Synthesis of Catechin-Rare Earth Complex with Efficient and Broad-Spectrum Anti-Biofilm Activity
Lu Liu
Department of Biomass Chemistry and Engineering, Sichuan University, Chengdu, 610065 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Xiao Xiao
Department of Biomass Chemistry and Engineering, Sichuan University, Chengdu, 610065 P. R. China
National Engineering Laboratory for Clean Technology of Leather Manufacture, Sichuan University, Chengdu, 610065 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorKe Li
Department of Biomass Chemistry and Engineering, Sichuan University, Chengdu, 610065 P. R. China
National Engineering Laboratory for Clean Technology of Leather Manufacture, Sichuan University, Chengdu, 610065 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorXia Li
Department of Biomass Chemistry and Engineering, Sichuan University, Chengdu, 610065 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorBi Shi
Department of Biomass Chemistry and Engineering, Sichuan University, Chengdu, 610065 P. R. China
National Engineering Laboratory for Clean Technology of Leather Manufacture, Sichuan University, Chengdu, 610065 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Xuepin Liao
Department of Biomass Chemistry and Engineering, Sichuan University, Chengdu, 610065 P. R. China
National Engineering Laboratory for Clean Technology of Leather Manufacture, Sichuan University, Chengdu, 610065 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorLu Liu
Department of Biomass Chemistry and Engineering, Sichuan University, Chengdu, 610065 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Xiao Xiao
Department of Biomass Chemistry and Engineering, Sichuan University, Chengdu, 610065 P. R. China
National Engineering Laboratory for Clean Technology of Leather Manufacture, Sichuan University, Chengdu, 610065 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorKe Li
Department of Biomass Chemistry and Engineering, Sichuan University, Chengdu, 610065 P. R. China
National Engineering Laboratory for Clean Technology of Leather Manufacture, Sichuan University, Chengdu, 610065 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorXia Li
Department of Biomass Chemistry and Engineering, Sichuan University, Chengdu, 610065 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorBi Shi
Department of Biomass Chemistry and Engineering, Sichuan University, Chengdu, 610065 P. R. China
National Engineering Laboratory for Clean Technology of Leather Manufacture, Sichuan University, Chengdu, 610065 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Xuepin Liao
Department of Biomass Chemistry and Engineering, Sichuan University, Chengdu, 610065 P. R. China
National Engineering Laboratory for Clean Technology of Leather Manufacture, Sichuan University, Chengdu, 610065 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorAbstract
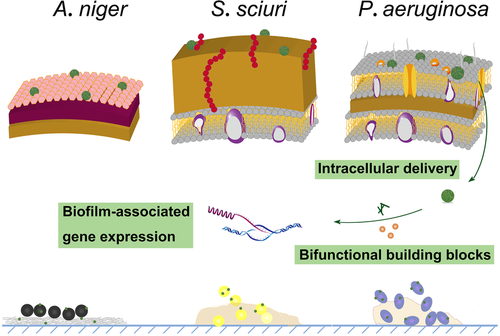
Biofilm is the crucial reason of clinical infections. Herein, green tea based polyphenol (catechin) and rare earth (RE) metal ions were employed for the preparation of catechin–RE complexes with significant anti-biofilm properties. The complexes were characterized by FT-IR, Raman spectroscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and dynamic light scattering (DLS), which suggested that catechin coordinated with RE3+ through its ortho phenolic hydroxy groups. The prepared catechin-RE showed significant effects in anti-biofilm growth against P. aeruginosa (Gram-negative bacteria), S. sciuri (Gram-positive bacteria), and A. niger (fungi), which significantly exceeded the utilization of catechin or RE3+. Morphological observations indicated that catechin supplied cell affinity to transfer RE3+ and helped to damage cell membrane, which act as a carrier to exert cytotoxicity of RE3+ to realize anti-biofilm. Differential gene expression analysis described gene expression changes induced by catechin-RE, including 56, 272 and 2160 downregulated genes for P. aeruginosa, S. sciuri and A. niger, respectively, which suggested critical changes in cellular metabolism, growth and other processes. These results illustrate the outstanding superiority of catechin-RE complexes in anti-infection aspect, i. e., the green tea based rare earth complexes are promising candidates for anti-biofilm applications to address serious challenges in the prevention of multiple infections.
