Insight into the Role of Isolated Gold Atoms-Ceria Conjunction in Catalyzing the Water-Gas Shift Reaction†
Xin-Pu Fu
Key Laboratory for Colloid and Interface Chemistry, Key Laboratory of Special Aggregated Materials, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Shandong University, Jinan, Shandong, 250100 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorHui-Zhao
Key Laboratory for Colloid and Interface Chemistry, Key Laboratory of Special Aggregated Materials, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Shandong University, Jinan, Shandong, 250100 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorWei-Wei Wang
Key Laboratory for Colloid and Interface Chemistry, Key Laboratory of Special Aggregated Materials, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Shandong University, Jinan, Shandong, 250100 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Chun-Jiang Jia
Key Laboratory for Colloid and Interface Chemistry, Key Laboratory of Special Aggregated Materials, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Shandong University, Jinan, Shandong, 250100 China
E-mail: [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorXin-Pu Fu
Key Laboratory for Colloid and Interface Chemistry, Key Laboratory of Special Aggregated Materials, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Shandong University, Jinan, Shandong, 250100 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorHui-Zhao
Key Laboratory for Colloid and Interface Chemistry, Key Laboratory of Special Aggregated Materials, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Shandong University, Jinan, Shandong, 250100 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorWei-Wei Wang
Key Laboratory for Colloid and Interface Chemistry, Key Laboratory of Special Aggregated Materials, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Shandong University, Jinan, Shandong, 250100 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Chun-Jiang Jia
Key Laboratory for Colloid and Interface Chemistry, Key Laboratory of Special Aggregated Materials, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Shandong University, Jinan, Shandong, 250100 China
E-mail: [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorDedicated to the Special Issue of Single-Atom Catalysis.
Comprehensive Summary
As the promising catalysts for the water-gas shift (WGS) reaction, the activity of Au-CeO2 composites is susceptible to the aggregation size and electronic state of Au species. Previous reports were extensively focused on the discrepancy between nonmetallic Au and metallic Au nanoparticles, whereas the understanding of the authentic role of the isolated Au atoms was limited. Herein, we investigated the catalytic behavior and structural information over two types of Au/CeO2 catalysts, in which the predominant conjunctions were isolated Au1-CeO2 and Aun-CeO2, respectively. Based on comprehensive characterizations, particularly by in-situ Raman and in-situ DRIFTS, we found that the isolated Au atoms were responsible for enhancing the reducibility of the CeO2 matrix. The CO adsorption ability on the isolated Au sites was significantly inferior to clustered Au atoms, especially at relatively high temperatures (> 200 °C). As a result, the boosted O vacancy on the isolated Au1-CeO2 conjunctions could improve the H2O activation ability for the Au-CeO2 catalysts and demonstrate a comparable activity to the clustered Aun-CeO2 sites. This work might deepen understanding of the catalytic function for the isolated Au1 site within Au/CeO2 systems while catalyzing the WGS reaction.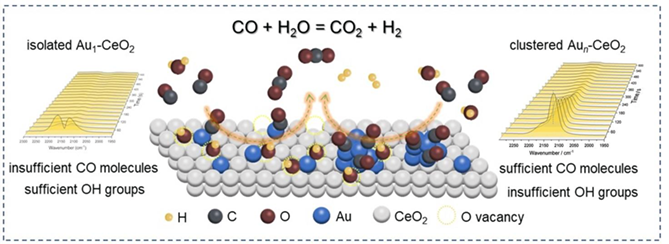
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| cjoc202300528-sup-0001-supinfo.pdfPDF document, 978.4 KB |
Appendix S1: Supporting information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1 Shen, Y.; Xu, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhan, Y. Hydrogen production from bioinspired methanol reforming at room temperature. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 5618–5624.
- 2 Lin, L.; Yu, Q.; Peng, M.; Li, A.; Yao, S.; Tian, S.; Liu, X.; Li, A.; Jiang, Z.; Gao, R.; Han, X.; Li, Y. W.; Wen, X. D.; Zhou, W.; Ma, D. Atomically Dispersed Ni/alpha-MoC Catalyst for Hydrogen Production from Methanol/Water. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 309–317.
- 3 Rodriguez, J. A.; Ma, S.; Liu, P.; Hrbek, J.; Evans, J.; Perez, M. Activity of CeOx and TiOx nanoparticles grown on Au(111) in the water-gas shift reaction. Science 2007, 318, 1757–1760.
