Optimizing the Selectivity of CH4 Electrosynthesis from CO2 Over Cuprates Through Cu─O Bond Length Descriptor
This article relates to:
-
Inside Front Cover: Optimizing the Selectivity of CH4 Electrosynthesis from CO2 over Cuprates through Cu─O Bond Length Descriptor (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 24/2025)
- Yunze Xu,
- Yu Zhang,
- Hongyan Zhao,
- Lei Shi,
- Zhenbao Zhang,
- Xueyan Li,
- Zhen Xue,
- Heqing Jiang,
- Yongfa Zhu,
- Jiawei Zhu,
- Volume 64Issue 24Angewandte Chemie International Edition
- First Published online: May 20, 2025
Yunze Xu
State Key Laboratory of Photoelectric Conversion and Utilization of Solar Energy, Qingdao New Energy Shandong Laboratory, Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Qingdao, 266101 China
These author contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorYu Zhang
State Key Laboratory of Photoelectric Conversion and Utilization of Solar Energy, Qingdao New Energy Shandong Laboratory, Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Qingdao, 266101 China
University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
These author contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorHongyan Zhao
State Key Laboratory of Photoelectric Conversion and Utilization of Solar Energy, Qingdao New Energy Shandong Laboratory, Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Qingdao, 266101 China
These author contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorLei Shi
Joint International Research Laboratory of Biomass Energy and Materials, College of Materials Science and Engineering, Nanjing Forestry University, Nanjing, 210037 China
Search for more papers by this authorZhenbao Zhang
School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Linyi University, Linyi, 276005 China
Search for more papers by this authorXueyan Li
State Key Laboratory of Photoelectric Conversion and Utilization of Solar Energy, Qingdao New Energy Shandong Laboratory, Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Qingdao, 266101 China
Search for more papers by this authorZhen Xue
State Key Laboratory of Photoelectric Conversion and Utilization of Solar Energy, Qingdao New Energy Shandong Laboratory, Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Qingdao, 266101 China
Search for more papers by this authorHeqing Jiang
State Key Laboratory of Photoelectric Conversion and Utilization of Solar Energy, Qingdao New Energy Shandong Laboratory, Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Qingdao, 266101 China
Search for more papers by this authorYongfa Zhu
Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Jiawei Zhu
State Key Laboratory of Photoelectric Conversion and Utilization of Solar Energy, Qingdao New Energy Shandong Laboratory, Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Qingdao, 266101 China
E-mail: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorYunze Xu
State Key Laboratory of Photoelectric Conversion and Utilization of Solar Energy, Qingdao New Energy Shandong Laboratory, Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Qingdao, 266101 China
These author contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorYu Zhang
State Key Laboratory of Photoelectric Conversion and Utilization of Solar Energy, Qingdao New Energy Shandong Laboratory, Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Qingdao, 266101 China
University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
These author contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorHongyan Zhao
State Key Laboratory of Photoelectric Conversion and Utilization of Solar Energy, Qingdao New Energy Shandong Laboratory, Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Qingdao, 266101 China
These author contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorLei Shi
Joint International Research Laboratory of Biomass Energy and Materials, College of Materials Science and Engineering, Nanjing Forestry University, Nanjing, 210037 China
Search for more papers by this authorZhenbao Zhang
School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Linyi University, Linyi, 276005 China
Search for more papers by this authorXueyan Li
State Key Laboratory of Photoelectric Conversion and Utilization of Solar Energy, Qingdao New Energy Shandong Laboratory, Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Qingdao, 266101 China
Search for more papers by this authorZhen Xue
State Key Laboratory of Photoelectric Conversion and Utilization of Solar Energy, Qingdao New Energy Shandong Laboratory, Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Qingdao, 266101 China
Search for more papers by this authorHeqing Jiang
State Key Laboratory of Photoelectric Conversion and Utilization of Solar Energy, Qingdao New Energy Shandong Laboratory, Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Qingdao, 266101 China
Search for more papers by this authorYongfa Zhu
Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Jiawei Zhu
State Key Laboratory of Photoelectric Conversion and Utilization of Solar Energy, Qingdao New Energy Shandong Laboratory, Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Qingdao, 266101 China
E-mail: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
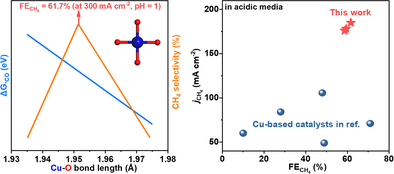
A selectivity descriptor based on Cu─O bond length was established to screen highly selective cuprates toward CH4 electrosynthesis. This descriptor revealed that CH4 selectivity exhibited a volcano-shaped correlation with the Cu─O bond length, with the optimal value accessible at ∼1.951 Å. Using this descriptor, three new cuprates were predicted, demonstrating better performance compared to the reported Cu-based catalysts in acidic electrolytes.
