Al3+-Dependent Anisotropic Facet Tailoring on SrTiO3 Single Crystal for Photocatalytic Overall Water Splitting
Yang Zhang
Key Laboratory for Ultrafine Materials of Ministry of Education, School of Materials Science and Engineering, East China University of Science and Technology, 130 Meilong Road, Shanghai, 200237 China
Both authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorZhi-Hao Wang
Beijing Computational Science Research Center, Beijing, 100193 China
Both authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorWenbo Li
Key Laboratory for Advanced Materials and Feringa Nobel Prize Scientist Joint Research Centre, School of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, East China University of Science and Technology, Shanghai, 200237 China
Search for more papers by this authorPeng Cheng Ding
Key Laboratory for Ultrafine Materials of Ministry of Education, School of Materials Science and Engineering, East China University of Science and Technology, 130 Meilong Road, Shanghai, 200237 China
Search for more papers by this authorMeng Min Wang
Key Laboratory for Ultrafine Materials of Ministry of Education, School of Materials Science and Engineering, East China University of Science and Technology, 130 Meilong Road, Shanghai, 200237 China
Search for more papers by this authorYu Yang Tang
Key Laboratory for Ultrafine Materials of Ministry of Education, School of Materials Science and Engineering, East China University of Science and Technology, 130 Meilong Road, Shanghai, 200237 China
Search for more papers by this authorHao Yang Lin
Key Laboratory for Ultrafine Materials of Ministry of Education, School of Materials Science and Engineering, East China University of Science and Technology, 130 Meilong Road, Shanghai, 200237 China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Yu Peng
Key Laboratory for Ultrafine Materials of Ministry of Education, School of Materials Science and Engineering, East China University of Science and Technology, 130 Meilong Road, Shanghai, 200237 China
Search for more papers by this authorMeng Yi Wang
Key Laboratory for Ultrafine Materials of Ministry of Education, School of Materials Science and Engineering, East China University of Science and Technology, 130 Meilong Road, Shanghai, 200237 China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Zhaoke Zheng
State Key Laboratory of Crystal Materials, Shandong University, Shandong University, Jinan, 250100 China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Shuang Yang
Key Laboratory for Ultrafine Materials of Ministry of Education, School of Materials Science and Engineering, East China University of Science and Technology, 130 Meilong Road, Shanghai, 200237 China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Sheng Dai
Key Laboratory for Advanced Materials and Feringa Nobel Prize Scientist Joint Research Centre, School of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, East China University of Science and Technology, Shanghai, 200237 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Xie Zhang
School of Materials Science and Engineering, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi'an, 710072 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Peng Fei Liu
Key Laboratory for Ultrafine Materials of Ministry of Education, School of Materials Science and Engineering, East China University of Science and Technology, 130 Meilong Road, Shanghai, 200237 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Hua Gui Yang
Key Laboratory for Ultrafine Materials of Ministry of Education, School of Materials Science and Engineering, East China University of Science and Technology, 130 Meilong Road, Shanghai, 200237 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorYang Zhang
Key Laboratory for Ultrafine Materials of Ministry of Education, School of Materials Science and Engineering, East China University of Science and Technology, 130 Meilong Road, Shanghai, 200237 China
Both authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorZhi-Hao Wang
Beijing Computational Science Research Center, Beijing, 100193 China
Both authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorWenbo Li
Key Laboratory for Advanced Materials and Feringa Nobel Prize Scientist Joint Research Centre, School of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, East China University of Science and Technology, Shanghai, 200237 China
Search for more papers by this authorPeng Cheng Ding
Key Laboratory for Ultrafine Materials of Ministry of Education, School of Materials Science and Engineering, East China University of Science and Technology, 130 Meilong Road, Shanghai, 200237 China