Graphical Abstract
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| cbdv201900734-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf3.4 MB | Supplementary |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1L. Hall-Stoodley, J. W. Costerton, P. Stoodley, ‘Bacterial biofilms: from the natural environment to infectious diseases’, Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 95–108.
- 2V. Wonoputri, C. Gunawan, S. Liu, N. Barraud, L. H. Yee, M. Lim, R. Amal, ‘Copper complex in poly(vinyl chloride) as a nitric oxide-generating catalyst for the control of nitrifying bacterial biofilms’, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 22148–22156.
- 3I. Kolodkin-Gal, D. Romero, S. G. Cao, J. Clardy, R. Kolter, R. Losick, ‘d-amino acids trigger biofilm disassembly’, Science 2010, 328, 627–629.
- 4T. Dubois, Y. D. N. Tremblay, A. Hamiot, I. Martin-Verstraete, J. Deschamps, M. Monot, R. Briandet, B. Dupuy, ‘A microbiota-generated bile salt induces biofilm formation in Clostridium difficile’, NPJ Biofilms Microbiom. 2019, 5, 1–12.
- 5B. Fu, Q. Wu, M. Dang, D. Bai, K. Duan, L. Shen, Q. Guo, ‘Inhibition of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation by traditional Chinese medicinal herb Herba patriniae’, BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 1–10.
- 6S. Stepanović, I. Dakić, S. Djukić, B. Lozuk, M. Svabić-Vlahović, ‘Surgical wound infection associated with Staphylococcus sciuri’, Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 34, 685–686.
10.1080/00365540110076949a Google Scholar
- 7P. Gilbert, T. Maira-Litran, A. J. McBain, A. H. Rickard, F. W. Whyte, ‘The physiology and collective recalcitrance of microbial biofilm communities’, Adv. Microb. Physiol. 2002, 46, 203–256.
- 8P. Speck, ‘Antibiotics: avert an impending crisis’, Nature 2013, 496, 169–169.
- 9U. Römling, C. Balsalobre, ‘Biofilm infections, their resilience to therapy and innovative treatment strategies’, J. Intern. Med. 2012, 272, 541–561.
- 10M. J. Fraqueza, ‘Antibiotic resistance of lactic acid bacteria isolated from dry-fermented sausages’, Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 212, 76–88.
- 11A. Adonizio, K. F. Kong, K. Mathee, ‘Inhibition of quorum sensing-controlled virulence factor production in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by south Florida plant extracts’, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 198–203.
- 12H. S. Cho, J. H. Lee, S. Y. Ryu, S. W. Joo, M. H. Cho, J. Lee, ‘Inhibition of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coli O157:H7 biofilm formation by plant metabolite epsilon-viniferin’, J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 7120–7126.
- 13A. R. Blanco, A. Sudano-Roccaro, G. C. Spoto, A. Nostro, D. Rusciano, ‘Epigallocatechin gallate inhibits biofilm formation by ocular staphylococcal isolates’, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 4339–4343.
- 14J. M. Zhang, X. Rui, L. Wang, Y. Guan, X. M. Sun, M. S. Dong, ‘Polyphenolic extract from Rosa rugosa tea inhibits bacterial quorum sensing and biofilm formation’, Food Control 2014, 42, 125–131.
- 15Y. Asahi, Y. Noiri, J. Miura, H. Maezono, M. Yamaguchi, R. Yamamoto, H. Azakami, M. Hayashi, S. Ebisu, ‘Effects of the tea catechin epigallocatechin gallate on Porphyromonas gingivalis biofilms’, J. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 116, 1164–1171.
- 16M. F. Siddiqui, M. Rzechowicz, H. S. Oh, N. Saeidi, L. J. Hui, H. Winters, A. G. Fane, T. H. Chong, ‘The efficacy of tannic acid in controlling biofouling by Pseudomonas aeruginosa is dependent on nutrient conditions and bacterial density’, Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2015, 104, 74–82.