Abstract
Precisely controlling the nature of Cu─O bond in Cu-based oxide catalysts and understanding its correlation with CH4 electrosynthesis (from CO2) for selectivity optimization is a long-standing challenge. Herein, taking a specific type of cuprates structured with CuO4 square-planar motifs as the platform, we report a selectivity descriptor of Cu─O bond length for screening highly selective catalysts toward CH4 electrosynthesis. We establish the descriptor by systematic investigations of several proof-of-concept cuprates. Their Cu─O bond lengths are precisely controlled ranging from 1.944 to 1.970 Å and these bonds remain stable in CH4 selectivity evaluation. Our investigations demonstrate that the CH4 selectivity exhibits a volcano-type dependence on the Cu─O bond length, and the optimized value is accessible at about 1.951 Å. This could be attributed to the optimal (neither too strong nor too weak) *CO adsorption created by the moderate Cu─O bond length, facilitating *CO hydrogenation. Furthermore, utilizing this descriptor, we predict three highly selective cuprates for CH4 electrosynthesis, with superior selectivity that is near the top of the volcano plot. And importantly, in an acidic electrolyte (pH = 1), they outperform the reported catalysts, achieving CH4 selectivity of up to 61.7% at 300 mA cm−2.
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie202503745-sup-0001-SuppMat.docx12.9 MB | Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1J. Artz, T. E. Müller, K. Thenert, J. Kleinekorte, R. Meys, A. Sternberg, A. Bardow, W. Leitner, Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 434–504.
- 2Z. Xu, R. Lu, Z.-Y. Lin, W. Wu, H.-J. Tsai, Q. Lu, Y. C. Li, S.-F. Hung, C. Song, J. C. Yu, Z. Wang, Y. Wang, Nat. Energy 2024, 9, 1397–1406.
- 3A. Caballero, P. J. Pérez, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 8809–8820.
- 4M. Fan, R. K. Miao, P. Ou, Y. Xu, Z.-Y. Lin, T.-J. Lee, S.-F. Hung, K. Xie, J. E. Huang, W. Ni, J. Li, Y. Zhao, A. Ozden, C. P. O'Brien, Y. Chen, Y. C. Xiao, S. Liu, J. Wicks, X. Wang, J. Abed, E. Shirzadi, E. H. Sargent, D. Sinton, Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3314.
- 5H. Kang, J. Ma, S. Perathoner, W. Chu, G. Centi, Y. Liu, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2023, 52, 3627–3662.
- 6J. Fernández-González, M. Rumayor, A. Domínguez-Ramos, Á. Irabien, Int. J. Greenhouse Gas Control 2022, 114, 103549.
- 7S. Nitopi, E. Bertheussen, S. B. Scott, X. Liu, A. K. Engstfeld, S. Horch, B. Seger, I. E. L. Stephens, K. Chan, C. Hahn, J. K. Nørskov, T. F. Jaramillo, I. Chorkendorff, Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 7610–7672.
- 8Y. Wang, J. Liu, G. Zheng, Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2005798.
- 9A. A. Peterson, J. K. Nørskov, J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2012, 3, 251–258.
- 10Y. Zhou, F. Che, M. Liu, C. Zou, Z. Liang, P. De Luna, H. Yuan, J. Li, Z. Wang, H. Xie, H. Li, P. Chen, E. Bladt, R. Quintero-Bermudez, T.-K. Sham, S. Bals, J. Hofkens, D. Sinton, G. Chen, E. H. Sargent, Nat. Chem. 2018, 10, 974–980.
- 11S. Chen, Y. Su, P. Deng, R. Qi, J. Zhu, J. Chen, Z. Wang, L. Zhou, X. Guo, B. Y. Xia, ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 4640–4646.