Search for more papers by this authorMeng Min Wang
Key Laboratory for Ultrafine Materials of Ministry of Education, School of Materials Science and Engineering, East China University of Science and Technology, 130 Meilong Road, Shanghai, 200237 China
Search for more papers by this authorYu Yang Tang
Key Laboratory for Ultrafine Materials of Ministry of Education, School of Materials Science and Engineering, East China University of Science and Technology, 130 Meilong Road, Shanghai, 200237 China
Search for more papers by this authorHao Yang Lin
Key Laboratory for Ultrafine Materials of Ministry of Education, School of Materials Science and Engineering, East China University of Science and Technology, 130 Meilong Road, Shanghai, 200237 China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Yu Peng
Key Laboratory for Ultrafine Materials of Ministry of Education, School of Materials Science and Engineering, East China University of Science and Technology, 130 Meilong Road, Shanghai, 200237 China
Search for more papers by this authorMeng Yi Wang
Key Laboratory for Ultrafine Materials of Ministry of Education, School of Materials Science and Engineering, East China University of Science and Technology, 130 Meilong Road, Shanghai, 200237 China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Zhaoke Zheng
State Key Laboratory of Crystal Materials, Shandong University, Shandong University, Jinan, 250100 China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Shuang Yang
Key Laboratory for Ultrafine Materials of Ministry of Education, School of Materials Science and Engineering, East China University of Science and Technology, 130 Meilong Road, Shanghai, 200237 China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Sheng Dai
Key Laboratory for Advanced Materials and Feringa Nobel Prize Scientist Joint Research Centre, School of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, East China University of Science and Technology, Shanghai, 200237 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Xie Zhang
School of Materials Science and Engineering, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi'an, 710072 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Peng Fei Liu
Key Laboratory for Ultrafine Materials of Ministry of Education, School of Materials Science and Engineering, East China University of Science and Technology, 130 Meilong Road, Shanghai, 200237 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Hua Gui Yang
Key Laboratory for Ultrafine Materials of Ministry of Education, School of Materials Science and Engineering, East China University of Science and Technology, 130 Meilong Road, Shanghai, 200237 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
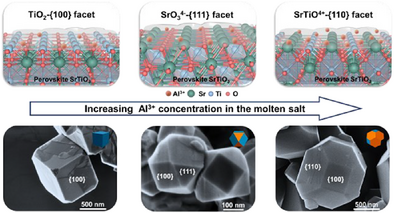
By precisely controlling Al3+ concentration in SrCl2 molten salt through the addition of miscible AlCl3, the anisotropic SrTiO3 single crystals with well-defined {100}, {111}, and {110} facets can be sequentially synthesized, achieving the optimal remarkable hydrogen evolution rate of 2621.85 µmol·h−1 and apparent quantum yield value of 50.5% at 350 nm for stoichiometric photocatalytic overall water splitting.
Abstract
Controllable fabrication of single-crystal metal oxide is of paramount importance for advanced photo(electro)catalytic applications, but achieving nonequilibrium crystal shapes with tailored facets through molten salt synthesis still remains a challenge. Herein, we systematically explored the effect of Al3+ concentration in tailoring crystal facets of SrTiO3 single crystals and developed a one-step molten salt strategy for engineering anisotropic structures by using miscible AlCl3 as Al3+ additive. By progressively increasing Al3+ concentration, a series of high-quality SrTiO3 single crystals exposing {100}, {111}, and {110} facets were sequentially synthesized. Theoretical calculations reveal an Al-doping stabilized {111} surface reconstruction and provide further atomistic insights into the surface structural evolution with Wulff constructions as Al3+ concentration increases. Experimental results demonstrate that the anisotropic facets dominate the efficient charge separation for the enhanced photocatalytic overall water splitting activity. Consequently, SrTiO3 single crystals enclosed by well-defined {100} and {111} facets exhibit a remarkable hydrogen evolution rate of 2621.85 µmol·h−1 and an apparent quantum yield value of 50.5% at 350 nm for stoichiometric overall water splitting. This work offers a molten-salt synthetic strategy and valuable insight for preparing facet-controlled single-crystal semiconductors.
