Solar-Driven Reversible Hydrogen Storage of Sodium Cyclohexanolate/Phenoxide Pair
Khai Chen Tan
Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, 116023 China
Center of Materials Science and Optoelectronics Engineering, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
Both authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorQijun Pei
Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, 116023 China
Both authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorJiafeng Yu
Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, 116023 China
Search for more papers by this authorLin Liu
Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, 116023 China
Search for more papers by this authorJiayin Li
Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, 116023 China
Center of Materials Science and Optoelectronics Engineering, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
Search for more papers by this authorLi Han
Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, 116023 China
Search for more papers by this authorYang Yu
Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, 116023 China
Search for more papers by this authorZhao Li
Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, 116023 China
Search for more papers by this authorAlexis Munyentwali
Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, 116023 China
Center of Materials Science and Optoelectronics Engineering, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
Search for more papers by this authorJiaquan Guo
Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, 116023 China
Center of Materials Science and Optoelectronics Engineering, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
Search for more papers by this authorYuting Wang
Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, 116023 China
Center of Materials Science and Optoelectronics Engineering, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Li Rao
Hubei International Scientific and Technological Cooperation Base of Pesticide and Green Synthesis, Key Laboratory of Pesticide & Chemical Biology of Ministry of Education, College of Chemistry, Central China Normal University, Wuhan, 430079 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Teng He
Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, 116023 China
Center of Materials Science and Optoelectronics Engineering, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
State Key Laboratory of Catalysis, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, 116023 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Ping Chen
Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, 116023 China
Center of Materials Science and Optoelectronics Engineering, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
State Key Laboratory of Catalysis, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, 116023 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorKhai Chen Tan
Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, 116023 China
Center of Materials Science and Optoelectronics Engineering, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
Both authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorQijun Pei
Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, 116023 China
Both authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorJiafeng Yu
Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, 116023 China
Search for more papers by this authorLin Liu
Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, 116023 China
Search for more papers by this authorJiayin Li
Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, 116023 China
Center of Materials Science and Optoelectronics Engineering, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
Search for more papers by this authorLi Han
Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, 116023 China
Search for more papers by this authorYang Yu
Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, 116023 China
Search for more papers by this authorZhao Li
Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, 116023 China
Search for more papers by this authorAlexis Munyentwali
Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, 116023 China
Center of Materials Science and Optoelectronics Engineering, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
Search for more papers by this authorJiaquan Guo
Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, 116023 China
Center of Materials Science and Optoelectronics Engineering, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
Search for more papers by this authorYuting Wang
Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, 116023 China
Center of Materials Science and Optoelectronics Engineering, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Li Rao
Hubei International Scientific and Technological Cooperation Base of Pesticide and Green Synthesis, Key Laboratory of Pesticide & Chemical Biology of Ministry of Education, College of Chemistry, Central China Normal University, Wuhan, 430079 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Teng He
Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, 116023 China
Center of Materials Science and Optoelectronics Engineering, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
State Key Laboratory of Catalysis, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, 116023 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Ping Chen
Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, 116023 China
Center of Materials Science and Optoelectronics Engineering, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
State Key Laboratory of Catalysis, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, 116023 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
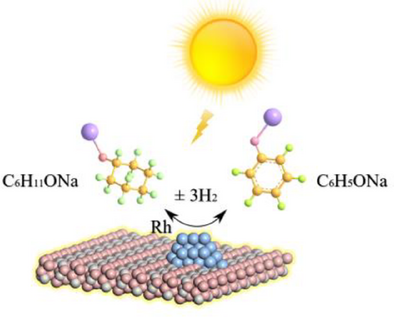
Solar-driven reversible hydrogen storage of sodium cyclohexanolate/phenoxide pair demonstrated 99.9% conversion and selectivity in both hydrogenation and dehydrogenation via photocatalysis without external heating. The synergy between high- and low-frequency light enhances the overall performance, i.e., low-frequency light provides heat, while high-frequency light facilitates the desorption of product from the catalyst surface.
Abstract
Reversible hydrogen storage is a key challenge for the implementation of hydrogen energy, with dehydrogenation being particularly difficult because of its endothermic nature, slow kinetics, poor selectivity, etc. Solar energy-driven hydrogen uptake/release represents an interdisciplinary approach that provides an effective solution to those problems. Herein, we report the solar-driven reversible hydrogen uptake of 4.9 wt.% over sodium cyclohexanolate/phenoxide pair, achieving over 99.9% conversion and selectivity in both hydrogenation and dehydrogenation via photocatalysis without external heating. Notably, the initial dehydrogenation rate reaches 23.4 that is ca. 2 orders of magnitude higher than thermocatalysis. The superior photocatalytic performance stems from the synergy between high- and low-frequency light, i.e., low-frequency light mainly provides heat, high-frequency light drives the desorption of product from the catalyst surface. This approach offers a path toward a sustainable solar-driven hydrogen energy system.