- 12J. Zhu, Y. Wang, A. Zhi, Z. Chen, L. Shi, Z. Zhang, Y. Zhang, Y. Zhu, X. Qiu, X. Tian, X. Bai, Y. Zhang, Y. Zhu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202111670.
- 13Z. Xu, C. Peng, G. Luo, S. Yang, P. Yu, S. Yan, M. Shakouri, Z. Wang, T.-K. Sham, G. Zheng, Adv. Energy Mater. 2023, 13, 2204417.
- 14C. Peng, Z. Xu, G. Luo, S. Yan, J. Zhang, S. Li, Y. Chen, L. Y. Chang, Z. Wang, T.-K. Sham, G. Zheng, Adv. Energy Mater. 2022, 12, 2200195.
- 15X. Tan, K. Sun, Z. Zhuang, B. Hu, Y. Zhang, Q. Liu, C. He, Z. Xu, C. Chen, H. Xiao, C. Chen, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 8656–8664.
- 16X. Zhou, J. Shan, L. Chen, B. Y. Xia, T. Ling, J. Duan, Y. Jiao, Y. Zheng, S.-Z. Qiao, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 2079–2084.
- 17J. Zhu, Y. Zhang, Z. Chen, Z. Zhang, X. Tian, M. Huang, X. Bai, X. Wang, Y. Zhu, H. Jiang, Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1565.
- 18T. Yang, M. Kuang, J. Yang, Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2024, 43, 100350.
- 19J. Dumesic, G. Huber, M. Boudart, Handbook of Heterogeneous Catalysis, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim 2008, pp. 1445–1462.
10.1002/9783527610044.hetcat0077 Google Scholar
- 20G. A. Somorjai, Y. Li, Introduction to Surface Chemistry and Catalysis, Wiley, Hoboken 2010.
- 21F. Chen, Z. Yao, Z. Lyu, J. Fu, X. Zhang, J. Hu, eScience 2024, 4, 100172.
- 22J. Zhang, Z. Wang, W. Chen, Y. Xiong, W.-C. Cheong, L. Zheng, W. Yan, L. Gu, C. Chen, Q. Peng, P. Hu, D. Wang, Y. Li, Chem 2020, 6, 725–737.
- 23P. C. P. Caldas, J. M. R. Gallo, A. Lopez-Castillo, D. Zanchet, J. M. C. Bueno, ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 2419–2424.
- 24Y. Sun, X. Wang, H. Zhang, X. Gao, X. Wang, S. Wang, Z. Tang, S. Li, K. Nie, J. Xie, Z. Yang, Y.-M. Yan, ACS Catal. 2024, 14, 1351–1362.
- 25Y. Zhang, Y. Li, N. Gao, E. P. Delmo, G. Hou, A. Luo, D. Wang, K. Chen, M. Antonietti, T. Liu, Z. Tian, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202404676.
- 26X. Tu, X. Liu, Y. Zhang, J. Zhu, H. Jiang, Green Carbon 2024, 2, 131–148.
10.1016/j.greenca.2024.03.006 Google Scholar
- 27R. Hord, H. Luetkens, G. Pascua, A. Buckow, K. Hofmann, Y. Krockenberger, J. Kurian, H. Maeter, H.-H. Klauss, V. Pomjakushin, A. Suter, B. Albert, L. Alff, Phys. Rev. B 2010, 82, 180508.
- 28M.-E. Boulanger, G. Grissonnanche, S. Badoux, A. Allaire, É. Lefrançois, A. Legros, A. Gourgout, M. Dion, C. H. Wang, X. H. Chen, R. Liang, W. N. Hardy, D. A. Bonn, L. Taillefer, Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5325.
- 29H. Zhang, Y. Xu, M. Lu, X. Xie, L. Huang, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2101872.
- 30D. Chen, C. Chen, Z. M. Baiyee, Z. Shao, F. Ciucci, Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 9869–9921.
- 31D. Guan, J. Zhou, Y.-C. Huang, C.-L. Dong, J.-Q. Wang, W. Zhou, Z. Shao, Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3755.
- 32P. Bordet, J. Capponi, C. Chaillout, D. Chateigner, J. Chenavas, T. Fournier, J. Hodeau, M. Marezio, M. Perroux, G. Thomas, A. Varela, Physica C 1992, 193, 178–188.
- 33R. D. Shannon, Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A Found. Crystallogr. 1976, 32, 751–767.
