Antioxidant, Diabetic and Inflammatory Activities of Alpinia calcarata Roscoe Extract
Abstract
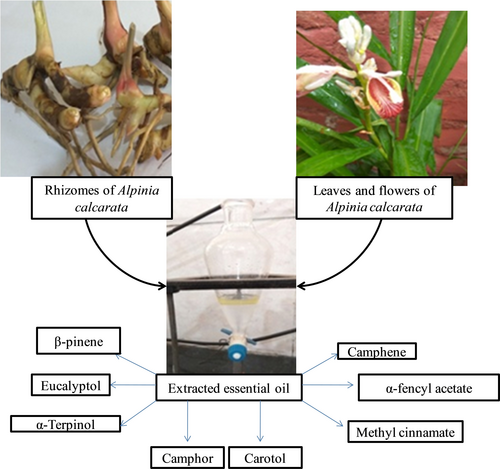
Background: Alpinia calcarata (AC) Roscoe of Zingiberaceae popularly known as lesser galangal has a widespread occurrence in China, India, Sri-Lanka, Bangladesh, Malaysia, Indonesia and Thailand. Essential oil (Eoil) was obtained from leaves/rhizomes of AC via hydro-distillation process. Methods: To identify chemical ingredients in oil from leaves/rhizomes of AC through GC/MS technique for volatile components and their anti-oxidant, inflammatory/diabetic activities. Results: The 38 and 65 components were found to make up 99.9 and 99.6 %, respectively in total of Eoil composition of AC leaves/rhizomes. Key chemical constituents were eucalyptol (28.7 % in leaves; 25.4 % in rhizomes), camphor (12.8 % in leaves; 4.2 % in rhizomes), and carotol (9.8 % in leaves; 5.6 % in rhizomes) found in oil of AC leaves/rhizomes. Colorimetric assay showed anti-oxidant activities in leaves and rhizomes are IC50=71.01±0.71 μg/mL and IC50=73.83±0.49 μg/mL, respectively in the Eoils. Eoils had high anti-oxidant capabilities in IC50-values of AC-L-Eoil=43.09±0.82&AC-Rh-Eoil=68.11±0.87 in reducing power in μg/mL was found. Albumin test of rhizome oil had IC50-values of 15.19±0.25 μg/mL. Concentrations range of 7.81 μg/mL and 250 μg/mL in the Eoils of AC leaves and rhizome, respectively by α-glucosidase inhibition assay. Conclusion: Our findings demonstrated that leaf oil was slightly more promising results than rhizome oil of AC extract, which was ultimately showed medicinal potential of secondary metabolites with anti-oxidant, diabetic/inflammatory activities. Further, Eoils of AC have a wide range of pharmacological potential and promising anti-diabetic effects.
Graphical Abstract
Conflict of interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy or ethical restrictions.