- 17Z. Samoilova, N. Muzyka, E. Lepekhina, O. Oktyabrsky, G. Smirnova, ‘Medicinal plant extracts can variously modify biofilm formation in Escherichia coli’, Anton. Leeuw. 2014, 105, 709–722.
- 18T. Wakabayashi, A. Ymamoto, A. Kazaana, Y. Nakano, Y. Nojiri, M. Kashiwazaki, ‘Antibacterial, antifungal and nematicidal activities of rare earth ions’, Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2016, 174, 464–470.
- 19C. H. Evans, ‘Interesting and useful biochemical-properties of lanthanides’, Trends Biochem. Sci. 1983, 8, 445–449.
- 20W. H. Zhu, J. X. Wang, H. S. Li, Y. Chen, ‘Research on transmembrane behaviors of La3+ to PC12 cells’, Prog. Biochem. Biophys. 2001, 28, 387–391.
- 21L. Cobrado, A. Silva-Dias, M. M. Azevedo, C. Pina-Vaz, A. G. Rodrigues, ‘In vivo antibiofilm effect of cerium, chitosan and hamamelitannin against usual agents of catheter-related bloodstream infections’, J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2013, 68, 126–130.
- 22R. J. Wiglusz, Z. Drulis-Kawa, R. Pazik, K. Zawisza, A. Dorotkiewicz-Jach, J. Roszkowiak, J. M. Nedelec, ‘Multifunctional lanthanide and silver ion co-doped nano-chlorapatites with combined spectroscopic and antimicrobial properties’, Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 6918–6925.
- 23L. Peng, W. Y. Zhang, L. Xi, L. Yi, ‘Structural basis for the biological effects of Pr(III) ions: Alteration of cell membrane permeability’, Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2007, 120, 141–147.
- 24L. Lekha, K. K. Raja, G. Rajagopal, D. Easwaramoorthy, ‘Synthesis, spectroscopic characterization and antibacterial studies of lanthanide(III) Schiff base complexes containing N, O donor atoms’, J. Mol. Struct. 2014, 1056, 307–313.
- 25Y. M. Song, J. P. Xu, L. Ding, Q. Hou, J. W. Liu, Z. L. Zhu, ‘Syntheses, characterization and biological activities of rare earth metal complexes with curcumin and 1,10-phenanthroline-5,6-dione’, J. Inorg. Biochem. 2009, 103, 396–400.
- 26J. L. Guo, B. L. Tardy, A. J. Christofferson, Y. L. Dai, J. J. Richardson, W. Zhu, M. Hu, Y. Ju, J. W. Cui, R. R. Dagastine, I. Yarovsky, F. Caruso, ‘Modular assembly of superstructures from polyphenol-functionalized building blocks’, Nat. Nanotechnol. 2016, 11, 1105–1111.
- 27J. L. Guo, Y. Ping, H. Ejima, K. Alt, M. Meissner, J. J. Richardson, Y. Yan, K. Peter, D. von Elverfeldt, C. E. Hagemeyer, F. Caruso, ‘Engineering multifunctional capsules through the assembly of metal-phenolic networks’, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 5546–5551; Angew. Chem. 2014, 126, 5652–5657.
- 28K. Nakamura, K. Ishiyama, H. Sheng, H. Ikai, T. Kanno, Y. Niwano, ‘Bactericidal activity and mechanism of photo-irradiated polyphenols against Gram-positive and -negative bacteria’, J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 7707.
- 29H. Mao, C. Chen, X. P. Liao, B. Shi, ‘Catalytic hydrogenation of quinoline over recyclable palladium nanoparticles supported on tannin grafted collagen fibers’, J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem. 2011, 341, 51–56.
- 30S. Kim, T. Gim, S. M. Kang, ‘Versatile, Tannic acid-mediated surface PEGylation for marine antifouling applications’, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 6412–6416.
- 31X. Huang, H. Wu, X. P. Liao, B. Shi, ‘Liquid phase hydrogenation of olefins using heterogenized ruthenium complexes as high active and reusable catalyst’, Catal. Commun. 2010, 11, 487–492.
- 32K. Yu, C. C. Tian, X. Li, X. P. Liao, B. Shi, ‘Synthesis, characterization, and antibacterial activity of rare earth-catechin complexes’, Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin. 2018, 34, 543–550.