- 34J. Zhao, P. Zhang, T. Yuan, D. Cheng, S. Zhen, H. Gao, T. Wang, Z.-J. Zhao, J. Gong, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 6622–6627.
- 35Y. Xie, P. Ou, X. Wang, Z. Xu, Y. C. Li, Z. Wang, J. E. Huang, J. Wicks, C. McCallum, N. Wang, Y. Wang, T. Chen, B. T. W. Lo, D. Sinton, J. C. Yu, Y. Wang, E. H. Sargent, Nat. Catal. 2022, 5, 564–570.
- 36Y. Li, F. Liu, Z. Chen, L. Shi, Z. Zhang, Y. Gong, Y. Zhang, X. Tian, Y. Zhang, X. Qiu, X. Ding, X. Bai, H. Jiang, Y. Zhu, J. Zhu, Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2206002.
- 37Y. Zhang, J. Zhao, S. Lin, Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2024, 43, 100415.
- 38J. K. Nørskov, T. Bligaard, J. Rossmeisl, C. H. Christensen, Nat. Chem. 2009, 1, 37–46.
- 39X. Y. Zhang, Z. X. Lou, J. Chen, Y. Liu, X. Wu, J. Y. Zhao, H. Y. Yuan, M. Zhu, S. Dai, H. F. Wang, C. Sun, P. F. Liu, H. G. Yang, Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 7681.
- 40M. Chen, K. Chang, Y. Zhang, Z. Zhang, Y. Dong, X. Qiu, H. Jiang, Y. Zhu, J. Zhu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202305530.
- 41P. Friebe, P. Bogdanoff, N. Alonso-Vante, H. Tributsch, J. Catal. 1997, 168, 374–385.
- 42S.-C. Lin, C.-C. Chang, S.-Y. Chiu, H.-T. Pai, T.-Y. Liao, C.-S. Hsu, W.-H. Chiang, M.-K. Tsai, H. M. Chen, Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3525.
- 43R. Casebolt, K. Levine, J. Suntivich, T. Hanrath, Joule 2021, 5, 1987–2026.
- 44J. Vavra, G. P. Ramona, F. Dattila, A. Kormányos, T. Priamushko, P. P. Albertini, A. Loiudice, S. Cherevko, N. Lopéz, R. Buonsanti, Nat. Catal. 2024, 7, 89–97.
- 45Z. Lian, F. Dattila, N. López, Nat. Catal. 2024, 7, 401–411.
- 46Y. Yang, S. Louisia, S. Yu, J. Jin, I. Roh, C. Chen, M. V. Fonseca Guzman, J. Feijóo, P.-C. Chen, H. Wang, C. J. Pollock, X. Huang, Y.-T. Shao, C. Wang, D. A. Muller, H. D. Abruña, P. Yang, Nature 2023, 614, 262–269.
- 47C. Deng, C. Qi, X. Wu, G. Jing, H. Zhao, Green Carbon 2024, 2, 124–130.
10.1016/j.greenca.2024.02.003 Google Scholar
- 48Q. Lei, L. Huang, J. Yin, B. Davaasuren, Y. Yuan, X. Dong, Z.-P. Wu, X. Wang, K. X. Yao, X. Lu, Y. Han, Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4857.
- 49P.-P. Yang, X.-L. Zhang, F.-Y. Gao, Y.-R. Zheng, Z.-Z. Niu, X. Yu, R. Liu, Z.-Z. Wu, S. Qin, L.-P. Chi, Y. Duan, T. Ma, X.-S. Zheng, J.-F. Zhu, H.-J. Wang, M.-R. Gao, S.-H. Yu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 6400–6408.
- 50R. Casebolt, K. Levine, J. Suntivich, T. Hanrath, Joule 2021, 5, 1987–2026.
- 51W. Wu, L. Xu, Q. Lu, J. Sun, Z. Xu, C. Song, J. Yu, Y. Wang, Adv. Mater. 2025, 37, 2312894.
- 52M. Zeng, W. Fang, Y. Cen, X. Zhang, Y. Hu, B. Y. Xia, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202404574.
- 53R. I. Masel, Z. Liu, H. Yang, J. J. Kaczur, D. Carrillo, S. Ren, D. Salvatore, C. P. Berlinguette, Nat. Nanotechnol. 2021, 16, 118–128.