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie202506275-sup-0001-SuppMatS1.docx2.4 MB | Supporting Information S1 |
| anie202506275-sup-0002-SuppMatS2.zip9.9 KB | Supporting Information S2 |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1D. Mateo, J. L. Cerrillo, S. Durini, J. Gascon, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 2173–2210.
- 2R. Tan, X. Wang, Y. Kong, Q. Ji, Q. Zhan, Q. Xiong, X. Mu, L. Li, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 14149–14156.
- 3L. Li, X. Mu, W. Liu, Z. Mi, C.-J. Li, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 7576–7579.
- 4C. M. Pelicano, H. Tong, Appl. Res. 2024, 3, e202300080.
- 5Y. Guan, H. Wen, K. Cui, Q. Wang, W. Gao, Y. Cai, Z. Cheng, Q. Pei, Z. Li, H. Cao, T. He, J. Guo, P. Chen, Nat. Chem. 2024, 16, 373–379.
- 6A. Fujishima, K. Honda, Nature 1972, 238, 37–38.
- 7L. Schlapbach, A. Züttel, Nature 2001, 414, 353–358.
- 8T. He, P. Pachfule, H. Wu, Q. Xu, P. Chen, Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016, 1, 16059.
- 9S.-I. Orimo, Y. Nakamori, J. R. Eliseo, A. Züttel, C. M. Jensen, Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 4111–4132.
- 10J. Yang, A. Sudik, C. Wolverton, D. J. Siegel, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 656–675.
- 11X. Zhang, Y. Sun, S. Ju, J. Ye, X. Hu, W. Chen, L. Yao, G. Xia, F. Fang, D. Sun, Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2206946.
- 12L. Zhang, L. Liu, Z. Pan, R. Zhang, Z. Gao, G. Wang, K. Huang, X. Mu, F. Bai, Y. Wang, W. Zhang, Z. Cui, L. Li, Nat. Energy 2022, 7, 1042–1051.
- 13Y. Yu, T. He, A. Wu, Q. Pei, A. Karkamkar, T. Autrey, P. Chen, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 131, 3134–3139.
- 14K. C. Tan, Y. Yu, R. Chen, T. He, Z. Jing, Q. Pei, J. Wang, Y. S. Chua, A. Wu, W. Zhou, H. Wu, P. Chen, Energy Storage Mater. 2020, 26, 198–202.
- 15Z. Jing, Y. Yu, R. Chen, K. C. Tan, T. He, A. Wu, Q. Pei, Y. S. Chua, D. Zheng, X. Zhang, Z. Ge, F. Zhang, P. Chen, Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 1944–1947.
- 16J. Zijun, K. C. Tan, H. Teng, Y. Yang, P. Qijun, W. Jintao, W. Hui, C. Ping, Acta Phys. Chim. Sin. 2021, 37, 2009039–2009030.
- 17Z. Jing, Q. Yuan, Y. Yu, X. Kong, K. C. Tan, J. Wang, Q. Pei, X.-B. Wang, W. Zhou, H. Wu, A. Wu, T. He, P. Chen, ACS Mater. Lett. 2021, 3, 1417–1425.
- 18T. He, H. Cao, P. Chen, Acc. Mater. Res. 2021, 2, 726–738.
- 19Y. Wang, Z. Song, D. Ma, H. Luo, D. Liang, X. Bao, J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem. 1999, 149, 51–61.
- 20M. Kawai, M. Uda, M. Ichikawa, J. Phys. Chem. 1985, 89, 1654–1656.
- 21J. C. Matsubu, V. N. Yang, P. Christopher, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 3076–3084.
- 22J. Yu, J. Yu, Z. Shi, Q. Guo, X. Xiao, H. Mao, D. Mao, Catal. Sci. Technol. 2019, 9, 3675–3685.
- 23W. Liao, M. Yue, J. Chen, Z. Wang, J. Ding, Y. Xu, Y. Bai, X. Liu, A. Jia, W. Huang, Z. Zhang, ACS Catal. 2023, 13, 5767–5779.
- 24H. Xu, G. Li, G. Zhu, K. Zhu, S. Jin, Catal. Commun. 2015, 62, 52–56.