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie202508114-sup-0001-SuppMat.docx14.6 MB | Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1H. Nishiyama, T. Yamada, M. Nakabayashi, Y. Maehara, M. Yamaguchi, Y. Kuromiya, Y. Nagatsuma, H. Tokudome, S. Akiyama, T. Watanabe, R. Narushima, S. Okunaka, N. Shibata, T. Takata, T. Hisatomi, K. Domen, Nature 2021, 598, 304–307.
- 2X. Tao, Y. Zhao, S. Wang, C. Li, R. Li, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 3561–3608.
- 3Q. Wang, K. Domen, Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 919–985.
- 4A. Fujishima, K. Honda, Nature 1972, 238, 37–38.
- 5D. Wang, T. Sheng, J. Chen, H.-F. Wang, P. Hu, Nat. Catal. 2018, 1, 291–299.
- 6R. Chen, F. Fan, C. Li, Angew. Chem. Inter. Ed. 2022, 61, e202117567.
- 7Y. A. Wu, I. McNulty, C. Liu, K. C. Lau, Q. Liu, A. P. Paulikas, C.-J. Sun, Z. Cai, J. R. Guest, Y. Ren, V. Stamenkovic, L. A. Curtiss, Y. Liu, T. Rajh, Nat. Energy 2019, 4, 957–968.
- 8D. Lee, W. Wang, C. Zhou, X. Tong, M. Liu, G. Galli, K.-S. Choi, Nat. Energy 2021, 6, 287–294.
- 9T. Takata, J. Jiang, Y. Sakata, M. Nakabayashi, N. Shibata, V. Nandal, K. Seki, T. Hisatomi, K. Domen, Nature 2020, 581, 411–414.
- 10R. Chen, Z. Ren, Y. Liang, G. Zhang, T. Dittrich, R. Liu, Y. Liu, Y. Zhao, S. Pang, H. An, C. Ni, P. Zhou, K. Han, F. Fan, C. Li, Nature 2022, 610, 296–301.
- 11Z. Luo, X. Ye, S. Zhang, S. Xue, C. Yang, Y. Hou, W. Xing, R. Yu, J. Sun, Z. Yu, X. Wang, Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2230.
- 12Y. Zhang, X. Wu, Z.-H. Wang, Y. Peng, Y. Liu, S. Yang, C. Sun, X. Xu, X. Zhang, J. Kang, S.-H. Wei, P. F. Liu, S. Dai, H. G. Yang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 6618–6627.
- 13L. Mu, Y. Zhao, A. Li, S. Wang, Z. Wang, J. Yang, Y. Wang, T. Liu, R. Chen, J. Zhu, F. Fan, R. Li, C. Li, Energy Environ. Sci. 2016, 9, 2463–2469.
- 14L. Pan, L. Dai, O. J. Burton, L. Chen, V. Andrei, Y. Zhang, D. Ren, J. Cheng, L. Wu, K. Frohna, A. Abfalterer, T. C. Yang, W. Niu, M. Xia, S. Hofmann, P. J. Dyson, E. Reisner, H. Sirringhaus, J. Luo, A. Hagfeldt, M. Gratzel, S. D. Stranks, Nature 2024, 628, 765–770.
- 15H. Huang, J. Wang, Y. Liu, M. Zhao, N. Zhang, Y. Hu, F. Fan, J. Feng, Z. Li, Z. Zou, Nat. Mater. 2024, 23, 383–390.
- 16X. Mao, P. Chen, Nat. Mater. 2022, 21, 331–337.
- 17R. Chen, F. Fan, T. Dittrich, C. Li, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 8238–8262.
- 18T. Takata, K. Domen, J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 19386–19388.
- 19Y. Qin, F. Fang, Z. Xie, H. Lin, K. Zhang, X. Yu, K. Chang, ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 11429–11439.
- 20D. H. K. Murthy, V. Nandal, A. Furube, K. Seki, R. Katoh, H. Lyu, T. Hisatomi, K. Domen, H. Matsuzaki, Adv. Energy Mater. 2023, 13, 2302064.
- 21R. Li, T. Takata, B. Zhang, C. Feng, Q. Wu, C. Cui, Z. Zhang, K. Domen, Y. Li, Angew. Chem. Inter. Ed. 2023, 62, e202313537.
