Type I-B Main-Chain Polyrotaxane Network
Graphical Abstract
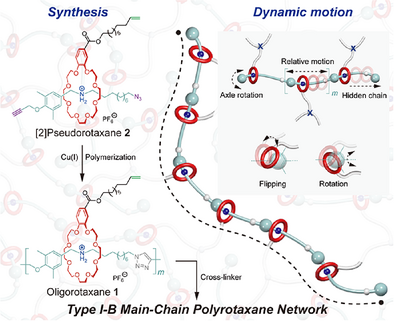
Utilizing “host−guest recognition followed by click polymerization” strategy, a Type I-B main-chain polyrotaxane (PR), featuring multiple wheels and stoppers along the polymer backbone, was efficiently synthesized. The first-ever Type I-B main-chain PR network (PRN) was then constructed to unveil the structure−property relationships of the PR. The special topological structures and dynamic characteristics of the PR skeleton provided multiple energy dissipation pathways, effectively toughening and strengthening the PRN.
Abstract
Polyrotaxanes (PRs) are recognized for their outstanding conformational flexibility, making them ideal candidates for the design of high-performance mechanically interlocked materials. However, Type I-B main-chain PRs, featuring multiple wheels and stoppers along the polymer backbone, remain underexplored due to the challenges in their design and synthesis. Herein, we introduce a facile “host−guest recognition followed by click polymerization” strategy for the synthesis of Type I-B main-chain PR, which is subsequently employed to prepare the first-ever Type I-B main-chain PR network (PRN). Compared to the control whose wheels are nonslidable under applied force, the distinctive dynamic behaviors of Type I-B main-chain PR impart extraordinary mechanical enhancements to PRN, with fracture strain, toughness, and puncture resistance all surging by more than 27-fold. Moreover, the combination of the host−guest recognition and multiple stoppers endows the PRN with great self-recovery capability due to the restriction of the motion range of mechanical bonds. This work not only presents a novel strategy for designing and synthesizing Type I-B main-chain PR networks but also highlights the pivotal role of Type I-B main-chain PRs in enhancing material performance, offering valuable insights for advancing the development of dynamic polymer materials.
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available in the Supporting Information of this article.