- 25K. C. Tan, Q. Pei, J. Yu, H. Wen, Y. Yu, J. Wang, N. I. Nordin, T. He, Y. S. Chua, P. Chen, Chem. Commun. 2023, 59, 4177–4180.
- 26Y. Tang, Z. Yang, C. Guo, H. Han, Y. Jiang, Z. Wang, J. Liu, L. Wu, F. Wang, J. Mater. Chem. A 2022, 10, 12157–12167.
- 27S. Sarina, H.-Y. Zhu, Q. Xiao, E. Jaatinen, J. Jia, Y. Huang, Z. Zheng, H. Wu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 2935–2940.
- 28H. Song, X. Meng, Z.-J. Wang, Z. Wang, H. Chen, Y. Weng, F. Ichihara, M. Oshikiri, T. Kako, J. Ye, ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 7556–7565.
- 29S. Linic, U. Aslam, C. Boerigter, M. Morabito, Nat. Mater. 2015, 14, 567–576.
- 30X. Li, H. O. Everitt, J. Liu, Nano Res. 2019, 12, 1906–1911.
- 31X. Zhang, X. Li, D. Zhang, N. Q. Su, W. Yang, H. O. Everitt, J. Liu, Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14542.
- 32N. Zettsu, J. M. McLellan, B. Wiley, Y. Yin, Z. Y. Li, Y. Xia, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 118, 1310–1314.
10.1002/ange.200503174 Google Scholar
- 33X. Zhang, P. Li, Á. Barreda, Y. Gutiérrez, F. González, F. Moreno, H. O. Everitt, J. Liu, Nanoscale Horiz. 2016, 1, 75–80.
- 34J. M. Sanz, D. Ortiz, R. Alcaraz de la Osa, J. M. Saiz, F. González, A. S. Brown, M. Losurdo, H. O. Everitt, F. Moreno, J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 19606–19615.
- 35D. Muñeton Arboleda, V. Coviello, A. Palumbo, R. Pilot, V. Amendola, Nanoscale Horiz. 2025, 10, 336–348.
- 36L. G. Devi, R. Kavitha, Appl. Catal. B 2013, 140-141, 559–587.
- 37D. Glass, E. Cortés, S. Ben-Jaber, T. Brick, W. J. Peveler, C. S. Blackman, C. R. Howle, R. Quesada-Cabrera, I. P. Parkin, S. A. Maier, Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1901841.
- 38Q. Guo, C. Zhou, Z. Ma, X. Yang, Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1901997.
- 39A. M. Watson, X. Zhang, R. Alcaraz de la Osa, J. M. Sanz, F. González, F. Moreno, G. Finkelstein, J. Liu, H. O. Everitt, Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 1095–1100.
- 40X. Li, Y. Yan, Y. Jiang, X. Wu, S. Li, J. Huang, J. Li, Y. Lin, D. Yang, H. Zhang, Nanoscale Adv. 2019, 1, 3941–3947.
- 41N. O. Balayeva, Z. Mamiyev, R. Dillert, N. Zheng, D. W. Bahnemann, ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 5542–5553.
- 42M. Zheng, J. Shi, T. Yuan, X. Wang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 130, 5585–5589.
- 43G. W. T. M. J. Frisch, H. B. Schlegel, G. E. Scuseria, M. A. Robb, J. R. Cheeseman, G. Scalmani, V. Barone, B. Mennucci, G. A. Petersson, H. Nakatsuji, M. Caricato, X. Li, H. P. Hratchian, A. F. Izmaylov, J. Bloino, G. Zheng, J. L. Sonnenberg, M. Hada, M. Ehara, K. Toyota, R. Fukuda, J. Hasegawa, M. Ishida, T. Nakajima, Y. Honda, O. Kitao, H. Nakai, T. Vreven, J. A. Montgomery Jr., J. E. Peralta, et al., Gaussian 09, revision d.01, Gaussian, Inc., Wallingford, CT 2013.
- 44H. Liu, M. Li, T. D. Dao, Y. Liu, W. Zhou, L. Liu, X. Meng, T. Nagao, J. Ye, Nano Energy 2016, 26, 398–404.
- 45J. Zhou, H. Liu, H. Wang, Chin. Chem. Lett. 2023, 34, 107420.
- 46X. Zhang, X. Li, M. E. Reish, D. Zhang, N. Q. Su, Y. Gutiérrez, F. Moreno, W. Yang, H. O. Everitt, J. Liu, Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 1714–1723.