- 22Z. Zhao, R. V. Goncalves, S. K. Barman, E. J. Willard, E. Byle, R. Perry, Z. Wu, M. N. Huda, A. J. Moulé, F. E. Osterloh, Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 1385–1395.
- 23L. Tian, X. Guan, Y. Dong, S. Zong, A. Dai, Z. Zhang, L. Guo, Environ. Chem. Lett. 2023, 21, 1257–1264.
- 24B. Wang, B. An, X. Li, S. Shen, Front. Energy 2024, 18, 101–109.
- 25Y. Ham, T. Hisatomi, Y. Goto, Y. Moriya, Y. Sakata, A. Yamakata, J. Kubota, K. Domen, J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 3027–3033.
- 26J. Xiao, T. Hisatomi, K. Domen, Acc. Chem. Res. 2023, 56, 878–888.
- 27Q. Yang, X. Tong, Z. Wang, MRE 2024, 4, 100253.
- 28X.-Y. Liu, Q. Cao, G.-X. Li, H. Liu, L.-L. Zeng, L.-L. Zhao, B. Chang, X.-W. Wang, H. Liu, W.-J. Zhou, Rare Met. 2024, 43, 2015–2025.
- 29Y.-G. Lee, Y.-C. Cheng, Y.-T. Lin, J. C. S. Wu, W.-Y. Yu, M. M. Kržmanc, S. Gupta, E. Kotomin, J. Phys. Chem. C 2023, 127, 9981–9991.
- 30G. Liu, H. G. Yang, J. Pan, Y. Q. Yang, G. Q. Lu, H. M. Cheng, Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 9559–9612.
- 31X. Liu, N. Fechler, M. Antonietti, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 8237–8265.
- 32Y. He, X. Jing, L. Qin, D. Wang, C. Wu, M. Liu, M. Yang, Z. Huang, Carbon Lett. 2024, 34, 1471–1480.
- 33G. Delarue, J. Electroanal. Chem. 1959, 60, 285–300.
- 34S. Wang, G. Liu, L. Wang, Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 5192–5247.
- 35J. Yu, J. Low, W. Xiao, P. Zhou, M. Jaroniec, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 8839–8842.
- 36C. Avcıoǧlu, S. Avcıoǧlu, M. F. Bekheet, A. Gurlo, ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2023, 6, 1134–1154.
- 37D. A. Tenne, I. E. Gonenli, A. Soukiassian, D. G. Schlom, S. M. Nakhmanson, K. M. Rabe, X. X. Xi, Phys. Rev. B 2007, 76, 024303.
- 38J. Živojinović, V. P. Pavlović, D. Kosanović, S. Marković, J. Krstić, V. A. Blagojević, V. B. Pavlović, J. Alloy. Compd. 2017, 695, 863–870.
- 39J. Jiang, K. Kato, H. Fujimori, A. Yamakata, Y. Sakata, J. Catal. 2020, 390, 81–89.
- 40M. Vračar, A. Kuzmin, R. Merkle, J. Purans, E. A. Kotomin, J. Maier, O. Mathon, Phys. Rev. B 2007, 76, 174107.
- 41Z. Wei, Y. Zhang, J. Yan, J. Chi, H. Huang, Q. Su, J. Liu, W. Shangguan, ACS Mater. Lett. 2024, 6, 5146–5153.
- 42B. Li, M. Lv, Y. Zhang, X. Gong, Z. Lou, Z. Wang, Y. Liu, P. Wang, H. Cheng, Y. Dai, B. Huang, Z. Zheng, ACS Nano 2024, 18, 25522–25534.
- 43B. Li, F. Tong, M. Lv, Z. Wang, Y. Liu, P. Wang, H. Cheng, Y. Dai, Z. Zheng, B. Huang, ACS Catal. 2022, 12, 9114–9124.
- 44D. Hirayama, T. Kawawaki, S. Oguchi, M. Ogano, N. Kon, T. Yasuda, A. Higami, Y. Negishi, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 26808–26818.