- 4 Yang, M.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Herron, J. A.; Xu, Y.; Allard, L. F.; Lee, S.; Huang, J.; Mavrikakis, M.; Flytzani-Stephanopoulos, M. Catalytically active Au-O(OH)x-species stabilized by alkali ions on zeolites and mesoporous oxides. Science 2014, 346, 1498–1501.
- 5 Yao, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, W.; Gao, R.; Xu, W.; Ye, Y.; Lin, L.; Wen, X.; Liu, P.; Chen, B.; Crumlin, E.; Guo, J.; Zuo, Z.; Li, W.; Xie, J.; Lu, L.; Kiely, C. J.; Gu, L.; Shi, C.; Rodriguez, J. A.; Ma, D. Atomic-layered Au clusters on α-MoC as catalysts for the low-temperature water-gas shift reaction. Science 2017, 357, 389–393.
- 6 Ta, N.; Liu, J.; Chenna, S.; Crozier, P. A.; Li, Y.; Chen, A.; Shen, W. Stabilized gold nanoparticles on ceria nanorods by strong interfacial anchoring. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 20585–20588.
- 7 Carter, J. H.; Hutchings, G. J. Recent advances in the gold-catalysed low-temperature water–gas shift reaction. Catalysts 2018, 8, 624.
- 8 Li, Y.; Kottwitz, M.; Vincent, J. L.; Enright, M. J.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Huang, J.; Senanayake, S. D.; Yang, W. D.; Crozier, P. A.; Nuzzo, R. G.; Frenkel, A. I. Dynamic structure of active sites in ceria-supported Pt catalysts for the water gas shift reaction. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 914.
- 9 Zhou, L.-L.; Li, S.-Q.; Ma, C.; Fu, X.-P.; Xu, Y.-S.; Wang, W.-W.; Dong, H.; Jia, C.-J.; Wang, F. R.; Yan, C.-H. Promoting molecular exchange on rare-earth oxycarbonate surfaces to catalyze the water–gas shift reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 2252–2263.
- 10 Si, R.; Flytzani-Stephanopoulos, M. Shape and crystal-plane effects of nanoscale ceria on the activity of Au-CeO2 catalysts for the water-gas shift reaction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 2884–2887.
- 11 Chen, B.; Ma, Y.; Ding, L.; Xu, L.; Wu, Z.; Yuan, Q.; Huang, W. Reactivity of hydroxyls and water on a CeO2(111) thin film surface: the role of oxygen vacancy. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 5800–5810.
- 12 Montini, T.; Melchionna, M.; Monai, M.; Fornasiero, P. Fundamentals and catalytic applications of CeO2-based materials. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 5987–6041.
- 13 Gokhale, A. A.; Dumesic, J. A.; Mavrikakis, M. On the mechanism of low-temperature water gas shift reaction on copper. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 1402–1414.
- 14 Fu, X.-P.; Guo, L.-W.; Wang, W.-W.; Ma, C.; Jia, C.-J.; Wu, K.; Si, R.; Sun, L.-D.; Yan, C.-H. Direct identification of active surface species for the water–gas shift reaction on a gold–ceria catalyst. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 4613–4623.
- 15 Abdel-Mageed, A. M.; Kučerová, G.; Bansmann, J.; Behm, R. J. Active Au species during the low-temperature water gas shift reaction on Au/CeO2: A time-resolved operando XAS and DRIFTS study. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 6471–6484.
- 16 Rodriguez, J. A.; Liu, P.; Hrbek, J.; Evans, J.; Perez, M. Water gas shift reaction on Cu and Au nanoparticles supported on CeO2(111) and ZnO(0001): intrinsic activity and importance of support interactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 1329–1332.
- 17 Yang, M.; Allard, L. F.; Flytzani-Stephanopoulos, M. Atomically dispersed Au-(OH)x species bound on titania catalyze the low-temperature water-gas shift reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 3768–3771.
- 18 Song, W.; Hensen, E. J. M. Mechanistic Aspects of the Water–Gas Shift Reaction on Isolated and Clustered Au Atoms on CeO2(110): A Density Functional Theory Study. ACS Catal. 2014, 4, 1885–1892.
- 19 Fu, Q.; Saltsburg, H.; Flytzani-Stephanopoulos, M. Active nonmetallic Au and Pt species on ceria-based water-gas shift catalysts. Science 2003, 301, 935–938.
- 20 Fu, X. P.; Guo, L. W.; Wang, W. W.; Ma, C.; Jia, C. J.; Wu, K.; Si, R.; Sun, L. D.; Yan, C. H. Direct identification of active surface species for the water-gas shift reaction on a gold-ceria catalyst. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 4613–4623.
