of limonene using cobalt substituted mesoporous SBA-16 Part 1: Optimization via Response Surface Methodology (RSM). Appl. Catal., B 2020, 260, 118049.
- 353 Jeon, W.; Park, J.-Y.; Kim, M.-C.; Lee, S.-J.; Kim, D.-K. Effect of oxidant on the epoxidation of methyl oleate over transition metal-based Al2O3 catalysts. Catal. Today 2023, 411–412, 113901.
- 354 Yan, W.; Wang, Z.; Luo, C.; Xia, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Du, F.; Jin, X. Opportunities and Emerging Challenges of the Heterogeneous Metal-Based Catalysts for Vegetable Oil Epoxidation. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 7426–7446.
- 355 Baek, H.; Minakawa, M.; Yamada, Y. M. A.; Han, J. W.; Uozumi, Y. In-Water and Neat Batch and Continuous-Flow Direct Esterification and Transesterification by a Porous Polymeric Acid Catalyst. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25925.
- 356 Jaudouin, O.; Robin, J. J.; Lopez-Cuesta, J. M.; Perrin, D.; Imbert, C. Ionomer-based polyurethanes: a comparative study of properties and applications. Polym. Int. 2012, 61, 495–510.