- 33C. W. Oo, M. J. Kassim, A. Pizzi, ‘Characterization and performance of Rhizophora apiculata mangrove polyflavonoid tannins in the adsorption of copper(II) and lead(II)’, Ind. Crops Prod. 2009, 30, 152–161.
- 34G. M. Chavez-Andrade, M. Tanomaru-Filho, M. I. Basso Bernardi, R. de Toledo Leonardo, G. Faria, J. M. Guerreiro-Tanomaru, ‘Antimicrobial and biofilm anti-adhesion activities of silver nanoparticles and farnesol against endodontic microorganisms for possible application in root canal treatment’, Arch. Oral Biol. 2019, 107, 104481.
- 35K. Kalishwaralal, S. BarathManiKanth, S. R. K. Pandian, V. Deepak, S. Gurunathan, ‘Silver nanoparticles impede the biofilm formation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus epidermidis’, Colloids Surf. B 2010, 79, 340–344.
- 36A. M. Konigs, H. C. Flemming, J. Wingender, ‘Nanosilver induces a non-culturable but metabolically active state in Pseudomonas aeruginosa’, Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1–11.
- 37K. Li, Y. L. Dai, W. Chen, K. Yu, G. Xiao, J. J. Richardson, W. Huang, J. L. Guo, X. P. Liao, B. Shi, ‘Self-Assembled Metal-Phenolic Nanoparticles for Enhanced Synergistic Combination Therapy against Colon Cancer’, Adv. Biosyst. 2019, 3, 1–6.
- 38J. P. Yuan, W. Li, C. Wang, ‘Effect of the La alloying addition on the antibacterial capability of 316 L stainless steel’, Mat. Sci. Eng. C Mater. 2013, 33, 446–452.
- 39Y. Yoda, Z. Q. Hu, W. H. Zhao, T. Shimamura, ‘Different susceptibilities of Staphylococcus and Gram-negative rods to epigallocatechin gallate’, J. Infect. Chemother. 2004, 10, 55–58.
- 40L. Moghadas, T. Narimani, M. Shahmoradi, ‘Antimicrobial activity of a new nanobased endodontic irrigation solution: In vitro study’, Dent. Hypotheses 2012, 3, 142.
10.4103/2155-8213.106838 Google Scholar
- 41R. Thomas, S. Mathew, A. R. Nayana, J. Mathews, E. K. Radhakrishnan, ‘Microbially and phytofabricated AgNPs with different mode of bactericidal action were identified to have comparable potential for surface fabrication of central venous catheters to combat Staphylococcus aureus biofilm’, J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2017, 171, 96–103.
- 42S. Rumbo-Feal, M. J. Gomez, C. Gayoso, L. Alvarez-Fraga, M. P. Cabral, A. M. Aransay, N. Rodriguez-Ezpeleta, A. Fullaondo, J. Valle, M. Tomas, G. Bou, M. Poza, ‘Whole transcriptome analysis of Acinetobacter baumannii assessed by RNA-sequencing reveals different mRNA expression profiles in biofilm compared to planktonic cells’, PLoS One 2013, 8, e72968.
- 43N. Trachoo, J. F. Frank, ‘Effectiveness of chemical sanitizers against Campylobacter jejuni – Containing biofilms’, J. Food Prot. 2002, 65, 1117–1121.
- 44H. Hsu, S. Sheen, J. Sites, J. Cassidy, B. Scullen, C. Sommers, ‘Effect of high pressure processing on the survival of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli (Big Six vs. O157:H7) in ground beef’, Food Microbiol. 2015, 48, 1–7.
- 45S. Sheen, J. Cassidy, B. Scullen, J. Uknalis, C. Sommers, ‘Inactivation of Salmonella spp. in ground chicken using high pressure processing’, Food Control 2015, 57, 41–47.
- 46X. Li, W. C. Zeng, D. Y. Zhu, J. L. Feng, C. C. Tian, X. P. Liao, B. Shi, ‘Investigation of collagen hydrolysate used as carbon and nitrogen source in the fermentation of Bacillus pumilus’, Process Biochem. 2017, 55, 11–16.