- 21 Reina, T. R.; Gonzalez-Castano, M.; Lopez-Flores, V.; Martinez, T. L.; Zitolo, A.; Ivanova, S.; Xu, W.; Centeno, M. A.; Rodriguez, J. A.; Odriozola, J. A. Au and Pt remain unoxidized on a CeO2-based catalyst during the water-gas shift reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 446–453.
- 22 Yi, N.; Si, R.; Saltsburg, H.; Flytzani-Stephanopoulos, M. Active gold species on cerium oxide nanoshapes for methanol steam reforming and the water gas shift reactions. Energy Environ. Sci. 2010, 3, 831–837.
- 23 Ziemba, M.; Ganduglia-Pirovano, M. V.; Hess, C. Insight into the mechanism of the water-gas shift reaction over Au/CeO2 catalysts using combined operando spectroscopies. Faraday Discuss. 2021, 229, 232–250.
- 24 Wu, Z.; Li, M.; Howe, J.; Meyer, H. M., 3rd; Overbury, S. H. Probing defect sites on CeO2 nanocrystals with well-defined surface planes by Raman spectroscopy and O2 adsorption. Langmuir 2010, 26, 16595–16606.
- 25 Lee, Y.; He, G.; Akey, A. J.; Si, R.; Flytzani-Stephanopoulos, M.; Herman, I. P. Raman analysis of mode softening in nanoparticle CeO(2-delta) and Au-CeO(2-delta) during CO oxidation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 12952–12955.
- 26 Guo, L.-W.; Du, P.-P.; Fu, X.-P.; Ma, C.; Zeng, J.; Si, R.; Huang, Y.-Y.; Jia, C.-J.; Zhang, Y.-W.; Yan, C.-H. Contributions of distinct gold species to catalytic reactivity for carbon monoxide oxidation. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 1–8.
- 27 Mihaylov, M.; Knözinger, H.; Hadjiivanov, K.; Gates, B. C. Characterization of the oxidation states of supported gold species by IR spectroscopy of adsorbed CO. Chem. Ing. Tech. 2007, 79, 795–806.
- 28 Daly, H.; Ni, J.; Thompsett, D.; Meunier, F. On the usefulness of carbon isotopic exchange for the operando analysis of metal–carbonyl bands by IR over ceria-containing catalysts. J. Catal. 2008, 254, 238–243.
- 29 Bozon-Verduraz, F.; Bensalem, A. IR studies of cerium dioxide: influence of impurities and defects. J. Chem. Soc., Faraday Trans. 1994, 90, 653–657.
- 30 Zhai, Y.; Pierre, D.; Si, R.; Deng, W.; Ferrin, P.; Nilekar, A. U.; Peng, G.; Herron, J. A.; Bell, D. C.; Saltsburg, H.; Mavrikakis, M.; Flytzani- Stephanopoulos, M. Alkali-stabilized Pt-OHx species catalyze low- temperature water-gas shift reactions. Science 2010, 329, 1633–1636.
- 31 Kalamaras, C. M.; Panagiotopoulou, P.; Kondarides, D. I.; Efstathiou, A. M. Kinetic and mechanistic studies of the water–gas shift reaction on Pt/TiO2 catalyst. J. Catal. 2009, 264, 117–129.
- 32 German, E. D.; Sheintuch, M. Quantum Effects in the Kinetics of H2O Dissociative Adsorption on Pt(111), Cu(111), Rh(111), and Ni(111). J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 3089–3097.
- 33 Tian, Y.; Liu, X.; Xu, L.; Yuan, D.; Dou, Y.; Qiu, J.; Li, H.; Ma, J.; Wang, Y.; Su, D.; Zhang, S. Engineering crystallinity and oxygen vacancies of Co(II) Oxide nanosheets for high performance and robust rechargeable Zn–Air batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2101239.
- 34 Bêche, E.; Charvin, P.; Perarnau, D.; Abanades, S.; Flamant, G. Ce 3d XPS investigation of cerium oxides and mixed cerium oxide (CexTiyOz). Surf. Interface Anal. 2008, 40, 264–267.
- 35 Nakajima, A.; Yoshihara, A.; Ishigame, M. Defect-induced Raman spectra in doped CeO2. Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter. 1994, 50, 13297–13307.
- 36 Vindigni, F.; Manzoli, M.; Damin, A.; Tabakova, T.; Zecchina, A. Surface and inner defects in Au/CeO2 WGS catalysts: relation between Raman properties, reactivity and morphology. Chemistry 2011, 17, 4356–4361.




