Design Considerations of Ionic Conductive Elastomeric Electrolyte for Solid-State Zinc Metal Batteries with High Safety and Long Life
Graphical Abstract
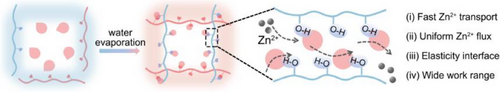
An ionic conductive elastomeric electrolyte rich in high-density hydrogen bond network was constructed through the cross-linked encapsulation of PA molecules with PVA chains during solvent evaporation. Unlike the conventional hydrogel electrolytes, elastomeric electrolytes (ZICE-4) demonstrate the fast Zn2+ ion transport, uniform Zn2+ flux, high volumetric adaptability, and wide working temperature range.
Abstract
Zn−ion batteries are regarded as one of the most promising candidates for energy storage, but the severe hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) and dendrite growth have impeded their application. In this study, we developed an Zn2+-ionic conductive elastomer solid-state electrolyte through the simultaneous hydrogen-bond cross-linking between phytic acid (PA) molecules and polyvinyl alcohol (PVA). The large PA molecules inside the polymer electrolyte are favorable to maintaining stretched conformation of PVA chain and uniform interpenetrating distribution, enhancing the amorphous region of PVA polymer. And the high-density hydrogen bond network constructed from PVA chains and PA molecules builds a novel transport mode to promote the efficient Zn2+ ion transport, displaying significant ion conductivity of 6.05 mS cm−1 at 30 °C and a higher transference number of 0.68. The special viscoelasticity of the elastomer facilitates close contact with electrodes, ensuring superior interface compatibility. The assembled Zn symmetric battery exhibits a stable cycle life of 2880 h under 0.5 mA cm−2/0.5 mAh cm−2, and the assembled Zn//VO2 full battery still maintains a capacity retention rate of 86.5% at 400 cycles under 1.0 A g−1. The development of ionic conductive elastomers offers a novel approach to solve the solid-state interface design of solid-state Zn−ion batteries.
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available in the supplementary material of this article.